directions
The human hand, as an integral part of the upper limb, is at risk every day. This is a strong, mobile, maneuverable and at the same time fragile and unprotected part of the human body. A large load is placed on the hand, because it is used to move, manipulate objects, and perform various types of actions, including dangerous ones. Therefore, the hands are injured more often than other parts of the body and are susceptible to various kinds of diseases.
Currently, work is underway on the website to change the price list; for current information, please call: 640-55-25 or leave a request, and an operator will contact you.
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Structural subdivision of Polikarpov Alley Polikarpov 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Structural subdivision of Zhukov Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Structural subdivision Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
We draw your attention to the schedule of technological breaks in the CT and X-ray rooms.
It is quite difficult to independently determine the cause of the ailment or make a diagnosis for mechanical damage to the hand. Therefore, in case of severe pain, swelling of soft tissue, restriction of movement of the hand, fingers, fever, as an accompanying symptom of hand pathology, if there has been an injury, you should urgently go to the emergency room; or to a surgeon, orthopedist and neurologist in case of discomfort in the hand area for no apparent reason. Any specialist in such situations, after collecting an anamnesis and a careful examination, will refer the patient for an x-ray of the hand to clarify the diagnosis.
Today, almost every medical institution has an X-ray room. But if you don’t want to waste time in line or the pain is so strong that it is impossible to wait, if you need a high-quality image, a high-quality study and consultation with a qualified specialist, then come to the Medicenter. In the traumatology department of the Medicenter, you will quickly and safely undergo an x-ray examination of your hands, provide first aid and consult with the leading doctors of the city. The Medicenter clinic network has a modern digital X-ray device Clinomat, which carries out all types of X-ray examinations in full. In the operating conditions of an emergency room, it is very important to quickly obtain research results and make a correct diagnosis based on them, so the clinic’s equipment allows you to almost instantly carry out a complete X-ray diagnosis, study the results obtained in various processing modes and make accurate diagnoses for further prescription of effective therapy.
Advantages of visiting CELT for an x-ray of the hand
X-rays of the hand in Moscow can be taken at the diagnostic center of our multidisciplinary clinic. As already mentioned, the quality of the images (including the dose of radiation received) directly depends on the skill of the radiologist. Our specialists have over 15 years of experience, and they have perfectly mastered the technique of performing X-rays of the hands, so the resulting images will be clear the first time. We use modern X-ray equipment that minimizes the radiation dose received and, in skillful hands, allows us to achieve high-quality images.
You can find out the price of a hand x-ray in the corresponding section of our website. You can make an appointment with us at any time convenient for you through our website or by phone.
Types and causes of hand injuries and diseases
Patients injure the hand, wrist, and fingers under various circumstances: as a result of a fall, playing sports, or as a result of accidents. Thus, sports injuries to the hand are one of the most common reasons for seeking medical help. When practicing boxing, karate and other types of wrestling, when hitting unsuccessfully, patients often receive a type of injury called “boxer’s knuckle,” i.e. damage to the metacarpophalangeal joints and tendons of the finger muscles. Skier's toe is another common sports hand injury in which the ulnar ligament of the thumb is torn. “Hammer finger” is caused by a ball hitting the straightened finger during volleyball, basketball, etc. This injury causes damage to the finger muscle tendon and limited movement of the fingertips. Wrist sprains are often diagnosed in children who fall while resting on their wrist. In addition, doctors are faced with damage to the tendons of the hand resulting from various mechanisms of injury, fractures of the wrist, fingers, phalanges, dislocations, etc.
But it also happens that there was no mechanical damage to the hand, but pain, numbness, swelling and other unpleasant symptoms are present. In this case, we are talking about hand diseases, such as carpal syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, peritendinitis, etc. Such diseases arise as a result of long-term work at the computer, long-term monotonous work that requires the participation of the hand and stress on it, due to an unbalanced diet, lack of certain microelements in the body, metabolic failure, etc.
Indications for hand radiography:
- bruises;
- dislocations;
- fractures;
- cracks;
- sports injuries;
- foreign bodies in the hand;
- tumor processes;
- arthritis, arthrosis of the hand joints, etc.
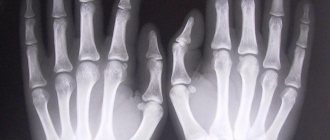
Radiography is carried out in 2 projections and, as a rule, of both hands. So children have X-rays of their hands to check the correct development and growth of bones. X-ray of the hands allows you to determine the condition of bone tissue, joints, etc. We must not forget about frequent dislocations and fractures of the fingers, which are an integral part of the hand. Such injuries also require urgent x-ray examination to determine the nature and extent of the damage.
Contraindications for x-ray examination of the hand:
- pregnancy;
- critical patient conditions.
Features of bone x-rays
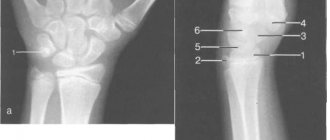
The procedure does not require any preparation from the patient - it is only important to take a referral from the attending physician with you and provide it to the radiologist. The procedure is carried out in a specially equipped room; before it begins, the patient is asked to remove all metal objects. If there are metal inserts in the diagnosed upper limb, you need to warn the doctor about this. Parts of the body that are not diagnosed are provided with protection in the form of a special membrane made of lead. The patient sits on a chair and places his hands on the table. The projection of the pictures can be different; for this, the hands are placed on the table in different positions.
| Projection | Distinctive features | What does it allow you to see? |
| Straight | Hands lie palms down; sometimes a cassette is placed under them, which allows you to take a photo from the outside of the palm. Photography is also carried out from the palm side. |
|
| Lateral | The hand lies on the cassette sideways so that the thumb protrudes slightly forward |
|
| Oblique external | The brush is placed in such a way that the outer side of the brush with the cassette creates an angle of 45°. |
|
| Oblique palmar | The hand is placed in such a way that the palm with the cassette creates an angle of 45°. |
|
Contraindications
X-rays do not require special preparation and are performed on all patients for emergency reasons. Difficulties arise when examining cysts and fingers in patients suffering from nervous disorders accompanied by tremors of the extremities, since absolute immobility is required for an informative photograph.
The procedure is not recommended for young children because radiation exposure does not have the best effect on their health. In this case, alternative studies are possible - CT or MRI.
X-ray of hand
Despite the recent emergence and intensive development of new hardware diagnostic techniques, X-ray examination has not lost its relevance today.
Information content, financial accessibility and simplicity of the procedure make x-rays a very popular method for diagnosing the condition of the musculoskeletal system.
Injury, acute or chronic pain in the arm is the main reason for prescribing an x-ray examination of the upper limb. Joints, ligaments, and soft tissues of the hand may hurt. Unpleasant or painful sensations in the hands are often evidence of a disease of the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Pain in the elbow, shoulder, or hand may be a sign of a sprain or dislocation. It has been noticed that the hands are more often than other parts of the body exposed to traumatic effects in industrial conditions. Wrist pain can be a symptom of a fracture, sprained or torn ligament, or other types of mechanical injury.
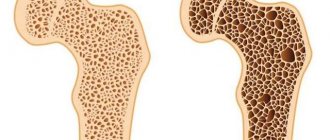
Typically, an X-ray of the hand is prescribed by the surgeon based on the results of the examination and based on the patient’s complaints. The basis for prescribing an x-ray is swelling of the limb, deformation of the arm, limitation of its mobility, decreased sensitivity, pain at rest and during physical activity. The listed symptoms may indicate developing rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, or inflammation (arthritis) of the joint. Already at the initial stage of rheumatoid arthritis, soft tissue swelling is visible on x-rays. As the disease progresses, x-rays reveal bone erosions. X-ray imaging will help monitor the progression of the disease.
An arm fracture is the most common reason for which a patient is referred for an x-ray of the upper limb. The diagnosis of a fracture is always confirmed by objective symptoms on an x-ray. Among the radiological signs of a fracture, it should be noted the presence of a fracture line, which is lighter in the image than the bone. A fracture is also characterized by a change in the bone structure, displacement of fragments, and bone deformation (with a compression fracture). An indirect symptom of a fracture is a change in the adjacent soft tissues, which is also clearly visible on the x-ray. This is a thickening and compaction of the soft tissue shadow due to hematomas and edema, deformation and complete disappearance of physiological clearing in the joint area.
If there is prolonged pain in the arm, x-rays can reveal non-traumatic changes in the size, shape and location of the bones. Most often, bone enlargement accompanies a tumor and its metastases. A decrease in bone size is characteristic of degenerative processes.
For many decades, X-ray remains the leading method for studying the structure, shape and size of soft tissues and bones. To obtain complete information about the condition of the limb, x-ray examination is carried out in several planes. Typically, x-rays are taken in two perpendicular projections. If in this case the picture remains insufficiently clear, then targeted photographs are taken in oblique projections. In some cases, a photograph of the upper limb is taken during a functional test, that is, during its flexion/extension, as well as during physical activity on the arm.
Before radiography, the limb is freed from clothing and jewelry. The area to be examined should be located in the center of the cassette, and the arm should be positioned along the axis parallel to the film. The X-ray beam is directed perpendicular to the plane of the cassette to its center. In case of injury, radiography is carried out on a large film with the aim that the image, in addition to the fracture zone, also contains a display of the adjacent sections of the healthy bone and, if possible, adjacent joints. To maintain the desired position of the hand during x-rays, special pads or bags filled with sand are used. If the patient cannot move or rotate the arm to obtain an image in a typical projection, then the tilt of the cassette or the angle of the X-ray tube is changed. To observe the formation of callus at the fracture site, it is necessary to remove the plaster cast before radiography. To study the condition of the fragments, there is no need to remove the plaster.
Author
Verbilov Petr Petrovich
traumatologist-orthopedist
10 years of experience
+7
Indications for x-rays of fingers
X-ray of the fingers is the most informative study; it allows you to assess the functional state and identify organic lesions. Indications for the diagnostic procedure are:
- suspected fractures and dislocations of the phalanges of the fingers;
- rheumatic diseases;
- assessment of the dynamics of the treatment;
- the presence of infected wounds with suspected damage to bone structures.
The study is indicated for tumor formations and congenital defects of the distal part of the upper extremities.
Features of the procedure
X-rays of the finger will allow you to diagnose osteoarticular pathologies and various changes in nearby tissues, neoplasms, fractures and purulent processes. Typically, examination of all fingers of the hand is performed in the lateral and direct projection. In the first case, the hand is placed with the palm on the table, in the second - with the edge of the palm.
Depending on the location of the injury, different finger placements are used; for direct radiographs of the phalanges of the second to fifth fingers, the hand is placed palm down. In a lateral view of the second finger, the hand is placed on the edge, while the thumb is located on the surface of the table, and the remaining fingers are bent into a fist. Lateral projections of 3–5 fingers are removed by placing the hand on the rib from the little finger side, while the patient fixes the fingers not involved in the examination with his free hand.