Creatinine tests
Doctors prescribe a laboratory test of urine and blood taken from a vein for creatinine levels to all hospital patients. It is also necessary for pregnant women and people
- with renal failure;
- undergoing hemodialysis;
- with hypertension.
To obtain the necessary data, a Reberg-Tareev test is prescribed. The patient gives a 24-hour urine sample, and then his blood is taken. To obtain a reliable result, it is necessary to accurately control and record the time of urine collection. It is carried out in three ways.
In the first case, the material is collected in two portions with an interval of 1 hour. The laboratory determines the amount of urine that is formed per minute and the creatinine content in it. With the second method, it is necessary to accumulate urine during the day. For most patients this is inconvenient, so the method is rarely used.
Another option is most often used in experimental medicine. It allows you to establish the glomerular filtration rhythm. The patient has to collect 2 portions of urine: daytime (from 8 to 20 o'clock) and night (from 20 to 8 o'clock).
Regardless of how urine is collected to determine creatinine in the blood, a single collection of biomaterial is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. Experts recommend not to engage in physical work the day before, and athletes to refuse training. And 2 days before the test, you do not need to abuse meat or fatty foods; it is better to limit baked goods in your diet.
Medications can make the test result unreliable. For example, vitamin C, hormonal agents, and some antibiotics increase creatinine. Thiazide diuretics, anabolic steroids, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can lower it.
Therapeutic measures
Low creatinine levels usually do not require treatment. They are limited to prescribing a diet with an increased protein content.
Treatment of elevated levels of this substance is carried out by a specialist - a urologist or nephrologist. He prescribes additional examinations and then gives recommendations on how to lower creatinine in the urine.
If the reason for the increase in the indicator is hypertension, diseases of the endocrine organs, drug therapy for these pathologies must be carried out. In parallel, agents for removing toxins (Polysorb, Enterosgel) are used.
If problems with the kidneys are detected, swelling occurs, use:
- diuretics (Furosemide, Indapamide);
- agents that stimulate the excretion of protein metabolic products (Lespeflan, Lespenefril, Chitosan);
- Dietary supplements based on alpha-lipoic acid, which normalizes protein metabolism.
Under no circumstances should you take medications on your own! The kidney is a vital organ. Its failure as a result of improper treatment can lead to death.
In case of renal failure, treatment is carried out in a hospital, where intravenous administration of sorbents is prescribed. In severe cases, dialysis is prescribed, which will need to be done for a long time.
The doctor and the patient must constantly monitor the content of creatinine and other toxins in the urine and blood - metabolites of protein metabolism, monitor blood pressure and sugar levels.
Drug treatment is carried out in parallel with the intake of medicinal teas from plants (rose hips, sage, cinnamon, lingonberries, rhubarb), which have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Causes and symptoms of deviations from the norm
The dangerous point is that it is impossible to identify the level of deviation at an early stage of the examination; the indicators change only when a large part of the kidney is already affected.
The table shows the general identified norms for men, but there are also individual ones.
Values can change both upward and downward. In this case, the following are observed:
- any form of renal failure;
- thyroid disease;
- violations of the contractile function of the heart muscle;
- development of cancer;
- dehydration;
- muscle spasms;
- crash syndrome.
If you have one of the symptoms, it is recommended to immediately seek advice from a specialist. Ignoring the problem can lead to the development of acute renal failure and complete kidney failure. In medicine, only an increase in creatinine is distinguished; a reduced level is not considered a pathology, but is a symptom accompanying the main diagnosis.
The reasons for the failure may be:
- infectious diseases;
- circulatory disorders due to injuries;
- malfunction of the renal glomerulus;
- severe blood loss;
- poisoning of the body with toxic substances.
The presence of creatinine in the blood (the norm in men) does not cause any discomfort. With severe deviations, many experience increased sweating, frequent urge to go to the toilet or difficulty urinating, increased abdominal volume, swelling, and a constant feeling of thirst.
There are cases when the level of the substance does not correspond to the clinical picture of the disease. This phenomenon occurs among bodybuilders and weightlifters. Taking non-protein supplements leads to a sharp jump in indicators, so before taking tests you need to inform your doctor about their use.

What determines the level of urea
Based on the mechanism of formation and the route of excretion of urea, the main factors influencing its performance are identified:
- liver performance;
- functional capacity of the kidneys;
- human nutrition;
- circulating blood volume (CBV);
- genetic diseases that disrupt metabolism;
- age.
With age, standards increase for both men and women. This is due to a gradual slowdown in metabolism and a decrease in kidney activity, as a result of which urea is less efficiently utilized.
Young men have slightly higher urea levels than women of the same age. Representatives of the stronger sex have a higher daily protein requirement. This is required by hormonal levels, especially if a man is engaged in physical labor.
In physically active people, urea levels are close to the upper limit of normal, especially when using steroids and protein shakes
In a normal pregnancy, a decrease in urea levels in the third trimester is possible for two separate or interrelated reasons:
- over the last 12 weeks, the fetus has been gaining muscle mass, so there are no extra amino acids left in the body of the expectant mother;
- a woman does not get enough protein from food.
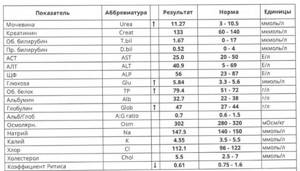
Table: normal levels of urea in the blood
| Period | Normal limits (mmol/l) |
| Newborns (up to a month) | 1,2–5,3 |
| 1–12 months | 1,4–5,4 |
| 1 year–14 years | 1,8–6,6 |
| 14–60 years (men) | 3,7–7,4 |
| 14–60 years (women) | 2,3–6,6 |
| Men and women over 60 years of age | 2,8–7,5 |
| Pregnant women (I–II trimester) | 2,5–7,1 |
| Pregnant women (III trimester) | 2,5–6,3 |
Reasons for deviation of indicators from the norm and signs of violation
The level of urea in the body increases or decreases under the influence of physiological and pathological reasons.
Table: deviations of urea from the norm - causes, symptoms
| Blood urea level | Demoted | Promoted | ||
| Causes | Physiological | Pathological | Physiological | Pathological |
| Diseases and conditions |
|
|
|
|
| Symptoms and signs | none | There are no specific symptoms, general signs:
| none | First, general symptoms appear:
The further manifestation of symptoms depends on the disease that causes the increase in urea. If the level of urea increases in parallel with other protein metabolites (creatinine, nitrogen), we are talking about the development of uremic syndrome. Its signs:
Uremic syndrome develops in severe kidney diseases and emergency conditions. |
Formulas for calculating clearance
If blood is taken from a vein for analysis, the clearance will be calculated as follows:
For women, a reduction factor of 0.85 is introduced.
There is also a similar formula, where instead of 72 the coefficients are used: 1.04 for women and 1.23 for men (Colcroft-Gault equation).
The same formula for children will have a slightly different form:
K is a coefficient that takes into account the age and gender of the child, it is respectively 0.7 for boys over 14, 0.55 for children of both sexes from 2 to 14 years old and older girls, 0.45 for children under 2 years, 0.33 – for premature babies up to 2 years old.
If a study is carried out using the Reberg-Tareev method (Reberg test), the initial data for the calculation will be minute diuresis, as well as the concentration of creatinine in the blood and urine, clearance is calculated as follows:
A coefficient that takes into account body area can also be entered into the formula (for example, for a child or an overweight patient).
When determining the concentration in daily urine, clearance is not calculated; the study reflects only changes in the renal nephrons and the quality of organ functioning. The analysis is more often used in a hospital setting to monitor the functioning of the excretory system over time.
Immediately before taking any samples (blood, daily urine, Rehberg test), you should follow some rules (for 1-2 days before the test):
- stop drinking alcohol, strong coffee and tea;
- do not overload the diet with heavy proteins and fatty foods;
- maintain a drinking regime (1.5-2 liters of fluid per day);
- limit physical activity.
If a patient’s blood is taken for research, it is donated in the morning, on an empty stomach.
When collecting daily urine, do not forget about the following recommendations:
- it is advisable not to neglect hygiene procedures before each act of diuresis during the day;
- Collect urine in a sterile container and store in the refrigerator.
The Rehberg test will require the donation of urine and blood, and the urine can be either in the form of a single portion or daily. In the second case, the algorithm is similar to a daily test, supplemented by donating venous blood.
If the portion is one-time, then the order of delivery will be as follows:
- On an empty stomach, drink 0.5 liters of water, then empty your bladder without collecting urine.
- After 30 minutes, blood is drawn from a vein.
- After another 30 minutes, urination occurs and the entire portion of liquid is collected.
Clearance and content of creatinine in urine helps to assess the overall performance of the kidneys and is a necessary study when prescribing and implementing hemodialysis, suspected urolithiasis or renal failure, as well as when calculating the safe dosage of certain medications. Testing is also inevitable for a potential organ donor. The research methodology is selected based on the required information content of the result.
source
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright holders
- Billirubin
- Hemoglobin
- Glucose
- Immunity
- Feces
- Coagulogram
- Cortisol
- Creatine
- Blood in urine
- Lymphocytes in the blood
- Luteinizing hormone
- Lactic acid
- General urine analysis
- Progestone
- Prolactin
- Rheumatoid factor
- Serotonin
- Spermogram
- Testosterone
- Fibrinogen
- Cholesterol
- Estradiol
Folk remedies
Folk remedies and potions from the following plants that have a diuretic effect will help bring creatinine to normal:
- Nettles;
- Calendula;
- knotweed;
- Sage;
- Burdock;
- Lingonberries;
- Rosehip;
- Dandelion;
- Chamomiles;
- Mint;
- Oak;
- Birches.
Nettle recipe
Nettle leaves have a diuretic and restorative effect. Pairs well with knotweed and calendula. Two spoons of the mix are poured with boiling water (a glass), infused, and filtered. Drink it in a couple of days.
Medicinal collection
Three spoons of a medicinal mixture containing sage, burdock, dandelion leaves, birch bark, pour boiling water (a glass), filter and drink three spoons before bed.
Infusions
Lingonberry foliage (60g) is poured with boiling water (a glass), kept in a water bath for 30 minutes, and cooled. Drink 1/3 glass three times a day. You can make a collection of lingonberries, motherwort, chamomile, dandelion, string, and violets. An infusion of chamomile and mint is prepared in the same way.
Lingonberry infusion
Four tablespoons of a mixture of dandelion root, aerial parts of St. John's wort, celandine and violet flowers, pour water (two glasses), boil, leave for an hour, filter. Drink 5 ml three times a day, half an hour before meals for 30 days.
Oak bark is used in a mixture with bearberry grass. In the first option, take two spoons of the mixture. Fill with water (glass). Bring to a boil, strain. Drink 6 tablespoons three times a day.
Another option is oak bark, birch bark, birch buds. Four spoons of the mixture are boiled for one hour. Cool, infuse, filter and drink 100 ml six times a day.
Fruit mixture
A mixture of fruits, leaves of rose hips, hawthorn, parsley root, and dill seeds has a good effect. A spoonful of the mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water and left overnight. Dosage: seven doses of five spoons per day.
The use of folk remedies is combined with adherence to the water regime. You need to drink at least one and a half and no more than two liters of fluid per day. Lack and excess of water prevents the excretion of excess creatinine.
What to do to prevent high creatinine? Promote moderation in lifestyle. Avoid excessive physical activity, exhausting religious fasts and weight loss diets. Regular examinations, morning exercises, and a balanced diet will help you avoid troubles caused by a distortion of nitrogen metabolism.
Creatinine is considered a reliable indicator of the functional capabilities of internal organs. Assessment and correction of the situation caused by hypercreatinimia must be carried out by medical professionals.
How to reduce creatinine levels in the blood?
There is no separate treatment to reduce the rate. Its reduction can only be achieved by treating the underlying disease that caused the increase. For this purpose, drug therapy is selected for the person and a rational diet is prepared.
A diet with elevated creatinine is extremely important; it helps improve the biochemical composition of the blood and facilitate therapy for the underlying disease. The patient is advised to limit or completely avoid the consumption of salt and salty foods.
How to control the amount of salt consumed? To do this, the patient is prohibited from adding salt to all prepared dishes. The permitted amount of table salt is given to the person, and he can independently add salt to the dishes. At the same time, do not exceed the permitted amount of salt.
The amount of animal protein consumed is also reduced. If the diet contains 70 grams of proteins, then only a third of them can be of animal origin. In severe stages of kidney damage, the amount of animal protein is reduced to 10-20 grams per day.
Alternatively, it is recommended to consume dairy products, eggs and lean lean fish.
Important: the duration of a low-protein diet is determined by the attending physician based on the patient’s condition
According to indications, the patient can be transferred to a protein-free diet.
After repeated tests, further treatment tactics are determined. A decrease in creatinine indicates the possibility of increasing the amount of animal protein consumed.
The absence of positive dynamics in returning the indicator to normal indicates the ineffectiveness of the chosen treatment methods and the need for their correction. In parallel with this, the patient is recommended to carry out fasting days.
How to treat?
Below is a little about how to treat this problem:
- Diet (excluding spicy foods, salt, seasonings, limiting animal fats);
- Elimination of excessive physical activity;
- Compliance with the regime of fluid intake, preferably water (for people suffering from kidney failure, the amount of fluid consumed per day by a person should not exceed the amount allocated by more than half a liter);
- Timely diagnosis;
- In complicated situations, they resort to hemodialysis (hemodialysis is a procedure by which the blood in the body is purified artificially);
- Drugs that promote protein metabolism (for example, Lempenefril);
- Homeopathy (herbal preparations).
Research methodology
Creatinine clearance is a diagnostic test used to determine renal filtration function (GFR). During the study, the rate normally required to purify blood plasma through the nephron is calculated per unit time.
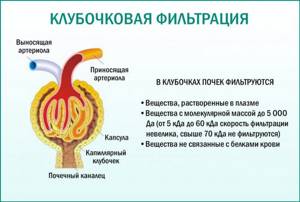
The nephron is a special anatomical and physiological unit of the kidney. It consists of a renal corpuscle (filtration glomerulus, capsule) and a tubular system that provides reabsorption (reabsorption) and excretion of various substances. International standards use glomerular filtration rate (GFR) to calculate the stage of kidney failure to provide an indication of the extent of organ damage.
Preparation
Despite the fact that the method is calculated, the key values for it must be determined in the laboratory. It is believed that test strips have a larger error, so preference is given to the classic test.
Calculation of creatinine clearance (Reberg-Tareev test) is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- 2-3 days before the analysis, exclude extractive substances (spices, excess salt), alcohol from the diet and temporarily stop taking other medications (after consultation with a doctor, since some medications are vital).
- The water regime is normal (1.5-2 l/day), protein consumption is moderate.
- The patient urinates in the morning, drinks 200 ml of clean still water and, still on an empty stomach, collects urine in designated containers for a certain time (usually two hours).
- In between the collection of urine samples, venous blood is taken from him for further research.
Cockcroft-Gault formula
The simplest and most accurate method, which is accepted in most laboratories, is to calculate the glomerular filtration rate, taking into account the age and weight of the patient. The Cockcroft Gault formula for calculating creatinine clearance is as follows:
- For men: GFR = 1.23 * ((140 – age in years) * weight in kg))/blood creatinine (µmol/l)).
- Women: GFR = 1.05 * ((140 – age in years) * weight in kg))/blood creatinine (µmol/l)).
- Example: 1.23 *( (140-35)*65/90) = 93.3 (ml/min).
Alternatively, any other standardized formulas may be used. These include CKD-EPI or MDRD, each of which has its own characteristics and percentage of error.
conclusions
Calculation of creatinine clearance and glomerular filtration rate is mandatory for pregnant women and people with severe forms of immunodeficiency, as well as congenital anomalies. If you accidentally notice changes in the tests (preventive examination), it is recommended to consult a therapist who will refer you to the necessary specialist with a more specialized profile (nephrologist, urologist, endocrinologist).
Normalization of indicators is possible when the causative disease is eliminated. Chronic damage often requires lifelong treatment and lifestyle modifications, so it is necessary to try to prevent progression by seeking qualified medical help in a timely manner.
Creatinine clearance - normal creatinine content
Evaluation of the index, which is creatinine clearance, allows us to determine the efficiency of glomerular filtration. Designated as GFR, it allows you to estimate how many milliliters of plasma can pass through the kidneys in one minute. In a healthy person whose kidneys are functioning properly, the GFR is 120 ml/min, which means that 120 milliliters of plasma is filtered through the glomeruli in one minute. Evaluation of the result using the GFR indicator allows you to determine the degree of renal failure.
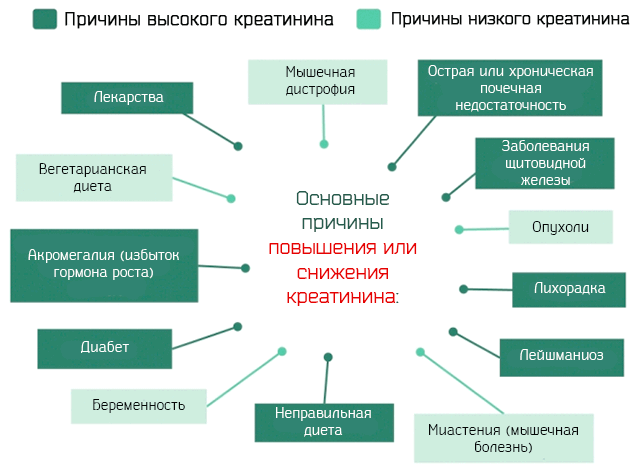
An increase in the GFR value, i.e. creatinine clearance, sometimes occurs during pregnancy. Other aspects that influence the increase in its concentration are physical activity and meat consumption. This can also be facilitated by diuretic drugs, so-called diuretics.
A reduced creatinine clearance is usually equivalent to a situation where blood flow to the kidneys is reduced. However, it sometimes occurs in cases of congestive heart failure or acute and chronic renal failure. Other ailments that reduce creatinine clearance are kidney obstruction and even urinary tract infection.
Creatinine in the blood is also reduced by specific groups of drugs. These include drugs such as cimetidine, used for gastric and duodenal ulcers, and cisplatin, which is used in chemotherapy. Antibiotics, including ephalosporins and aminoglycosides, also negatively affect the GFR index.
When is it necessary to check?
The doctor, when examining the patient and collecting anamnesis, will definitely write out a referral for a biochemical examination, including a urine test for creatinine, if the latter complains:
- for pulling, cutting or sharp pain in the lower back;
- feeling of insufficient emptying of the bladder;
- frequent urge to urinate, including false ones;
- the presence of purulent, mucous or bloody impurities in the urine;
- discomfort when urinating, accompanied by burning and pain;
- severe swelling of the face, lower (legs) and upper extremities.
In addition to the primary diagnosis, by studying the level of creatinine, the functional characteristics of the organs of the urinary system are assessed in multiple pathological conditions, which include the following. Acute and chronic kidney diseases - glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the renal glomeruli) and pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis) in many cases become the cause of renal failure, which can develop even to the stage of decompensation.
To regularly monitor the filtration work of the kidneys, patients periodically determine their creatinine level. In these pathologies, it is reduced. Metabolic pathologies - diseases caused by its disruption, require constant monitoring and the creation of normal conditions for kidney activity. Thus, with diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland (hypo- and hyperthyroidism), adrenal glands and pituitary gland, creatinine values may go beyond the limits of indicators accepted as normal.
An acute form of inflammatory and infectious diseases - excessive intoxication leads to problems with filtration in the renal glomeruli, which will cause an increase in creatinine. This category includes diseases of a bacterial and viral nature. Drug therapy with drugs that can affect the condition of the urinary system. The content of this metabolite is checked to assess the performance of the kidneys and minimize the risks of reduced filtration supply.
Autoimmune pathologies such as lupus erythematosus (structural damage to connective tissue) and vasculitis (destruction of the walls of blood vessels). Arterial hypertension - increased pressure can lead to a pathological shift in creatinine parameters. Oncological neoplasms, both benign and malignant, in some cases influence the content of this substance.
Checking the concentration of creatinine in urine is also carried out for preventive purposes:
- patients who have suffered acute forms of diseases of the urinary system, in particular the kidneys;
- as a screening examination before and after surgical operations in the genitourinary area;
- monitoring the course of pregnancy complicated by various manifestations of insufficient renal function;
- people with a genetic predisposition to pathologies of the urinary system;
- obtaining a comprehensive assessment of the functioning of the urinary internal organs.
Reference! Daily urine, due to its approximately constant creatinine content, can be used for other diagnostic techniques, for example, hormonal tests.
Analysis to determine creatinine clearance in the body
Detecting creatinine in the blood, as well as in urine tests, is required quite often.
Most often, the calculation of creatinine clearance is carried out for the following categories of people:
- people with high blood pressure;
- pregnant women;
- patients whose normal kidney function has been replaced by dialysis;
- people undergoing treatment in a hospital;
- patients with recently diagnosed renal failure.
Also, endogenous creatinine clearance is checked during LBC, since its units of measurement also affect overall health.
The amount of creatinine clearance is currently determined in several ways:
- urine collection, which is carried out throughout the day;
- Reberg's test;
- blood donation performed once.
Such an analysis should be stored at home in a cool and dark place - it is best to place it in the refrigerator so as not to spoil the test results.
How not to spoil the result of the creatinine clearance test?
Before collecting, there are a few important tips to follow:

- Before donating urine, you should limit the intake of foods that can change the color of urine. These include some vegetables, foods and dishes that contain a lot of dyes. Drinking coffee and tea is also prohibited.
- The urine container must be dry, clean and sterilized. To avoid doing this yourself, you can purchase it at the pharmacy.
- Before each trip to the toilet, you must wash yourself thoroughly. Women are advised to use cotton pads, which will prevent vaginal discharge from getting into the urine. When collecting urine from children, they should wash it themselves.
If the doctor has directed the patient to donate blood, with the help of which it will be possible to determine the amount of creatinine clearance, serious physical activity on the body cannot be performed within 2 days. Otherwise, exercise or lifting weights will cause an increase in the amount of creatinine in the muscles, which will also increase the amount of this substance.
The patient should also follow these rules:
- in the evening you should not take heavy meals, which include meat, legumes, baked goods and fatty foods, because they increase the thickness of the blood, which makes it impossible to conduct the study correctly;
- the patient should also drink 1.5-2 liters of liquid;
- Eating in the morning is strictly prohibited.
Increasing performance
Most often, children may experience an increase in creatinine in the blood. This deviation indicates a violation of the kidneys. In addition, high creatinine in children is observed with active breakdown of muscle tissue. This can be caused by injury or poor circulation in the muscles.
Among the pathological causes of increased creatinine are:
- Kidney failure.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Polycystic disease.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Nephropathy.
In addition, creatinine in the blood may be elevated due to taking certain medications. A blood test for creatinine is not an accurate diagnostic tool. That is, if there are deviations, the doctor cannot immediately make an accurate diagnosis. However, this study can significantly narrow the search for pathology.
You can reduce the indicator only by determining the true cause of the deviation. If kidney disease is suspected, the child will undergo additional examinations. If the initial diagnosis is confirmed, you will be prescribed treatment. In the case where the increase in indicators was caused by poor nutrition or taking medications, you will be advised to eliminate these factors and conduct a repeat blood test. It is impossible to lower creatinine without identifying the reasons. This is not an independent disease, but only a consequence of certain abnormalities in the functioning of the body.
In addition to treatment aimed at getting rid of the underlying disease, children with high creatinine are prescribed a certain diet that helps cleanse the body and relieve the load on the kidneys.
With this deviation, the following food products are prohibited:
- Fat meat.
- Whole milk.
- Fatty fish.
- Spicy food.
- Coffee and tea.
- Delicious baked goods.
- Canned food.
- Fast food.
- Sweets.
- Crackers and chips.
- Fried and smoked food.
The list of restrictions includes:
- Poultry meat.
- Low-fat fish varieties.
- Salt and sugar.
- Eggs.
These products can be consumed, but only according to the schedule that your attending physician will draw up for you. If the baby has a pronounced deviation, the doctor may completely prohibit these products. A diet with high creatinine helps normalize kidney function and cleanse the body of waste products.
Recommended products include:
- Any plant food.
- Berries and drinks made from them.
- Fermented milk products.
- Low-fat varieties of cheese and cottage cheese.
- Butter.
- Olive oil.
- Cereals.
- Honey.
Food from these products should be prepared by boiling, stewing or steaming. You can also make casseroles in the oven
It is important to follow all doctor's instructions. In this case, it will be much easier for the body to defeat the disease
Reasons for deviation from the norm
The final result is influenced by the secretion of the substance by the renal tubular system, which means that creatinine clearance can be significantly higher than the actual GFR values, especially in patients with chronic pathology. Incorrect collection results in a false rejection.
Increased GFR
Increasing filtration capacity in the long term is fraught with depletion of functional reserves, that is, the organ will simply be “exhausted.” In the future, the kidney will simply lose the ability to increase GFR in response to damage (stimulus). This occurs in the following diseases:
- glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome;
- early stage of hypertension;
- focal hyalinosis;
- segmental sclerosis;
- diabetes;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- intense physical activity;
- taking cephalosporins (antibiotics).
The earliest sign of hyperfiltration is microalbuminuria (the appearance of protein in the urine). The “gold standard” for diagnosing renal damage is a biopsy followed by morphological examination.
Decrease in GFR
In clinical practice, cases of deterioration in the filtration capacity of the kidneys are most often encountered, which may be due to the following reasons:
- pyelonephritis;
- bleeding (injuries, surgical interventions);
- dehydration (profuse vomiting, diarrhea, diabetes insipidus, adrenal insufficiency, burns);
- shock of any etiology;
- vasculitis;
- sepsis, anaphylaxis;
- taking medications (diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, etc.);
- malignant hypertension;
- jades;
- urolithiasis disease;
- long-term compartment syndrome;
- tumors;
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- decompensated heart or liver failure.
What is endogenous creatinine clearance?
A more accurate assessment of kidney function can be made by calculating the rate of creatinine excretion from the body. This indicator is called endogenous creatinine clearance and characterizes the glomerular filtration rate. Endogenous creatinine clearance can be calculated in two ways:
- Creatinine clearance (CrCl, ml/min) is calculated using a formula using the measured serum creatinine level (CrCl, mg/dL). The patient's age in years is subtracted from 140, and the resulting value is multiplied by his weight in kilograms. The result of the calculation is divided by the serum creatinine level multiplied by 72. For women, the resulting value is multiplied by a factor of 0.85. Briefly the formula looks like this:
- Men: KlKr = ((140 – age)×weight)/(72×KrPl);
- Women: KrKr = ((140 – age)×weight)/(72×KrPl)×0.85.
- Creatinine clearance can also be calculated by measuring the level of creatinine in a 24-hour urine sample and its level in the blood (Rehberg-Tareev test). The obtained values are compared. 6 hours before urine collection and blood sampling, the patient should not eat meat, poultry, fish, coffee and tea. During the day while urine collection is being carried out, the patient should not be subjected to heavy physical activity. Urine is collected in a container with a volume of about three liters. The container with collected urine is stored in a cool place; no preservatives are added to it. If necessary, the patient's weight and height are noted. At the end of the day, the volume of collected urine is assessed, about 20 ml of urine is poured into a special container, which is sent to the laboratory to determine the level of creatinine. The remaining volume of urine is destroyed. At any time of the day, while urine is being collected, a blood sample is taken from a vein, followed by determination of creatinine.
Normal values of endogenous creatinine clearance
| Age | Clearance of endogenous creatinine | |
| Men | Women | |
| Children under 1 year | 65 — 100 | 65 – 100 |
| Ages 1 to 30 | 88 — 146 | 81 – 134 |
| Adults aged 30 to 40 years | 82 — 140 | 75 – 128 |
| Adults aged 40 to 50 years | 75 — 133 | 69 – 122 |
| Adults aged 50 to 60 years | 68 — 126 | 64 — 116 |
| Adults aged 60 to 70 years | 61 — 120 | 58 – 110 |
| Adults over 70 years of age | 55 — 113 | 52 — 105 |
If creatinine clearance is below normal
The measured values of creatinine clearance can be reduced by taking thiazides, diazoxide, triamterene, nephrotoxic drugs, opioid drugs and cannabis.
Low creatinine clearance may indicate the presence of the following diseases:
- Kidney diseases: glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, nephrotic syndrome, congenital kidney diseases, interstitial nephritis, acute tubular dysfunction, papillary necrosis,
- Common diseases: amyloidosis, malaria, myeloma, cystinosis, Wilson-Konovalov disease, vitamin D-resistant rickets.
- Conditions accompanied by decreased blood supply to the kidneys: shock, blood loss, dehydration, heart failure.
- In obstetrics: preeclampsia, eclampsia.
By degree of reduction:
| up to 30 ml/min/1.7 m2 | moderate decrease in kidney function; |
| 30-15 ml/min/1.7 m2 | renal failure, compensated, subcompensated; |
| < 15 ml/min/1.7 m2 | decompensated renal failure. |
If creatinine clearance is higher than normal
The clearance of endogenous creatinine can be increased by: a protein diet, excessive physical activity, amino acid-based drugs, furosemide, carbenoxone, levodopa, methylprednisolone.
High clearance rates can occur with hypertension, diabetes, burns, and pregnancy.
Formulas for calculating GFR based on creatinine
The development of methods for assessing glomerular filtration rate has been carried out since the mid-twentieth century. Ideally, they should be financially accessible and not labor-intensive (to get results as quickly as possible). Independent application of formulas is very inconvenient for the doctor and the patient, as it takes a lot of time and errors in calculations are possible (human factor). A much easier way is to use a normogram or a nephrological ruler.
Various medical calculators are also suitable for calculations. They can be installed on the doctor/patient's phone or determine GFR online within a few seconds. Simply enter the required data.
In adults
The most widely used formulas are for calculating GFR based on serum creatinine and several other auxiliary data (for example, urea, weight, height). By the way, the most accurate results are determined by inulin clearance. Creatinine is not reabsorbed (due to its low molecular weight). That is, the amount of it that has been filtered is excreted in the urine irrevocably.
- CKD-EPI: GFR = 141 × min(Scr) α × max(Scr) -1.209 × 0.993 Age
- CKr – blood creatinine in mg/dl;
- α: -0.329 (F) and -0.411 (M);
- women need to multiply the result by 1.018 at the end.
- MDRD: GFR = 170 x (GFR) -0.999 x age -0.176 x 0.762 (F only) x residual urea nitrogen (mmol/L) -0.17 x serum albumin level (g/L) 0.318.
- Cockcroft-Gault: GFR = ((140 - age) x body weight in kg): SCr (µmol/l):
You can use a simplified formula, where GFR = 186 x (GFR in mg/dL) -1.154 x (age) -0.203 x 0.742 (for F). Example calculation for a 25 year old woman:
186 x 1 -1.154 x 25 -0.203 x 0.742 = 71.8 (ml/min)
In children
In pediatric practice, it is advisable to determine the glomerular filtration rate taking into account body area, since children develop unevenly. The following formulas are used:
- Schwartz: GFR (ml/min/1.73m2) = (height in cm x K): GFR in mg/dL, where K is a coefficient of 0.55 for girls, 0.70 for boys.
- Kunaha-Barr: GFR = (height in cm x 0.43) : SCr in mg/dL.
- Leger: GFR (ml/min) = ((55.5 x body weight in kg) + (0.147 x height 2 in cm)) : SCr in mg/dl.
Notes[ | ]
- About E. M. Tareev. Official website of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. I. M. Sechenova
- Chizh A. S. Nephrology in therapeutic practice, Minsk - 1998, 557 p. (unspecified)
(inaccessible link). Access date: February 15, 2013. Archived April 27, 2012. - Kozinets G.I. Interpretation of blood and urine tests and their clinical significance. M.: "Triad-X", 1998, - 104 p. ISBN 5-86021-018-3
- ↑ 12
Medical reference book of diseases, medicines, preparations, recipes. Rehberg's test
Estimation of creatinine clearance (adults)
Creatinine clearance is the volume of blood plasma that is cleared of creatinine in 1 minute when passing through the kidneys. A decrease in creatinine clearance indicates kidney damage.
– Fill in the fields. – Click “Calculate”.
The following formulas provide a reasonable estimate of creatinine clearance unless:
- There is a rapid change in plasma creatinine levels (both rise and fall).
- The patient is significantly exhausted.
In these situations, the following assumptions must be made:
- In the case of a rapid rise in plasma creatinine levels (i.e., more than 0.5-0.7 mg/dL per day), it is best to assume that the creatinine clearance does not exceed 10 ml/min.
- In malnourished patients, it can be assumed that the actual clearance will be less than the estimate, but its exact value cannot be determined.
When using the calculation formula, it should be remembered that the obtained creatinine clearance value is an estimate and may differ from the actual one either up or down, therefore the resulting estimate should be taken into account only in conjunction with other factors identified during the examination of the patient. DECISIONS REGARDING DRUG THERAPY AND DOSAGE SHOULD BE BASED ON CLINICAL PICTURE EVALUATION
Significant changes in creatinine levels can also be caused by other factors (dehydration, use of nephrotoxic drugs, excess creatinine production due to injury or excessive exercise, or decreased creatinine production due to kidney disease or exhaustion).
Particular care should be taken when assessing creatinine clearance in:
- Elderly (over 90 years old)
- Patients with low body weight (less than ideal)
- Patients after liver transplantation
Note: Using actual body weight to calculate clearance in obese patients (and possibly in patients with ascites) may result in creatinine clearance estimates that are significantly higher than actual values. Some experts prefer in such cases to use an indicator such as “corrected body weight” (it can be calculated, for example, using the following formula: ideal body weight 0.
Formulas according to Cockcroft-Gault:
- For men: KrKr=((140-age)*weight)/(72*KrPl)
- For women: KlKr=(((140-age)*weight)/(72*KrPl))*0.85, where
CrCl – assessment of creatinine clearance, ml/min weight – body weight, kg CrPl – plasma creatinine, mg/dl
Formulas according to Jelliffe:
- For men: KrKr=(98-0.8*(age-20))/KrPl
- For women: KrKr=((98-0.8*(age-20))/KrPl)*0.90, where
ClCr – estimation of creatinine clearance, ml/min/1.73 sq.m.
Indications for analysis
Patients with chronic renal failure (CKD), dysfunction of the urinary system or cardiovascular diseases and during treatment with potent drugs need to know exactly their individual creatinine clearance values.
A study on the ability of the urinary system to adequately perform its function of filtering and removing waste substances is prescribed in the following cases:
- If the patient has had inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract progressing for a long time, a nephrectomy operation was performed and urolithiasis with the formation of large stones was diagnosed. Also to determine kidney failure and the need for dialysis.
- During the period of chemotherapy and radiation therapy in patients with cancer.
- To control and calculate individual dosages of drugs used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, chronic and toxic hepatitis, antiretroviral therapy, immunosuppressants and other drugs with serious side effects that affect kidney function.
- During pregnancy, to assess the load on the kidneys, it is especially important if the expectant mother is carrying several babies.
- For congenital pathologies of the urinary system in a child.
- If the patient is diagnosed with serious endocrine diseases with energy metabolism disorders.
- To control metabolic processes in athletes during active training.
- If there is a need to determine for research purposes an individual protein intake, optimal exercise, diet, dose of vitamins and minerals.
Decoding the result
It is important to know! Creatinine clearance alone without additional tests and general clinical examination of the patient is not a sufficient basis for making a diagnosis.
If other criteria for damage are present (for example, proteinuria), the severity of chronic kidney disease can be determined:
| Stage | Characteristic | GFR ml/min | Compliance with chronic renal failure* |
| I (C1) | Lesion with preserved filtration capacity | >90 | — |
| II (C2) | Slight decrease | 89-60 | — |
| III (C3a) | Moderate | 59-45 | Latent |
| III (C3b) | Moderate | 44-30 | Compensated |
| IV (C4) | Heavy | 29-15 | Intermittent |
| V (C5) | Critical (uremia) | <15 | Terminal (need for hemodialysis) |
*CRF – chronic renal failure
What values are considered normal?
If the kidneys are healthy, then creatinine will be eliminated completely within a day - this is the norm for the body; in case of problems, some part of the molecular structure will remain in the body and will accumulate over time.
A creatinine clearance test will reveal kidney problems. The higher this indicator, the more serious the problems, so it is necessary to periodically conduct general monitoring of your health.
You can figure out the analysis yourself; for this you need to know the norms of creatinine clearance, they vary by gender and age. For men, the ideal value is 70-110 µmol/l; for women, the norm is lower and is 40-90 µmol/l.
Each person has his own indicator, which in most cases fits within the established framework. There is a situation where the analysis is abnormal, but the kidneys are fine. If you take a young, healthy man with an athletic build, then his norm may be 10-30 µmol/l above average. This is due to the physical level of development, which differs from the standard.
For the same reason, in elderly people, the norm is several tens of units lower than usual, while the kidneys can be completely healthy. In addition, low analysis rates were recorded in people suffering from low body weight, those suffering from rickets, and those who eat a poor and monotonous diet.
If a person has only one kidney, then the norm of this indicator is increased to 180 µmol/l. This level of creatinine indicates a high load on the only remaining filtering organ.
If the indicator is above 200 µmol/l, it indicates problems in the body. Determining them specifically should be the next task after going through this analysis. The critical level is considered to be 800 µmol/l. These figures indicate that it is necessary to cleanse the kidneys artificially and begin to look for a donor for this organ.
For children, reduced standards have been established, ranging from 20-80 µmol/l. It is worth considering that the child is growing rapidly, his body weight is increasing, both due to muscles and due to adipose tissue, so sharp increases in the indicator are possible in a short period of time - this is not always a sign of kidney problems. You need to worry if the analysis shows more than 90 µmol/l.
Standards may vary due to many factors, so an objective interpretation of the tests is carried out by a doctor.