Urologists warn that men who do not take care of their health already at the age of 50 risk getting many unpleasant diseases and forgetting about sex life forever. This is due to a huge number of negative factors affecting the organs of the male genitourinary system. All problems can be identified in a timely manner using a pelvic ultrasound.
Which organs in men belong to the pelvis?
The content of the article
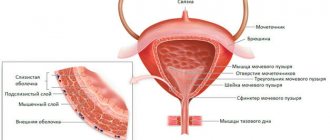
In men, the pelvic area contains the prostate gland (prostate), seminal vesicles, bladder and nearby lymph nodes. If a urologist suspects some kind of pathology, he can prescribe a detailed examination of one organ, but more often an ultrasound of all pelvic organs is performed, since they are nearby and closely connected.
Using ultrasound diagnostics, the size and structure of organs, the condition of tissues, and their position relative to neighboring organs are determined. An ultrasound machine visualizes various pathologies: cysts, tumors, abscesses, and also reveals hidden PPP infections. Ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to detect diseases at the earliest stages, significantly reducing the mortality rate of men from cancer of the reproductive system.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of pelvic ultrasound:
- The procedure is painless;
- The condition of the internal organs and tissues is clearly visible to the specialist on the monitor screen;
- It is relatively inexpensive;
- You can find out the stage of the disease;
- Ionized radiation is not used during the procedure;
- Diagnosis is non-invasive (no surgery is performed on the surface of the skin);
- Visually, the specialist sees a picture of deviations and violations;
- The procedure is carried out in a mode called “present time”, which makes it easier for the doctor to assess the condition of the body.
A pelvic ultrasound should be prescribed by a specialist, therefore, if a person wants to undergo the procedure on his own without visiting a doctor, this may result in a new pathology. The doctor tells you how to properly prepare for the diagnosis. There are practically no side effects from ultrasound, but caution should still be observed.
What diseases are detected on ultrasound of the pelvic organs in men?
Ultrasound diagnosis of the pelvic organs in men is based on the ability of high-frequency waves to penetrate tissue and be reflected back. Areas of different density reflect ultrasonic waves differently. Various compactions have increased echogenicity, while hollow neoplasms and cysts have decreased echogenicity. The capabilities of the ultrasound machine allow you to interpret the information received and obtain an image of the organ on the screen.
Ultrasound is recommended to be performed both as a preventive measure and for symptoms that bother the patient:
- increased number of red blood cells in the urine (hematuria);
- increased sperm content in urine;
- absence of ejaculate during orgasm (aspermia);
- infertility;
- pain in the groin area;
- erectile dysfunction (too short or prolonged);
- problems with urination;
- detection of blood or pus in the urine;
- various neoplasms and compactions in the scrotum;
- ultrasound-guided puncture and biopsy;
- age over 40 years (at this age the likelihood of problems with the prostate gland increases);
- presence of STDs (STIs).
Ultrasound diagnostics helps diagnose the following diseases:
Prostate diseases:
- acute and chronic prostatitis;
- prostate abscess;
- stones in the prostate gland;
- tuberculosis (drying) of the prostate;
- cyst;
- adenoma;
- hyperplasia (excessive tissue growth);
- nodes;
- prostate cancer.
Seminal vesicle diseases:
- vesiculitis (inflammation);
- cysts;
- carcinoma (cancer);
- amyloidosis (pathological deposition of protein metabolism products).
Ultrasound is a very informative method in establishing the exact cause of male infertility, but requires accompanying studies. In most cases, the main cause of infertility is pathology of the prostate gland or seminal vesicles. An ultrasound shows abnormalities in the structure of the organ, but without a spermogram it is impossible to talk about an accurate diagnosis.
What ultrasounds and tests do you need to undergo: a gentleman’s kit for a comprehensive examination
Every year the number of necessary preventive procedures is growing. The body does not get younger, the susceptibility to diseases increases, therefore, more and more organs require research. But examining the body from head to toe is a utopia, because there are countless possible pathologies. A reasonable solution is to limit ourselves to the most “fragile” organ systems in terms of susceptibility to disease.
The minimum examination schedule for a man without any particular pathological heredity is as follows:
| Age | Surveys | Specialists |
| 30 years | Blood tests (general, biochemical), urinalysis, fluorography, ultrasound of the prostate gland, smear for infections | Therapist, dentist, urologist, ophthalmologist |
| 40 years | + blood test for sugar concentration, ultrasound of the heart, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the thyroid gland | + gastroenterologist |
| 50 years | + X-ray of the lungs (instead of fluorography), ultrasound of the intestines, Dopplerography, gastroscopy | + cardiologist, vascular surgeon |
| 60 years | + ECG, EEG, rheoencephalography, colonoscopy | The same |
How to perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs in men
Ultrasound diagnostics is one of the most reliable methods for detecting tumors in the early stages and other pathologies of the male reproductive system.
At the same time, depending on the expected diagnosis, urologists use different research methods:
- Transabdominal (through the abdominal wall).
The method is convenient in that it does not cause psychological discomfort, because it is not invasive and does not require penetration into the body. The wide sensor allows you to emit and capture a large volume of ultrasonic waves. However, compared to TRUS, the transabdominal method has limited accuracy and does not see small changes in tissue structure. - Transrectal (TRUS, through the rectum).
This is the most effective method of examining the prostate and studying its structural changes. The disadvantages of the method are an unpleasant examination process. The examination is carried out through the rectum in close proximity to the prostate gland. Despite the small sensor area, TRUS allows visualization of a cyst or tumor as small as 2 mm. The great advantage of the method is that there is no need to fill the bladder, unlike the transabdominal technique. This makes it possible to diagnose patients suffering from urinary incontinence and having a small bladder volume. - Dopplerography.
This is a special function available in modern expert ultrasound machines that allows you to assess the blood circulation of the pelvic organs. Doppler examination reveals vascular pathology and oncological tumors that have a vascular network.
Transabdominal examination is performed with a full bladder. The patient is asked to avoid foods that cause gas. During a transrectal examination, a man adheres to a certain diet, and the night before he takes medications that help cleanse the intestines. The accuracy of the results depends on compliance with the diagnostic rules.
Procedure for conducting the examination
When the patient lies down on the tomograph table, there should be no metal decorations or elements on him, and all gadgets remain behind the door, in the next room, where he will be observed by an x-ray technician and a radiologist. The patient is given special clothing that he wears during the scan - it does not restrict movement and does not have rough seams. This can also be the patient’s personal clothing, the main thing is that it is loose, comfortable, and made of cotton fabric.
Having positioned himself on the retractable table of the tomograph, the subject takes the most relaxed, free and comfortable position, and prepares to freeze in it for the entire time he is in the tomograph. The doctor monitors him and from time to time gives instructions to hold his breath for a while.
During the examination, while the patient is on the table, a scanner ring rotates around him, which produces X-rays at a certain interval. The rotation lasts 1 second, and produces a series of layer-by-layer images of the area being studied. Next, a special computer program, using the obtained images, models the pelvic area on the monitor.
The procedure with contrast practically does not differ in technology. The only difference is that after the initial scan, before the subject enters the tomograph again, he is injected intravenously with a contrast agent. A syringe or auto-injector can be used for this purpose. Getting a coloring drug into the body can cause a burning sensation, dizziness, fever, increased blood pressure, and nausea, which should be reported to the doctor immediately.
During scanning, the device makes specific sounds - crackling, buzzing. If they cause discomfort in the subject, he is given earplugs or headphones. As a rule, they are always given to children.
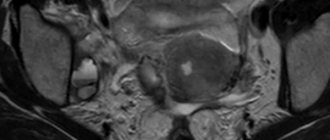
What a healthy and diseased prostate gland looks like on a pelvic ultrasound
The prostate gland, despite its small size, has both glandular and fibromuscular tissue. The ultrasound method gives a complete picture of the condition of the tissues, as well as the ducts of the gland. Both transabdominal and transrectal methods determine the same changes, but the second option differs in the accuracy of the results.
According to statistics, more than 20% of men over 40 years of age suffer from prostate adenoma (benign growth of organ tissue), closer to 50 years of age, half of the stronger sex, and after 70 years of age, the disease occurs in every 8 out of 10 men. Therefore, the study is carried out for medical reasons and for preventive purposes.
Prostate adenoma causes a lot of trouble: it brings pain, reduces the quality of sexual life and causes other diseases. Thus, the growing tissue of the prostate gland deforms the urethra. This causes urinary retention and disrupts the outflow of urine, which leads to inflammation, creates a favorable environment for the development of infections and contributes to disruption of the kidneys and bladder. Therefore, if there are problems with the bladder in men, the prostate gland must be examined.
The main characteristics and parameters determined by ultrasound include the following:
- prostate size. Normally, the length of the organ is 2.5-4 cm, width - 3-4.5 cm and thickness 1.5-2.5 cm;
- the contours of the prostate are smooth and clear;
- medium echogenicity;
- glandular tissue is well distinguished from fibromuscular tissue;
- the structure is fine-grained and heterogeneous;
- gland volume up to 26.8 cm3;
Problems with the prostate gland are shown on ultrasound by the following indicators:
- increase in size over 45 mm in length, 40 mm in width and 25 mm in thickness;
- general increased echogenicity indicates chronic prostatitis, decreased echogenicity indicates acute;
- hyperechoic inclusions against the background of general average echogenicity, uneven contours and increased sizes indicate nodular formations;
- with inflammation (prostatitis), the contours cease to be clear,
- glandular and muscle tissues are not differentiated; along with average echogenicity, areas with hypo- and hyperechogenicity alternate;
- anechoic lesions indicate an abscess (accumulation of pus);
- cysts are visualized as hypoechoic or anechoic areas of a clear round shape, however, small cysts up to 5 mm in size are also found in young healthy men;
Preparation for ultrasound OMT
Pelvic ultrasound requires preliminary preparation. It will be the same for men and women. You are on a diet for 3–4 days before the procedure. You need to remove gas-forming foods from your diet. These are cabbage, legumes, yeast baked goods, carbonated drinks. It is better to give preference to cereals, vegetable broths, lean meat and fish.
You need to eat food in small portions so as not to overload your stomach. It is important to maintain a drinking regime, drink at least 1.5 liters of clean water without gas per day.
On the recommendation of a doctor, on the eve of a transrectal ultrasound, you should use a microenema. The large intestine must be clean.
Additional diagnostics to detect stones and cancer in the prostate gland
The main reason for the formation of stones in the prostate gland is the inability of the gland’s secretions to completely exit the ducts due to tissue proliferation or an inflammatory process. As a result, the secretion stagnates and mineralizes against the background of impaired blood supply to the prostate gland. In some cases, stones are formed as a result of the activity of bacteria that enter the ducts of the gland along with urine.
Stones in the prostate gland are visualized as small hyperechoic foci of different sizes, located singly or in groups. It is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis using ultrasound without additional diagnostics, so the patient is additionally prescribed a general blood test (leukocytes and ESR increase) and a urine test. In urine tests, leukocyturia (pus in the urine), proteinuria (protein in the urine), bacteriuria (microorganisms in the urine) are observed. Also, a direct indication of stones in the prostate is the detection of blood and leukocytes in the ejaculate taken through masturbation (spermogram). Blood enters the sperm as a result of trauma to blood vessels damaged by the sharp edges of stones.
In some cases, stones in the prostate gland are a symptom of a more serious disease - genitourinary tuberculosis (inflammation is caused by the same bacteria as pulmonary tuberculosis). For this reason, a patient who has signs of stones in the prostate is sent to a phthisiurologist (a specialist who treats organs of the reproductive system affected by the tuberculosis bacillus).
It is also difficult to detect oncological tumors on ultrasound. Despite the fact that the echogenicity of cancer changes somewhat, there is no specific pattern indicating oncology. Enlarged lymph nodes near the prostate gland should alert you. In this case, the patient is sent for a fine-needle biopsy to remove tissue for more detailed examination.
Comprehensive examination of men aged 25–30 years
At this age, the list of recommended examinations is small. Taking tests every 1 – 1.5 years will allow you to timely identify diseases of the blood system or an asymptomatic chronic inflammatory process.
The main male doctor is a urologist. It is he who identifies and treats all pathologies of the genitourinary organs, male infertility, and genital infections. Even at a young age, you need to visit a urologist at least once a year. Minimum mandatory examinations under the program:
- Smear for infections and prostatitis.
- Ultrasound of male organs - insurance against early prostatitis.
- If a man has an active sex life or is partial to tattoos, it makes sense to get tested for hepatitis and HIV.
An annual blood pressure measurement will allow you to timely suspect hypertension, and undergoing fluorography will help rule out tuberculosis and lung cancer. It is recommended to visit a dentist and ophthalmologist. Diseased teeth can later cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract or provoke infection of the entire body.
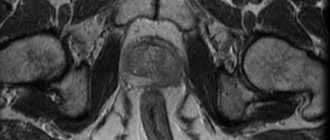
Seminal vesicles on ultrasound: norms and deviations
Ultrasound diagnosis of the seminal vesicles is of great importance in establishing the cause of male infertility. They, along with the vas deferens, play a decisive role in the process of fertilization and conception.
The seminal vesicles are visualized by an ultrasound machine on either side of the bladder, slightly behind it. The degree of obstructive damage to the seminal vesicles is determined by the organ’s ability to contract, so ultrasound is performed twice: the first time - before ejaculation, then the patient is asked to discharge the ejaculate by masturbation. Thus, the doctor receives measurements of the seminal vesicle and, based on the results, draws conclusions about the condition of the organ.
The normal diameter of the organ is 15-16 mm, but when sexual activity ceases, it increases slightly, and this is not a pathology. After ejaculation, the size of the bubbles decreases slightly. If this does not happen, there is a suspicion of obstruction of the vas deferens, through which the product of the seminal vesicles enters the urethra.
One of the reasons for the impossibility of conception is obstruction of the vas deferens - a blockage of the paths through which sperm come out. The obstruction can be complete, and in this case azoospermia is observed - a complete absence of sperm in the ejaculate. With unilateral obstruction, the pathology is asymptomatic, the semen contains sperm, but their concentration is insufficient (oligozoospermia), their mobility and activity are not enough to pass through the cervical canal (asthenozoospermia) or there are too few healthy sperm suitable for fertilization (teratozoospermia).
When diagnosing male infertility, a transrectal ultrasound machine with a highly sensitive sensor is used. The length of the ducts is 45-50 cm, diameter 3-4 mm, but the walls of the ducts are thicker than the width of the lumen, which is no more than 0.5 mm, so any minor pathology completely covers it. Using a sensor, the doctor assesses the condition of the ducts along their entire length, visualizes the lumen and diameter of the duct, taking pictures of areas with abnormally thickened walls or areas where the lumen of the duct is not visible.
Ultrasound characteristics of healthy seminal vesicles are as follows:
- diameter from 10 to 16 mm, but a slight increase in
- older men
- located above the prostate gland behind the bladder, slight asymmetry is acceptable
- the shape resembles a butterfly or mustache
- seminal vesicles have a cellular structure, the tissues are characterized by average echogenicity
- hyperechoic inclusions indicate a tumor, areas with anechoicity indicate cysts with fluid inside
Men, young and sexually active, face a problem such as vesiculitis - inflammation of the seminal vesicles. On ultrasound, the disease is visualized as areas with reduced echogenicity and poorly visible transitions between zones. The vesicles themselves are enlarged to 2.5 cm, and isolated calcifications are noticeable. When inflamed, they become vascularized - enriched with a network of capillaries, which becomes noticeable in Doppler mode. Vesiculitis is usually a secondary disease caused by an STI. Chronic disease leads to infertility, because... healthy sperm die.
What does a pelvic CT scan show?
The human pelvic cavity is represented by two sections: upper (wider) and lower (narrowed). It is based on the paired pelvic bones (iliac, pubic and ischial), the sacrum and the coccyx. The upper section (pelvic cavity) is the lower part of the abdominal cavity, which borders the chest. The small pelvis is separated from it by a boundary line that passes through the crests of the pubic bones, the upper part of the symphysis pubis, the arcuate lines of the iliac bones and the anterior edge of the sacral promontory.
In the pelvic cavity are located:
- bladder;
- lower part of the large intestine (rectum);
- uterus, ovaries, vagina (in women);
- prostate gland, seminal vesicles (in men);
- large vessels and nerve plexuses.
A CT scan of the pelvis visualizes the condition of bone elements and cartilaginous structures in the study area. The method is based on the selective intensity of absorption of X-ray radiation by the tissues of the human body, which depends on the density of the structures being illuminated. The denser the substance, the higher its radiopacity, therefore the pattern will be clear and bright. During a CT examination, soft, loose elements appear as dark areas, which makes it difficult to assess their structure and reduces the information content of the method. To study them, contrast computed tomography or MRI is used.
During a CT scan, the pelvic area is scanned using a tomograph. The ring part of the device is movable - it rotates the emitters and sensors located inside. Thanks to this device, scanning takes place at different depths.
The device converts the information it reads into images of thin spiral sections of the area in question. Based on these images, if necessary, a 3D model of the studied area is reconstructed, which is as informative as video. Thanks to the photographs taken, the radiologist gets a complete picture of the condition of the elements being examined.
A CT scan of the pelvic cavity will show the condition of the forming bones:
- abnormalities in the development of bone structures;
- destructive changes and areas of resorption;
- hyperostosis (pathological increase in the volume and structure of bone tissue with changes in contours);
- neoplasms in the area of solid elements;
- injuries of the pelvic bones (cracks, fractures);
- inflammatory processes of structure-forming bone elements (osteomyelitis, periostitis).
In the postoperative period, CT visualizes regeneration processes and makes it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of surgical intervention.
Thanks to layer-by-layer scanning, MSCT of the pelvis determines the slightest disturbances in the shape, structure, structure of the element in question and helps in the differential diagnosis of pathological changes.
Additional examination of the seminal vesicles by ultrasound
Ultrasound diagnosis of the seminal ducts when establishing the causes of infertility in men requires mandatory confirmation by the results of other tests.
In addition to ultrasound diagnostics, a very informative spermogram is an analysis of the qualitative characteristics of sperm. It applies not only to couples in which there is suspicion of infertility in the man. A spermogram can show the presence of STIs, tumors and inflammation of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles in the body. If ultrasound shows changes in the structure of tissues, then a spermogram shows the state of hormonal levels, the quality of the sperm produced and, in general, their ability to fertilize.
The spermogram can be basic (the volume of the ejaculate, its color, viscosity, consistency, acidity, the number of motile sperm, biochemical composition are examined), the MAR test (mixed antiglobulin reaction or mixed antiglobulin test), which detects antibodies that suppress the viability of sperm, as well as the Kruger spermogram ( reveals under a microscope the percentage of spermatozoa suitable for fertilization).
In case of prostate adenoma, bacteriological culture of urine will reveal pathogenic microorganisms causing inflammation or abscess. If a patient is suspected of having a cancerous tumor, a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test will give an accurate answer. As prostate tissue grows, serum PSA levels increase significantly. If the reading is above 10 ng/ml, the man is prescribed a fine-needle biopsy, which is also performed under ultrasound guidance.
If an ultrasound visualizes the absence or pathological narrowing of the vas deferens, the man is prescribed a genetic examination. In men with bilateral absence of the vas deferens, a mutation of the CFTR gene is detected. The only way to become a father for such patients is ICSI - sperm collection directly from the testicle followed by in vitro fertilization of the egg. If there are no signs of mutation, but a man has a pathologically low concentration of healthy sperm, he is prescribed karyotyping - the study of the chromosome set (karyotype).
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs in men helps to identify the most common diseases of the reproductive system, and also helps to see pathologies that interfere with conception.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Contraindications
Before referring you for an MRI of the pelvis, a specialist doctor will examine the patient and analyze the collected medical history.
The reasons that do not allow this type of diagnosis are considered:
- during the first trimester of pregnancy;
- the presence of mental or psychosomatic disorders leading to the inability to remain motionless for a long time, inappropriate behavior of the patient;
- fear of being in a confined space;
- the patient's body weight is more than 130 kg or waist circumference is more than 140 cm;
- any metal objects in the human body (prostheses, pacemakers, cochlear implants, clips, fragments and shot after wounds);
- increased susceptibility to a contrast agent if a comprehensive examination with its administration is planned.
In order to avoid unforeseen situations during the study, you must tell the doctor about all the characteristics of your body and any health problems.
Doctors manage to correct certain individual nuances. Thus, patients with a mild form of claustrophobia at the DiMagnit center can undergo examination without medical sedation, since the tomograph is light and open in front and behind. Therefore, when performing an MRI of the pelvis, the head is already at the exit of the tomograph, which means the discomfort is not so pronounced.
Comprehensive examination of men aged 40–50 years
The main enemies of men's health at this age are prostate adenoma and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, the importance of annual examination of the prostate and heart remains. Peak mortality from heart failure in men occurs between 45 and 55 years of age.
Often after 40 years of age, men's vision decreases, and if in addition headaches appear, this is a symptom of glaucoma. Therefore, you should not forget to visit an ophthalmologist.
An annual examination of the heart condition remains mandatory, and Doppler ultrasound of the lower extremities will prevent the development of thrombosis or varicose veins.
During this period, the risk of developing cancer of any part of the gastrointestinal tract increases due to men’s high commitment to alcohol and tobacco, that is, ultrasound of the abdominal organs is more relevant than ever. Once every 50 years, you need to undergo an intestinal examination to exclude the development of an oncological process. It is a good idea to undergo a comprehensive urological ultrasound.
What all men aged 50+ need to check
With age, your health should be under special control, since the risks become much greater. A tendency to thrombosis and its complications, hearing impairment, the threat of intestinal cancer and others are only part of the impending threat.
Once every 2 years it is necessary to take a blood test for coagulation. The heart and blood vessels should be examined at similar intervals (to assess the blood supply to the brain and lower extremities). It is recommended to replace fluorography with an x-ray of the lungs. It is also necessary to take tests for sex hormones, this will prevent early male menopause. We will consider below which ultrasounds of organs are performed for men over the age of 50.