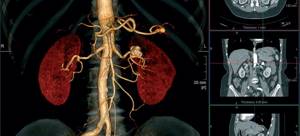
Computed tomography of the kidneys and adrenal glands is one of the most accurate diagnostics, as it allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of internal organs, study their structure, see pathological changes and identify diseases at an early stage. This method is based on x-rays and allows you to obtain detailed images in the form of “slices” in increments of 3 to 10 mm and see the smallest changes in organs. The CT scan of the kidneys is performed with and without contrast.
Computed tomography of the kidneys
CT diagnostics of the kidneys and adrenal glands also has another name - CT urography, since it also examines the organs of the retroperitoneal space. This method is very important for identifying various diseases, neoplasms, urolithiasis, vascular abnormalities in the kidneys and adrenal glands.
When is kidney diagnostics necessary?
The kidneys and adrenal glands are different organs, each performing its own function, so the indications for computed tomography of the kidneys and adrenal glands can be completely different. It is necessary to resort to the CT method for diagnosing the kidneys and adrenal glands in case of hormonal changes, severe causeless changes in weight, back injuries, suspected urolithiasis, tumor, or injury to internal organs. You should also undergo an examination in case of chronic infectious pathology of the kidneys and dysfunction of their function, to determine the causes of renal colic, diagnose developmental abnormalities, in inflammatory processes, pathology of blood vessels and lymph nodes.
CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast: indications
Indications for diagnosing adrenal pathologies using contrast-enhanced CT are the following disorders:
- Pale or reddened skin.
- A persistent increase in blood pressure that is difficult to treat with hypertension medications.
- Decreased potency, lack of sexual desire.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Depression, increased aggressiveness.
- Joint pain, numbness of limbs, cramps.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Dramatic weight loss.
- Sudden weight gain.
- Women have male pattern hair.
- Hirsutism.
- General malaise, headache.
- Increased blood sugar.
Contrasting allows you to clearly identify the boundaries of an organ, determine its size, and defects in the tissues of the organ. Using contrast-enhanced CT, the density of adrenal tissue, disruption of the structure of the organ, the presence of tumor formations, changes in the size of the organ, and vascular pathology are determined. CT scans can detect the following adrenal gland diseases:
- Adenoma.
- Carcinoma.
- Hemangioma.
- Fibroma.
- Paraganglioma.
- Pheochromocytoma.
- Mixed tumors of the adrenal medulla and cortex.
- Metastases of malignant tumors.
- Injury.
- Vascular insufficiency.
- Pathology of lymph nodes.
CT scanning of the adrenal glands is performed before surgery, for dynamic monitoring during treatment, as a postoperative examination method.
How to prepare for a kidney tomography?
. However, preparation for a CT scan of the kidneys and adrenal glands with and without contrast is slightly different.
Preparation for a CT scan of the kidneys and adrenal glands without contrast involves a light diet that the patient will need to follow a couple of days before the examination. It is advised to exclude gas-forming foods from the diet, and the last meal should be eight hours before the CT scan.
A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the kidneys suggests a more restrictive diet. In this case, the patient needs to eliminate spicy, fatty foods from the diet, give up alcohol, coffee and tea for 4-5 days.
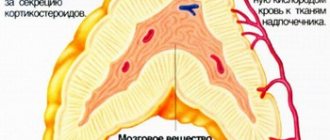
Classification of adrenal cancer
By tumor location:
- Neoplasms of the medulla: ganglioneuroma;
- pheochromocytoma.
- corticosteroma;
- lipoma;
Cancer may be primary
– from gland tissue, and
secondary – developed as a result of metastasis of neoplasms of other organs.
Primary tumors are divided into:
- hormonally inactive – incidentalomas, or “clinically silent” neoplasms;
- hormonally active.
Incidentalomas are often benign tumors.
How is the procedure performed?
A computed tomography scan of the kidneys takes no more than 30 minutes. The patient is asked to sit on a special couch, after which the specialist secures his limbs with special belts to avoid unnecessary movements during scanning. During a CT scan, the technician is in the next room, but the patient can hear him and can communicate via speakerphone. During the scanning process, a series of images are taken, which are then deciphered by a specialist and issued a conclusion.
CT scan of kidneys without contrast
A CT scan of the kidneys without contrast is performed if the patient is allergic to iodine. In this case, the scanning procedure is no different from the usual one. The patient will need to hold their breath for 3-4 seconds while the machine takes the image.
Kidney CT scan with contrast
CT scan of the kidneys and adrenal glands with contrast allows you to get the most accurate picture of the tissue structure, as well as see the rate of spread and removal of the contrast agent. This allows you to determine the function of the organ. The drug itself is administered intravenously several hours before the scan. If the patient is allergic to iodine, then the use of contrast is contraindicated. Computed tomography of the kidneys with contrast can detect pathologies in tissues, neoplasms and various diseases.
Causes and risk factors of the disease
The exact causes of adrenal cancer have not been established. It is believed that an important role in its occurrence is played by a hereditary factor, as well as genetic disorders, in particular, a specific mutation of TP53.
The following factors can trigger the development of the disease:
- bad habits – alcohol, smoking, drugs;
- lumbar region injuries;
- frequent stress, depression;
- other hereditary pathologies or endocrine tumors;
- contact with physical or chemical carcinogens.
Contraindications for the procedure
Diagnosis using computed tomography is not suitable for all people. This procedure is prohibited for pregnant women and those who are breastfeeding. Also, the method is not suitable for people suffering from claustrophobia, mental disorders, or acute pain that will not allow them to remain motionless for a long time. CT scanning is not recommended for patients with diabetes and children under 14 years of age. Kidney CT with contrast is prohibited for patients with an allergic reaction to a contrast agent, as well as in the presence of renal failure.
Treatment tactics
To treat adrenal cancer, a comprehensive approach is used - surgical removal of the tumor.
together with the gland and nearby lymph nodes and subsequent
chemotherapy, radiation therapy
, and the introduction of radioactive isotopes. Surgical treatment is also indicated for relapses of the disease, for surgical removal of metastases (available for intervention).
Sometimes chemotherapy and exposure to radioactive isotopes are used before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor. To reduce the toxic effects, adjuvant chemotherapy can be prescribed, in which the active substance accumulates in the area of pathological cell proliferation.
Depending on the hormonal status of the tumor, hormone therapy
.
Doctors take a very balanced approach to making a decision about surgery, since removal of an adrenal tumor is a complex procedure with a high risk of complications. For inoperable tumors, detection of cancer in late stages, and the presence of distant metastases, symptomatic and palliative treatment
.
After surgical treatment, during chemotherapy or radiation therapy, during the recovery period and throughout their lives, patients should be under the supervision of an endocrinologist and oncologist.
Symptoms of adrenal diseases
There are a number of symptoms, the appearance of which is a reason for examination:
- General and muscle weakness up to atrophy and decreased vitality;
- Increased pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes;
- Dyspeptic disorders (decreased appetite, constant nausea and vomiting, frequent diarrhea);
- Obesity, accompanied by characteristic hyperemia of the moon-shaped face;
- Hypotension – a decrease in blood pressure below 90/60 mmHg;
- Hypoglycemia – decreased blood sugar levels;
- Osteoporosis – increased bone fragility;
- Irritability, attacks of apathy, decreased memory and mental activity.
In general, adrenal dysfunction significantly reduces the quality of life, and in particularly severe cases it is a direct threat to life.
Diagnosis of an adrenal tumor
For surgeons, the most interesting question is the statistical probability of various nosological forms (cortisol- and aldosterone-producing adenomas, pheochromocytoma, adrenocortical cancer, metastasis to the adrenal gland of cancer) within incidentalomas (identified adrenal tumors). Assessment of probability is important from the point of view of the most pressing problems: malignant potential and hormonal activity of tumors.
With increased production of sex hormones, the clinical manifestations are quite striking; examination of the adrenal glands is usually carried out purposefully. Aldosterone, cortisol and catecholamines should be examined. Fractionated determination of metanephrines (separate determination of metanephrine and normetanephrine, if indicated - methoxytyramine) in urine or plasma has the greatest diagnostic sensitivity in relation to the initial (i.e. true tumor) amount of catecholamines and is recommended as a first-line diagnostic test for suspected pheochromocytoma.
Determining the malignant potential of a tumor is an equally important task for the surgeon when choosing a method of surgery for an adrenal tumor. Adrenocortical cancer can be detected in 4.2% of patients with incidentalomas. To assess the likelihood of tumor malignancy, two parameters have traditionally been used: tumor size and, during follow-up, growth rate. When the tumor size is more than 4 cm, about 25% of tumors are malignant. A sign of the rate of tumor growth can also be assessed as a diagnostic factor: the fastest rate is typical for cancer of the adrenal cortex. A 2-fold increase in tumor size over several months of observation is described. In absolute values, cancer describes an increase in size from 3 to 10 cm in 1 year. There are observations in the literature when the tumor was not detected on an initial CT scan, but after 1 year on a repeat CT scan, the size of the adrenal tumor was 12 cm. The minimum growth is typical for benign adenomas—several millimeters per year. The growth rate of pheochromocytoma is 0.5 - 1 cm per year, the growth rate of metastatic carcinoma is variable and depends on the morphological type of the primary tumor.
Very important!
When the tumor size is more than 4 cm, the frequency of the malignant nature of the tumor is more than 25%. If during dynamic observation the tumor grows by 1 cm per year or 0.5 cm in 6 months, immediate surgical intervention is necessary, since benign adenomas typically grow only 2-3 mm per year.
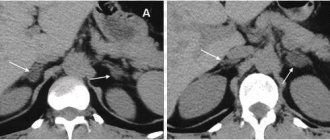
If a tumor is detected, it is necessary to perform CT semiotics of the tumor. When examining CT density at different wash-out phases, adrenal adenomas rapidly decrease density, while other adrenal masses tend to retain contrast. Decrease in CT density after 10 min. after contrast administration, more than 50% of the difference in density values in the pre-contrast and contrast phases indicates a benign adenoma of the adrenal cortex. The measurement of this indicator has close to absolute sensitivity in the differential diagnosis of adenomas from pheochromocytoma, adrenocortical cancer and metastatic carcinoma.
Very important!
Repeat CT is usually recommended at 6, 12, and 24 months after initial detection. In case of suspicious CT data (high density and accumulation of contrast) and a small tumor size (up to 3 cm), an initial observation interval of 3 months is considered optimal. For larger sizes, surgery is also indicated without further observation.
Surgical treatment of adrenocortical cancer
Surgery for adrenal cancer is the only radical method that can, in some cases, completely cure the patient. Given the rapid metastasis of adrenal cancer, tumor removal should be performed as quickly as possible after its identification and assessment of hormonal activity.
When planning the operation, the following points should be taken into account.
Surgical treatment of patients with adrenal cancer should be performed in a specialized center for endocrine surgery
, who performs a significant number of adrenal surgeries annually. Diagnostics, preoperative preparation, surgical intervention - all these stages have a lot of “pitfalls”, knowledge of which is achieved only with increasing experience of doctors after several years of work in this field. That is why performing operations on the adrenal glands in general surgery departments is unacceptable.
When preparing and performing surgery, special attention should be paid to the prevention of thrombosis.
. The main cause of death in patients after surgery for adrenocortical cancer is thromboembolic complications. They are due to several reasons:
- high levels of blood cortisol and/or male sex hormones, which increases blood clotting;
— blood loss during surgery with the need for transfusion;
— separation of tumor blood clots in the veins of the abdominal cavity during surgery;
— illiterate preparation of the patient for surgery, insufficient prevention of the development of thrombosis.
The operation should be carried out with maximum preservation of the integrity of the capsule
tumors. If the capsule is damaged, adrenal cancer recurs in 100% of cases. The absence of tumor trauma is ensured by the experience of the surgeon performing the operation, as well as the use of modern equipment - ultrasonic harmonic scalpel, bipolar coagulator with feedback, etc.
The most important rule to ensure radical surgery is to remove the tumor within healthy tissue
(so-called R0-resection).
An important stage of surgery for adrenal cancer is prophylactic lymph node dissection.
– removal of retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Some scientific studies have shown that lymph nodes are affected in 20-30% of patients - this fact alone dictates the need for prophylactic removal of lymph nodes in all patients. Scientific evidence suggests that lymph node removal improves patient survival and reduces the risk of tumor recurrence.
In some cases, with a small tumor, it is possible to perform endoscopic surgery to remove adrenal cancer, but the endoscopic method of surgical treatment for this tumor is not the main one
.
Traditional open access surgery allows for the most complete examination of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, performing a thorough lymph node dissection, reducing the risk of damage to the tumor capsule and the associated spread of metastases throughout the peritoneum. It should be borne in mind that the disadvantage of open surgery is its traumatic nature. In any case, any surgical intervention (open or endoscopic) should be planned only in a specialized center for endocrine surgery
- this rule is not questioned.
In case of tumor recurrence, when the tumor center or its metastasis is surgically removed, one should be inclined to repeat surgery
, aimed at completely removing cancer, since scientific evidence shows the advantages of this approach - patient survival increases. Given that tumor recurrence in adrenal cancer can be common, this recommendation is very important.
Registration for surgery
To sign up for surgery to remove the adrenal gland, you need to consult with a specialist at the North-Western Endocrinology Center with all the examinations you have. The center specialist will study the available medical documentation and, if necessary, conduct additional research. If the diagnosis is confirmed and there are indications for surgery, you will be hospitalized at the center for removal of the adrenal gland using the most modern technologies. Surgeries on the adrenal glands are performed free of charge at the center.
.
Consultations for patients with adrenal adenoma are carried out:
| Sleptsov Ilya Valerievich, Endocrinologist surgeon, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Surgery with a course in surgical endocrinology, member of the European Association of Endocrine Surgeons | |
| Rebrova Dina Vladimirovna, Endocrinologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences. Assistant at the Department of Endocrinology named after Academician V.G. Baranov, North-Western State Medical University named after I.I. Mechnikov. Member of the European Society of Endocrinologists, International Endocrinological Society, St. Petersburg Association of Endocrinologists. | |
| Fedorov Elisey Alexandrovich, Surgeon-endocrinologist of the highest qualification category, Candidate of Medical Sciences, specialist at the North-West Center for Endocrinology. One of the most experienced surgeons in Russia performing operations on the adrenal glands. The operations are performed using a minimally traumatic retroperitoneoscopic approach through lumbar punctures, without incisions. | |
| Chinchuk Igor Konstantinovich , Endocrinologist surgeon, oncologist, candidate of medical sciences, member of the European Thyroid Association (ETA). Performs endoscopic operations on the adrenal glands. Retroperitoneoscopic approach. More than 350 surgical interventions per year, half of which are endoscopic. |
Consultations are carried out in outpatient branches of the center:
- Petrograd branch
(St. Petersburg, Kronverksky pr., 31, 200 meters from the Gorkovskaya metro station, telephone for appointment, from 7.30 to 20.00, daily);
— Primorsky branch
(St. Petersburg, Savushkina st., 124, building 1, 250 meters to the right from the Begovaya metro station, telephone for appointments from 7.00 to 21.00 on weekdays and from 7.00 to 19.00 on weekends).
For consultation, please bring all available examination results.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention of the disease. A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and the absence of bad habits are recommended to prevent various pathologies, not only malignant tumors.
If you identify any warning symptoms, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible so as not to miss the onset of the disease. People with chronic diseases need to undergo periodic examinations and tests prescribed by the doctor.
To prevent relapses after treatment for adrenal cancer and the occurrence of complications, you need to undergo follow-up examinations on time and follow all medical recommendations.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
ATTENTION PATIENTS!
Currently, the North-Western Endocrinology Center provides free surgical treatment for patients with adrenal tumors
. Treatment is carried out within the framework of the compulsory medical insurance program or the SMP program (specialized medical care).
To obtain free hospitalization for out-of-town patients
you must send copies of documents (passport: page with photo and basic data, page with registration; compulsory health insurance policy, SNILS, results of existing examinations - a detailed list is presented below) to the address
Questions about hospitalization can be asked to the responsible administrator, Valentina Petrovna Kleshnina, by calling +7 900 6291427 (weekdays, from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m.).
Package of necessary examinations
should include the following list (if there are no results from the listed studies, they must be performed in any case):
- CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity, if there is only an ultrasound report, then it is necessary to perform a CT scan of the abdominal cavity without contrast, indicating the native density of the adrenal tumor (if necessary, print this item and show the CT scan to the doctor before the study).
The following laboratory parameters must be determined:
- Aldosterone, renin, potassium in the blood, in case of taking diuretics, they must first be discontinued for three weeks (tests are taken in the morning from 8 to 9 am, sit for 15 minutes before taking the tests), after taking these blood tests, resume taking your previous medications;
- Analysis of 24-hour urine or blood for total metanephrines;
- Performing a test with 1 mg of Dexamethasone (in the evening, at 23:00, take 2 tablets of Dexamethasone, in the morning of the next day - from 8 to 9 in the morning, determining the level of cortisol in the blood), the analysis is taken separately from the others, in the last place.
You must also provide information
about the normal level of blood pressure in the patient (working blood pressure), if the pressure increases, indicate the maximum blood pressure numbers, how long ago the increase has occurred and how often rises in blood pressure occur.
To carry out the above examinations, there is no need to go to the hospital; they can be performed at your place of residence or in the nearest laboratory.
For patients from St. Petersburg
It is advisable to apply for a face-to-face consultation before entering the clinic (make an appointment by phone (812) 565-11-12, Primorsky branch of the center, address: Savushkina St., 124, building 1, make an appointment by phone (812) 498-1030, Petrograd branch of the center, address: Kronverksky pr., 31).
Corticoster Clinic
This variant of adenoma is more common in women 20-40 years old. Significant production of cortisol by the tumor (hypercortisolism) leads to the development of “Itsenko-Cushing syndrome” in the patient. Hypercorticism in most patients is manifested by obesity, which has specific features: fat is deposited on the face, neck, and chest. A rounded face is characteristic, the skin becomes thinner, and on the back of the hand there is a disappearance of subcutaneous fat. The muscles of the buttocks, shoulders, and legs become weak as the muscles atrophy. It is difficult for a person to move and get up. Hernias may occur, as atrophy of the abdominal wall muscles also occurs; O. Characteristic stretch marks of purplish-red color, called “striae,” appear on the skin of the abdomen, mammary glands, thighs and shoulders. Osteoporosis is formed due to the fact that bones lose mineral salts from their structure, fractures and a decrease in the height of the vertebral bodies are observed. There are femoral neck fractures. Steroid-induced diabetes mellitus occurs in one in 10 patients. Such diabetes is usually compensated by diet and antidiabetic tablets. Women experience excess hair growth and the menstrual cycle is disrupted. The psyche of patients suffers - depressive reactions occur.
Therapeutic tactics for adrenal tumors
When identifying an adrenal tumor larger than 1 cm, it is first necessary to exclude or confirm the hormonal activity of the formation, which can manifest itself as hypercatecholaminemia, ACTH-independent hypercortisolism, and primary hyperaldosteronism.
At the second stage, to diagnose the malignant potential of a tumor, it is recommended to evaluate quantitative densitometric parameters using three-phase multislice CT:
- density of the tissue component before contrasting (native);
- density in the tissue phase of contrast (arterial and venous phases);
- density in the delayed (10 minutes after contrast administration) contrast phase (washout phase).
When obtaining high-density CT values in the native phase, contrast delays in the delayed phase - the malignant potential of the tumor should be assessed as high.
In the differential diagnosis of adrenal tumors, needle biopsy has no proven advantages and is associated with low sensitivity, specificity and a high likelihood of complications. The same thing seems to apply to such a diagnostic method as PET CT; it has been revealed that not all neuroendocrine malignant tumors of the adrenal gland accumulate a contrast agent, so this method is not specific and reliable, and can give a false-negative result.