Computer examination (CT) is a diagnostic technique based on the generation of radiological exposure at a dosage acceptable for humans. Using screening, you can carefully examine the local bones and soft tissues with organs, as well as identify diseases in the initial stages of development. Tomography results allow us to establish the causes of deviations, diagnoses and correct treatment regimens for patients.
In some situations, a CT scan of the brain is necessary for children, for example, with pathologies of the brain, nervous system, or traumatic injuries. In this article, our team will understand how safe computer scanning is for a child, what features the diagnosis has, and for what indications the study is prescribed.
What you need to know about CT scans for children?
Children are prone to illness due to incompletely developed immunity and other factors. Some are asymptomatic, and parents may not even know about it. Due to abnormalities present in infancy and adolescence, the child will subsequently experience consequences throughout his life. Any abnormal abnormalities cannot be ignored. This is especially true for regular headaches and dizziness in children.
Timely diagnosis using a computer scanner will allow you to display the condition of the tissues and examine their anatomical structure in detail. It’s just that CT scans are never performed even on adults. Tomographic screening can only be done with a referral from the attending physician. Additionally, you should check with the diagnostician about the type of examination and device settings. The latter should be optimized for children, where their low weight is taken into account.
How does X-ray radiation affect a child's body?
A special feature of a child’s body is that active growth is ensured by active cell division. Cells that actively and quickly divide are very vulnerable to any damaging factors, including the effects of x-ray radiation. In this regard, the sensitivity of the child’s body to the harmful effects of X-rays is 5 times higher than that of adults.
Research by American scientists has made it possible to calculate the percentage of cases in which X-ray radiation-induced cancer can develop. It can be said right away that the risk of getting sick is low: of the four million children who are exposed to X-rays (that’s how many children in the United States undergo CT scans in a year), only about 5 thousand have a risk of developing cancer or leukemia during their lifetime due to received radiation dose.
These figures could not be taken into account at all when going with your child for examination. But American doctors believe that :
- in almost half of the cases, children are exposed to an unjustified risk, since the CT examination could easily have been replaced by any other examination method safe for the body;
- in a certain percentage of cases, children received a higher dose of radiation than was necessary to obtain images due to the fact that the tomograph settings are the same for children and adults.
At what age can you have a CT scan?
Doctors can prescribe a brain tomography for a child at any age: an infant, an infant, a child over three years old, and so on. Infants usually undergo ultrasound examination - neurosonography. And only when preliminary testing showed a violation to confirm or refute the medical conclusion, a referral for a CT scan is issued.
The peculiarity of a computer scan of the brain in pediatric patients is that anesthesia is used before it so that the baby falls into deep sleep. During the session, the patient is required to remain motionless in order to obtain high-quality and non-blurred images. It is impossible to force children not to move for a long time.
What pathologies can the study detect?
Computer diagnostics are prescribed in the most extreme cases. This study is characterized by high accuracy of visualization of tissues and body systems. Thanks to it, a radiologist can detect and study the features of such pathologies:
- tachycardia;
- stones inside the urinary tract (if pathology is suspected, the child is prescribed a CT scan of the kidneys);
- appendicitis;
- intestinal diseases (acute, chronic);
- defects of lung tissue (congenital);
- dysfunction of the bladder;
- pathologies of the hip joints;
- tumor, ovarian cyst;
- complication due to lung infection;
- abdominal tumors;
- neoplasms inside the lung tissue;
- congenital abdominal defects;
- injuries to blood vessels, lungs;
- inflammation of the bronchi;
- diseases of the respiratory system.
When is a child's brain CT scan prescribed?
It is not possible to undergo a CT examination only at the request of the parents. This requires compelling reasons. Parents can receive a referral for diagnostics from a pediatrician, neurologist, oncologist or neurosurgeon. The main indications for the study are:

- the likelihood of developing a neoplasm - screening visualizes the size of the tumor, its location, what boundaries it has and will show the degree of influence of the pathology on adjacent structures (for a more in-depth analysis, CT uses contrast, since the drug is able to display the nature of the blood supply to the abnormality, which will allow us to understand its nature);
- birth injuries - due to such injuries, the baby lags behind mentally and physically (cannot stand, walk, sit, talk when he is old enough), and in older children, injuries may occur due to falls or blows;
- mental disorders - manifested by epileptic seizures with or without convulsions (such patients have increased convulsive activity, so some factors, even the most harmless ones, can provoke a seizure);
- hydrocephalus, high levels of cranial pressure - pathologies are manifested by headaches, increased sensitivity to light, noise, tactile stimuli, gagging;
- anomalies of the pituitary gland - are distinguished by a sudden and causeless failure of auditory and visual function;
- disorders of the blood supply to the brain - represented by ecephalitis, meningitis and other inflammatory pathologies.
Each situation carries a danger to the baby’s life, so timely detection of the source of poor health is extremely important.
Brain CT perfusion is used to:
- Assessment of the severity of acute stroke (stroke is a disease of the blood vessels in the brain, which is accompanied by either thrombosis (blockage) or rupture of the vessel wall). In both cases, the blood supply to vital structures of the brain is disrupted;
- Determination of indications for the use of thrombolytic therapy in the post-stroke period and in case of infarction of a region of the brain;
- Assessing the degree of vasospasm (sudden narrowing) that may occur as a result of subarachnoid (between the membranes of the brain) hemorrhage;
- Preoperative preparation of patients for endovascular (intravascular) intervention to dissolve a blood clot;
- Diagnosis and evaluation of treatment effectiveness in patients with various tumors.
When should a child not have a CT scan?
A computer scan of the head is not performed if you are allergic to drugs used as an additional enhancer, for example, iodine. Doctors do not prescribe the test for patients with severe renal failure. If the baby has metal structures (implants, staples) in his body, tomography is not performed.
Screening may be refused in the presence of acute mental disorders, which are accompanied by inappropriate behavior towards anesthesia. The restrictions apply to children with severe diabetes, myeloma and certain thyroid diseases. If there are no contraindications, parents will be able to get a referral from a doctor for a CT scan, and use mrt-v-msk.ru to select a clinic and make an appointment.
The main disadvantages and advantages of CT scans for coronavirus
Russian doctors are talking about another side effect of the coronavirus pandemic – CT hysteria, which has begun in society. Almost all patients who have even minor symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection require that they be referred for a computed tomography scan of the lungs, and if they do not receive a referral, they are enrolled in paid centers. On the one hand, the total radiation dose is growing, on the other hand, widespread diagnosis sometimes leads to the identification of diseases that are not at all related to COVID-19.
In conditions where even leading experts admit that every second PCR test gives a false-positive or false-negative result, radiation diagnostics, of course, plays an important role in the diagnosis of pneumonia. And CT scans have become one of the most popular studies in recent months.
In city CT centers, patients sit (and sometimes lie) in queues for several hours; in private appointments, appointments are scheduled several days in advance. People who suspect that the virus has entered their lungs tend to get a CT scan at all costs, even if they have no cough, no shortness of breath, no chest pain, and sometimes no fever.
On the other hand, experts emphasize that identifying lung damage in 6 or 15% will not affect treatment tactics in any way. Igor Tyurin, chief radiology specialist at the Russian Ministry of Health, emphasizes that the course of the disease often does not depend at all on whether the patient’s CT scan reveals pneumonia or not: “This, of course, does not apply to patients with obvious severe respiratory failure. But out of curiosity, a CT scan cannot be done, just as this study cannot be performed for prevention, as today those who have someone sick at home are trying to do it.”
“COVID-19 is not only a violation of the sense of smell, high fever, weakness, cough and difficulty breathing, but also panic. Fear caused by completely objective reasons and greatly amplified by general hysteria. Computed tomography is becoming the gold standard for diagnosis, despite the fact that the changes on it are non-specific and do not change anything in the tactics of action, and radiation is quite real and completely unsafe,” says the famous doctor Pavel Brand.
Cardiologist, red zone doctor, associate professor of the Faculty of Medicine at Sechenov University Anton Rodionov urges people not to do a CT scan on their own: “I can only repeat after my colleagues that it is not the CT scan that is being treated, but the patient. And changes in CT scans do not affect treatment tactics.”
“CT should be performed when a patient has moderate to severe COVID-19,” says Igor Sergienko, a “red zone” doctor, cardiologist, professor at the Federal State Budgetary Institution National Medical Research Center of Cardiology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. – It is impossible not to say that just visiting CT centers is dangerous because you can become infected with the new coronavirus, and mass visits there by healthy people accelerate the spread of the pandemic. It is very important that a CT scan for coronavirus infection does not have specific signs - any other viral pneumonia will look the same. And medical calculations about the percentage of lung damage and frosted glass are a little from the evil one. The main thing is not the percentages, but the patient’s condition. CT data is sometimes needed to develop treatment tactics about the possibility of connecting oxygen and (sometimes) to connect antibiotics (this is one of the points to help a doctor make a diagnosis).”
However, there are other arguments. As Vladimir Sergienko, head of the department of radionuclide diagnostics of the Federal State Budgetary Institution National Medical Research Center of Cardiology of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, told MK, if he receives a positive PCR test for the virus, he would still recommend undergoing a CT examination: “COVID-19 in some cases develops unexpectedly and lightning fast, and a person may die in a day or two. If we talk about the radiation exposure that this study of the lungs entails, it is quite standard, about 8 millisieverts (about the same exposure a person receives when flying by plane over a distance of 2 thousand kilometers - Author). In these situations, we have even stopped talking about any loads. Of course, this does not mean that CT scans can be done ten times a year, no, under no circumstances! But two or three times a year is quite acceptable. As for COVID-19, a CT scan is usually done twice - the second time for control. Twice a month is quite normal, but three is already too much. In any case, this should be decided solely by the doctor who is caring for the patient, and not by the patient himself.”
Meanwhile, other doctors began to talk about the other side of the CT hysteria of Russians: thanks to such mass lung screening, lung cancer was more often detected in the early stages. “It’s too early to talk about any trends, but the number of random finds of early cancer has become much greater,” an oncologist noted in a conversation with an MK columnist.
During the pandemic, doctors began to identify other chest pathologies not related to coronavirus. “A huge number of people go to CT scans for psychotherapy of their COVID anxiety,” says neurologist Oybek Turgunkhuzhaev on his social network. “They invariably say: “These tests of yours are inaccurate. But CT scan – yes. Frosted glass. Now everyone knows about this glass. In most cases, responsible doctors react with irritation to such patients going to CT scans of the lungs without the appropriate direction from the doctor. But sometimes research can yield an interesting find that you didn’t even think about at the reception.”
The doctor spoke about one patient who complained of back pain for several years; he was even prescribed acupuncture and manual therapy, but the pain did not subside. And then the patient independently did a CT scan of the lungs (due to Covid anxiety, just like that). No frosted glass was found on him, which made him calm down. However, a CT scan showed a thoracic aortic aneurysm, which was found by chance.
Such cases, however, are extremely rare. “And, of course, they cannot be the basis for including CT in methods of mass screening of the population,” Igor Sergienko told MK. – We cannot recommend this method to everyone, such as measuring cholesterol levels. CT requires clear indications, and chest pain without other symptoms is not an indication; first, the doctor must differentiate this pain, and then decide what additional studies the patient needs.”
Dr. Pavel Brand, meanwhile, believes that today people do not hear reasonable explanations, so introduce CT into the list of methods performed strictly as prescribed by the doctor: “I’m only afraid that in this situation, people will panic even more and start taking radiology departments by storm. The unknown is more frightening than the coronavirus.”
Link to publication: Moskovsky Komsomolets
Do you need to prepare for a tomography?
Preparatory measures are required. 3 hours before the session, the patient stops feeding and drinking if an examination using anesthesia is planned. Children whose age no longer requires anesthesia can have their last meal a couple of hours before the scan. The child needs to be explained the essence of the procedure, what will happen and be sure to tell him that he will not be sick. CT scanning is safe and nothing bad will happen inside the scanner. You can use a trick and suggest imagining that the board is a spaceship from “Star Wars” or “Guardians of the Galaxy”. Tell your child to lie still during the CT scan.
The patient's breathing during the examination should be complete, so doctors advise dripping his nose with drops with a vasoconstrictor effect before the session. Parents need to provide the radiologist with all the necessary tests:
- conclusion of the attending physician;
- ECG results;
- blood and urine test data.
If you have allergies or the patient is young, visit an allergist or pediatrician so that the diagnostician has more information about the baby’s allergy status. Show the radiologist a certificate of no negative reaction to iodine before starting the procedure. If tomography is performed as an emergency (due to injury), preliminary preparations are skipped. Doctors are limited to only a quick express test for contrast on an individual child’s sensitivity.
Is this dose of radiation acceptable?
Computed tomography is performed using high-precision digital equipment. Modern devices use minimal doses of radiation. The radiation dose is slightly higher than with x-rays, but the scanning results are more accurate and informative.
Modern tomographs are adjusted in accordance with the purposes of the study and the age of the patient. For children, lower doses of X-rays are used than for adults. In some cases, it is impossible to significantly reduce the radiation dose, since this will adversely affect the quality of the images (when studying head structures, etc.)
Given the risk of negative consequences in the long term, pediatricians try to resort to x-ray diagnostic methods as rarely as possible. When prescribing a CT scan, the doctor is guided by specific medical indications. Safer procedures are used whenever possible.
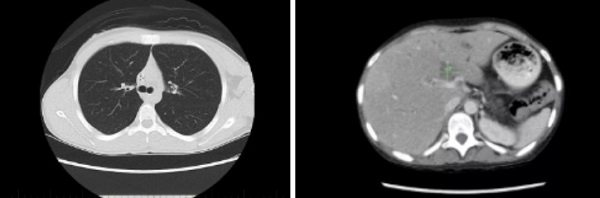
Computer tomograms of the child’s chest and abdominal organs
How is CT performed on children?
For tomographic diagnostics, specialized clinics have equipped rooms with a computer installation. This is quite complex equipment, thought out by engineers down to the smallest detail, and is equipped with fasteners with a high level of sensitivity to the reflection of radiological waves. Information from the detectors is transmitted to a computer, where it is converted into a picture. Installed processing programs allow you to accurately decipher the information received and show an image of the brain in a three-dimensional projection.
Before the examination, children are always weighed so that the anesthesiologist can accurately calculate the amount of substance to put the patient into medicated sleep. An additional amplifier, which contains iodine, is injected into the child’s vein. When screening the head, contrast tomography is considered one of the most reliable and informative procedures.
The patient is placed on the couch on his back. The head is secured with fasteners to prevent uncontrolled movements. The couch is moved inside the tomograph. Doctors and parents leave the research room for the duration of the diagnosis. On average, the examination lasts about 30–90 minutes. CT results are released an hour after the scan or in emergency situations after half an hour.
Contraindications
Before performing a CT scan on a child, it is important to rule out contraindications. This is a child weighing more than 120 kg, and if it is a teenage girl, pregnancy. In addition, the list includes:
- age under 6 years;
- pronounced agitation of the baby, constant anxiety, the presence of claustrophobia;
- trembling of limbs;
- inadequate mental state.
In these cases, the study, if necessary, can be performed under anesthesia. If a contrast study is needed, it is permissible only after 12 years and only after assessing kidney function and creatinine levels. Contrast studies are prohibited for all children with allergies to contrast and iodine, or with kidney problems.
Conclusion
To summarize, we can safely say that CT scans of the brain are performed in children at any age for certain indications.
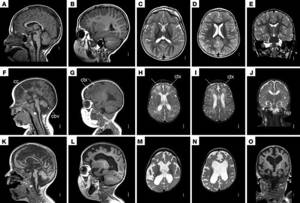
The study does not harm the patient's health if all safety rules are followed. Using this type of tomography, a correct diagnosis can be established in a relatively short time. Some hospitals in Russia today use open CT devices, which are optimal for children. Such tomographs perform similar functions to conventional ones, but do not cause panic and stress.
Using the search service, you can select just such clinics for diagnostics, find out reliable information about them and current prices for tomography. To make an appointment, call the hotline. Our managers provide free consultations and fill out applications for CT scans with a discount of up to 1,000 rubles.
How many times can a child have a tomography?
The permissible frequency of CT scans for adults and children is identical. Without harm to health, you can undergo tomography once every six months. If the clinical situation allows, alternative research methods are used. Computed tomography is used as many times as necessary for timely detection of the disease or objective monitoring of the dynamics of the pathology. Even if the child has already had two CT scans in a year, a third study will be carried out if there are indications and it is not possible to use other diagnostic methods.
CT results
After the procedures, the doctor evaluates the data obtained - this takes some time to give a full conclusion. On average, it takes up to 20 minutes, if the situation is complex – up to 2 hours. Results can be obtained by waiting at the clinic or immediately after readiness by email. Additionally, a doctor may be consulted to clarify further tactics and make a final diagnosis. A complete CT protocol is provided and recorded on disk; if necessary, detailed images of the sections can be taken.
At SM-Clinic, you can perform a CT scan of the head of children on a modern tomograph, which allows you to perform the study quickly, with maximum information content. Registration is carried out by phone or on the clinic’s website - leave a request and wait for a call from the operator.