Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic scan of the human body based on the natural ability of hydrogen atoms to emit energy when exposed to a magnetic field. This phenomenon is called nuclear magnetic resonance.
The apparatus for conducting magnetic resonance examination is called a tomograph (from the Greek words “tomos” - layer, plate and “grapho” - to write).
The tomograph for this examination consists of two parts: a powerful coil that creates a magnetic field, and sensitive sensors that receive pulses from excited hydrogen atoms. The tomograph is a tunnel into which a movable table with the patient lying on it gradually moves.
What happens in tissues under the influence of a magnetic field?
Hydrogen atoms are the most numerous group of atoms in the human body: they are part of water molecules, of which 60-70% of the human body consists. Excited hydrogen atoms, in response to the influence of a powerful magnetic field, begin to resonate, emitting energy. This energy is captured by special sensing sensors built into the body of the tomograph.
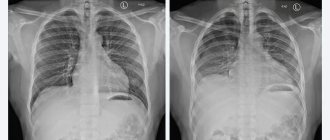
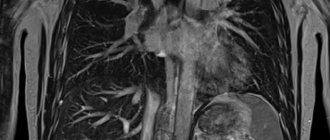
Using a computer program, the pulses from the atoms are converted into a digital image - a slice. On this section, depending on the density of the tissue, shadows of varying intensities are displayed. Overlapping each other, layer-by-layer sections are converted into a three-dimensional image, in which you can study in detail the anatomical structure of the scanned area and evaluate the functioning of the structures located there.
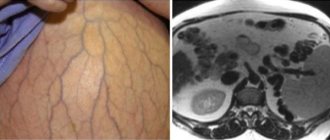
To enhance the contrast of some organs, tissues and structures, for example, kidneys, uterus, cerebral vessels, MRI is performed with contrast. As a contrast, drugs based on gadolinium, a paramagnetic metal, are used. Paramagnetic metals have a slight positive magnetic susceptibility, due to which they slightly enhance the magnetic field, so contrasted tissues produce light, clear shadows on tomograms.
The gadolinium contrast agent is inert for the human body, does not cause allergies or anaphylaxis, and does not have the ability to accumulate. After the procedure, it is excreted in the urine within 12 hours.
The MRI procedure, while highly informative and safe, has a number of contraindications that limit its use in certain categories of patients. The magnetic field interacts with metal objects located in the human body, leading to their heating and displacement. The procedure is prohibited for patients with pacemakers, dental implants, metal braces, pins, knitting needles and other metal-containing products in the tissues.
What is spinal tomography?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine is a high-tech method for diagnosing back pathologies. The operating principle of the tomograph is based on the effect of nuclear magnetic resonance. The scanning device itself consists of an installation that creates a powerful magnetic field and radio frequency signal detectors. When a patient gets inside the scanning part of the device, under the influence of a strong magnetic field and RF signals, the hydrogen atoms in the body's cells begin to resonate, that is, make oscillatory movements. The tomograph's computer translates these impulses into three-dimensional images, which the radiologist sees on the monitor screen.
How is the procedure done?
MRI is performed in the room where the tomograph is installed. The study can be performed with or without contrast. Before the session begins, the patient is told about the procedure and the sensations that he may experience.
Next, the subject undresses to his underwear, takes off all jewelry, belts, and accessories. In some diagnostic centers, the patient may be given disposable medical clothing (gown, cap, shoe covers) for examination.
In the MRI room, the patient is placed on a movable table, a contrast agent is injected intravenously (with contrast) and the tomograph coil is placed over the area that will be scanned: for MRI of the head - around the head, for examination of abdominal organs - above the abdomen, for examination of several areas - the coil is rearranged. During the session, the patient must lie still: any movement can distort the results of the study.
The patient is given a remote control with a panic button. If the person being examined feels pain or severe discomfort during the procedure, he can press a button to pause the examination and call the medical staff. At the time of the examination, the medical staff leaves the rooms and observes the procedure from the equipment room through a viewing glass. The doctor has the opportunity to simultaneously see the scanning process both on the monitor and in the room with the patient.
You can find out which Moscow diagnostic centers perform MRI and at what price on our website LocalLab.ru. Here you can sign up for the procedure and read reviews from real patients about the procedure and the quality of services provided in different clinics.
Questioning
Upon arrival at the medical center, you will be asked to sign an agreement for the provision of medical services, and then fill out a questionnaire that will allow the staff to identify contraindications to undergoing an MRI examination.
The most serious of them are the pacemaker and the first trimester of pregnancy.
You can find all the absolute and relative contraindications in the questionnaire.
Administrators will always help you fill out the form.
How long does an MRI procedure take?
Magnetic resonance scanning of one part of the body lasts 20-30 minutes. If contrast is used, the duration can increase to 50 minutes (excluding preparation time), and when examining several parts of the body - up to 1-1.5 hours.
How long does an MRI examination take? The duration of the procedure depends on several factors:
- type of tomograph and its power;
- contrasting;
- scope of examination;
- compliance with the study rules (patient immobility).
For example, examining the knee takes about 30 minutes, the cervical, lumbar or lumbosacral spine without contrast takes about 40 minutes, and cerebral vessels with contrast takes up to 1 hour.
How long should I wait for test results? Typically, the entire procedure, from issuing a medical card to obtaining a doctor’s report, lasts no more than 2 hours. In cases where the issuance of a conclusion requires consultation with related specialists or a consultation, the wait for results may take up to 2-3 days.
How is MRI performed on children?
MRI is considered a safe examination method, so it can be performed on patients of any age, including children. The only condition for high-quality diagnosis is complete immobility of the examined child during the procedure.
The approach to examining each little patient must be individual:
- If it is necessary to perform an MRI of soft tissues or the brain on a child of conscious age who can lie motionless for up to an hour but feels restless, a relative of the child may be allowed to be present in the room during the procedure.
- For a balanced school-age child, it is often enough to explain how the procedure works.
- If there are indications for MRI, but it is not possible to ensure the child’s immobility (for example, up to 5 years), then the examination can be carried out after preliminary sedation, that is, under anesthesia.
Examinations under anesthesia require the presence of an anesthesiologist and special equipment, so they are not carried out in every diagnostic center, which must be taken into account when registering small children for the procedure.
Can pregnant women undergo an MRI?
No teratogenic effect from the magnetic field created by the tomograph has been clinically identified. However, doctors recommend refraining from prescribing this procedure during pregnancy without compelling reasons, for example, to diagnose acute cerebrovascular accidents or if a tumor process is suspected. When prescribing an MRI for pregnant women, the doctor always compares the expected benefits of the study and the possible harm from it.
Among the many hardware diagnostic methods, MRI is considered one of the most preferable (after ultrasound) during pregnancy. How is this diagnostic procedure performed in pregnant women? They try to conduct the study in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, when the formation of all organs in the fetus has already occurred. In this case, procedures with contrast are avoided.
Gadolinium rarely causes allergic or anaphylactic reactions. The contrast is excreted unchanged by healthy kidneys within 12 hours. In pregnant women, the kidneys experience increased stress, which can lead to a retention of the drug in the blood of the expectant mother. Prolonged circulation of gadolinium contrast in the blood can theoretically lead to its sedimentation in tissues, which can lead to unpredictable consequences.
There is no information in official medical sources about the dangers of gadolinium-based contrast agents for the intrauterine development of the fetus. And the point is not that the contrast is absolutely safe, but that its clinical trials have not been conducted on pregnant women. Given the lack of reliable data on the possible danger of gadolinium contrast for the fetus, contrast should not be used during forced MRI during pregnancy.
MRI of the brain MRI of the hip MRI of the shoulder MRI of the knee MRI of the kidneys MRI of the abdominal cavity MRI of the pancreas MRI of the paranasal sinuses MRI of the eye orbits MRI of the hippocampus MRI of the pituitary gland MRI of the adrenal glands MRI of the liver MRI of the spleen MRI of the salivary glands MRI of the inner ear MRI of the heart MRI of the gallbladder MRI of the thyroid gland MRI of the maxillary sinuses MRI of the sella turcica MRI of the spinal cord MRI of the whole body MRI of the retroperitoneum MRI of the hand MRI of the pelvis MRI of the prostate MRI of the bladder MRI of neck vessels MRI of brain vessels MRI of the temporomandibular joints MRI of the soft tissues of the hip MRI of the soft tissues of the neck MRI of the sacral spine MRI entire spine MRI lumbosacral spine MRI thoracic spine MRI cervical spine MRI sacroiliac joints MRI wrist joint MRI foot MRI ankle joint MRI elbow joint MRI auditory nerve MRI optic nerve MRI coccyx MRI mammary glands MRI jaw MRI stomach MRI mediastinal organs MRI of the lymph nodes MRI of the brachial plexuses MRI of the intestine MRI of the trigeminal nerve MRI of the facial nerve MRI of the sciatic nerve MRI of the teeth MRI of the lungs and bronchi MRI of the uterus
Advantages and disadvantages
Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine has a number of advantages:
- high quality and informative images;
- display of back structures in a three-dimensional model;
- absence of pain and discomfort during scanning;
- no radiation exposure;
- the ability to detect neoplasms and pathologies at the development stage.
The disadvantages of this method include:
- higher cost of MRI compared to radiography and CT;
- poor visualization of bones (computer tomography is better suited to assess the composition of the bone tissue of the vertebrae);
- incompatibility with metal in the body and electronic implants.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
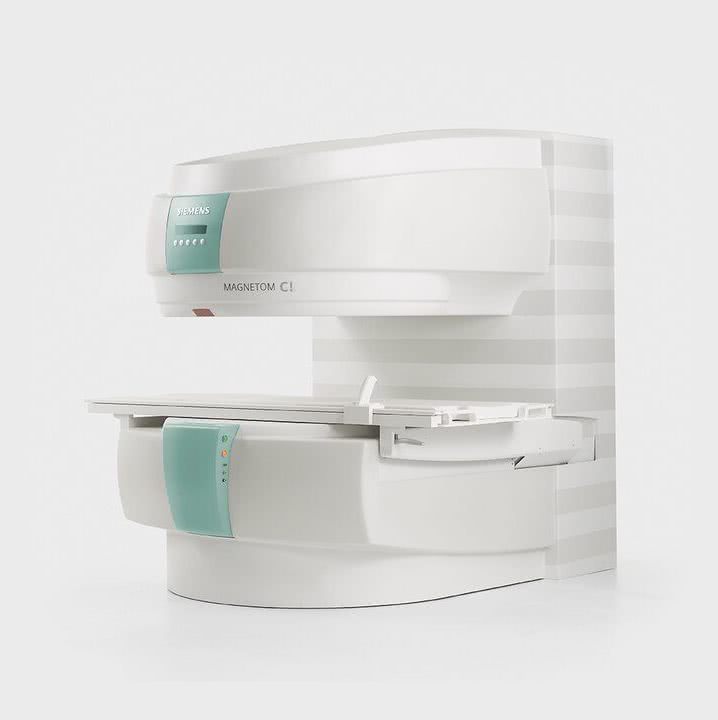
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
results
The study is interpreted by a diagnostician - a radiologist. The conclusion is issued on the day of the examination, but a description of the images may take the doctor several hours.
The doctor examines the obtained images and compares them with normal values:
- size and location of organs, symmetry;
- presence/absence of abnormal formations;
- presence/absence of an aneurysm, free fluid, blood clots in the blood stream;
- signs of infection and inflammation;
- stagnation in the ducts;
- traumatic injuries.