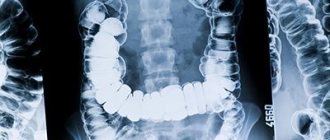
Contrast-enhanced X-rays of the stomach and esophagus can detect diseases such as hiatal hernia, ulcers or cancer. To increase the information content of an X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract, a polypositional study is used in the vertical, horizontal and lateral position of the patient.
For the diagnosis of paraesophageal (near the esophagus) hiatal hernia, the Trendelenburg position is important, since it increases intra-abdominal pressure.
How does radiography differ from fluoroscopy?
Radiography allows you to obtain an analogue (on film) or digital (on a computer screen) image simultaneously. And when performing fluoroscopy, the doctor sees the pathology of the organ being examined at the moment of its functioning, i.e. in real time. Thus, he can not only establish the exact localization of the source of pathology, but also observe all changes in the functioning of the organ. Both radiography and fluoroscopy are methods of radiation diagnostics, but the difference between them is about the same as between static and motion. However, radiography is not a thing of the past, and is successfully used to diagnose various pathologies of internal organs and bone structures, and fluoroscopy is its improved version.
Contraindications
X-rays in a certain dose are relatively safe for humans, and the method itself is quite informative. But in some cases, it is better to refuse x-rays in favor of other diagnostic methods.
X-ray is contraindicated for:
- ongoing bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract
- the presence of pregnancy in a woman, as well as during breastfeeding;
- an existing allergic reaction to the administered contrast;
- serious condition of the patient with decompensation of vital organs and systems.
Radiography is justified if the proposed diagnostic value is greater than the possible harm.
Important: Radiation used in X-rays in high doses is harmful to the body. Modern devices reduce radiation exposure as much as possible, which makes it possible to carry out the procedure 3-4 times a year without negative effects.
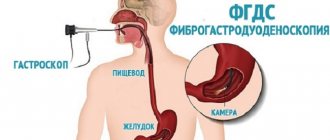
How is the study carried out for gastrointestinal diseases?
The study is multi-positional (the position of the patient's body changes relative to the direction of the X-ray beam) and multi-projection, carried out using contrast (barium sulfate solution is used). This allows you to obtain optimal images of all segments of the digestive tract, stomach, small and large intestines, and duodenum. And also observe pathological processes and the extent of their spread, for example, diagnose cardiac sphincter insufficiency and gastroesophageal reflux, identify tumors.
The study is prescribed when the following symptoms occur:
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing);
- sore throat, hoarseness, chronic cough and other atypical manifestations of gastroenterological pathologies;
- pain in the stomach and abdomen;
- heartburn, belching;
- flatulence;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- stool disorders;
- an admixture of mucus and blood in the stool.
The study is indicated for diagnosing the following conditions:
- functional dyspepsia;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- gastritis;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- hiatal hernia;
- narrowing, protrusion of the wall of the esophagus;
- esophagitis, peptic ulcers and other inflammatory diseases;
- benign and malignant tumors of the stomach, colon and rectum.
Preparation and execution
You must stop eating 8 hours before radiography or fluoroscopy. Immediately before the test, you should not drink liquids or smoke. During the examination, you will be asked to remove all jewelry, glasses, and clothing containing metal.
First, the specialist will take a survey of the gastrointestinal tract, then ask you to drink an aqueous barium solution, which will gradually fill all parts of the digestive tract. In the process of advancing the contrast agent, a series of photographs will be taken polypositionally. The radiologist will then evaluate the result and issue a medical report.
Pregnancy is a contraindication to the study, however, in exceptional cases when it cannot be done without it, it is performed with all the precautions necessary to reduce the effect of radiation on the fetus.
Advantages and disadvantages
The Trendelenburg position is a body position that improves access to internal organs. It was developed and proposed for use by the gynecologist Trendelenburg, who noted that in the normal position of the body, the omentum and internal organs complicate access to the uterus and ovaries.
And when the body tilts, raising the lower part of the body and lowering the upper, the diaphragm rises up, freeing up space in the abdominal cavity.
Nowadays, special operating tables and chairs have been developed that provide the ability for the patient to tilt on them at different angles, which simplifies the operation and shortens its time. Their mechanism makes it possible to easily transfer a patient from one position to another, even by one specialist, without outside help and without the expenditure of effort and time.
| Pros of the position: | Disadvantages of the position: |
|
|
All effects of the Trendelenburg position are short-lived. They usually go away after the physiological situation is restored, and sometimes it takes some time for the indicators to return to normal. But sometimes this position leads to adverse consequences (cerebral edema, acute cerebrovascular accident, hemorrhage).
The Trendelenburg position is the most optimal option for operations in gynecology. But in people with large body weight, it is practically useless.
When the body tilts, the diaphragm with internal organs moves to the upper part of the body, freeing up the space in the pelvis necessary for surgery or research. But with obesity, the omentum is too large and, even with a significant tilt, fills the entire abdominal cavity.
Surgeons use it quite often, since with a minimum investment of time, effort and expensive equipment, it is possible to create optimal conditions for the required operation. But, at the same time, in obese patients, the position does not provide the necessary effect or a sharper angle of inclination is necessary to achieve it.
During general anesthesia, the Trendelenburg position prevents aspiration of vomit, but is accompanied by regurgitation of stomach contents into the esophagus.
Anesthesiologists note that the position makes it difficult to intubate the larynx with an endotracheal tube, since in this position it is difficult to examine the epiglottis and glottis and insert the tube directly into the larynx.
Advantages of polypositional radiography/fluoroscopy of the esophagus and stomach at the Rassvet clinic
At the Rassvet clinic, radiography and fluoroscopy of the esophagus and stomach are performed. Our radiology department is equipped with an X-ray machine with an active worktable and digital fluoroscopy. Modern equipment allows Dawn's radiologists to conduct highly accurate and informative examinations necessary to establish the correct diagnosis and surgical interventions.
We care about our patients, therefore we guarantee high speed and simplicity of the study, high-quality assessment of the result and accurate diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases.
Price
The cost of X-ray examination of the stomach and duodenum in Moscow and St. Petersburg is approximately the same. The price range starts from 1.2 thousand rubles and ends at 4 thousand rubles.
The price depends on the clinic where the patient wants to be examined, on the number of images and the contrast administered. In the Sverdlovsk, Novosibirsk, and Tula regions, prices are slightly cheaper - from 870 rubles.
Help The procedure is included in the list of studies that are carried out under the compulsory medical insurance policy. Therefore, in public medical institutions, if indicated, stomach X-rays can be taken free of charge with a doctor’s referral.
Advantages over other types of diagnostics

Fluoroscopy has a number of advantages over other research methods
There are many advantages to this research method, such as fluoroscopy, and the following stand out among them:
- speed of obtaining results - the doctor sees a picture of what is happening in real time, there is practically no need to confirm what he saw using other methods;
- painless examination that does not require the use of anesthesia - important for elderly patients;
- affordable cost and simplicity - fluoroscopy equipment is installed in every municipal clinic;
- a minimum number of restrictions, excellent tolerability and easy preparation for the study, which is available to every person, regardless of age and financial situation.
Indications for prescribing X-ray of the gastrointestinal tract
Symptoms for which fluoroscopy of the esophagus is performed:
- pain in the stomach;
- pain in the upper part of the esophagus;
- burning sensation, itching and sensation of a foreign body in the sternum;
- difficulty swallowing;
- atypically frequent vomiting and regular nausea;
- frequent regurgitation;
- pain in the sternum while eating;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- signs of the presence of achalasia cardia during the initial examination of the patient (in this case, an x-ray of the gastrointestinal tract and esophagus is prescribed immediately);
- suspicion of esophagitis - inflammatory damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus.
Safety tests for pediatrics
- When providing emergency care to a child with the “pink” type of hyperthermic syndrome, it is contraindicated
a) warming
b) use of craniocerebral hypothermia
c) applying an ice pack to the area of large vessels
d) rubbing the skin with 40-50% ethyl alcohol solution
- The set of emergency medications for stenosing laryngotracheitis includes:
a) thermopsis tincture
b) tincture of valerian
c) prednisolone, hydrocortisone
d) vikasol
- The main antipyretic drug in pediatric practice, used to combat hyperthermic syndrome
a) analgin
b) paracetamol
c) pipolfen
d) baralgin
- The decisive factor in emergency care for true croup is the introduction
a) antibiotic
b) anti-diphtheria serum according to Bezredko
c) diphtheria vaccine
d) toxoid
- To relieve convulsive syndrome in children, it is used
a) diphenhydramine intramuscularly
b) phenobarbital tablets
c) seduxen tablets
d) seduxen IM or IV
- Anaphylactic shock in children most often occurs after injection
a) penicillin
b) insulin
c) iron supplements
d) vitamin B1
- When providing emergency care to a child with anaphylactic shock, he should be given
a) horizontal position on the side, cover with heating pads
b) semi-sitting position, cover with heating pads
c) position with the head end down, apply an ice pack to the head
d) sitting position, apply an ice pack to your head
- The most effective means for relieving anaphylactic shock in a child
a) adrenaline, prednisolone
b) papaverine, dibazole
c) aminophylline, ephedrine
d) lasix, magnesium sulfate
- When providing emergency care to a child with hyperglycemic (diabetic) coma, use
a) insulin
b) penicillin
c) biseptol
d) furagin
- When providing emergency care to a child with hypoglycemic coma, a solution is used
a) sodium chloride
b) hemodesis
c) novocaine
d) glucose
Preparatory stage
We are talking about a diagnostic method that requires certain preparation: cleaning the gastrointestinal tract in order to provide the proper conditions for the examination.
Nutritional considerations on the eve of the event
For patients with an established digestive process, a special diet is recommended for 2-3 days. Persons suffering from chronic constipation and flatulence should follow the principles of dietary nutrition for 3-5 days.
Experts advise eliminating gas-forming products from the subject’s menu:
- legumes;
- fresh vegetables;
- bakery products;
- cakes;
- carbonated drinks;
- pork meat;
- dairy products;
- lamb;
- beef.

It is worth replacing the above items with cereal porridges (in water), chicken broth with meat, fish and seafood, and hard cheeses. Food should be steamed or boiled in water.
Immediately before the x-ray, the patient’s stomach should be empty, since food on the walls of the organs will prevent the contrast mass from covering the mucous membrane, which may look like an oncological formation in the picture.

The patient should not eat food 9-12 hours before the x-ray. A few days before the procedure, the patient should give up alcohol and cigarettes.
Taking medications
Before the examination, it is recommended to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract of waste and toxins. Medications can help partially.
A few days before the procedure, the use of one of the following medications is indicated:
- Activated carbon;
- "Espumizan";
- "Polysorb" and a number of others.
Taking such medications must be stopped 12 hours before the examination.

If the patient is treating an ulcer, suffers from chronic gastritis or other diseases, the course of which requires constant use of drugs, then the use of drugs must also be suspended for 1-2 days. These funds are aimed at changing the functional activity of organs; you cannot count on an objective result when using them.
Cost of the procedure
The cost of conducting the examination of organs in question using barium depends on the location of the diagnosis and the corresponding pricing policy of the clinic. The average price for radiography of the esophagus is 300-1000 rubles.
X-ray of the esophagus is a simple and effective diagnostic procedure used to identify local pathologies and foreign objects in the organ cavity. Clear indications for examination are pain and discomfort in the epigastric region.
The study is preceded by cleansing the patient's gastrointestinal tract of toxins. This is achieved by following a diet for several days before the x-ray. The procedure is carried out using one of three methods and takes no more than 40 minutes. The radiograph results are interpreted by a radiologist within the next 30 minutes. MRI is also an alternative technique.