Computed tomography (CT) of the adrenal glands is one of the most informative methods for studying this organ. It is not always easy to suspect its pathology, however, if there is evidence, CT scanning of the adrenal glands is successfully used in endocrinology and surgery. In St. Petersburg, the medical sector uses the latest technology of multislice computed tomography (MSCT). The modern Siemens Somatom Emotion 16 device allows you to perform CT scans of the kidneys and adrenal glands with minimal radiation and the most accurate results, making it possible to identify the earliest morphological changes in these organs and conduct detailed diagnostics.
What will a CT scan of the adrenal glands show?
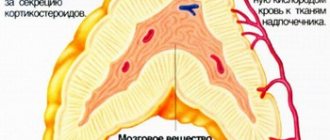
The adrenal glands are paired endocrine glands that are located above the upper lobes of the kidneys. They are part of the human endocrine system and produce biologically active substances (hormones) necessary for normal life: they participate in mineral metabolism, ensure the body’s resistance to stress, regulate the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and also affect libido and fertility. Even minimal changes in the structure or functioning of the adrenal glands can greatly worsen a person’s condition and lead to diseases of other organs and systems.
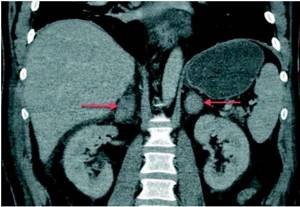
Adrenal glands on CT (indicated by arrows)
During the examination, the organ is examined layer by layer and the slightest deviations from the norm become visible to the specialist.
In the photographs you can see:
- structure and size of the adrenal glands (with the possibility of diagnosing nodular or diffuse hyperplasia of the organ), kidneys, nearby lymph nodes;
- the presence of an adenoma (benign formation), lipoma, cyst, hematoma;
- malignant neoplasms and involvement of regional lymph nodes in the pathological process.
When using a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast, the vessels of the organ are clearly visible, and you can easily distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one. First of all, the diagnostician will be interested in the size of the adrenal glands. If the size of the glands exceeds the established limits, this is a reason for a more thorough study. If a tumor is detected during a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast, it will be necessary to identify the nature of the tumor, its density and structure; for this, the scan is supplemented with contrast enhancement.
Anatomy of the site
The adrenal glands belong to the elements of the endocrine system; they are paired endocrine glands that produce a number of hormones for the normal functioning of the body. The secretion produced is based on substances of the adrenaline and corticosteroid type. They are responsible for the regulation of water metabolism, the electrolytic composition of body fluids, and the absorption of proteins. Any deviation in the volume of hormones produced leads to immediate failure of almost all body systems. Disruption of the adrenal glands leads to metabolic imbalance, reproductive problems, sudden changes in weight, the development of chronic diseases and deterioration in overall well-being.
Computed tomography is indicated if the patient is in a situation that results in injury to the abdominal area. Blunt and penetrating wounds can cause serious damage to the glands. The subsequent process of tissue replacement with scar fibers affects the functionality of the organs.
Indications for CT scanning of the adrenal glands
CT allows you to quickly examine the adrenal glands for the presence of a pathological process. More often, this type of diagnosis is prescribed as a clarifying method if the presence of tumors is suspected, but other reasons for the malfunction of this gland are also possible. A doctor will suspect adrenal pathology if a person experiences the following symptoms:
- sudden fluctuations in body weight for no apparent reason;
- increased sweating;
- excessive growth of body hair;
- the appearance of bronze spots or depigmentation of areas of the skin;
- in women, the voice becomes rough, and in men, the mammary glands grow;
- muscle weakness;
- cardiopalmus;
- blood pressure surges;
- infertility (can also be a consequence of a malfunction of the pituitary-adrenal system).
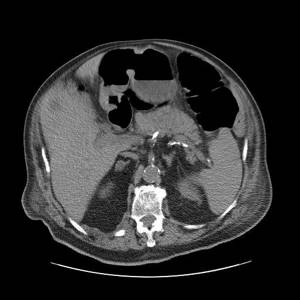
Enlargement of both adrenal glands according to CT data (indicated by arrows)
As a result of a CT scan of the adrenal glands, the following diseases can be diagnosed:
- benign and malignant tumors;
- adrenal cysts;
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome;
- Addison's disease;
- primary hyper- and hypoaldosteronism;
- hemorrhage in the adrenal cortex (Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome);
- congenital anomalies of organ development.
Computed tomography of the kidneys
CT diagnostics of the kidneys and adrenal glands also has another name - CT urography, since it also examines the organs of the retroperitoneal space. This method is very important for identifying various diseases, neoplasms, urolithiasis, vascular abnormalities in the kidneys and adrenal glands.
When is kidney diagnostics necessary?
The kidneys and adrenal glands are different organs, each performing its own function, so the indications for computed tomography of the kidneys and adrenal glands can be completely different. It is necessary to resort to the CT method for diagnosing the kidneys and adrenal glands in case of hormonal changes, severe causeless changes in weight, back injuries, suspected urolithiasis, tumor, or injury to internal organs. You should also undergo an examination in case of chronic infectious pathology of the kidneys and dysfunction of their function, to determine the causes of renal colic, diagnose developmental abnormalities, in inflammatory processes, pathology of blood vessels and lymph nodes.
How is a CT scan of the adrenal glands performed?
Computed tomography is one of the methods of radiological diagnostics. It allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the required organ and study its structure in the smallest detail. The study helps to diagnose the disease in the initial stages and begin the treatment process on time.
Immediately before the procedure, the patient is asked to remove all metal products. The patient is then placed on the tomograph table. To ensure that there are no motion artifacts during scanning, a special roller system is used to make it easier for the patient to maintain correct positioning.
The doctor and his assistant are in the next room during a CT scan of the adrenal glands, while specialists carefully monitor the patient’s condition. Then the doctor gives a command, and the patient stops breathing for a short period of time. Using X-rays, multiple layer-by-layer images are taken. A contrast agent allows you to get a clearer picture. It contains iodine, which may trigger an immune response in certain groups of people. Therefore, when a contrast agent is administered, the patient is closely monitored. For most of the population, iodine-containing drugs are harmless and are quickly eliminated from the body. After taking pictures, the data is processed on a computer using special software. Next, the research results are printed out, and all digital data is recorded on a CD.
Contrasting
To obtain clearer scans, stain enhancement is often used, administered intravenously.
Iodine spreads through the bloodstream, accumulating in soft tissue structures and displaying them in more contrast on tomograph images. The procedure differs little from the standard one, only one more step is added in the form of an intravenous injection. At this time, the patient is on the conveyor of the device, native photographs are taken in advance, and then the dye is injected. After a 10-minute wait, layer-by-layer shooting is repeated. Based on the results, a software comparison of non-contrast and enhanced images is carried out, and hidden anomalies are searched for. The injected drug is eliminated naturally within two days after the session - with urine through the kidneys.
In what situations is a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast required?
The study will almost always be performed with contrast, since without it the adrenal glands are not clearly visible on the images, and the information content of the method is conditionally equivalent to ultrasound. Iodine-containing preparations are used as a contrast. The enhancing substance helps to distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one if it is present, as well as to determine the extent of involvement of surrounding tissues in the case of oncology.
Hemorrhage into the tissue of both adrenal glands
Important! Patients are accepted for CT scans with contrast in our clinic only if they have a test - CREATININE! If necessary, you can submit this indicator on site using the express method for an additional fee or bring your own result (good for 10 days).
After a CT scan of the adrenal glands with contrast, you may experience a slight metallic taste in the mouth.
What to do before the procedure itself
Before diagnosis, the patient is placed on a special moving table and then sent to a tomography machine. During the examination, in order to avoid obtaining unclear images, it is forbidden to move. Sometimes (for mental disorders or if necessary) the patient is secured with belts. At the doctor's command, the person must not breathe for several seconds. During a CT scan, a specialist examines the condition of the kidneys and adrenal glands on the monitor and assesses the extent of their damage.
Afterwards, the result can be transferred to disk and decrypted on your doctor’s computer. In any case, the doctor evaluates the image and, taking into account the information received, confirms or refutes the diagnosis.

Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 5054 Date of publication: 08/21/2018
Urologists - search service and appointment with urologists in Moscow
Contraindications
CT scanning of the adrenal glands has a number of contraindications, and the use of a contrast agent expands this list:
- pregnancy;
- the patient’s weight is more than 150 kg or the waist circumference is more than 150 cm;
- children under 5 years of age (up to 12 years of age in contrast studies);
- allergic reactions to iodine preparations (with contrast);
- diabetes mellitus, provided it is treated with metformin;
- severe kidney disease.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to inform the doctor about all the drugs that the patient took the day before or takes constantly, since their interaction with the contrast agent can lead to an unpredictable reaction of the body. If a breastfeeding mother is being examined, then after a CT scan she must pump her breast twice before feeding her baby.
It is important to ensure that the patient does not have contraindications. To exclude a possible allergic reaction to contrast, before making a diagnosis, our specialists carefully study the patient’s medical history. Thus, the development of possible complications after a CT scan of the adrenal glands becomes extremely unlikely.
Adrenal adenoma: diagnosis, symptoms, treatment
WHAT IS ADRENAL ADENOMA
Adrenal cortical adenoma is a common benign tumor that arises from the adrenal cortex, small paired endocrine organs located near the upper edge of the kidneys. It is more common in adults, but can be found in people of any age. These formations can be either hormonally active and secrete increased amounts of hormones, or clinically “silent”. Adenomas are not considered to have a potential for malignancy.
Adrenal cortical adenoma can be diagnosed with a high degree of accuracy: the specificity of the analysis of the results of imaging methods such as CT and MRI varies from 95 to 99%, and the sensitivity exceeds 90%. These impressive numbers are the result of the relatively high prevalence of adrenal adenomas in the general population and extensive radiographic imaging studies, primarily CT and MRI.
Get a CT scan of the adrenal glands in St. Petersburg
CAUSES AND SYMPTOMS
The exact cause that leads to adrenal adrenoma is unknown. However, some scientists and researchers believe that this condition may be caused by a mutation in certain genes. Secondly, in most cases it has been established that adrenal adrenoma is present in people suffering from hereditary genetic disorders. Adrenomas of the adrenal glands can be of two types: functional and non-functional. Some adenomas secrete hormones and are therefore known as functional adenomas. Other adenomas do not secrete hormones and are therefore nonfunctional. Functional adenomas are more dangerous because the hormones produced by these adenomas can cause serious disorders such as Cushing's syndrome (due to the hormonal cortisol), Conn's syndrome (due to the hormone aldosterone), hyperandrogenism (due to the hormonal androgens). There are no specific symptoms associated with adrenal adrenoma, but symptoms associated with any of the above-mentioned conditions can be observed.
ADENOMA OR CANCER METASTASIS?
Among all organs, the adrenal gland is in fourth place in the frequency of metastasis of malignant tumors. The most common tumors that metastasize to the adrenal glands are lung, breast, colon, and pancreatic cancer. Adrenal metastases occur in 25% of patients with identified primary tumor foci. Therefore, radiologists are often faced with the task of determining whether a mass is benign or malignant. Resolving this issue is extremely important and can directly affect the patient’s treatment strategy. For example, additional examination of a patient for operable lung cancer will help identify the presence of an adrenal mass and suggest the possibility of metastatic lesions. In case of ambiguous study results, a second opinion is used to reduce the risk of medical errors. Re-evaluation of CT or MRI results is carried out by a highly qualified specialist from a specialized medical center. The differential diagnosis of adrenal tumors includes a variety of primary, metastatic, benign, and malignant neoplasms, most of which are not discussed in detail here. Instead, the article contains practical information that applies to adrenal adenomas.
RADIATION DIAGNOSTICS OF ADRENAL ADENOMAS
The modalities of choice for evaluating adrenal masses are computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET). Ultrasound has a role in assessing the possible presence of adrenal tumors in infants, but there are no specific ultrasound features to determine whether an adrenal adenoma is benign. When analyzing images, clinicians need to note that on CT and MRI scans, the appearance of intracytoplasmic lipids is different from macroscopic fat, as is the case with myelolipoma.
DECODING CT AND MRI OF THE ADRENAL GLANDS
How should a radiologist proceed to evaluate an incidentally discovered small adrenal mass? Two important questions need to be answered.
First, does the patient have hormonal or biochemical abnormalities that could be caused by an enlarged adrenal gland? If this is the case, then the lesion should be surgically removed, regardless of the imaging features.
Second, does the patient have an identified malignant disease? In the absence of established cancer, the likelihood that a small, well-circumscribed adrenal mass is malignant is almost zero. Description of the nature of the mass is critical for patients with established malignant disease, for whom the diagnosis of adrenal metastases precludes surgical intervention.
Researchers suggest that CT without intravenous contrast enhancement should be the initial study. If the density of the mass is less than 10 Hounsfield units (HU), then a diagnosis of adrenal adenoma can be made. If the adrenal mass is more than 10 HU in density, a CT scan with intravenous contrast should be followed and calculation of its washout; benign lesions typically demonstrate greater than 50% washout. In cases where CT results are questionable, MRI should be performed using programs sensitive to the chemical shift phenomenon. If the results of both methods are inconclusive, a second opinion may be sought. An adrenal biopsy is recommended only if there is a malignant tumor in another organ.
LIMITATIONS OF THE METHODS
For obvious reasons, the availability and cost of CT and MRI should be taken into account. Delaying CT imaging due to a queue at the scanner potentially reduces the effectiveness of the procedure itself, as it can lead to numerous preliminary examinations and also expose the patient to additional exposure to ionizing radiation. MRI examination allows diagnosis without exposing the patient to radiation; however, MRI may not be as accessible as CT and may be more expensive.
RADIOGRAPHY IN ADRENAL ADENOMA
Although plain radiographs may be useful in describing old adrenal hemorrhage or primarily calcified adrenal masses, they do not play a significant role in the diagnosis of adrenal adenoma and should not be performed at this time.
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY FOR ADRENAL ADENOMA
CT, along with MRI, is one of the methods of choice when diagnosing an adrenal tumor. On CT scanning, adrenal cortical adenomas are well-contoured volumetric formations, homogeneous in their density characteristics. Evaluation should be performed using a slice thickness of 5 mm or less to ensure that density measurements are not affected by volume averaging.
What does an adrenal adenoma look like? In the right adrenal gland, a homogeneous, clearly circumscribed ovoid formation with an X-ray density of 7-HU is visible; its detection is characteristic of a benign adenoma.
CT WITHOUT CONTRAST ENHANCEMENT
Results from several studies confirm that a density of 10 HU or less is diagnostic of adrenal adenoma with 79% sensitivity and 96% specificity. At a threshold of 0 HU, the diagnosis can be made with 47% sensitivity and 100% specificity. The decision on how to measure density must be made carefully. The selected area of interest should be as large as possible, but should not include adjacent tissue, especially the fatty tissue surrounding the gland.
CONTRAST ENHANCED CT
The initial contrast enhancement patterns of adrenal adenoma and metastases are largely the same; therefore, simple density measurements are of no value in their differential diagnosis. A delayed density measurement (10 minutes after injection) of 30 HU or less is diagnostic of a benign adenoma, but this is found in only a small percentage of adrenal adenomas.
A calculation called contrast washout can be used to reliably determine whether an adrenal mass is benign or malignant. Washout is calculated as follows:
- Intravenous contrast is administered, and the first phase of the scan is performed after an 80-second delay.
- The next scanning phase is done after a 10-minute delay.
- An area of interest is marked in the tumor. Density is measured on scans taken at 80 seconds and at 10 minutes.
- The washout percentage of the contrast agent is [1 - (density at 10 minutes / density at 80 seconds)] x 100. Density is expressed in Hounsfield units.
In a group of 101 adrenal tumors, washout of more than 50% was specific for cases of benign adrenal adenoma, and washout of less than 50% was specific for metastases. Interestingly, these parameters do not correlate with the proportion of intracytoplasmic fat, and the physiological mechanism leading to this difference is not entirely understood. At a threshold of 50%, using the washout value gives 98% sensitivity and 100% specificity.
In this group, 2 missed tumors turned out to be benign adenomas, which had washout rates of 0% and 40%. Both lesions had density values less than 30 HU on delayed images and were correctly diagnosed as benign adrenal adenomas without using washout criteria. If 2 tumors are excluded from the group, then the accuracy of this method will be 100%.
Larger groups are further needed to confirm these surprising results. It is important to remember that benign masses, such as adrenal hematomas or pseudocysts, do not increase density with intravenous contrast; therefore, they are not suitable for assessing washout at all.
Studies comparing CT histogram analysis and mean CT density analysis for the evaluation of adrenal lesions have shown that histogram analysis has greater sensitivity in diagnosing adenoma. In a study of lipid-poor adenoma on unenhanced CT, Ho et al. found that although both methods had 100% specificity, using a threshold of more than 10% negative pixels gave a sensitivity of 84%, compared with 68% for a mean density threshold of less than 10 HU.
If the CT results are ambiguous or there are doubts about the diagnosis, the study can be sent for review to a specialized center in order to obtain a Second opinion.
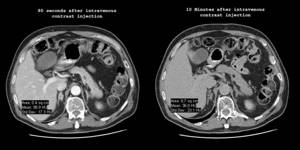
Mass formation of the right adrenal gland. Dynamic and delayed contrast-enhanced CT scan demonstrates a homogeneously enhancing mass in the right adrenal gland. The degree to which contrast decreases over time is called washout, which can be calculated using the following formula: [1 - (density at 10 minutes / density at 80 seconds)] x 100, where densities are expressed in Hounsfield units. In this case, the washout is [1 - (36/99)] x 100 or 64%. Findings from a recent publication in a major journal indicate that any washout greater than 50% is diagnostic of a benign neoplasm.
MRI OF ADRENAL GLANDS IN ADENOMA
On MRI, adrenal adenomas appear as well-demarcated masses characterized by uniform intensity and signal enhancement. For small lesions (<1.5 cm), fine 5 mm scanning steps should be used to ensure that the signal intensity measurement is not affected by volume averaging.
Get an MRI of the adrenal glands in St. Petersburg
The signal intensity characteristics of benign adrenal adenomas and metastases on T1 and T2-weighted images are not specific and largely overlap. However, phase and antiphase scanning (chemical shift imaging) can be used to diagnose adenomas with 81-100% sensitivity and 94-100% specificity.
Out-phase T1WI images of adrenal adenomas show a decrease in signal intensity due to a chemical shift when visualizing lipid-rich lesions. The signal intensity from the spleen can be used as a reference for comparison, but it is important to ensure that the pre-imaging settings are the same in both image sequences. A 20% decrease in signal intensity on out-of-phase images compared to in-phase images is diagnostically significant. The signal intensity from the liver should not be used as a reference because the liver may contain fat.
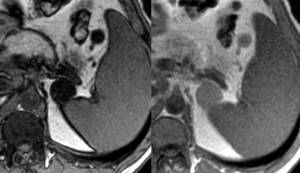
Massive formation of the left adrenal gland - MRI. Images obtained by scanning in phase (right) and antiphase (left). Note that the signal intensity in the mass is less (i.e., the mass appears darker) compared to the intensity of the spleen. As in this case, a decrease in signal intensity of 20% or more is a diagnostic sign of a benign tumor.
Scientific research shows that the degree of signal intensity reduction in chemical shift images is directly proportional to the amount of intracytoplasmic fat. Thus, MRI findings are unlikely to be diagnostic if the adrenal mass has density values greater than 30 HU on unenhanced computed tomography. MRI cannot be used for definitive diagnosis of fat-poor adenomas.
Metastatic adrenal lesions located in or adjacent to an adrenal adenoma have been termed collision tumors. There is a documented case of MRI findings of a benign adrenal adenoma with associated adrenal hemorrhage that mimicked an impingement tumor.
To reliably evaluate MRI results, you can use a second opinion from a radiologist.
ULTRASOUND FOR ADRENAL ADENOMA
Ultrasound may be used to evaluate abdominal masses in infants and children. There are no ultrasound findings specific to adrenal adenoma. Please note that these tumors are rare in children, accounting for less than 1% of all neoplasms in this population. Among all adrenal tumors in children, adenomas are much less common than neuroblastomas, but slightly more common than pheochromocytomas. Typically, functional (hormone-producing) adenomas appear earlier than nonfunctional adenomas, and, compared with benign adenoma, adrenal adenocarcinoma is more often functional.
RADIONUCLIDE RESEARCH
Studies have shown promising capabilities of PET in the differential diagnosis of adenomas and malignant processes in the adrenal glands. Malignant neoplasms tend to increase the uptake of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose relative to benign ones. In a meta-analysis of 1391 adrenal neoplasms, fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) had a sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 91% for differentiating benign from malignant lesions. Because this study is not dependent on the presence of fat, there is potential for its use in imaging both lipid-poor and lipid-rich adenomas. The use of whole body PET in lung cancer is likely to reduce the number of adrenal biopsies performed to evaluate unclear lesions.
Iodomethyl-19-norcholesterol (NP-59) is an experimental radiopharmaceutical that is taken up by the adrenal cortex. A Japanese study found that norcholesterol uptake rate had greater sensitivity compared with CT density value and MRI suppression index (96%, 79%, and 67%, respectively) for functional adrenal adenomas of 2.0 cm or larger.
ANGIOGRAPHY
No angiographic findings specific for adrenal adenoma were obtained.
Endovascular blood sampling from the adrenal veins may be useful in the differential diagnosis of bilateral adrenal hyperplasia and unilateral functional aldosteroma.
TREATMENT OF ADRENAL ADENOMA
In a number of sources you may come across descriptions of various herbal and other “natural” remedies for the treatment of adrenal adenoma. It should be noted that this condition cannot be treated with “natural” methods. Surgical removal of the tumor or adenoma is the only treatment for this condition. Today, the main type of surgery performed to remove a benign adrenal tumor is laparoscopic adrenalectomy. In the case of a laparoscopic adrenalectomy, several tiny incisions are made to perform the procedure, while in the case of a laparotomy, a large incision is made in the abdominal wall. The patient needs more time to recover after abdominal laparotomy. Age does not matter during surgery for adrenal tumors unless there are concomitant severe diseases.
In most cases, treatment of adrenal adenoma is successful. However, it is important that a person consults a doctor in due course. It is also important to control hormonal levels for effective treatment of the disease.
There is currently no developed prevention of the disease.
It should be remembered that adrenal adenoma is a serious health problem that can lead to complications. Therefore, it is wise to diagnose and treat the condition immediately. In any case, remember that for the right treatment, an accurate diagnosis is first necessary.
Materials used in compiling this article:
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/376240-overview#showall
https://www.buzzle.com/articles/adrenal-adenoma-treatment.html
Pavel Popov
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Member of the European Society of Radiologists
What preparation is needed before a CT scan of the adrenal glands?
CT scan of the adrenal glands is a completely safe and virtually painless procedure. Thanks to the latest Siemens Somatom Emotion 16 device, the radiation load on the body will be minimal.
Some preparation for performing a CT scan of the adrenal glands is necessary, but it is not at all difficult. First of all, you need to stop eating 4 hours before the scheduled test. Immediately before performing a CT scan of the adrenal glands, it is necessary to remove all metal objects, since their presence may distort the results of the study. No further special preparation is required for the examination.
It is better to take with you all previous studies in this area and a referral from your attending physician, if available.
Research methodology:
The examination is carried out lying on your back (if necessary, it can be supplemented by a position on your stomach or side), clothing should be free of metal objects. A body scan is performed. A CT scan of the urinary system without contrast agent lasts up to 1 minute. If necessary, the doctor may ask the patient to hold their breath for a few seconds.
Dose load – about 12 mSv (depending on the patient’s body weight)
Volumetric constructions (reconstructions):
After the study is completed, volumetric reconstructions of the urinary system and bone structures are constructed at the study level (images in 3D or 4D, MPR (multiplanar reconstructions)) with color highlighting of stones.
Adrenal CT results
After a CT scan of the adrenal glands, the best medical specialists will decipher the images. All doctors working in our clinic have valid certificates and at least 7 years of experience in this industry.
Computed tomography procedure
Within 2 hours you will receive the results of the examination. The doctor will conduct a consultation, give recommendations on further actions and answer all your questions. All images obtained during a CT scan of the adrenal glands will be sent to you electronically or recorded on a CD. You will also receive a written report from a radiologist.
Advantages over X-ray and MRI:
- CT examination using the Dual Energy method (using two X-ray tubes) allows you to assess the chemical composition of urinary tract stones, which affects the further tactics of treating physicians.
- speed of research
- three-dimensional and four-dimensional modeling of the organs of the urinary system allow a more clear assessment of the organs of the urinary system
- the ability to diagnose radiopaque stones and their density
- CT examinations of patients with metal implants (joints, internal and external fixation devices, etc.), including those with a pacemaker, are performed in full
Disadvantages of the study for diagnosing a specific pathology and localizing pathological changes:
- The study is not carried out on pregnant women
Additional studies if necessary:
- Ultrasound of the retroperitoneum, abdomen and bladder.
- Urethrography, retrograde cystography.
- If clinically indicated, supplement with radiography of the pelvic bones (exclusion of a fracture) or CT scan of the pelvic bones.
Benefits of a CT scan of the adrenal glands
Computed tomography of the adrenal glands helps to quickly identify the cause of the pathology of this paired gland. This examination is performed very quickly (the scanning itself takes less than a minute), and is highly informative. It helps to find the smallest changes in the structure of the organ, make a conclusion on the same day and hand it over to the patient along with the pictures.
Another advantage over another good diagnostic method, MRI, is the low cost of computed tomography. To make an appointment, you can call the phone number on the website or leave a request - our call center employees will call you back within 10-15 minutes.
What does a multispiral study show?
The adrenal glands and kidneys are examined using a high-speed tomograph capable of making hundreds of very thin sections per revolution around the patient's body. The three-dimensional images obtained after reconstruction show all the structures of the internal organs.
MSCT shows:
- developmental anomalies;
- stones in the kidneys;
- post-traumatic injuries;
- occlusive processes in the renal vessels;
- abscesses and hemorrhages;
- kidney prolapse;
- neoplasms (cysts and tumors);
- adrenal hyperplasia and other dangerous conditions.
Compared to computed tomography, MSCT has a lower x-ray load. Scanning is faster and the pictures are of higher quality. This helps to detect even minor changes in the functioning and structure of organs.
Ultrasound:
PROS:
low cost, availability, no radiation exposure. DISADVANTAGES: Significant dependence on the experience of the ultrasound doctor, on the quality of the device, on the size of the patient (the larger the patient, the more difficult it is to obtain an accurate result), the risk of “missing” small tumors of the adrenal glands up to 15 -20 mm, the need for preliminary preparation (gases in the intestines can make it difficult study) and the most important disadvantage is that if a tumor is detected by ultrasound, in conclusion, it will often be recommended to perform an MRI or CT scan. ⠀