Computer scanning refers to radiographic diagnostic methods. Screening is performed both in the usual mode and according to a contrast protocol, when an enhancing stain is introduced before or during the procedure. Thanks to the drug injected into the bloodstream, even microscopic abnormalities become visible on scans.
If during alternative studies of the abdominal cavity the causes of the disease were not found, a referral is made for a CT scan of the liver with contrast. The price for this examination is higher than for ultrasound and classic x-rays, but compared to MRI, diagnostics will be half the price.
How does a liver CT scan with contrast work?
The basis of hardware screening is the generation of an ionizing field. Biological structures entering the area of effect of the installation are illuminated by X-rays and accumulate them in quantities depending on the density of the tissue. Dense fibers transmit X-ray particles less well, so they are more clearly visible in photographs. Soft tissue organs are less well visualized, so a liver CT scan with contrast is recommended. What the installation shows during the session becomes the basis for making a subsequent diagnosis.
When the coloring agent enters the bloodstream through a syringe or auto-injector, it travels throughout the body, accumulating in areas of high blood supply. A powerful vascular network is formed in areas with foci of inflammation, infection or tumor objects. Since the device captures the “dye,” pathological zones clearly appear in photographic images.
Most diagnostic centers specializing in computer diagnostics have switched to working with spiral and multispiral machines. Unlike outdated step-by-step tomographs, which performed one slice at a time, in new generation tomographs the sensors are located across the entire surface of the equipment in a spiral direction. Multiple scans are performed in the same amount of time, reducing examination time and radiation exposure.
Indications
CT scan of the liver and biliary tract is used to diagnose diseases of the liver and gallbladder, such as:
- Tumors or other mass formations
- Liver injuries
- Bleeding
- Infections
- Abscesses
- Unexplained abdominal pain
- Thrombosis
- Other pathological conditions
- A CT scan of the liver may be performed in cases where other examination methods, such as x-rays, ultrasound and physical examination, do not confirm the diagnosis.
- A CT scan of the liver can also be used to guide precise needle placement during liver biopsy. A liver biopsy involves taking a small amount of tissue and analyzing it in a laboratory.
- CT scan of the liver can also serve as a visual guide to remove fluid from the fluid area and also to clarify the genesis of jaundice, which may be associated with liver pathology.
- A CT scan of the liver may also be ordered by your doctor to diagnose other conditions.
When is a referral for a liver CT scan with contrast prescribed?
A targeted study of an organ covers all its departments, providing maximum information for making a diagnosis. The reasons for computer scanning are the following:
- low information content of other diagnostic methods;
- assessment of the patient's operability in preparation for surgery;
- rapid deterioration in health, change in body weight towards weight loss, suspicion of cancer;
- previous injury to the abdominal area;
- monitoring recovery after surgery or therapeutic treatment.
If an oncological process is suspected, the described diagnostic method is able to detect an anomaly at an early stage of formation, as well as at a precancerous stage.
Second opinion for liver cancer
Despite the fact that CT gives good results, the probability of error remains quite significant. This is due to the fact that the structure of liver cancer tumors is similar to some other formations: hemangioma, focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenoma. And in case of lack of experience, it is quite easy to confuse them. The diagnosis of liver cancer in this case can lead to incorrect subsequent treatment and significant negative consequences for the patient.
Having another doctor interpret the CT scan results can significantly reduce the risk of error. In small towns, and even in fairly large regional centers, it can be difficult to find a second equally or even more qualified specialist. With the help of the National Teleradiological Network (NTRS), this is very easy to do. All you need is a computer or phone with Internet access. With their help, you need to upload CT data to our server, and within a day you will receive an alternative opinion that will either confirm the diagnosis made by the attending physician, or refute it, or point out weaknesses. Consultation will be provided by highly qualified doctors from leading institutes of the country and with extensive experience in diagnosing liver cancer of all types. In other words, you will receive the best advice available in our country and reduce the risk of error to a minimum.
Preparation for CT scan of the liver with contrast
Since the scan is performed in the abdominal cavity, it is necessary to first “calm” and cleanse the gastrointestinal tract. 4-6 days before screening, a diet is prescribed that excludes foods that cause flatulence. It is required to limit the consumption of boiled food, unsweetened drinks without gas and lactose.
If necessary, the attending physician prescribes medications that improve digestion. On the day of the procedure, it is recommended to completely abstain from food; it is advisable to do a preliminary intestinal lavage. If you plan a session in the afternoon, a light breakfast is allowed. 6-8 hours before the procedure you must completely stop eating.
Risks
The patient can ask the radiologist about the amount of radiation he will receive during the CT scan.
It is imperative to inform your doctor about the fact of pregnancy. Radiation exposure in utero to the fetus can lead to the development of birth defects.
If contrast is planned to be used for liver CT, the patient should report allergies to contrast medications or iodine.
It is also necessary to inform the doctor about the presence of kidney pathology, especially if there is renal failure, since contrast can in certain cases significantly worsen kidney function. Patients with kidney disease are at greater risk of kidney damage from exposure to kidney disease contrast.
A patient with diabetes should inform the doctor about taking metformin.
Certain circumstances may reduce the information content of liver CT. These include:
- Metal objects in the abdomen (such as surgical clamps)
- Presence of barium in the gastrointestinal tract after a recent study
- History of a recent study using intravenous contrast or oral contrast
Stages of a liver CT scan with contrast
The first step in preparing for a scan is to find a clinic to perform a liver CT scan with contrast. In St. Petersburg, the price of screening consists not only of the cost of using the device, but also the amount of contrast agent required. The calculation is made based on the patient's weight. The total amount can be found at the registry of the selected medical organization.
After registering for the procedure, it is necessary to prepare a package of documents, including a passport, a referral from a doctor, and the results of other examinations, if they were carried out previously. After registration at the clinic, the staff provides detailed instructions to eliminate the patient’s anxiety during the session.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- Preparing for scanning. The client is placed on a retractable conveyor, secured in a supine position, and a catheter is inserted to gradually inject the contrast enhancer or a full dose is injected with a syringe before the session. It is necessary to lie quietly for some time so that the substance is evenly distributed throughout the body.
- Screening. The conveyor moves inside the tomograph, and the annular part begins to rotate along the table with the patient. A perpendicular photograph of the area under study is performed. The computer receives multiple scans of the organ with a small indentation (from 0.5 cm).
- Interpretation of results. After completing the diagnosis, you need to wait until the radiologists study the obtained photographic images, prepare a description, and print the images on film. At this time, the client can sit in the waiting room or go about his business until the appointed hour.
Classification of computed tomography
Doctors divide clinical equipment depending on the nuances of the task and the design of the device. There are three types:
- Step-by-step research (classical technique) - during the test, the transforming table is moved inside the tunnel with slow movements, sensors record readings and simulate an image. To create a new cut, the couch must be in constant motion. The photo shows the desired section in section.
- Spiral analysis (SCT) - the workplace moves at a constant pace, and the X-ray emitter independently describes a trajectory in a circle of a certain area. The installed detectors will record vibrations that have penetrated into the anomalous area. The survey takes much less time compared to the first method and shows detailed and specific summary information.
- Multislice tomography (MSCT) is a multilayer assessment of the condition, which stands out from others due to the location of the clamps. They are placed in several lines.
What does a liver CT scan with contrast show?
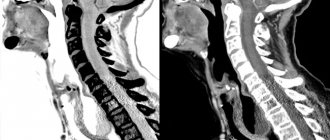
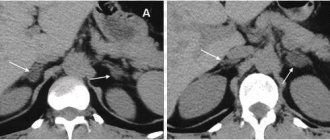
The tomograph scans clearly show all the structures of the organ, as well as adjacent tissues and the vascular network. During the screening process, the following pathologies can be detected:
- compactions in the bile and hepatic ducts;
- venous blockage;
- liver hemangioma on CT scan with contrast;
- parenchyma porosity;
- change in the configuration of the gallbladder.
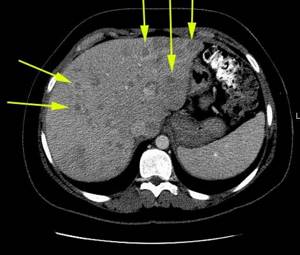
If a tumor is present in the imaging area, the scan reveals not only the exact location, but also the size of the liver hemangioma. CT scan with contrast helps determine the degree of malignancy of the tumor, the presence of metastatic migration, and the possibility of removing the pathological object.
results
The images obtained during a CT scan of the liver are described by a radiologist. The study helps determine the etiology of jaundice, detects hidden bleeding, anomalies in the structure of the organ, and malignant tumors at any stage. The doctor determines in which segment of the organ the changes have occurred and assesses the extent of metastases spreading to other structures.
The conclusion based on the results of the study is stored in the electronic medical record. The patient can see it in his Personal Account on the website.
What to choose: MRI or CT scan of the liver with contrast?
An alternative to computer research is magnetic resonance screening. The diagnostic progress and external technical data differ little when using the indicated hardware methods. However, the operating principle of two different tomographs differs significantly, as well as the indications and preparation time. CT scan of the liver with contrast is an advanced x-ray performed with additional staining. MRI does not use ionizing rays, as it is based on the production of a magnetic field. Once in the zone of a strong magnet, cellular elements begin to resonate and emit signals that are picked up by the tomograph.
MRI diagnostics is not suitable for people with metal implants or fixed electronic devices. Computer examination cannot be carried out frequently, as there is a high risk of receiving a critical dose of radiation exposure. In terms of information content, the methods differ little. At the same time, the duration of MRI is several times longer, while the alternative method allows you to complete the study in a few minutes.
The choice of tomographic method falls on the shoulders of the attending physician, who is called upon not only to make a correct diagnosis, but also not to harm the patient during diagnostic procedures. Anamnesis data, general condition indicators, the presence of direct or conditional contraindications determine the type of scan that will be prescribed. If the subject has metal prostheses, tattoos, electrical stimulators, or has recently undergone fluorography, mammography or other types of radiographic screening, he must inform the doctor about this.
Restrictions
The test is considered a fairly safe medical procedure for identifying abnormalities, but due to the radiation generated by clinical equipment, testing is not suitable for all patients. To prevent the development of radiation sickness, it is recommended to undergo testing only after a specific period of time, which is specified by the attending physician. Additional contraindications include:
- For women carrying a child, toxic rays can have an adverse effect on the fetus.
- Nursing mothers - the additional enhancer has the ability to penetrate into breast milk, which can cause abnormal processes in the development of the newborn.
- For children under 14 years of age - to prevent negative effects on the condition of internal structures, bones and organs.
- For obese people, standard devices in metropolitan medical centers can withstand a load of up to 150 kg.
- Patients suffering from liver and kidney failure, diabetes mellitus.
- People with individual intolerance to active ingredients and iodine.
In such situations, doctors write out referrals for a similar examination - magnetic resonance scanning.
Where is the diagnosis carried out?
In St. Petersburg, CT scans of the liver with contrast are performed in hundreds of medical institutions equipped with the necessary equipment. To quickly find the nearest tomography center, you can use the unified recording service Piter-mrt. The website presents all diagnostic clinics of the northern capital. Medical institutions are distributed according to prices and ratings, provided with general and contact information, and customer reviews.
Compare offers, look for the best price and convenient location. Sign up for procedures through the portal and receive additional discounts on all types of scans. The time booking number is located at the top of the page. In addition, recording service operators will answer any remaining questions. Consultation and call are provided free of charge.
Carrying out the procedure
A standard multislice CT scan of the liver takes about five minutes. When using contrast, the examination time increases to 15-30 minutes.
Before starting the procedure, the patient must remove watches, jewelry, and clothing with metal accessories. Then he lies down on the tomograph table, body position - lying on his back. You should not move during the examination, as this will negatively affect the quality of the images. CT scan of the liver is painless and does not cause any discomfort in the patient.