| CT examination | Old price | Offer of the month | Record |
| CT soft tissue of the neck | 4900 rub. | 3100 rub. |
Record
Multislice computed tomography of the neck is one of the possible ways to study cervical structures using MSCT. CT scan of the soft tissues of the neck is used to identify diseases of the organs: thyroid and parathyroid glands, nasopharynx, larynx, initial parts of the esophagus/trachea, as well as regional lymph nodes and soft tissues.
What will a CT scan of the larynx and neck show?
The patient underwent the prescribed CT scan of the larynx. What can the examination show? What does the specialist see in the photographs?
The method is based on the use of X-rays from sources rotating in a circle around the patient’s body and processing information through computer algorithms. This technology makes it possible to obtain detailed layer-by-layer (a couple of millimeters thick) images of the organ of interest in the transverse plane, which are significantly superior in quality and accuracy to simple x-rays.
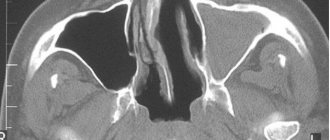
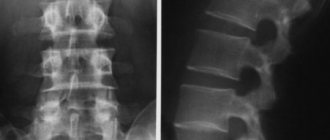
A series (more than 100) CT images examine all the anatomical structures of the neck and larynx, including the cricoid, thyroid, epiglottis, arytenoid, sphenoid and corniculate cartilages, their muscles, ligaments and joints. The mucous membrane of the throat and hypopharynx, the initial part of the trachea and its cartilage are determined. The vocal apparatus, soft tissues and tissue spaces of the neck, lymph nodes, and blood vessels are visualized. The condition of the organs is assessed, pathological signs and foreign bodies are identified. When using angiography, the great vessels are studied.
If the latter are present, the nature of the disorders (inflammatory or tumor), their source, extent, severity, connection of the pathology with surrounding tissues, volume and size of the pathological formation are determined. The information obtained during scanning will allow you to draw a conclusion, assess the prospects for treatment, and choose a method of combating the disease.
During the procedure
- The technologist will explain the essence of the procedure to the patient.
- A neck CT scan takes only a few minutes.
- The x-ray technician can see and hear the patient at any time during the scan.
- A CT scan of the neck requires the patient to be positioned on the scanner table.
- If contrast is needed, the nurse will place a catheter in a vein in the arm and the contrast will be given through an IV.
- When a contrast agent is used, the patient often feels a warm sensation throughout the body and a metallic taste in the mouth within one to two minutes.
- During a neck scan, the patient will be asked to hold their breath for 10-15 seconds to minimize movement.
- It is very important that the patient remains still during the scan to ensure quality scans are obtained.
- Once the scan is complete, the IV will remain in the patient's arm and the technician will move the patient to a rest area. The patient will be asked to remain in the CT scan room for approximately 10 minutes after the scan is completed.
- If the patient experiences itching, sneezing, nasal congestion, sore throat, swelling of the neck or face, then this should be reported to the laboratory assistant immediately.
- The nurse will remove the IV (if used) and provide instructions on what to do after the examination.
Indications and contraindications for CT scan of the neck
Computed tomography of the neck area is used to diagnose a wide variety of pathologies. Depending on the suspected disease, advanced examination techniques may be used. An example of such a procedure is CT angiography of neck vessels, prescribed to detect vascular diseases. If metastatic lesions of regional lymph nodes or malignant diseases of the blood system (lymphomas, lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia) are suspected, a CT scan of the lymph nodes of the neck is performed.
Indications
The following human complaints may serve as a reason to consult a doctor and then be referred for a CT scan of soft tissues and organs of the neck:
- Lymphadenopathy (enlarged cervical lymph nodes);
- The presence of a volumetric formation, determined visually or by touch;
- Pain, swelling, redness in the neck and head;
- Difficulty swallowing, feeling of a lump in the throat, accompanied by lack of air;
- Hoarseness or lack of voice, dry cough lasting more than one month.
List of diseases diagnosed using CT examination:
- Soft tissue tumors and metastases to lymph nodes;
- Benign and malignant neoplasms of the thyroid gland;
- Tumors originating from the parathyroid glands;
- Laryngeal cancer;
- Tumor lesion of the initial part of the esophagus and trachea;
- Salivary gland cancer;
- Malignant diseases of the blood system (lymphomas, lymphogranulomatosis, etc.);
- Cellulitis, neck abscesses.
Contraindications
Contraindications to computed tomography of the soft tissues of the neck may be associated with the peculiarities of the technique or with the administration of a contrast agent.
- It is not recommended to do MSCT for children under 5 years of age without good reason. A referral from a doctor is necessary if the patient is a child;
- Pregnancy;
- The patient’s weight is more than 150 kg, body circumference is more than 150 cm;
- Allergy to iodine and iodine-containing drugs. May manifest as chills, difficulty breathing, itching, decreased blood pressure and other symptoms. If you have an allergy to iodine, be sure to inform our clinic staff;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland accompanied by hyperthyroidism (Graves' disease). A massive intake of iodine into the body can provoke a thyrotoxic crisis - a serious complication of thyrotoxicosis, with a high risk of death. If you have endocrine pathologies, be sure to inform our clinic staff about this;
- Diabetes. Metformin, a drug for the treatment of diabetes, in combination with iodine-containing contrast agents, can provoke a complication of diabetes in the form of ketoacidosis. Metformin should be stopped 48 hours before a CT scan with contrast. You will be able to continue taking your medication after a few days. Be sure to inform our clinic staff if you are taking medications to treat diabetes;
- Breast-feeding. Iodine-containing contrast agents are excreted in the milk of a nursing mother and can cause problems with the thyroid gland in the child, therefore, after a CT scan of the neck and larynx with contrast, it is necessary to express milk twice, and only then resume feeding;
- Chronic or acute renal failure. In patients suffering from chronic diseases of the excretory system accompanied by renal failure, the use of contrast may worsen the condition. The most important principle of medicine is to do no harm. For this reason, our medical center is forced to ask its patients referred for contrast-enhanced computed tomography to provide a recent blood test for creatinine. It shows the condition of the kidneys before the examination, and therefore prevents possible complications. This is a must.
Indications
A neck CT scan may be ordered for the following symptoms:
- Feeling of a lump in the throat
- Swelling
- Hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Sore throat
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Goiter
A CT scan of the neck can detect the following conditions:
- Lesions or infections of the parotid/submandibular glands
- Head and neck diseases
- Various abscesses or formations
- Foreign body in the neck/upper respiratory tract
- Vocal cord tumors/infections
- Cancer
- Trauma, damage
- Tumors
- Infections
- Other diseases of the neck area
- CT scans of the neck are often used to examine masses in the area, as well as identify large lymph nodes. CT scan of the neck is the preferred imaging modality for assessing the soft tissue structures of the neck.
- A neck CT scan takes an average of 15 minutes
Why do you need contrast?
Typically, neck anatomy is studied using CT without contrast. Carrying out a CT scan of the neck with contrast containing iodine can increase the sensitivity and specificity of the method, making the diagnosis even more accurate; contrast is also used in angiography. Contrast agents are administered intravenously directly during the examination. Our medical center uses the non-ionic iodine-containing drug “Ultravist”, with a reduced risk of side effects. We should remember that the cost of the examination depends on the amount of contrast used. The volume, in turn, depends on the patient’s weight. Below is a table containing the required volumes of the drug.
| Weight | Volume |
| <70 kg | 50 ml |
| 70-100 kg | 100 ml |
| >100 kg | 150 ml |
Preparation
- The patient is advised to wear comfortable clothing (no metal) and leave jewelry and valuables at home.
- The patient will be asked to fill out a questionnaire.
- If the examination requires intravenous contrast, the patient must complete a specific consent form.
- The patient should inform the radiologist if there are allergies, pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Tests using intravenous contrast require the results of a renal panel (laboratory tests) performed within the last 3 months before the scan, especially in the following cases:
- The patient is 60 years or older
- The patient has a history of kidney disease
- The patient has a history of diabetes mellitus
- The patient has a history of multiple myeloma
MRI of the neck or CT – what to choose and which is better
Each diagnostic method has its own advantages and disadvantages. MRI, as a more modern technology, may offer a better safety profile and soft tissue contrast. MSCT, in turn, allows you to obtain images in higher resolution at a lower cost and time. In most cases, CT is used to examine the soft tissues of the neck and larynx, as a more accessible and no less accurate diagnostic method. In addition, CT is the method of choice if the bone structures of the neck and base of the skull are involved in the pathological process. Moreover, in most cases, the simultaneous use of both CT and MRI is recommended, which maximizes diagnostic accuracy and minimizes the risk of missing something important.
After the procedure
- If intravenous contrast was used during the scan, the patient is advised to drink at least 6-8 glasses of water over 24 hours to flush the contrast agent out of the body.
- If a patient has diabetes and has received an iodine-based contrast injection, some medications should be stopped for 48 hours.
- After a CT scan of the neck, there are no dietary restrictions.
- The images obtained during the CT scan will be reviewed by a radiologist and the results will be sent to the treating physician, who will discuss the scan results with the patient.
- After the scanning procedure, no restrictions are imposed on the patient. The patient can eat and drive as usual.
What diseases can MRI detect?
An MRI of the cervical spine is performed for diagnostic purposes, that is, as a result, the doctor can confirm or refute a particular diagnosis. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect the following diseases:
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- Spondylosis or spondyloarthrosis;
- Abnormal structure or location of the vertebrae;
- Developmental defects;
- Intervertebral hernia;
- Tumor processes;
- Destruction of the myelin sheath or multiple sclerosis;
- Arachnoiditis and myelitis;
- Damage to the structure of the spinal cord;
- Impaired blood flow in the cervical spine.
Benefits of MRI of the cervical spine
Unlike other research methods, MRI allows you to assess the work and condition of any structure of the human body. Regarding the cervical spine, MRI has the following advantages:
- X-rays and CT scans can only examine bone tissue;
- The use of Doppler allows one to evaluate blood flow in the area being examined;
- Ultrasound is only applicable to soft tissue.
While magnetic resonance imaging is used for any tissue, showing their structure in three-dimensional image mode.
When is an MRI of the cervical spine prescribed?
An MRI scan is prescribed if there is pain in this area, as well as with functional disorders in the brain. In addition, the following reasons are worth noting:
- Suspicion of the presence of blood clots in the vessels;
- Diagnosis of the inflammatory process;
- Examination of the neck area for the presence of tumors and metastases;
- Diagnosis of osteochondrosis;
- Spinal stenosis and other abnormalities.
Make an appointment now!
How to scan
The specialist helps the patient take the correct position on the CT scanner table. Soft straps or tape may be used to help keep the neck in the correct position.
During the scan, the patient will be inside the CT scanner. X-rays will pass through the patient's body as the X-ray tube rotates around him. The device will take pictures from many angles, creating cross-sectional images (slices) of the neck.
The x-ray technician leaves the room and during the scan the patient will be alone in the room, but can always see, hear and talk to him through a special feedback device.
The patient must remain still while the table is moved to the center of the scanner.
If a contrast study is necessary, patients will receive contrast (x-ray dye) during the scan. The contrast makes tissues and blood vessels more visible to the doctor's view in CT scans.
The essence and advantages of the method
Using CT, all structures of the cervical spine are visible: vessels, bones, lymph nodes, spinal canal, cartilage tissue.
Advantages of the method:
- non-invasive;
- painlessness;
- speed of the procedure;
- safety for health (a single dose of radiation is harmless, repeated examinations are prescribed extremely rarely and are performed after a certain period of time).
Computed tomography provides more information about the condition of the organs being examined than classical radiography, therefore it is often used to clarify the diagnosis. MRI examination is more effective when examining soft tissues. If it is necessary to assess the condition of bone structures, doctors usually choose CT.
Interpretation of MRI results of soft tissues of the neck
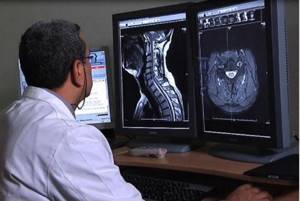
Interpretation of visual patterns obtained from MRI should only be carried out by an experienced functional physician - diagnostician or radiologist. The study of photographic images is carried out visually by a specialist; in parallel, analytics is carried out using a computer program, which is aimed at identifying obvious differences in the structural formations of the “original” from the “norm”. The program shows even minimal deviations from the norm on the computer monitor. After comparing the doctor’s conclusion and computer data, the result is established in the form of a written preliminary diagnosis of the violation.
The results are issued in printed or digital form (at the client’s request); they must be shown to the specialist who referred you for diagnostics. After reviewing the radiologist’s report, the attending doctor develops a plan for subsequent medical actions or redirects the patient to a specialized doctor who is more competent in the identified pathology.
Features of MRI with contrast
The use of contrast can improve the information content several times, and is also used in case of suspicion of the presence of a tumor process, as well as determining their structure, size and boundaries. In addition, the injected contrast allows the state of the vascular system to be assessed with maximum accuracy and the blood flow in the cervical spine to be analyzed.
Due to the fact that tumors or areas of inflammation are characterized by an increased concentration of vascular branches, the contrast agent will accumulate in these areas, which will indicate the exact location of the tumor or inflammation. Currently, gadolinium or drugs based on it are used as a contrast agent. Its use is explained by its safety, low likelihood of developing an allergic reaction, and rapid spread through the vascular network. It is safe to say that contrast-enhanced MRI is much more effective and informative than the standard procedure, but, at the same time, it is a more complex procedure and takes more time to complete.
- MRI of the back muscles of the spine.
- MRI of the lumbar region.
- Spinal examination - MRI or radiography.
Contraindications
Pregnancy is a limitation to CT scanning. Because ionizing radiation has a negative effect on the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Also, CT scans are not performed on children under 6 years of age.
There are also contraindications for administering contrast. They are as follows:
- renal failure;
- disorders of carbohydrate metabolism in the stage of decompensation;
- allergy to contrast;
- pathology of the thyroid gland.
There are restrictions on the patient’s weight: our device is designed for weights up to 120 kg.