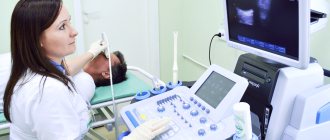
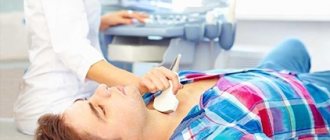
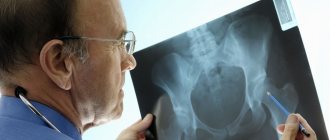
The hip joint is a component of the musculoskeletal system of the human body. The joint is responsible for the activity of the hip (circular rotation/flexion/extension/abduction/adduction) and allows a person to maintain balance. The bone joint is subject to many pathologies - from mechanical damage to cancer or inflammatory processes. To prevent or timely diagnose diseases, ultrasound is used. What do you need to know about the diagnosis, how exactly is it done and is it necessary to undergo an ultrasound as a preventive measure?
Ultrasound of the hip joint in adults
The procedure is mainly prescribed for newborns and young children. Ultrasound of the hip joints
It is performed infrequently in adults, usually as an additional study.
Magnetic resonance imaging
is most often prescribed .
If a person has metal objects in the body (prostheses, fragments, pins), has an insulin pump or a pacemaker, then ultrasound becomes the only alternative.
Contraindications
Ultrasound examination of joints has no serious contraindications and is safe for all categories of patients - adults and children. Sometimes doctors find it difficult to diagnose patients who have scars in the scan area. For bumpy skin, the sensor of the device has poor contact with the surface, so the examination may not be informative. The presence of endoprostheses or metal in the body is not a contraindication to ultrasound. Therefore, it is sometimes used as an alternative for MRI of the hip joints of patients with metal structures in the body.
How is an ultrasound of the hip joints done?
The technique by which ultrasound examination of the hip joint is performed is similar to the technique of ultrasound examination of any other organ through sonography. It is worth noting that no preliminary preparation is required. During the examination, the patient lies on the couch, exposing the pelvic area, and the doctor conducting the diagnosis applies a special gel in the groin area that helps to conduct ultrasound better, and moves a sensor over the skin, through which an image is transmitted to the screen of the device. To display information in detail and accurately, the examination is carried out in different projections: lateral, posterior, anterior, medial. Depending on the projection from which the doctor examines the joint, he asks the patient to take one position or another.
Lateral access
To examine the joint in this projection, the patient is asked to lie on his side. Then the doctor is able to examine the greater trochanter of the femur, thigh muscles, and tibia.
Rear access
Lying on his side, the patient bends his leg and pulls it towards his stomach. This projection provides access to the gluteal muscles, ischial tuberosity, nerves, and tendons of the back of the thigh.
Anterior approach
To obtain an anterior approach, your doctor will tell you to lie on your back and extend your legs. This will make it possible to study the lymph nodes, the wing of the ilium, muscles and ligaments in the groin area, and part of the head of the femur.
Medial approach to the tibia
To examine from this angle, the doctor will ask you to move your leg outwards, first bending it at the knee. In this position, the ligaments, pubic bone, muscles and inner thigh are examined for abnormalities.
Restrictions
The diagnostic capabilities of modern ultrasound machines make it possible to clearly visualize the cartilage and soft tissues (muscles and tendons) surrounding the joint, but examination of the pelvic bones using ultrasound is difficult. The fact is that the ultrasound beam cannot pass through the bone, so damage to bone structures during this diagnosis will be poorly visible, and the patient will be referred for further examination using an X-ray or CT scan.
Initial appointment with an ORTHOPEDIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
What does an ultrasound of the hip joint show in adults?
Despite the fact that sonography images are not as clear as MRI, for some categories of patients this is the only option to make a correct diagnosis and determine the causes of the disease. An ultrasound of the hip joint shows what is currently happening in the joints of adults. There are two groups of diseases that ultrasound can detect: extra-articular and intra-articular. Intra-articular diseases include diseases associated with the pathology of the joints themselves and adjacent tissues:
- arthritis, arthrosis;
- presence of liquid;
- effusions;
- tuberculosis;
- dysplasia;
- necrosis of the head of the tibia.
Non-articular problems include changes in the soft tissues that are located near the joints. These can be hematomas, various tumors, metastases, ruptures and damage to ligaments and tendons, bursitis, and other injuries and damage.
Dislocation
There are two types of hip dislocation: acquired and congenital. Acquired dislocation can be caused by various injuries resulting from road accidents, falls, blows, etc. If a person suffers a dislocation of the hip joint, he is unable to sit or stand.
Dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a congenital dislocation of the hip. Most often, the pathology is detected in children, but it happens that adults are also susceptible to it. This disease arises during intrauterine development from the fact that the child’s bones and cartilage are formed incorrectly. Up to a certain point, the disease may not manifest itself at all, but with a surge in hormones or increased physical activity on the pelvic area (for example, at the end of pregnancy), problems may arise that are manifested by a decrease in joint mobility and severe pain.
Presence of liquid
A pathology such as the presence of fluid in the synovium is called “synovitis.” Fluid accumulates during excessive physical exertion, injuries, enters the joint with blood from other infected organs, and other diseases of the internal organs. The disease is accompanied by severe aching pain, swelling and increased body temperature.
Features of the procedure
Ultrasound diagnostics of the hip joints does not require special preparation. Anyone can undergo the examination, even if there are no indications (pain, stiffness of movement). Ultrasound is absolutely safe, therefore it is actively used in orthopedics, including for preventive examinations, assessing the condition of soft tissue structures after chronic injuries, operations, and in cases of family history.
During ultrasound diagnostics, the patient is on the couch. The doctor applies a special gel to the skin, which enhances the passage of ultrasound. During the ultrasound, the specialist examines both hip joints and the formations adjacent to them. Dense bone tissue reflects ultrasound waves more strongly, so it appears lighter. Soft tissue formations are darker.
In adults, pelvic ultrasound is performed using 4 approaches:
- front;
- rear;
- lateral;
- medial.
The procedure lasts 10-15 minutes. At the end of the study, the diagnostician interprets the ultrasound, determines indicators that relate to normal and pathological conditions, and gives a professional opinion.
Anterior approach
Using an anterior approach (transverse, longitudinal projection) in the groin, the diagnostician examines the contours of the neck and head of the femur, the joint capsule, cartilage, and measures the cervical-capsular space.
In the longitudinal projection, in diseases and injuries, a characteristic narrowing of the joint space and its deformation are revealed. There may be fluid in the cervical-capsular space. In the transverse projection, you can examine the contours of the head of the hip bone, identify signs of bone deformities, dysplasia, erosive surfaces and osteophytes.
Medial and lateral approaches
Using medial and lateral approaches, it is possible to evaluate the soft tissue components of the joint, muscle and tendon, and determine the contours of the greater trochanter. In pathologies, the trochanteric bursae are filled with effusion. If necessary, the diagnostician evaluates the quality of blood flow in the artery that goes around the femoral head.
Rear access
Using a posterior approach, the posterior portion of the hip joint can be viewed. The specialist assesses the condition of the sciatic nerve and muscle tissue. He also examines the tendons of the back of the thigh, identifying characteristic changes that help make an accurate diagnosis and determine further treatment tactics.
To make an echoscopic conclusion, the doctor analyzes the obtained images of the hip joint, measures the angles between the diagnostic coordinates, and compares the obtained values with the established norm. With the help of ultrasound, it is possible to carry out differential diagnostics - to make an accurate diagnosis for diseases and injuries that have similar symptoms: arthrosis deformans, rheumatoid arthritis, osteochondropathy.
Who should not have an ultrasound?
Ultrasound procedure
It is so harmless that it can be done if indicated for both children and pregnant women. The reason for a temporary contraindication to the procedure may be a violation of the integrity of the skin at the examination site: an abrasion, rash, unhealed wound, purulent inflammation, etc.
The only contraindication due to the inability to conduct an informative examination is excess weight. In this case, you will have to look for another method of obtaining information ( MRI
,
radiography
,
computed tomography
).
How does an ultrasound machine work?
Ultrasound is powerful sound waves. The human hearing organs can perceive frequencies from 16 to 20 kHz, so ultrasonic vibrations (from 20 kHz) are beyond our acoustic perception. However, some groups of animals (whales, dolphins, bats and others) communicate using ultrasound. Each wave is characterized by an oscillation period, frequency and length. They all depend on the elasticity/density of the medium through which this wave propagates. Any environment, including the tissues of the human body, prevents the propagation of sound vibrations. This is called acoustic impedance. The speed and density of sound waves depend on the magnitude of acoustic resistance.
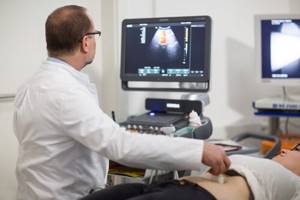
As soon as a sound wave reaches the boundary of two media with different acoustic resistance (for example, soft and hard tissue), one part of it propagates in the new medium and is absorbed by it, and the other is reflected. The intensity of reflection depends on the magnitude of the acoustic impedance. The higher the indicator, the brighter and lighter the signal that the ultrasonic equipment receives. Additionally, the technique records the distance to the separation boundary, the travel time of the wave, the speed of movement, the difference in densities, and so on.
Human skin reflects 99.99% of sound vibrations, making ultrasound examination impossible. That is why the scanned area is lubricated with a special aqueous jelly, which acts as a transition medium.
The reflected sound wave enters an amplifier and special reconstruction systems. They process the information received and transform it into sections of the body part being studied. The picture is painted in black and white, which uses no less than 64 different gradients of the black and white scale. The maximum intensity of sound vibrations is recorded in white, and the minimum - in black.
There are three operating modes of ultrasound - A, B, M. A-mode provides a one-dimensional image, B-mode provides a two-dimensional image of anatomical structures in real time. M-mode is a one-dimensional image with a time coordinate. It is used to diagnose the functionality of the heart.
To make the image as informative and accurate as possible, contrast agents (echo contrast) are used. The contrast agent contains free gas microbubbles (less than 5 microns in diameter). They improve visualization of blood flow or individual organs, increase contrast between tissues and increase diagnostic accuracy.
Indications for ultrasound
This examination is rarely prescribed for adults; magnetic resonance imaging is more often used. But sometimes such an examination is unacceptable - for example, if there are metal fragments in the area being examined. The same applies to the presence of prostheses and pacemakers.
Indications for the study are the patient’s feeling of discomfort and pain, the presence of swelling, and decreased mobility. The procedure is also carried out for diseases that are fraught with the development of pathologies.
Often, ultrasound of the hip joints in Yekaterinburg is performed on adults as part of a comprehensive examination, when previous methods did not provide sufficient information.
In infants, the procedure first of all makes it possible to identify dysplasia (deformations, incorrect development of the joint) at the initial stages.
FAQ
- Do I need to somehow prepare for an ultrasound diagnosis of a joint?
No special preparation is required for ultrasound examination of joints and soft tissues. A contraindication to an ultrasound examination may be the presence of a plaster cast, wound or abrasion.
- How often can an ultrasound be done?
The ultrasound diagnostic method is absolutely harmless; if necessary, it can be done as many times as necessary.
- Is it possible to consult a specialist after an ultrasound?
Yes, you can get advice from a specialized specialist - a traumatologist, orthopedist, physiotherapist or sports doctor. You can also undergo treatment with us, and you can start on the same day you contact us.
- Is it painful to have an ultrasound examination?
No, this is a non-invasive and painless diagnostic method.
- Does ultrasound replace radiography of the joint?
No, ultrasound does not make it possible to assess the nature of the bone fracture, the presence of fragments and displacement. Therefore, in case of injuries and suspected fracture, it is better to first conduct an X-ray diagnosis.
What are the advantages of the method
Since 1989, ultrasound has been used in pediatrics. It is noteworthy that the first studies were aimed at studying the hip joint. The problem of dysplasia was encountered everywhere, which means it required an effective solution and constant monitoring. Ultrasound examination still does not lose popularity and remains the safest, most informative and accurate diagnostic method. The production and use of ultrasound equipment is strictly regulated by the World Health Organization, so parents can be confident in their quality and functionality.
The main advantage of ultrasound is safety. Unlike X-rays or computed tomography, after which radiation doses accumulate in the body, ultrasound does not affect a person in any way. It is this type of diagnosis that is suitable for the most vulnerable categories of patients - newborns, pregnant/lactating women and the elderly.
The second advantage is maximum patient comfort. During the examination, the baby does not need to be fastened with soft belts or forcibly held in your arms for the device to record the state of the body. On the contrary, activity within normal limits will help the doctor better study the hip joint and will not darken the mood of the little patient. Additionally, a specialist can track the dynamics of changes, record inflammatory processes or defects in muscles, ligaments, tendons, joint capsule and cartilage.
Difference between X-ray and ultrasound
X-ray scanning is used in traumatology; during the examination, bone tissue pathologies are identified. During the ultrasound scanning process, the condition of bones, ligaments, cartilage, synovial bursa, and articular surfaces is assessed.
The advantage of ultrasound diagnostics is that it is harmless to the human body. X-rays affect the body with ionizing radiation and are prohibited for pregnant women. The radiation exposure received during the examination is taken into account.