Determining the size of lymph nodes
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with Doppler sonography is prescribed for enlarged lymph nodes. Their increase may indicate both an inflammatory process and the formation of a tumor. It is important to identify the cause and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Detection of thyroid lesions
Often, Doppler sonography of the thyroid gland is prescribed for lesions of the organ or suspected pathology. Inflammation of the thyroid gland, or thyroiditis, is common.
Detection of malignant tumors
Determining the nature of blood flow in the gland, as well as the size and condition of the organ, will allow us to draw a conclusion about the presence of a tumor process. Moreover, diagnostics allows us to determine the location of the tumor and its exact size.
Determining the size of the thyroid gland in the fetus in the womb
Doppler ultrasound of the thyroid gland may be performed to evaluate fetal development during a woman's pregnancy. All results obtained during the diagnostic process are carefully recorded in a report, with which you can go to your doctor.
Performing an aspiration biopsy
It involves taking thyroid tissue to determine the nature of the neoplasm. No matter how informative an ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound is for examining the thyroid gland
, it will not be able to show the nature of the tumor. However, research is indispensable when planning such an intervention.
What does Doppler sonography of the thyroid gland show?
You need to find out what this is - a Doppler ultrasound of the thyroid gland, and also what will become known based on its results if you have been prescribed such an examination. The procedure allows you to obtain a large amount of information regarding the condition of the organ.
Diffuse toxic goiter
Deviations from the norm of Dopplerography of the thyroid gland may suggest manifestations characteristic of diffuse toxic goiter, otherwise known as Graves' disease. It is manifested by increased production of hormones that are responsible for the self-regulation of the body.
Hypothyroidism
Accompanied by a constant lack of production of thyroid hormones. It is almost always accurately diagnosed during Dopplerography of blood vessels and examination of the thyroid gland using ultrasound.
Thyroiditis
If you find out that this is a Doppler ultrasound of the thyroid gland, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the diseases that it can detect. These include thyroiditis - inflammation of the thyroid gland. The disease is accompanied by an enlargement of the organ, clearly visible foci of inflammatory and infectious lesions of the gland during ultrasound.
The appearance of neoplasms
Dopplerography of the thyroid gland (what it is, was said above) can identify a neoplasm of any nature, assess its position, size and structure. However, it is not possible to draw a conclusion about the nature of the tumor. To do this, a biopsy is performed, and based on its results a diagnosis is established.
What is Doppler ultrasound?
The standard examination for identifying pathology of the thyroid gland necessarily includes ultrasound diagnostics with Dopplerography, that is, using an additional (color) imaging mode, in which the doctor can not only see the gland itself, but also assess how the organ is supplied with blood.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with Doppler – a combined examination. When performing ultrasound, the waves emanating from the sensor are reflected from the tissues of the target organ and transmit its image to the device monitor. When using the Doppler effect, the doctor also sees on the screen the blood flow that occurs in and around the gland. The difference in the movement of blood (to or from the sensor) allows you to obtain a color image, perform the necessary measurements and draw conclusions about the adequacy of the blood supply. Accordingly, the doctor can not only analyze the appearance of the gland, but also evaluate its function, how this complex differs from a regular ultrasound.
How is the examination carried out and do you need to prepare for it?
No preparation is required for this manipulation. All you need to do is show up for your appointment on time. The doctor will provide consumables - for example, gel and wipes - during the examination.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland with Dopplerography of blood vessels is carried out in the same way as conventional ultrasound diagnostics. The patient needs to bare his neck (remove or unbutton outer clothing, remove jewelry) and lie down on the couch. The doctor applies a gel to the skin that improves ultrasound performance and facilitates the movement of the transducer over the skin. The gel is neutral in composition, does not sting or irritate the skin. Then a device sensor is installed on the area of the gland (on the neck), which sends an ultrasonic wave to the organ. The doctor moves the sensor in the area of the gland, maybe pressing it a little tighter or tilting it. At this moment, the specialist sees an image of the gland on the monitor. When the Doppler mode is turned on, the image becomes color - this is the visualization of blood flow in the vascular lumens of the gland.
The monitor of the device allows you to capture the image and make the necessary measurements. At the end of the procedure, the patient is given a napkin to clean the skin of any remaining gel. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor issues a conclusion describing the gland and the processes occurring in it.
When is an ultrasound of the thyroid gland necessary?
Are you depressed or worried about causeless irritability? Are you starting to gain weight or are you losing weight quickly?
These, as well as many other seemingly unrelated symptoms, occur in various pathologies of the thyroid gland. We are talking about identifying them using ultrasound with Anna Viktorovna Poskrebysheva, an ultrasound diagnostics doctor at Clinic Expert Orenburg LLC.
- Anna Viktorovna, tell me, in what cases is ultrasound of the thyroid gland prescribed?
Usually, its implementation is advisable in the presence of complaints that occur in diseases of this organ, and their characteristic feature is often their diametric opposite. Some examples: increased or decreased heart rate, increased sweating or dry skin, increased fatigue, apathy, depression or agitation, short temper, nervousness, constipation, or loose stools. There may be a feeling of a lump in the throat, coughing, choking, hand tremors, hair loss, peeling of the nail plates.
The need for an examination can also be indicated by a change in the contours of a person’s neck, its volume, or the presence of any formations when palpated by a doctor.
In some cases, this study is prescribed when pathological changes are detected in other tests, even those not directly related to this gland.
I would also like to note the following point. Anatomically, in the area where the thyroid gland is located there are two more pairs of important glands - the parathyroid (or, otherwise, parathyroid). Sometimes, with their tumors, they begin to produce an increased amount of a hormone (its name is “parathyroid hormone,” parathyroid hormone, “parathyrin”). An increase in its content leads to increased release of calcium from bone tissue into the blood. Therefore, ultrasound of the thyroid gland can also be indicated for complaints such as bone pain, pathological (disproportionate to injury or load) bone fractures, spinal deformities (due to osteoporosis), increased urine output, nausea, abdominal pain, increased blood pressure, detection of kidney stones. This disease is statistically quite rare.
- What are the types of thyroid diseases and how often do you encounter this category of patients in your practice?
We see patients with one or another pathology of this organ almost every day. I will name some of the diseases. This is, first of all, diffuse and nodular goiter; inflammation of the gland tissue - thyroiditis (can be of an infectious or autoimmune nature), congenital (hereditary) thyropathies, neoplasms (benign and malignant), as well as damage to the gland due to diseases of other organs.
- What diagnostic methods are used when thyroid disease is suspected?
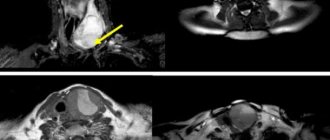
First of all, as with other diseases, complaints and anamnesis are collected in detail, and a thorough examination is carried out with palpation of the gland area. After this, clarifying studies are prescribed. To study the structural features of the organ, in addition to ultrasound, MRI of the soft tissues of the neck or computed tomography can be used. It is indicated, for example, when the anatomically the gland is located quite low, in some cases even located behind the sternum, or when the visual picture of its tissue is unclear on ultrasound.
The study of the level of gland hormones and antibodies against its components is widely used. Sometimes there is a need for a puncture, for example, to clarify the presence of a tumor and its type. In some cases, radioisotope research is used - scintigraphy.
-What does ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland reveal?
Using ultrasound, the location of the organ, its size, the volume of each lobe and the total (depending on age and gender), structure (homogeneous, heterogeneous, presence of inclusions), blood flow in the gland itself and the detected formations are determined. The latter also determines the signs of benignity/malignancy.
In addition, local (regional) lymph nodes, large great vessels of the neck, and soft tissues are also examined.
- Anna Viktorovna, tell us how to properly prepare for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland?
No special preparation is required. Clothing with a loose collar is recommended, and the neck should be free of jewelry.
Sometimes, in older people, in particular with certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, during the examination, slight painful sensations under the ultrasound sensor may occur due to its slight pressure on the tissue, as well as a feeling of nausea. Therefore, we recommend that they come for examination on an empty stomach or after a light breakfast.
- How is an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland performed?
The procedure is performed in a horizontal position, lying on your back, with your head slightly tilted back. In people with a short neck, as well as obese people, sometimes it is necessary to place a special cushion under the shoulder blades.
On average, the study lasts 10-15 minutes.
- How safe and informative is thyroid ultrasound?
The method is safe, like diagnostic ultrasound in principle, and is quite informative.
- What is ultrasound of the thyroid gland with Color Doppler?
The abbreviation “CDC” stands for “color (or color) Doppler mapping.” This is a method that expands the capabilities of ultrasound and is used to study blood flow in an organ.
- Suppose an ultrasound of the thyroid gland reveals a pathology. What to do next?
Contact your doctor. Depending on the results of the examination, either a treatment plan is developed or additional clarifying studies are prescribed.
-Which doctor should I contact?
To an endocrinologist. Depending on the diagnosis, according to indications, he may additionally refer the patient to a surgeon, oncologist or other specialists.
For reference:
Poskrebysheva Anna Viktorovna
Graduate of the Orenburg State Medical Academy in 2007 (currently Orenburg State Medical University).
In 2007-2009 she completed clinical residency in the specialty “Skin and sexually transmitted diseases”.
In 2011, she underwent professional retraining at the Faculty of Education and Training of Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy in the specialty “Ultrasound Diagnostics”.
Since 2021, he has been working as an ultrasound diagnostic doctor at MRI Expert Orenburg LLC.
Other interviews with Anna Poskrebysheva:
How to prepare for an abdominal ultrasound?
What does an ultrasound of the mammary glands show?
Important parameters
So, what parameters will be necessarily assessed by the doctor and indicated in the conclusion?
To begin with, this is an analysis of the structure and location of the thyroid gland. The size and volume of the organ are indicated (for each of the two lobes and the isthmus, as well as the general one), its shape and structure (uniform or not). The presence of formations is noted; if there are nodes, then their sizes.
During Doppler ultrasound, firstly, the intensity of blood flow is taken into account, which is measured in each lobe and isthmus separately. An increase in this indicator, that is, an increase in blood flow, means that the organ is working with some overstrain.
The second indicator is called blood flow speed. By its change, one can understand the activity with which pathological processes occur.
If there are nodes or neoplasms, the specialist evaluates the blood flow in them. This helps not only to make a diagnosis, but also to predict the development of the pathological process.
What does Doppler ultrasound diagnose?
This method of examination makes it possible to make with high accuracy any diagnosis associated with disorders of the thyroid gland. Upon examination, the doctor sees nodules or growths, signs of inflammation, increases or decreases in function, and even general structural changes (diffuse changes), which help make the diagnosis of autoimmune thyroiditis.
The only thing that cannot be done during the examination is to reliably assess the malignancy of the tumor. It is only possible to guess from indirect signs what the nature of the tumor is. The final diagnosis in this case will be made after a biopsy.
What do they look for during the examination?
During a standard ultrasound examination, the doctor examines the thyroid gland: its size, density, the presence or absence of nodes, the presence of tumors or signs of inflammation. The specialist also necessarily examines the lymph nodes near the gland: their enlargement may indicate the onset of a disease.
During Dopplerography of the thyroid vessels, the doctor evaluates the functioning of the organ. If there are nodes, it is necessary to know whether they are “cold” (do not produce hormones) or not, and here a comprehensive study is necessary, as in the differential diagnosis of a malignant or benign tumor.
Assessing blood flow using Dopplerography allows not only to see structural changes in the organ, but also to reliably answer the question of whether there are disturbances in the functioning of the gland.
If a tumor is suspected, the next stage of diagnosis will be the so-called TIAB - fine-needle aspiration biopsy. During this study, gland tissue, under the control of an ultrasound probe, is taken with a needle, piercing the front surface of the neck. This procedure is already invasive, and therefore it is much easier and simpler to do a Doppler ultrasound first, which can answer many questions without resorting to more traumatic procedures.
ELASTOGRAPHY FROM DIFFERENT MANUFACTURERS
Despite the fact that elastography is now offered by almost all manufacturers of ultrasound equipment, the generally recognized leader in this field is Hitachi Corporation, which first developed this technology and introduced it into commercial operation in its ultrasound scanners in 2002. 10 years of clinical experience have strengthened the company's position as a leader in tissue elastography. Hitachi's clinically proven method accuracy is 95%.
In 2010, the first worthy competitor appeared on the market - the French company Supersonic Imaging introduced the Aixplorer ultrasound scanner with automated shear wave elastography technology. In this device there is no need for compression, tissue compression occurs under the influence of a strong ultrasound wave, and the software analyzes and displays a color map of elasticity and a digital elasticity indicator expressed in kilopascals. For the first time in this device, elasticity received an objective digital indicator. The Aixplorer device received very high marks from specialists in Russia and the CIS and set a new trend in technology development.
Following Supersonic Imaging, shear wave elastography technology was implemented in their devices by Siemens and Philips. These manufacturers are currently the only ones on the market that offer users both compression and automated elastography, which makes their devices very interesting for doctors.
Companies such as GE, Toshiba, Aloka, Esaote, Medison, Mindray, Sonoscape, Ultrasonix offer only compression elastography, which is currently the industry standard.
Elastography – what is it?
This method is based on measuring the mechanical properties of fabric - physical characteristics - elasticity - the ability to deform under the influence of force and return to its previous shape.
Malignant lesions are usually characterized by increased stiffness, that is, decreased elasticity. The opposite picture is given with inflammatory lesions.
Elastography
Modern devices measure elasticity not directly (under pressure), but analyze the propagation of ultrasound in the structure under study - so-called dynamic elastography or the speed of tissue movement under pressure - pseudostatic elastography. In this case, the doctor performing the test creates a slight alternating pressure on the head; the remaining measurements are carried out by the device.
Some devices do not require pressure - they themselves cause vibrations: the device generates a supersonic transverse wave in the structure under study, creating a Mach cone that causes vibration of the tissue. This method is called dynamic shear wave elastography (SWE).
Indications and contraindications
Indications for referral for Doppler ultrasound may include problems in the thyroid gland, as well as the general condition of the body, which has signs of disruption in the hormonal system.
Ultrasound with Doppler is prescribed when:
- there is swelling (painful or not) in the neck area
- difficulty swallowing
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck
- there is pain when palpating the thyroid gland area
- there was a sudden loss or weight gain in a fairly short period of time
- palpitations are felt at rest
- there is excessive sweating not associated with physical activity
- there is causeless anxiety, insomnia, and mood disturbances.
Also, an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland with Doppler mode is performed when looking for the cause of a constant increase in blood pressure (with hypertension), and for other disorders of the hormonal system (for example, with a history of diabetes mellitus).
Since this type of combined examination is carried out non-invasively, that is, without violating the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, without injuring the body, and also because ultrasound does not provide radiation exposure (that is, it does not “irradiate” the patient), this study has no contraindications. At any age and for any concomitant conditions, ultrasound diagnostics with Doppler is possible.
Women during pregnancy also do not need to worry - both ultrasound and Doppler mode are safe for her health and the health of the fetus.
How the procedure works
This procedure does not require any preliminary preparation. It is only recommended to take with you the results of previous studies and a towel to place under your head and wipe your neck after using the special gel.
Ultrasound examination occurs as follows. The patient is placed on the couch, he throws his head back. A little gel is applied to the front of his neck (this is necessary for better passage of ultrasound). Then a special sensor is used that produces ultrasound waves.
The signal reflected from the thyroid tissue is picked up by the sensor. The wave returns, is processed by computer technology and appears on the display as a clear image.
This procedure is completely painless. However, it is recommended for elderly patients to perform it on an empty stomach, so as not to provoke a gag reflex due to pressure from the sensor on the neck.