Biopsy is the most informative method for diagnosing neoplasms. It consists of taking a sample of tumor tissue for subsequent examination under a microscope. This tissue sample is called a biopsy.
Our expert in this field:
Allahverdyan Alexander Sergeevich
Surgeon-oncologist, professor, MD. Head of the ROH expert group. International expert
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Trephine biopsy is the removal of tissue using a large-diameter hollow needle. As a result, the doctor receives a biopsy sample. This gives him the opportunity to conduct a full histological examination, determine the type and nature of the tumor (malignant or benign), and also study the cellular structure of the tumor.
A less traumatic option is fine needle aspiration biopsy. In this case, tissue is collected with a thin needle.
The needle is inserted into the tumor, after which a small amount of biopsy material is drawn into it. The disadvantage of the aspiration technique is that it can only obtain individual cell samples for cytological examination.
When examining lymph nodes for the presence of cancer cells, fine-needle aspiration biopsy is considered sufficient. But this is not enough for a full-fledged study of breast tumors.
Trephine biopsy is currently recognized as the gold standard for diagnosing breast cancer.
Indications
Trepanobiopsy of the breast is prescribed for symptoms such as:
- discharge from the nipple with an unpleasant odor, the presence of blood, yellowish, greenish or brown in color,
- a lump in the mammary gland that can be felt upon palpation,
- nipple retraction,
- formation on the chest of an area of peeling, ulceration, wrinkling, redness, darkening, increased sensitivity,
- formation of ulcers.
In diseases such as mastopathy and fibroadenoma, a biopsy helps to assess the risk of malignancy of tumors.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Differences from other methods
Most often, breast biopsy is performed in two ways. The first is a trephine biopsy. To carry it out, you need a special needle, which has a large diameter and is hollow inside. This feature allows you to obtain a column of tissue of a fairly large size.
The second common method is fine needle aspiration biopsy. As the name suggests, in this case a small diameter needle is used, which reduces the risk of bleeding and tissue trauma. Due to safety and high information content, fine-needle biopsy allows you to obtain material from several foci, which is important if there are several nodes in the mammary gland. Among the disadvantages of the method, one can note the possibility of obtaining samples only for cytological examination.
Another type of method is excisional biopsy. It is somewhat different from the types described above. An excisional biopsy is performed after surgical removal of the tumor. In this case, you can select the desired area of the tumor and examine it in detail.
Experts do not compare different types of biopsies and do not identify the best or worst way to obtain the material. Each method has specific indications and areas of application, but each of them has the right to exist and is actively used at the present time.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
What does trephine biopsy show?
Histological examination of a tissue sample of a tumor (biopsy) not only makes it possible to establish an unambiguous diagnosis and differentiate a benign neoplasm from a malignant tumor.
During histological examination, the doctor determines the degree of hormonal dependence of the neoplasm, the presence of estrogen receptors, progesterone, HER-2/neu.
Tumor cells are exposed to chemotherapy, targeted drugs, and immune drugs to assess the degree of their sensitivity to drug therapy.
Based on all this data, the doctor can choose the optimal treatment tactics, the use of hormonal, targeted, immune therapy, and chemotherapy for breast cancer.
In addition, histological examination shows the degree of differentiation (malignancy) of the tumor. This information is also of great importance for choosing treatment tactics.
Carrying out
The procedure is carried out under sterile conditions. The following stages can be distinguished:
- Taking blood for clotting.
- Position of the patient (lying on her stomach or back).
- Fixation of the breast.
- Treatment of the puncture site with antiseptic and gel.
- Anesthesia, if necessary.
- Inserting a needle into the seal.
- Taking a biopsy sample for histological examination.
- Treating the puncture site and applying a compress.
After the bleeding has stopped and the patient has fully regained consciousness, the doctor applies a bandage. Now she can go home. If the mammary gland becomes inflamed, the woman remains in the hospital.
Advantages
- Exceptional information content. Trephine biopsy provides diagnostic information that cannot be obtained by other methods - mammography, CT, MRI. These methods make it possible to detect a tumor, estimate its size, determine its location, and study its structure, but they do not provide information about the cellular type of the tumor. Meanwhile, it is precisely this information that can be of key importance for choosing tactics for treating tumor diseases of the mammary gland, both benign and malignant.
- No hospitalization. A biopsy does not require hospitalization, long-term recovery, or rehabilitation. As a rule, the procedure is performed under local anesthesia in a day hospital at the international clinic Medica24. Trepanobiopsy of the mammary glands at the international clinic Medica24 does not cause complications. The procedure is carried out by highly qualified specialists who have extensive experience in carrying out such procedures. This guarantees maximum diagnostic information and safety.
- Speed of implementation. The procedure takes very little time. After the anesthesia wears off, you can return to normal life within a few hours.
- No traces. Performing trephine biopsy does not require soft tissue incisions, sutures, and does not leave scars.
Possible biopsy complications and how to prevent them
The risk of complications if the biopsy technique is followed is minimal. Sometimes there is slight bleeding. To prevent it at an early stage, it is recommended to press the bandage tightly to the wound. The consequence of minor bleeding is a hematoma on the wound. You can fight it if you apply cold after the procedure.
In modern clinics, the rules of asepsis and antisepsis are observed, breast biopsies are performed under sterile conditions, and disposable needles or special sterilizable instruments are used. Therefore, the risk of infectious complications is excluded. But if hygiene is not observed, the dressing is removed early and the wound is palpated with your hands, pathogenic bacteria can be introduced into it, which will cause inflammation. Therefore, you should not remove the patch before the time recommended by your doctor.
Our Surgery Center employs certified doctors who have extensive experience in performing breast biopsies. For manipulation, we use modern instruments and highly sensitive ultrasound machines. You will receive an accurate histologist's report in a short time. Make an appointment with a mammologist and a biopsy by calling the numbers listed on the website, or request a call back.
How is trepanobiopsy performed?
As a rule, trephine biopsy is performed under local anesthesia. Before the procedure, the needle insertion site is numbed.
A small incision is made on the mammary gland, through which a flexible needle with a cutting end is inserted into it.
Unlike aspiration biopsy, trephine biopsy takes a tissue sample not by suction, but by cutting. As a rule, 3–6 biopsy samples are taken to obtain maximum diagnostic information.
The accuracy of needle insertion is controlled by ultrasound. As a rule, the procedure takes no more than 10–15 minutes.
Since the tissue incision is minimal, no stitches are required after the procedure. The puncture area is covered with a sterile bandage, on which a cooling compress is applied.
The obtained tissue samples are sent to the laboratory of the international clinic Medica24 for morphological examination. Waiting for a conclusion may take several days.
After the diagnostic procedure, the woman is under the supervision of doctors at the international clinic Medica24 for several hours in a day hospital. After this she can leave the clinic.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
How many days does a biopsy take?
A routine biopsy may take 5-10 days from the time the sample is taken. The doctor warns the patient in advance about the time the results will be received. With an urgent biopsy (not performed in all clinics), the time to obtain results is reduced to half an hour. Urgency is allowed in severe cases, when the patient requires serious immediate assistance, for the adequacy and usefulness of which it is necessary to have a conclusion about the nature of the formation. Interpretation of the results obtained, consultation and treatment prescription are carried out by mammologist-oncologist Stepyko Stanislav Borisovich.
SINAI
Services
Preparation
Trephine biopsy is a relatively minimally invasive diagnostic method. However, it requires a full preliminary examination, which includes:
- visual examination, palpation by a mammologist,
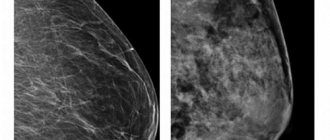
- mammography,
- Ultrasound of the breast,
- blood tests.
If additional information is needed, a CT or MRI of the breast may be prescribed.
A few hours before the procedure, you should stop smoking and drinking alcohol. If you are taking medications, you should inform your doctor. Some of them may have to be canceled for a while.
To perform trepanobiopsy, local anesthesia is usually sufficient. But in some cases, intravenous anesthesia may be used. Then the procedure must be performed strictly on an empty stomach.
The best time to perform this procedure is the first half of the menstrual cycle. In menopausal and postmenopausal women, it can be performed on any day.

Breast biopsy
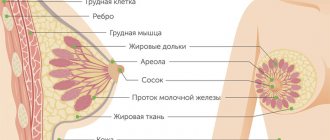
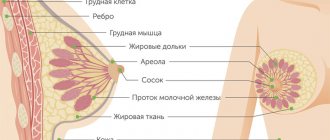
Breast biopsy is a research method that involves removing cells or tissue from the breast and then examining them microscopically. Breast biopsy is a mandatory method of confirming the diagnosis if breast cancer is suspected. Depending on the type of breast biopsy performed, anesthesia may be used for the examination. Biopsy methods can be either non-operative or surgical. Modern methods of breast diagnostics, such as mammography and ultrasound (ultrasound), cannot fully assess the nature of changes in breast tissue. Only a diagnostic procedure - a breast biopsy - can determine whether a tumor is malignant or benign. Thus, the main objective of a breast biopsy is to identify the benignity or malignancy of the identified process. The breast biopsy procedure involves taking a specific piece of altered breast tissue, or the entire tumor formation, for subsequent pathological analysis or histological examination. As practice shows, pathomorphological analysis is the only highly accurate method that allows us to exclude or confirm the presence of cancer in suspected areas of the breast with a high degree of confidence.
In addition to malignant neoplasms, a breast biopsy can also reveal benign changes in the mammary gland tissue. This pathology usually includes cysts (one or more thin-walled cavities filled with fluid, formed from the milk ducts), intraductal papillomas (a tumor of the mammary gland located in the lumen of the milk duct, in which discharge from the nipples is observed) and tumors representing fat necrosis (death of fat cells in the mammary gland, often occurring after various types of injury).
Breast biopsy: practice of prescribing
A breast biopsy can only be recommended to a patient by the attending physician and only in certain cases. Before a breast biopsy, the patient usually undergoes other diagnostic tests that help initially determine the extent and distribution of pathological changes. Previous methods of diagnostic research include mammography and ultrasound of the mammary gland, and less often other methods. To perform a breast biopsy of deep-lying tumors, the examination is often carried out under the control of radiography or ultrasound.
A mammologist may recommend and prescribe a breast biopsy to a patient in the following four main cases. First, the patient or his doctor discovered a lump in the mammary gland. Secondly, the patient’s mammogram revealed suspicious areas of the breast. Thirdly, an ultrasound examination of the breast also revealed suspicious areas. And the final, but no less important reason for performing a breast biopsy is the appearance of changes in the nipple area. For example, the presence of crusts, peeling, the appearance of ulcers or bloody discharge from the breast.
The psychological aspect of prescribing a breast biopsy is also worthy of attention and requires a correct and understanding approach from the doctor and medical staff to the patient. Typically, when a woman is scheduled for a breast biopsy, the patient experiences the stress of being in the dark, because a breast biopsy can accurately identify suspicious tissue. In this situation, it is necessary to inform the patient that 80 percent of women after a breast biopsy find out that they do not have breast cancer. This percentage, taking into account the general cancer incidence in Russia, is a very good indicator.
Preparing for the breast biopsy procedure
Preparation for the diagnostic procedure of breast biopsy should include a number of specific actions on the part of the patient. For example, the patient should not take medications that inhibit the activity of the blood coagulation system and prevent the formation of blood clots (aspirin and other anticoagulants). It is imperative to notify the doctor if the patient experiences a reaction of the body’s immune system to various substances (allergies). If a breast biopsy is planned to be performed using magnetic resonance imaging and the patient has a pacemaker or other implanted electronic device, or if the woman is pregnant or suspected of being pregnant, then MRI is not recommended. Immediately before the procedure, you must follow all the recommendations and instructions of your attending physician, as well as report any unexpected reactions of your body.
Breast biopsy: procedure
A breast biopsy is usually performed by a breast surgeon, radiologist, or surgeon. Breast biopsy tissue samples can be obtained in a variety of ways. The attending physician may recommend to the patient a certain method of performing a diagnostic procedure depending on the size, location and other characteristics of the area of the breast lesion.
To examine the mammary gland, special needles are used and a so-called “puncture biopsy” is performed. The specialist performs a puncture with a needle, often under the control of X-rays, ultrasound and other control methods. A column of tissue obtained from the lumen of the needle is sent for histological examination. This method is often used to obtain material from the mammary gland. The injection is usually easily tolerated by the patient; superficial anesthesia is often used, when the area of skin through which the needle will pass is “frozen” using spraying or subcutaneous injection of an anesthetic. The development of medicine leads to the emergence of both new methods and new tools for performing certain diagnostic studies. For example, a biopsy gun and disposable needles can be used to perform a breast biopsy. This diagnostic equipment is intended for “cutting biopsy” of all types of soft tissue, including the mammary gland. With a fine-needle biopsy, the puncture is performed with a special disposable needle, which is inserted into a puncture gun. This needle consists of two parts, a knife and a special tube. When working, the gun fires a knife at high speed, which “cuts” a thin column of fabric. This procedure allows you to obtain not just a few cells, but a full-fledged tissue of formation. The accuracy of the study is 93–95 percent and is comparable in information content to conventional histology.
Breast biopsy: methods of execution
Fine needle aspiration biopsy is the simplest and most commonly used way to evaluate breast masses that are not palpable during breast physical examination. A fine needle aspiration biopsy is performed as follows. During the procedure, the patient is in a sitting position. The biopsy site is marked on the skin of the breast, and the surface is treated with an antiseptic. Next, a long thin needle on a syringe is inserted into the thickness of the gland. After the needle penetrates into the thickness of the tumor, the syringe plunger is pulled back several times. This technique sucks a small amount of glandular tissue into the needle and syringe. Fine needle aspiration biopsy is a rapid and minimally invasive diagnostic procedure that can differentiate between a fluid cyst and a tumor. A needle biopsy (core needle biopsy) is used if a breast mass is visible on a mammogram or ultrasound, or if the attending physician can palpate a lump during examination. In this case, the radiologist or surgeon uses a fine needle, but it is slightly larger than the one used in a fine needle aspiration biopsy. Several tissue samples obtained from a needle biopsy are promptly sent to the laboratory, where a histological examination is performed to determine the presence of cancer cells. Various imaging modalities, such as mammography, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging, are often used to accurately guide the needle during a needle biopsy.
Stereotactic needle biopsy is designed to precisely guide the needle into the area of the suspected lesion. Stereotactic needle biopsy is most often used in cases where the tumor cannot be felt and is located deep in the tissue. This diagnostic procedure is performed as follows. The patient is positioned face down on a special soft table; the table has characteristic openings for the mammary glands. Thus, the woman's breasts are in a hanging position. Next, the table rises slightly higher and the specialist performing the biopsy procedure firmly fixes the patient’s breast between two plates (cassettes). Then a mammogram is taken from different angles in order to form a three-dimensional image, which in turn ensures high accuracy in localizing the area of suspected damage. A small incision is made, no more than 0.5–0.7 centimeters long. A needle is inserted through this incision to collect material. To obtain a more accurate result, the doctor takes several tissue samples, which subsequently undergo special testing.
There are also several other ways to perform the diagnostic procedure of image-guided breast biopsy. These are needle biopsy using ultrasound and needle biopsy using MRI. The method of taking material for research fully complies with the technique described in stereotactic needle biopsy. The main differences between the above methods of performing a biopsy are the imaging methods. In one case, this is high-frequency sound (ultrasound), in the other, a 3-d reconstruction created by images of the breast in many planes (MRI). The advantage of these types of biopsies is that a larger area of tissue for histological examination allows for a more accurate diagnosis, as well as high accuracy of material sampling.
An incisional biopsy involves cutting out a small piece of tumor tissue. This method of research is more similar to surgical intervention. An incisional biopsy is performed under local anesthesia. As practice shows, incisional biopsy is performed when the results of aspiration biopsy are not sufficiently reliable. Both aspiration and incisional biopsies can sometimes give false results. However, their main advantage is efficiency. An excisional biopsy is a mini-surgery during which the surgeon removes part or all of the tumor. This procedure cannot be classified as therapeutic, since if cancer cells are detected, in addition to the tumor itself, it is also necessary to remove the lymph nodes. If the size of the tumor during excisional biopsy is less than 2.5 cm, then the entire tumor is excised. If the tumor is large, only part of it is removed.
In conclusion, it should be noted that breast biopsy is a mandatory method of confirming the diagnosis if the presence of cancer is suspected. As practice shows, in most cases, up to 80 percent, the results of breast biopsy reject malignant processes.
After the procedure
Trepanobiopsy at the international clinic Medica24 does not cause complications. The rehabilitation period takes no more than 7 - 10 days.
At this time, you should avoid physical activity, visits to the bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, taking baths, regularly treat the area where the needle is inserted with antiseptics, and change bandages.
After the procedure, there may be minor bleeding, redness, mild inflammation, slight pain, and bruising (hematoma). These phenomena disappear on their own within a week.
Contraindications
Trephine biopsy of the breast is not performed if:
- acute infectious disease,
- high temperature,
- infectious skin rashes of the chest,
- decompensated diabetes mellitus,
- bleeding disorders,
- as well as during pregnancy, lactation,
- after recent breast surgery.
The material was prepared by oncologist, thoraco-abdominal surgeon, head of the department of surgery at the international clinic Medica24, Alexander Valerievich Korotaev.