With the advent of x-rays, the task of making a diagnosis for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract has been significantly simplified. Further development of technology served as the basis for the development of new, less harmful to the body, examination methods. Today, more and more often, if it is necessary to examine the gastrointestinal tract, patients turn to magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography, which allows them to look inside the body without resorting to instrumental intervention. However, the interpretation of MRI and CT results is simpler compared to interpretation; x-ray.
Computed tomography of the stomach
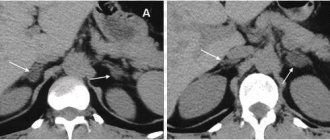
CT scan provides a clear image of the esophagus and stomach, their internal cavity, walls and circulatory system.
Why do you need a CT scan of the stomach?
CT scan of the esophagus and stomach provides comprehensive information in diagnosing a number of pathologies and diseases of the abdominal cavity, from oncology to damage to the lymph nodes. CT scan of the esophagus and stomach differs from other diagnostic methods in that it shows not only the mucous membrane of the internal cavity, but makes it possible to see blood vessels and a section of the walls in any plane.
Do they do MRI of the stomach and intestines with contrast?
Magnetic resonance imaging can be performed with contrast. This technique allows you to increase the information content and sensitivity of the method to some gastrointestinal diseases. Contrast agents for intravenous administration can accumulate only in those tissues that are affected by an inflammatory or tumor process. The affected areas of the intestines or stomach will be highlighted in the images, making diagnosis easier.
In some cases, the use of contrast during MRI helps to clarify the preliminary diagnosis, confirming the results of the biopsy with high accuracy. The reason is that the dynamics of absorption and release of the contrast agent is directly dependent on the type of pathological process and is a constant indicator for a particular disease.
How to prepare for the examination
Before a CT scan of the stomach, you must follow a diet and follow a number of simple instructions. The study is carried out on an empty stomach. Therefore, before a CT scan of the stomach, it is recommended to take drugs that reduce gas formation, for example, activated carbon.
Diet
Intestinal motility and gases in the intestinal tract can distort CT scan data. Therefore, CT scans are done on an empty stomach or there is no point in the procedure. For best results, it is recommended to adhere to a certain diet.
For a couple of days, it is necessary to limit the proportion of foods in the diet that interfere with peristalsis. For example, peas, legumes, fermented milk products, black bread.
FAQ
What are the advantages of CT scan of the stomach and intestines over other diagnostic methods?
The “gold standard” for examining the stomach and intestines today are endoscopic methods - gastroscopy and colonoscopy. But if it is impossible to perform a colonoscopy or as a screening examination of the colon, CT colonography can be used.
How to prepare for a CT scan of the intestine?
A CT scan is performed only after bowel cleansing (as is an endoscopic colonoscopy). This means that it should not contain feces and food masses. Three days before the tomography you need to follow a certain slag-free diet. On the eve of the study, you take a special laxative drug, which will be recommended to you by your attending gastroenterologist or therapist.
Answers questions:
Chervonenko Svetlana Vladimirovna
Radiologist
doctor
CT scan of the stomach: how it is performed
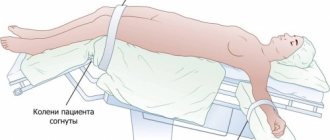
During the examination, the patient takes a horizontal position on a table that is placed inside the tomograph. The specialist for CT scanning of the esophagus and stomach is in the next room, but continues to observe the patient through the glass and maintains contact with him through two-way communication.
Contrast enhancement
A CT scan of the stomach with contrast is performed when tumors are suspected or when examining blood vessels. An iodine-based contrast agent is administered orally (drunk by the patient) or intravenously. After a CT scan of the stomach with contrast, the substance is naturally eliminated from the body.
What to choose: CT or MRI?
When choosing between CT and MRI, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of each type of examination and the doctor’s recommendations. When making a decision, the following factors should be considered:
- Clinical picture. If diseases such as an ulcer, polyp, other disorders in the structure of the intestinal wall or obstruction are suspected, computed tomography is most often used. This examination can detect internal bleeding, which helps save the patient’s life. Due to the fact that the study takes no more than 10-15 minutes, the diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract injury and the prescription of the necessary treatment occurs quite quickly.
- Suspicion of cancer. MRI of the gastrointestinal tract allows you to obtain an accurate diagnosis regarding oncological tumors. Finding a tumor, especially in the pancreas, is quite difficult, especially with acute inflammation. This method provides an accurate diagnosis of such pathology and makes it possible to prescribe effective therapy.
- Restrictions. A CT scan involves exposing the patient to radiation. Radiation exposure is becoming limiting in the use of CT as a diagnostic method. CT scanning is recommended no more than once a year. In the case of MRI, examination of the gastrointestinal tract can be performed at any time. The only limitation of MRI is the contraindications that are observed in the patient himself.
- Pregnancy. Pregnant women are prohibited from undergoing examinations involving computed tomography. MRI examinations are carried out starting from the third month of pregnancy.
Our equipment
In our hospital, diagnostics of the digestive tract using MRI and CT methods is carried out by experienced specialists using modern digital tomographs from Philips, (Netherlands).
MRI of the gastrointestinal tract is performed on an Ingenia 1.5 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging scanner , which provides highly informative images of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, vessels and soft tissues, specifically examined areas. Speeds up examination by 40% compared to other tomographs.
CT of the gastrointestinal tract is performed on an Ingenuity Elite 128-slice computed tomograph, which is capable of visualizing small details, which is important in the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms. Equipped with iMR technology, which improves image quality by 60-80% while reducing radiation exposure.
If you need to undergo a CT or MRI of the gastrointestinal tract in Moscow , contact the Clinical Hospital on Yauza. You will receive expert-level research in the shortest possible time.
Contraindications to MRI of the abdominal cavity
Absolute contraindications to MRI of the abdominal organs, in which this procedure cannot be performed under any circumstances, is the presence of electronic or ferromagnetic medical devices installed in patients (pacemaker, Ilizarov apparatus, cochlear implants, etc.). A high-intensity magnetic field can damage these products or cause burns to the surrounding soft tissue.
Relative contraindications allow MRI to be performed, but subject to a number of conditions. Thus, in patients suffering from claustrophobia, MRI of the abdominal organs is performed on open-circuit tomographs.
Due to the fact that during the procedure the patient must maintain a motionless position for quite a long time, relative contraindications to it are preschool age children and the patient’s condition, accompanied by increased motor excitability. In these cases, an MRI of the abdominal organs can be done in a state of medicated sleep.
It is undesirable to perform MRI in women in the first trimester of pregnancy, since today there is not yet a sufficiently large amount of statistical data available to confirm that this diagnostic method does not have a teratogenic effect. If necessary, when the expected benefit to the life and health of the woman significantly exceeds the possible risk to the fetus, MRI of the abdominal organs in pregnant women can be performed.
Contraindications for MRI of the abdominal organs with contrast are:
- chronic renal failure;
- allergy to contrast agent;
- pregnancy of any stage.
Preparation
High-quality CT of the intestine requires preparation aimed at reducing the mobility of the digestive tract. The preparatory stage begins 2-3 days before the study with a transition to a diet that reduces gas formation. You should first buy laxatives to clean the intestinal cavity, which should be cleared of excess feces on the day of diagnosis. Computed tomography of the intestine with contrast requires scanning on an empty stomach with a minimum pause in food intake of 6 hours.
Before entering the room with the tomograph, you should remove all metal objects and jewelry. Clothes should be loose. Some clinics provide a set of disposable clothing, which is included in the price of the examination.
Indications for MRI of the abdominal cavity
Indications for MRI are the following diseases of the abdominal organs:
- portal hypertension;
- acute or chronic pancreatitis;
- hepatomegaly of unknown origin;
- obstructive jaundice;
- cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis);
- identifying the presence of metastases;
- diagnosis of volumetric processes that do not have a tumor nature (parasitic cysts, organized hematomas, abscesses);
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- fatty liver;
- the presence of an inflammatory process of various etiologies;
- suspicion of a tumor;
- heart attacks or transient ischemic disorders in parenchymal organs;
- detection of foreign non-metallic objects;
- structural anomalies of the abdominal organs;
- abdominal injuries.
How is MRI of the gastrointestinal tract performed?
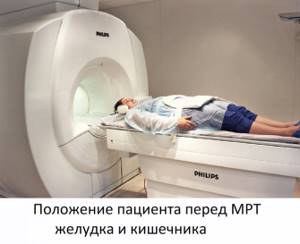
Magnetic resonance imaging of the gastrointestinal tract is an extremely simple, painless and safe procedure. All that is required of the patient is to lie still and follow the operator’s instructions exactly.
Before starting the procedure, you will be asked to put on headphones - they will protect you from the rather loud noise coming from the equipment. They also transmit operator instructions and music to help you relax and make waiting less tiring. The duration of the study is about 40 minutes (for studies with contrast - 55-60 minutes).
After completing the examination, you need to wait for the images to be decrypted. In our center it takes no more than 30 minutes. The images themselves on a CD, together with a specialist’s report, must be handed over to your attending physician. In addition, images can be obtained on film or a flash drive if you pay a little extra - CDs are not always convenient for storing research results.
Enterography with contrast agent
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (also called enterography) is most often performed to diagnose cancer, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis. These diseases are difficult to study using other non-invasive methods.
Contrast containing iodine is administered intravenously before CT scanning. After a few minutes, the substance is distributed throughout the body and makes visualization clearer and more effective. The contrast can be not only iodine, but also barium. The barium solution is drunk 20 minutes before the start of the procedure. Further diagnostic steps are fully followed.
Procedure
Before the examination, the patient must sit comfortably on the retractable table of the device. Then the couch is moved to the scanning part of the tomograph and the screening program is started. The duration of a CT scan of the intestine takes on average several minutes. When contrast is used, the duration of the scan increases to half an hour. The results of the computed tomography scan will need to wait 30-40 minutes while the doctor completes the decoding procedure and description of the tomograms. Based on the results of the examination, the patient will receive a written doctor’s report and a recording of CT images on electronic or film media. With this data, he needs to make an appointment with the attending physician so that he can complete the diagnostic procedure and decide on a treatment plan.