until September 30
We're giving away RUR 1,000 for all services per visit in September More details All promotions
X-ray of the spine (x-ray of the spine)
is a simple and effective diagnostic method that allows you to identify pathologies, primarily associated with spinal deformity.
The human spine is adapted to upright posture: it connects various parts of the skeletal system, maintains the vertical position of the body and acts as a shock absorber when walking. That is why the spinal column has an S-shaped, curved shape and is not a rigid rod, but a complex structure consisting of elements attached to each other - vertebrae. Between the vertebrae there are intervertebral discs that absorb shocks and shocks.
The spine is divided into sections. Highlight:
- cervical spine, consisting of 7 vertebrae (designated C1-C7);
- thoracic spine: 12 vertebrae (designated D1-D12);
- lumbar: 5 vertebrae (designation L1-L5);
- sacrum or sacrum: 5 fixed vertebrae that form the sacrum;
- coccyx.
Why do you need an x-ray of the spine?
An X-ray machine is a complex system consisting of a beam tube and a table for fixing the patient. The beam tube accelerates particles that pass through the patient's body. The skeletal system and soft tissues have different capacities, as a result, a detailed image of the bones can be seen in the resulting image.
Passing through the body, the rays leave a mark on a special screen: an exact image of the bones remains on special paper (additionally stored as an electronic image). Diagnosing soft tissue injuries using x-rays is problematic, since this type of examination is suitable for studying the skeletal system and damaged joints. Using this diagnostic method, injuries, chronic diseases and inflammatory processes are determined.
Content:
- Why do you need an x-ray of the spine?
- What does an x-ray show?
- Indications for the procedure
- Contraindications to the procedure
- Features of the procedure
- How to prepare for an x-ray?
- Taking an X-ray
- Sample procedure
- Research results
- Photo interpretation
How X-Rays Work
Functional diagnostics using rays discovered by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, the world famous German physicist, is based on the ability of a special apparatus to generate this radiation. The particles that make up the rays, passing through the tissues of the human body, tend to accumulate in formations containing large amounts of calcium, such as bone structures.
In this case, soft tissues remain completely unnoticed, and, therefore, it is not possible to study them. After refraction, the rays are displayed on a monitor screen or on special devices to create X-ray photographs of the parts of the spinal column being studied. Because of its peculiarity, radiography of the spine has become one of the most popular methods for diagnosing multiple diseases of the vertebrae and the parts they form.
What does an x-ray show?
X-rays passing through the human body increase the background radiation in the body. The procedure is performed only in urgent cases, when other research methods are not available for some reason and therefore cannot provide information about the exact picture of the disease. In the case of tuberculosis or cancerous tumors, an image of the spine allows one to see additional tumors and metastases. Modern devices reduce radiation exposure and prevent possible complications due to exposure to X-rays.
An X-ray of the spine is performed in two projections, which allows you to view the tumor or injury in volumetric form, assess its size and degree of damage. X-rays of the spine are taken in the supine position and on the side - the rays are directed at one angle. Using modern techniques, acquired or congenital skeletal deformities, pathologies of the spinal column, and changes in bone structure are determined. X-rays show tumors on the spinal column, changes in joints and bone formations. If the physiological integrity of the skeletal system is compromised, the resulting image will show the extent of the destruction.
What can an ordinary person see in the photo?
Of course, only a specialist can read an X-ray correctly, but anyone can recognize some deviations from the norm. The image shows a black and white image of the organ under study with areas of differing color intensity. The lightest and most pronounced are the bone structures, but the soft tissues are practically invisible - the rays do not linger in them and are not fixed, passing through them.
A fracture can be easily seen in the image – it looks like a crack or displacement of sections of the bone. Scoliosis is defined as a deviation of the spine to the side. Rounded darkening with clear visualization of boundaries often indicates the presence of neoplasms. Cartilage, as a rule, is not determined by x-rays, but a decrease in their thickness can be determined by the distance between the vertebrae, which is characteristic of osteochondrosis.
Indications for the procedure
A two-dimensional image determines the degree of damage to the spine: fractures, cracks, bruises. Compression and compression of the vertebrae are clearly visible in the image obtained after radiography. The method is used to diagnose back curvature, as well as for osteochondrosis and osteoporosis. Developmental anomalies that were not detected after the birth of the child are clearly visible in the photographs.
X-rays are ordered to determine the extent of damage due to injury. Images can refute the diagnosis or confirm the fears of the attending physician. Direct indications for the procedure are frequent headaches (migraines, for which painkillers do not help) and dizziness. In such cases, a study of the cervical spine is prescribed. Choking pain in the chest area is a problem that is also investigated using x-rays. The direct purpose of the procedure is partial or complete numbness of the lower and upper extremities. To confirm an accurate diagnosis, additional research methods are prescribed (soft tissues and healthy internal organs are examined).
What is the technique?
An x-ray is a fairly common radiation diagnostics, which is carried out in an equipped office using special equipment. Gamma rays are passed through the body and are absorbed differently by different parts of the body. Therefore, in the image, denser areas will be light, and soft tissues will be dark. Studying the result obtained, the doctor sees changes in tissues, degenerative processes or deformation, injury, or developmental anomaly. This allows him to determine the appropriate treatment tactics.
The main advantages of the technique are:
- Ease of implementation - the equipment is available in almost every municipal clinic.
- Cheap - in regional departments, if you have compulsory medical insurance, you can make a referral for free; in private clinics the price is approximately 500–800 rubles.
- Efficiency – the speed of the result obtained directly depends on the workload of the specialists, but in general you can get an image within 15–20 minutes after the procedure. Most hospitals will issue it the next day.
- High accuracy of the result - to identify an injury or pathological process in the bone, only this technique is sufficient to make a diagnosis.
- Safety - subject to the rules of execution and frequency of no more than once a year, such a study does not harm the human body or health.
- Painlessness – during the examination the patient does not feel any discomfort, pain or discomfort.
X-rays are taken in a special room, but the decoding is done exclusively by the doctor. It is he who, taking into account the existing symptoms, the results of blood and urine tests, can make a final conclusion and prescribe the correct treatment tactics.
X-rays are used not only to examine the condition of the back, but also to determine the condition of internal organs. The accuracy of the image is achieved due to different degrees of absorption of gamma rays (also called X-rays) by soft and hard tissues. The image represents about 250 shades of black and white, which make it possible to identify anomalies and pathological processes, fractures, and processes on the bones.
Areas that are not examined are protected with special protective screens
Contraindications to the procedure
The main difficulty in carrying out the procedure is the radiation that the person receives. For one spine scan, the patient is exposed to radiation equal to 6 months of natural radiation. Children suffer from radiation exposure twice as severely as adults, so X-rays of a child are performed only in extreme cases (an urgent need to examine the spine). To carry out diagnostics, images are taken of only certain areas, and the rest of the child’s body is covered with a special lead apron.
There are very few categorical contraindications to the procedure - it does not cause adverse reactions or allergies. A contraindication for this examination is pregnancy, when the internal organs of the fetus are forming and developing. Radiation can disrupt this process, so radiography is not prescribed unless absolutely necessary.
Low effectiveness of the procedure for overweight patients: the presence of a large amount of subcutaneous fat and a small amount of muscle tissue leads to deterioration in image clarity. Directly during the scan, the patient must remain motionless, which is difficult for people with nervous tics or tremors of the limbs.
How harmful is the examination?
X-rays are harmful to humans, as they are absorbed by bones and soft tissues and, in large concentrations, can cause the development of blood pathologies and oncology. Therefore, many patients ask the doctor to prescribe an alternative method - MRI, which is unable to create a radiation field. But this is an erroneous approach, since the technique is not able to provide the doctor with enough information about the condition of the bone tissue, since it cannot visualize it.
But are x-rays really that harmful? Old equipment actually produces a higher dose of healing, while modern devices have a reduced rate. At one time, a person receives 1.5 m3V (milisievert), which is equal to the amount of natural radiation that a person receives for six months. And if you consider that the study allows you to show the pathology of the vertebrae and prescribe treatment on time, then its benefit outweighs the possible harm.
For reference! If the local clinic uses only outdated equipment, it is worth spending a little time and finding modern equipment in private institutions. They are safer and the radiation dose is lower, but the effectiveness and accuracy are no different. The price for passing is usually from 500 to 800 rubles.
Features of the procedure
X-raying the entire spine is dangerous, so individual parts of the vertebrae are examined to identify a specific problem. An X-ray of the cervical spine is performed in the presence of severe headaches, pain when turning the neck and head, after injury to the neck or upper spine.
Pain in the chest and upper abdomen when turning the body requires examination of the thoracic spine. It is advisable to conduct two studies: take pictures from above and from the side. Chest pain may indicate serious neurological disease, so the risk of radiation exposure is justified by the study result.
A curvature of the back requires x-rays of the lumbar region. Pathologies associated with the lower part of the spinal column are expressed by unpleasant symptoms: spontaneous severe pain, numbness of the legs and arms. If a tumor is suspected, a two-dimensional radiography of the lumbar region is performed.
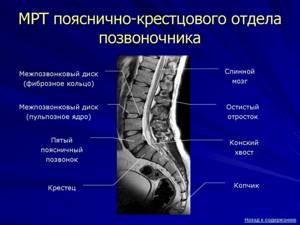
Normal MRI findings of a healthy spine
In order to find out what disorders a patient has, you need to know well what a normal MRI of the spine shows. Each image obtained using magnetic resonance imaging is a virtual slice with a thickness of 1 mm in several planes and modes. Each sequence of images contains up to several tens or even hundreds of images taken in increments of 1 mm.
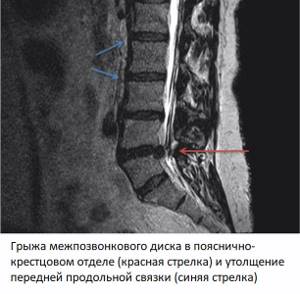
A healthy spine primarily has a normal height of cartilage discs, half the height of the vertebra. There are no signs of degenerative changes, such as protrusions or hernias. The structure of the subchondral areas of the bone bordering the cartilage is preserved. There are no marginal bone growths. There is no compression of the spinal cord membranes. The spinal cord has no space-occupying formations or foreign inclusions, its structure is homogeneous. The spinal cord roots pass freely through the intervertebral foramina, without signs of compression or swelling. The ligaments of the spine can be traced throughout.
How to prepare for an x-ray?
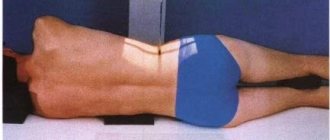
Preparing for the study does not take much time. After receiving an appointment, the patient can undergo the procedure on the same day. When ordering x-rays of the lumbar region, you must:
- cleanse the intestines in advance;
- in emergency cases, cleanse the intestines with an enema;
- the day before the procedure, drink a remedy that reduces gas formation in the intestines.
Gases do not transmit X-rays well, and the image may be blurry. A routine examination requires little preparation: the patient goes on a balanced diet and excludes from the diet foods that contribute to excessive gas formation. Before the procedure, the patient removes all excess clothing and metal objects.
After the patient lies down on the table, his body is fixed in a certain position. In these cases, it is necessary to get rid of any clothing that may distort the resulting image. The examination of the lumbosacral region is sometimes accompanied by additional preparation: before the procedure, the patient does an enema and undergoes a complete cleansing of the intestines.
An X-ray of the cervical spine involves the following preparation: the patient undresses to the waist, removes all jewelry from the neck and ears. In total, the procedure takes no more than 15 minutes, during which the patient lies motionless. Before the procedure, you need to visit the toilet and drink painkillers if the patient cannot lie on the table without moving. X-ray of the thoracic region is carried out without preliminary preparation - the patient takes off clothes and jewelry and takes the desired position.
Preparing for magnetic resonance imaging of the spine
MRI of the spinal column is performed without any special preparation. There is no need to diet or abstain from food and water. However, before the procedure, you should remember that due to powerful magnetic fields, it is strictly forbidden to undergo the examination with metal objects or electronic devices on your body or in your pockets - jewelry, piercings, magnetic cards, cell phones.
The presence of metal zippers, buttons or fasteners on clothing is also undesirable - metal, when exposed to a magnetic field, can heat up, leading to burns. Electronic devices malfunction and may cause a fire. Large metal objects, such as multitools or cigarette cases, are attracted to magnetic fields with enough force to cause serious injury if a person gets in their path.
Taking an X-ray
X-rays are performed only as prescribed by a specialist: in emergency cases or for routine examination. The procedure is carried out quickly and without noticeable discomfort for the patient. Preparatory activities contribute to obtaining clear, informative images. Unpleasant sensations depend on the temperature of the table on which the study is carried out - the body quickly gets used to the cold metal surface. Diagnosis is carried out in a sitting or lying position. The patient undresses and removes jewelry (if the cervical spine is being diagnosed). Metal elements may distort the resulting image.
To protect the body from excessive radiation, a special lead apron is used, which is placed on the patient’s chest. This detail protects the body and minimizes the effect of X-rays on healthy organs and tissues. A shielding plate is placed over the chest and neck if the lower part of the spinal column is being examined.
The procedure with two transverse images takes no more than 20 minutes. During this time, the patient fixes the position of the body twice. A two-dimensional view (front and side) allows you to assess the extent of the problem.
MRI of the spine: how the procedure works
The procedure for performing MRI of the spine is no different from examining other areas of the body. During diagnosis, the patient is located in the center of the cylindrical block, in an installation tunnel 60 cm long and 60 cm in diameter, lying on the table. Before the procedure begins, the patient is asked to put on headphones - MRI is a fairly noisy procedure. The operator transmits his instructions through headphones, and you can also listen to music. The patient is given a button to call an operator, by pressing which he can contact doctors or report his condition.
The duration of scanning one part of the spine is 15 minutes. To diagnose some diseases, the study is performed with contrast. Contrast is an intravenous solution that helps to see inflammation and tumors in the spinal cord or other tissues. The drug itself is injected intravenously into the cubital vein - the volume of contrast depends on the patient’s body weight. When performing an MRI of the spine with contrast, the duration of the procedure increases by another 15 minutes.
After completing the study, the patient must wait 15-30 minutes - during this time, doctors will decipher the images and prepare a conclusion. The doctor will report in detail to the patient or his accompanying person about the diagnostic results, show pictures and tell what was discovered during the procedure. The pictures themselves can be obtained on a free CD or on film/flash drive (in this case you will have to pay a little extra for convenience).
Sample procedure
A functional study is suitable for examining the moving areas of the spine. The body is scanned in a lateral projection with the patient completely motionless. Then the patient begins to bend and unbend with maximum bending. Functional diagnostics are carried out: standing and sitting. This research method helps to study all moving areas of the spine and determine even minimal damage.
Three-dimensional imaging allows you to thoroughly examine every area of the spine. Projections for diagnosis: posterior, extension, flexion. Each position must be recorded. Tests are carried out only if the patient is able to take opposite body positions. Together with the position of the body, the correct tilt of the apparatus tube is selected.
Expert equipment
The study is carried out on the latest generation X-ray system DIGITAL DIAGNOST (PHILIPS, the Netherlands). This is a completely digital x-ray station. Its advantages:
- Maximum data transfer and processing speed
- Obtaining the highest resolution (quality) image possible
- Lowest radiation exposure comparable to a short flight
The results of radiation diagnostics of the Yauza Clinical Hospital are accepted anywhere in the world, which is important for patients planning to undergo certain stages of treatment abroad.
Research results
The image – the diagnostic result consists entirely of dark and light segments of different contrasts. The light areas are bones, and the dark areas are soft tissues. The outline of fat and muscle tissue is almost invisible (they completely transmit x-rays).
The study is carried out in a specialized room equipped with an X-ray machine. Medical staff performs the procedure and develops the images (the electronic version is downloaded to removable media).
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Advantages of spinal radiography at the CELT clinic
Have you been referred for an x-ray of the spine and want to be sure that the images will be of the highest quality? Contact CELT. We have modern X-ray machines made in Germany and Japan, which allow us to carry out the procedure in accordance with international standards.
Our radiologists have over 15 years of experience, which means that they have mastered the methods of obtaining high-quality images and know how to identify any pathology at the initial stage of their development. You can make an appointment with us at any time convenient for you, online or by phone: +7.
Impact of X-ray radiation on the human body
The disadvantage of X-rays of the spine or other organs is that X-ray radiation, when passing through body tissue, interacts with molecules and leads to their damage (ionization), which can negatively affect human health, causing:
- Changes in blood composition that disappear over time;
- Irreversible deviations in blood composition;
- Diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- The appearance of malignant neoplasms;
- Genetic diseases of offspring, etc.
However, it is important to take into account that all organs are not equally susceptible to the negative effects of X-ray radiation. For example, bone marrow and breast tissue are at 4 and 5 times the risk, respectively. Therefore, if we talk about the harmful effects on the spine, the risk of negative manifestations is several times lower than with X-rays or CT scans of other organs.