This effective and safe procedure is necessary for assessing the condition of the stomach using respiratory diagnostics. A test for Helicobacter is required to accurately determine the presence of the infectious agent, to be able to control it and evaluate the results of treatment prescribed by a gastroenterologist or therapist.
COST OF Gastrointestinal Examination IN OUR CLINIC IN ST. PETERSBURG
| Price for Helicobacter test | 3200 rub. (Helix, LabStory) |
| Production time | up to 9 days |
| Comprehensive abdominal ultrasound | 1300 rub. |
| Call free: 8-800-707-1560 *The clinic is licensed to provide these services | |
Infections with this strain of bacteria initially do not cause symptoms; over time, peptic ulcers and inflammation in the stomach make themselves felt by pain and disorders in the gastrointestinal tract.
What is Helicobacter pylori and why is it dangerous?
The content of the article
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a spiral-shaped bacteria that produces a huge amount of toxins in the human stomach that affect its mucous membranes. According to medical statistics, approximately 60% of the world's adult population is infected with the bacterium. H. pylori infections are not always dangerous, although in most cases they are responsible for the formation of ulcers in the stomach and small intestine.
pylori bacteria are adapted to live in the harsh, acidic environment of the stomach. But they don’t like it, so they reduce the acidity around them. Over time, the walls of the infected organ are destroyed by the hydrochloric acid produced by the stomach to fight bacteria, and the person experiences severe pain.
The spiral shape allows the bacteria to penetrate under the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, so immune cells cannot reach them. In addition, these dangerous microorganisms can influence the immune response, guaranteeing themselves a peaceful existence. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a spiral-shaped bacteria that produces a huge amount of toxins in the human stomach that affect its mucous membranes.
Results
- there are several ways to determine Helicobacter in stool using a laboratory method;
- each analysis option has its own advantages and disadvantages;
- To obtain the most accurate results, it is recommended to take several tests of different types;
- feces for analysis are collected taking into account a number of rules;
- a few days before the procedure, coarse fiber, fried, fatty foods, hot spices and seasonings, alcohol and any orange or red fruits are excluded from the diet;
- the container for feces must be sterile (pharmacy containers are the best option).
Video on the topic: Why is the Helicobacter pylori bacterium dangerous?
Symptoms
Most infected people do not have any symptoms.
When infection leads to peptic ulcers, symptoms include abdominal pain, especially on an empty stomach or several hours after eating. The pain is usually described as aching.
A number of other symptoms are associated with the infection, including:
- belching;
- feeling of bloating;
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- fever;
- lack of appetite or anorexia;
- unexplained weight loss.
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience:
- problems with swallowing;
- anemia (low hemoglobin);
- blood in the stool.
However, these are common symptoms that can be caused by other conditions. Some of the symptoms of infection can also be experienced temporarily by healthy people, for example after a heavy meal. If any of these symptoms persist or bother you, you should get tested for Helicobacter.
Who is recommended to have a stool test tested for Helicobacter?
Helicobacter pylori is present in the body for a long time without symptoms. Signs of disturbances in the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract appear only when bacteria are active. One of the main provoking factors is decreased immunity.
If a patient has certain diseases or individual symptoms, the test procedure for helicobacteriosis becomes mandatory.
Indications for analysis:
- carrying out antibacterial therapy (to monitor treatment results);
- erosions and ulcers of the duodenum or stomach;
- symptoms of dysfunction of the digestive tract (regular constipation or diarrhea, flatulence, pain in various locations);
- genetic predisposition to diseases caused by Helicobacter pylori (malignant tumors of the digestive organs, chronic pathologies of the digestive tract);
- progressive atrophy of the mucous membranes of the stomach;
- regular pain in the stomach after eating food;
- Iron-deficiency anemia;
- a sharp decrease in body weight in combination with other symptoms of abnormalities in the functional state of the digestive tract;
- presence of blood in vomit or feces;
- identified neoplasms and polyps in the digestive system;
- esophageal ulcer or gastroesophageal reflux.
We recommend watching the video:
Complications
H. pylori infections lead to peptic ulcers, which lead to even more serious complications:
- Internal bleeding caused by the spread of a peptic ulcer to a blood vessel;
- Obstruction (blocking) if swelling or swelling blocks the entrance or exit of the stomach;
- Perforation (through ulcer) of the stomach wall;
- Peritonitis is a severe infection of the peritoneum.
Research shows that people infected with Helica also have an increased risk of developing cancer - it is a leading cause of stomach cancer.
When is a Helicobacter test prescribed?
When is it appointed?
- The reason for prescribing a study is the patient’s complaints, as a rule, these are:
- pain in the stomach after every meal;
- constant belching;
- loss of appetite and weight for no apparent reason;
- regular heartburn;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- difficulty swallowing food;
- gagging.
Based on the listed symptoms, it cannot be said that this is an infection; laboratory analysis is required.
What does the test result show?
A conclusion with a “positive” result indicates the presence of an infection in the body (presence of IgA antibodies). A negative test means the absence of IgA antibodies, this may indicate that the person is healthy or the disease is in remission. The result may be indeterminate, in which case testing is repeated after about 2 weeks.
The conclusion with a description remains with the gastroenterologist. The degree of damage is expressed as a percentage:
- norm – up to 1%;
- mild degree – from 1 to 3.5%;
- average degree – from 3.5 to 6.4%;
- severe degree – 6.5 to 9.4%.
More than 9.5% - emergency treatment is required, the degree of infection is extremely severe. Antibiotics are considered effective therapy. The analysis gives a clear picture of the interaction of immunoglobulins with the causative agent of the disease, which makes it possible to determine the presence/absence of bacteria.
How long does it take for repeat tests to be taken?
For reference. Each method used in identifying Helicobacter has its own characteristics, which are present not only in the conduct and delivery of the analysis, but also in the timing.
After all, tests to detect an intestinal infection will be necessary even after the course of treatment. And from what research method will be prescribed it will be clear not only how to get tested for Helicobacter pylori, but after what period of time after the course of treatment.
If a doctor prescribes a urease breath test for re-examination, it is better to do it 4 to 6 weeks after the end of the course of treatment. An immunological study can show a more accurate result. But only if there is an intestinal infection in the body.
Unfortunately, the negative answers they often show turn out to be erroneous. Constipation is often the cause of a false answer. It is best to conduct a study using this method 2 weeks after treatment.
For reference. Gastroscopy is an effective method. It allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and clarify the likelihood of developing cancer pathology. But due to the specifics of its implementation, many refuse to conduct it.
If you decide which method is better and simpler, then, of course, urease respiratory. But if you are interested in which one is more accurate, the result will be FGDS.
Preparing for the test
It is proper preparation that affects the accuracy of the result, so it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations:
- refuse antibiotic treatment a month before the procedure;
- do not drink alcohol for three days;
- do not eat anything, do not smoke, do not chew gum 6 hours before the examination;
- an hour before the test you are allowed to drink no more than 10 ml of water;
- Immediately before the test, brush your teeth and use mouthwash.
- It is also undesirable to eat legumes - soy, beans, peas and corn.
Preparation
In order for the results of the Helicobacter pylori antigen test to be informative, a number of measures must be observed:
- It is necessary to submit biomaterial strictly before starting antibacterial therapy;
- 24-48 hours before collecting stool, do not take laxatives, and do not use rectal suppositories, oils and ointments;
- 72 hours before the test, do not take medications and products that affect the color of stool (iron preparations, barium sulfate, beets, black currants);
- Avoid smoking, drinking coffee and strong tea 24 hours before;
- 48-72 hours in advance, abolish foods rich in plant fiber (bran, cabbage, carrots, radishes).
Important! Before collecting feces, it is necessary to toilet the perineum and genitals, as well as urinate.
How is it carried out?
Despite the simplicity of the examination, it is carried out under the supervision of a specialist in a hospital. Respiratory diagnostics last no more than 15 minutes, are performed using a special tube and are divided into two stages. The use of an electronic device reduces the procedure time to 10 minutes. The patient is positioned in a comfortable position, breathing is even, a tube is placed in the mouth, and the tongue should not be touched.
If you need to spit or swallow saliva, you can do this by first removing the tube. The patient is given a solution of urea to be taken orally, so that gas is formed during hydrolysis and released into the oral cavity. Exhaled air is taken for analysis, during which the level of gas formed during the hydrolysis of urea is compared with the initial level of this gas content. A repeat test is done after a month to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
How to treat an infection
If Helicobacter is detected, the doctor prescribes a combination of two antibiotics along with a drug that reduces stomach acidity. Reduced acidity helps antibiotics work more effectively. This treatment is called triple therapy. Some of the drugs that are used in triple therapy include:
- clarithromycin (or analogues);
- proton pump inhibitors (PPI): lansoprazole (Prevacid), esomeprazole (Nexium), pantoprazole (Protonix), or rabeprazole (AcipHex);
- metronidazole (7 to 14 days);
- amoxicillin (7 to 14 days).
Treatment may vary depending on the medical history (treatment can be primary or secondary), and the presence of an allergy to any of the drugs.
How to take the test correctly?
The result depends on the correct preparation and collection of material. No human presence is required; it is enough to deliver the correctly collected material on time.
Medical products (drugs, medicines, vitamins, dietary supplements) are mentioned for informational purposes only. We strongly do not recommend using them without a doctor's prescription. We recommend reading: “Why can’t you take medications without a doctor’s prescription?”
Preparing for the test
When preparing, you must strictly follow the following rules:
- donate stool for analysis no earlier than 1 month after the last dose of antibiotics;
- during the 3 days preceding the collection of material, you should not consume coloring products (tea, coffee, red and orange fruits and vegetables, turmeric, curry, soy sauce),
- exclude coarse fiber - cabbage, radish, radish, pearl barley, bran, beets;
- You should not take medications that enhance intestinal motor function - Lactulose, Motilium and the like;
- give up alcohol;
- do not take antacids (Almagel and the like);
- collect material during the first week after the onset of symptoms of the disease (then the concentration of Helicobacter in feces decreases).
3 days are enough for preparation. At this time, it is advisable to stop taking all medications (if this is not possible, tell your doctor the names and dosage). You need to reduce your consumption of fish and meat, steam or boil them. The best food for this time is porridge and fermented milk products, vegetable and fruit purees, weak soups, neutral natural juices (apple, white grape), compotes, fruit drinks, weak tea, rosehip decoction.
Be sure to read:
Analysis of feces for carbohydrates in infants: delivery and interpretation of readings
Preparing containers
Some laboratories provide containers for analysis, including their cost in the total price.
This is the best variant. A container for stool can be purchased at a pharmacy, it costs a few rubles. The container is sold sterile and must not be opened, wiped or washed. A plastic spoon is attached to the lid, which is used to scoop up the material. As a last resort, you can use a glass jar with a well-fitting lid (baby food). The jar needs to be washed well and then boiled along with a lid and a spoon or other object that will be used to collect feces. If bacteria remains on the dishes, the analysis will be incorrect.
Collection of material
You cannot collect material from the toilet or diaper. The toilet should be covered with a clean plastic bag, and instead of a diaper (for a child or a bedridden patient), an oilcloth should be laid. It is allowed to take material from a clean pot.
The container is filled no more than one third, close the lid tightly. Attach the directions to the container or write on the label (legibly) the patient's first and last name, year of birth.
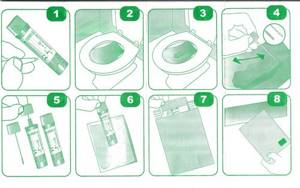
How and for how long can the material be stored?
The container with the material is delivered to the laboratory as early as possible, optimally on the day of collection. If there is no possibility of urgent delivery, storage in the refrigerator for no more than 2 days at a temperature not exceeding +4 °C is allowed. If longer storage is necessary, the material is frozen once at a temperature of -20 °C.
Other research methods
Your doctor may order many other tests and procedures to help confirm the diagnosis:
- Physical examination.
During a physical examination, the gastroenterologist examines the abdomen to check for signs of bloating, abdominal wall tension, and pain. - Blood analysis.
The biomaterial is taken from a vein, the indication is a clear clinical picture of infection, everyday contact with the patient, and preventive measures. Blood samples are needed to look for antibodies against H. pylori. - Stool analysis.
Stool analysis is highly accurate (up to 95%). In order for a stool test to give a reliable result for the presence of Helicobacter, you must stop taking antibiotics before the test. - Endoscopic methods.
The most unpleasant examination option is examination with an endoscope. In this case, the doctor inserts a tube through the mouth into the stomach and duodenum. A camera attached to the end of the tube transmits images to a monitor. The method is quite accurate - the gastroenterologist can see ulcers and other changes on the mucous membrane and take tissue particles from their surface. But at the same time, this procedure is painful for patients, so it is better to resort to endoscopy in extreme cases, when you need to make sure that the process is benign.
If we compare all the tests for Helicobacter pylori, we can conclude that most of them do not have the proper accuracy, while the breath test gives a truly objective result. If we compare this analysis with an endoscopic examination, it is preferable for many people who do not want to endure nausea and discomfort during the examination.
The Helicobacter breath test is truly a wonderful alternative to outdated methods.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
FGDS with Helicobacter pylori
The endoscopic examination method is considered the most accurate test. A biopsy of the gastrointestinal tract reveals not only the presence or absence of bacteria, but also determines the stage of the disease, and also allows you to immediately find out whether the organs are affected or not.
This study is carried out using a gastroscope (a long tube inserted into the gastrointestinal tract through the mouth and equipped with a camera and a device for taking a tissue sample). In addition to taking biomaterial for biopsy, the gastroenterologist visually examines the condition of the walls of the duodenum and stomach.
Two hours before the biopsy, you should not smoke or drink, and your last meal should be 12 hours before.
FGDS with Helicobacter pylori can be performed under anesthesia. The procedure lasts about twenty minutes. The doctor will determine the ulcer, if any, during the examination, and the patient will receive the test results the next day.
Our clinic has the opportunity to conduct FGDS with Helicobacter pylori and other studies.