Anatomical location of the thyroid gland
A thyroid MRI uses a magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed images of the neck area. Doctors evaluate the scans to distinguish normal, healthy tissue from abnormal tissue.
After the examination, a conclusion will be prepared within 20 minutes, based on the results of which a radiologist will talk with you. If there is a suspicion of a tumor, it is necessary to understand that final verification of the diagnosis is possible only after performing a biopsy followed by a morphological examination of the tissue taken.
When to get diagnosed
MRI of the thyroid gland is performed when it is necessary to assess the size and shape of the organ, incl. with invasive growth into the chest (ultrasound scanning is hampered by bone structures), if a malignant neoplasm or goiter is suspected (determining the degree), in cases of lymphadenopathy. MRI of the thyroid gland may be recommended instead of CT if there are contraindications, since in most cases magnetic resonance imaging does not require injection of a contrast agent and does not involve the use of radiation, as in a computer scan.
The examination can be performed on children, elderly patients and pregnant women, starting in the second trimester if indicated.
MRI of the thyroid gland is often used after laboratory and ultrasound examinations, when the results obtained cannot be interpreted unambiguously.
MRI scanning can be useful before performing a fine-needle biopsy or planning surgery, as it allows you to clarify the localization of suspicious areas, the architecture of blood vessels, the anatomy of the organ and nearby structures, metastatic lesions and their location in thyroid cancer.
Magnetic resonance imaging is justified for monitoring after surgery or conservative therapy.
Sometimes the study allows you to decide on management tactics: drug therapy or surgical intervention, including its scope - resection of a site, lobe or total removal of an organ and affected regional lymph nodes.
MRI of the thyroid gland is a highly informative, painless and non-invasive way to clarify the diagnosis.
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging
MRI diagnostics is an effective method for detecting various diseases. The reasons for its appointment are the following conditions:
- increasing neurological symptoms;
- cerebral circulatory disorders, brain injuries of varying severity;
- increased intracranial pressure, epileptic seizures;
- problems in the abdominal, thoracic, and pelvic organs, which are visible only on MRI;
- presence of cancer or suspicion of it;
- disruption of the musculoskeletal system, spine and spinal cord;
- damage to soft tissues and pathological formations in the paranasal sinuses and oropharynx.
These are the indications for conducting this study. These also include heart diseases, such as coronary disease, myocardial infarction, and defects. Often problems with blood vessels, arteries and veins are a signal that you need to undergo an MRI. For most people, this procedure is safe, however, before you sign up for it, you should definitely familiarize yourself with the contraindications.
Anatomy and physiology of the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is a hormone-secreting organ, which is a vascular encapsulated structure consisting of the right and left lobes, which are connected along the midline by an isthmus. The main role of the organ in question is the production of hormones (triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)) responsible for metabolic processes (metabolism), growth and development of the body, mental health, sexual functions, immunity and activity of the cardiovascular system. The production of these biologically active substances is regulated by the pituitary gland, which synthesizes thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The higher its level, the larger the size of the thyroid gland.
The production of TSH is inhibited, in turn, by T3 and T4. This is an interconnected system, so the concentration of hormones in the blood is almost constant.
References
- Troshina, E.A., Sviridenko, N.Yu., Vanushko, V.E. and others. Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of thyrotoxicosis with diffuse goiter (diffuse toxic goiter, Graves-Bazedow disease), nodular/multinodular goiter, 2014. - 25 p.
- Semkina, G.V., Abrosimov, A.Yu., Abdulkhabirova, F.M. and others. Comparative analysis of cytological reports and diagnostic categories of independent cytologists. Clinical and experimental thyroidology, 2013. - No. 3. — P.29-34.
- Singaporewalla, R., Hwee, J., Lang, T. et al. Clinico-pathological Correlation of Thyroid Nodule Ultrasound and Cytology Using the TIRADS and Bethesda Classifications, 2021. - Vol. 41(7). — P.1807-1811.
For what symptoms can an MRI of the thyroid gland be done?
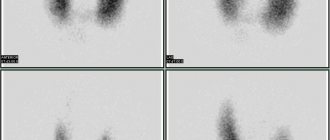
View of the thyroid gland on MRI tomograms (the arrow indicates the area of pathological changes)
Symptoms for which an MRI of the thyroid gland is recommended include:
- enlargement of the organ upon palpation or visible to the naked eye;
- the appearance of a tumor mass in the neck;
- difficulty swallowing;
- unexplained weight fluctuations, both down and up;
- enlargement of the cervical, subclavian and supraclavicular lymph nodes;
- hoarseness of voice;
- insomnia, tearfulness, mood swings, rapid heartbeat (symptoms characteristic of hyperthyroidism).
Magnetic resonance imaging will help clarify the situation if there are changes in clinical and laboratory parameters: an increase or decrease in the level of thyroid hormones in the blood serum (hyper- and hypothyroidism), the presence of a large number of specific antibodies (Hashimoto's disease, Graves' disease, thyroiditis, type 1 diabetes , rheumatoid arthritis).
The level of calcitonin in the blood is higher with a certain type of thyroid cancer, but the same result may be present in other diseases - chronic renal failure, disorders of calcium metabolism. In this case, MRI will help confirm or refute tumor pathology and direct the diagnostic search in the right direction.
Pathologies of the thyroid gland can be asymptomatic or manifested by a variety of complaints.
What does an MRI show?
Diagnostic results depend on which organ was examined, for example, the brain or the abdominal cavity. However, there are a number of serious changes in a person's health that can be detected after undergoing an examination. These include the following:
- disorders of soft tissues of different parts of the body;
- various formations and tumors that only MRI diagnostics shows;
- neurological disorders, damage to the central nervous system;
- damage to the musculoskeletal system;
- problems of the brain and blood vessels;
- acute conditions of the arteries, aortic aneurysm;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, liver.
This diagnosis provides high-quality visualization of various organs, which is not available with radiography or ultrasound. Thanks to this, it is possible to detect serious diseases in the early stages, which gives a chance for their successful treatment. Often, research reveals hidden diseases that are asymptomatic. For this reason, undergoing an MRI will be useful not only for those who have health problems.
What pathologies are diagnosed using MRI?
Pathologies that can be detected during magnetic resonance examination of the thyroid gland include:
- malignant neoplasm and its interaction with neighboring tissues;
- foreign body;
- metastasis from the lung, kidney, colon or other organs. There is evidence of direct invasion of the tumor from neighboring structures: pharynx, trachea, esophagus; cases of metastasis to the thyroid gland in melanoma have been described;
- inflammation;
- goiter (enlargement) and reduction of the organ.
To reveal functional ability, scintigraphy is performed. MRI, CT and ultrasound provide important anatomical information about the thyroid gland, as well as related structures in the neck: the presence or absence of an isthmus, mediastinal lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes in the mediastinum), growth of the organ into adjacent soft tissues and cavity formations. Carrying out thyreostatic therapy is a contraindication to scintigraphy: in these cases, it is more reasonable to perform an MRI scan.
MRI diagnostics: prices and discounts
Sign up for a diagnostic and treatment center in Moscow: we offer MRI at competitive prices, with discounts on weekdays and weekends!
You can find out details about the preparation, as well as about the current DISCOUNTS for MRI, by calling our call center +7 495 478-10-03 or by leaving a request on the website.
MRI of the soft tissues of the forearm MRI of the soft tissues of the thigh MRI of the brachial plexuses MRI of the spleen MRI of the retroperitoneal space MRI of the seminal vesicles MRI of the costosternal joints MRI of the sternoclavicular joints MRI of the adrenal glands MRI of the gallbladder MRI of the coccyx MRI of the uterus and ovaries
Contrast-enhanced MRI
MRI of the thyroid gland with contrast is rarely performed, since native diagnosis is usually sufficient. The pharmaceutical drug (usually gadolinium chelates) is administered intravenously. The resulting tomograms are distinguished by higher accuracy, which is important in diagnosing a tumor process at the initial stage.
There are practically no side effects of MRI contrast, but the literature describes pathological changes that can develop in patients with severe renal failure (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis).
A systemic allergic reaction to gadolinium salts is also rare; in some cases, skin itching and tingling are possible at the injection site.
In our Northern Capital Medicine center, we use the drug, which is approved for use, with maximum safety.
There are no harmful effects on organs and systems during native MRI or examination with contrast, so all fears in this regard are groundless.
MRI of soft tissues of the neck at Clinic No. 1
| Name | Price |
| MRI examination of the soft tissues of the neck, assessment of the condition of the lymph nodes. | 5 600 |
Examinations in our medical center are carried out by appointment, which can be made by phone or on our website any day of the week from 8 a.m. to 9 p.m. If you urgently need to undergo examination in the city of Moscow, contact our administrator and he will help resolve your issue. Registration is possible without a doctor’s referral and a previously confirmed diagnosis.
How to prepare for research
MRI of the thyroid gland does not require special preparation; it is enough to remove all metal jewelry, watches, hairpins and choose comfortable clothes (including underwear) without buttons, zippers or fasteners.
It is necessary to warn the doctor about possible or existing pregnancy and installed implants: pacemakers, terminals, insulin pumps, structures, etc. Fixed dentures are not a contraindication to MRI.
There are drugs (including herbal ones) that, when taken for a long time, affect the functions of the thyroid gland and can change its parameters. These include:
- acetylsalicylic acid;
- steroid hormones;
- thyroid medications;
- diuretics;
- St. John's wort.
If you are taking anything from this list, notify your doctor.
Take with you all the results of previous instrumental studies and blood tests for thyroid hormones, if any, were performed.
Contraindications
Before scheduling an MRI scan, you should consult your doctor. If contraindications are identified, the study will not be conducted. Contraindications include:
- the presence of a metal foreign body in the orbit;
- intracranial aneurysm clipped with ferromagnetic material;
- the presence of pacemakers and other electronic devices in the body;
- hemolytic anemia;
- claustrophobia and mental disorders;
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks;
- state of alcohol and drug intoxication.
The final decision on the use of magnetic tomography is made by the radiologist immediately before the study and after assessing the patient’s condition.
How is the procedure performed?
In the diagnostic center Medicine of the Northern Capital, the examination is carried out on a modern high-field German MRI machine Siemens 1.5 T.
The patient is placed on a table that immerses him deep into the tomograph ring. A special scanner, rotating, takes a series of images in specified projections with a set slice thickness. All images are processed using a computer program. The operation of the equipment is accompanied by mechanical sounds: if the patient wishes, you can use headphones and listen to music. A prerequisite is complete immobility, which is important for the quality of tomograms: any movement leads to the appearance of artifacts (defects) on the film.
The radiologist monitors the progress of the procedure; if necessary, there is a special call button.
Our advantages:
- All employees undergo annual retraining.
- Expert class MRI machine.
- Tea and coffee are free.
- Convenient location of the center 5 minutes walk from the Universitet metro station.
- Affordable prices.
- Large, free parking. Check-in from Vernadsky Avenue.
- Diagnostic duration is up to 40 minutes.
- Social discounts.
- After the examination, the patient receives a high-quality image and a specialist’s report, after studying which the attending physician will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment. Electronic versions of images and descriptions of study results are stored in the database of our institution.