Combined prenatal screening is carried out at 11-14 weeks of pregnancy when the embryo size is not less than 45 mm and not more than 84 mm. This is a comprehensive examination of the fetus to assess the parameters of its development. Its main task is the early detection of fetal malformations, the prevention of childhood disability, and the reduction of infant and child mortality.
The first screening consists of an instrumental part - an ultrasound and a laboratory - a blood test to determine the concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin (βhCG) and pregnancy-associated protein A (PAPP-A). The combined results of these indicators make it possible to plan pregnancy management tactics.
Who needs to be tested
Based on the results of the study, we can judge the risk of having children with chromosomal diseases and congenital malformations, so it is recommended that all pregnant women carefully consider the issue and be examined. Indications for mandatory prenatal screening in the first trimester are:
- Women who have a history of spontaneous abortions, ectopic and frozen pregnancies, premature births, stillbirths, and the birth of a child with developmental anomalies.
- Hereditary diseases in the family of the mother or father of the child
- A disease suffered in the first trimester with treatment with antibiotics or drugs contraindicated during pregnancy.
- Marriage between relatives.
- The woman is over 35 years old.
- Presence of occupational hazards
Timing of planned and unscheduled ultrasound in the 1st trimester, indications
The content of the article
Pregnancy is a special period in the life of the expectant mother and in the intrauterine development of the child. The woman’s body gets used to new stress, and the baby, meanwhile, grows and develops. A normal pregnancy lasts for 9 months or 38-42 weeks. This period is conventionally divided into three parts, each of which is called a trimester. The first three months of pregnancy take place in the first trimester. It is during this period that all the child’s organs are formed.
Ultrasound in the first trimester corresponds to the period from 9 weeks to 12 weeks of gestation (in some cases it is prescribed from 11 to 14 weeks). The scheduled inspection does not cause alarm and proceeds as normal. There are medical indications that are alarming with dangerous consequences. Such unscheduled examinations must be carried out in consultation with the attending physician.
How to prepare
Preparation for the first screening involves a gentle diet. Nutritional errors can affect a woman’s general condition and reduce the accuracy of the results. One week before the examination:
- Salty, spicy, fatty, fried foods should be excluded from the diet.
- Do not consume allergenic foods.
- Avoid carbonated drinks.
One day before screening:
- Do not eat chocolate, seafood, fatty meats, flour, limit sweets.
- If the study is scheduled for the morning, eat a light dinner no later than 20:00.
It is advisable to maintain moderate physical activity unless there are contraindications. Walking and proper rest are also important.
Conducting a survey
The blood test and ultrasound are performed on the same day to avoid errors due to the difference in timing.
- Ultrasound screening is carried out first, since its results make it possible to determine the exact gestational age, which affects the normative values of hormone levels. The study is carried out both through transabdominal and transvaginal access. The procedure is painless, safe for women and children, and has no contraindications.
- Blood is donated from a vein on an empty stomach or 4 hours after a meal. The material is collected on the day of the ultrasound. The study determines the concentration of hormones and compares them with standard values.
Only by deciphering the results of ultrasound and hormone analysis can a conclusion be made about possible risks.
Why is it recommended to choose a paid clinic?
Paid clinics are equipped with modern equipment for conducting research. In government institutions you need to take a number of things with you (diaper, shoe covers, towel, etc.), but in paid clinics all this is usually provided.
It is worth considering that this procedure is performed not only for pregnant women. When performing a free ultrasound, there are queues; as a rule, the procedure is carried out by appointment, and people sign up for the queue a month or two in advance, but in a paid clinic there are rarely queues. When selecting a clinic, you should pay attention to the availability of a license, work experience and qualifications of specialists. When you contact the Diamed clinic, you will be provided with all the necessary documents. Come to us!
What does an ultrasound show?
During pregnancy screening, fetal fetometry is performed - the size of body parts is determined and all anatomical structures are assessed.
The results obtained are compared with a statistical table that indicates the percentile of normative values included in the sample. If the indicators are less than 5 and more than 95, additional examinations are prescribed.
During an ultrasound examination in the 1st trimester, the following parameters are assessed: the bones of the cranial vault and brain, spine, anterior abdominal wall, fetal limbs, facial structures, chest and abdominal organs, as well as the main echographic markers of chromosomal abnormalities.
Neck thickness (TCT)
The area between the inner surface of the fetal skin and the outer surface of the soft tissue covering the cervical spine. TVP is considered the most important marker of chromosomal abnormalities.
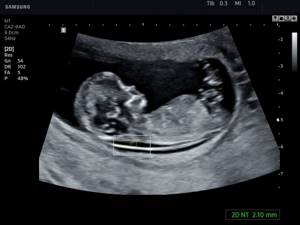
This space begins to decrease after week 13, so it can only be assessed at the first screening.
| Term | Thickness of the collar area in mm | ||
| Percentile 5 | 50th percentile | 95th percentile | |
| 11 weeks | 0,8 | 1,6 | 2,4 |
| 12 weeks | 0,7 | 1,6 | 2,5 |
| 13 weeks | 0,7 | 1,7 | 2,7 |
The discrepancy between the results and normative values indicates an increased risk of developing chromosomal pathologies. Depending on the formed set of chromosomes, these may be Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome. To clarify the diagnosis in this case, a biopsy of the chorion or placenta, analysis of umbilical cord blood, and amniotic fluid may be prescribed. Only after additional research can an accurate diagnosis be made.
Coccygeal-parietal size (CTR)
Shows the distance between the coccygeal and parietal bones. Using this parameter, ultrasound determines the exact gestational age, and also establishes the ratio of fetal weight to its CTE.
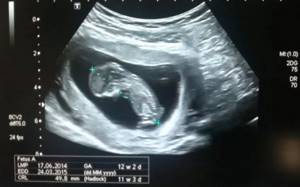
A slight deviation from the norm indicates the characteristics of the physique and is not a cause for concern.
| Term | Coccygeal-parietal size in mm | ||
| Percentile 5 | 50th percentile | 95th percentile | |
| 11 weeks | 34 | 42 | 50 |
| 12 weeks | 42 | 51 | 59 |
| 13 weeks | 51 | 63 | 75 |
If screening during pregnancy showed results exceeding the norm, this indicates that the fetus is quite large. The indicator speaks significantly less about either an incorrectly determined gestational age (in this case, a re-examination is carried out after 1-1.5 weeks), or a slowdown in development due to intrauterine death, disrupted hormonal levels or an infectious disease of the mother, or genetic abnormalities.
Bones of the cranial vault and brain
Already from the 11th week, an ultrasound examination can detect defects in the bones of the skull, which indicates severe malformations of the fetus that are incompatible with life. Brain assessment is based on the study of the so-called “butterfly” - the choroid plexuses of the lateral ventricles. Clear visualization and its symmetry indicate normal brain development.
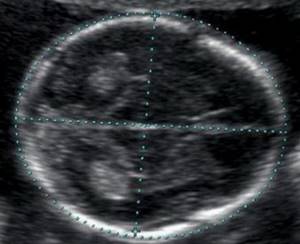
| Term | BPR, LZR in mm | ||
| Percentile 5 | 50th percentile | 95th percentile | |
| 11 weeks | 13, 19 | 17, 21 | 21, 23 |
| 12 weeks | 18, 22 | 21, 24 | 24, 26 |
| 13 weeks | 20, 26 | 24, 29 | 28, 32 |
Nasal bone
By the end of the trimester it should be formed and clearly visualized.
| Term | Nasal bone in mm | ||
| Percentile 5 | 50th percentile | 95th percentile | |
| 11 weeks | visualized, not measured | visualized, not measured | visualized, not measured |
| 12 weeks | 2 | 3,1 | 4,2 |
| 13 weeks | 2 | 3,1 | 4,2 |
Pathology of the nasal bone is considered to be its absence, hypoplasia (very small size) and a change in its echogenicity.
The diameter of the chest, the circumference of the head and abdomen, and the length of the femur also allow us to judge the proportionality of development.
Heart condition
When examining the heart, its location is assessed, the presence of four chambers of the heart is established - two atria and two ventricles, and their symmetry is assessed. Heart rate is measured.
| Term | Heart rate in beats per minute | ||
| Percentile 5 | 50th percentile | 95th percentile | |
| 11 weeks | 153 | 165 | 177 |
| 12 weeks | 150 | 162 | 174 |
| 13 weeks | 147 | 159 | 171 |
The ductus venosus (DV) is a direct communication between the umbilical vein and the central venous system. During a normally developing pregnancy, blood flow in the VP is a three-phase curve. The appearance of reverse blood flow may indicate the presence of fetal pathology.
Second trimester screening
The pregnant woman is sent for a second planned ultrasound at 18–22 weeks. This study will definitively confirm or refute the presence of congenital malformations, even those that may not be detected during the first screening. Prenatal determination of their presence becomes the reason for prescribing additional diagnostic procedures that will finally determine whether such a pregnancy needs to be prolonged. Otherwise, at up to 22 weeks, it is still possible to terminate the pregnancy for medical reasons without causing artificial labor.
It is important to do a maternal assessment at this stage of pregnancy and determine whether the woman needs corrective therapy, which is usually aimed at maintaining the pregnancy. Screening during pregnancy allows you to assess the condition of the internal os of the cervix. The cervix must remain closed until the last weeks of pregnancy, otherwise the patient is given special sutures or pessaries to prevent spontaneous miscarriage.
A diagnostician examines the condition of the placenta. The most important characteristics are:
- location of the placenta;
- its thickness;
- its degree of maturity.
The data obtained is used for preliminary planning of the method of delivery, identifying the likelihood of fetoplacental insufficiency, assessing the development of maternal organs and the ability to fully carry a pregnancy to term.
In the second trimester, the amount of amniotic fluid is of great importance. By calculating the amniotic fluid index using ultrasound, it is possible to determine polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, which can negatively affect the development of the fetus.
What does a blood test show?
Ultrasound results are compared with maternal plasma pregnancy-associated protein A (PAPP-A) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The values are shown in the table:
| Term | hCG in ng/ml | PAPP-A in honey/l |
| 11 weeks | 17,4 – 130,4 | 0,46 – 3,73 |
| 12 weeks | 13,4 – 128,5 | 0,79 – 4,76 |
| 13 weeks | 14,2 – 114,7 | 1,03 – 6,01 |
Differences from reference values may indicate pathologies of the mother or fetus.
| Deviation | hCG | PAPP-A |
| Above normal |
|
|
| Below normal |
|
|
Fetometry in the second trimester
The second ultrasound screening of pregnant women also involves conducting detailed fetometry of the fetus and assessing the dynamics of fetal development. To do this, a competent diagnostician first studies the results of the first screening carried out at 10–13 weeks of pregnancy, after which he conducts an ultrasound examination of the fetus to determine the most important parameters of the fetus:
- Head circumference;
- abdominal circumference;
- size and location of internal organs;
- thigh length;
- biparietal size, etc.
Based on the ultrasound results obtained, the doctor makes a conclusion about the exact duration of pregnancy and determines whether the fetus has intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR). If there is a suspicion of IUGR, ultrasound diagnostics are performed on the patient every 2 weeks.
The second ultrasound screening is the most anticipated for most parents, as it allows one to determine the gender of the unborn child with great certainty. This fact comes under the control of a doctor only in the case when the future parents have a serious hereditary disease in their family that is transmitted only to a certain gender, for example, hemophilia in boys.
What can affect the result
- Improper preparation, characteristics of the woman’s condition.
- Outdated equipment with low measurement accuracy and insufficient resolution.
- Qualification of the doctor in the ultrasound room, errors in decoding.
- Correctness of MoM calculation algorithms.
Modern diagnostic equipment makes it possible to evaluate more than 15 parameters of the fetus, construct its volumetric reconstruction for studying organs in the early stages of development, and calculate possible risks with high accuracy. Contact well-equipped clinics and trust specialists with proven qualifications.