An inguinal hernia is a pathological condition in which complete or partial protrusion of the abdominal organs occurs through weakened tissue of the inguinal canal.
- Classification
- Causes of inguinal hernia in men
- Diagnosis of the disease
- How to prepare for inguinal hernia removal
- Preparation immediately before surgery
- Indications and contraindications for surgery
- Information about the types of operations to remove hernias and their features
- Laparoscopic surgery
- Treatment without surgery
- Postoperative period
- Possible complications
- Forecast
Classification
Depending on the period of occurrence, congenital and acquired inguinal hernias are distinguished. Congenital hernias occur when the testicle descends from the abdominal cavity into the scrotum. Normally, at the end of this process, fusion of the gonadal layer of the peritoneum should occur, which will cover the inguinal canal. If this does not happen, a defect is formed through which internal organs can lobby. Acquired hernias form throughout life due to thinning or weakening of the muscular aponeurotic apparatus under the influence of provoking factors.
The second classification is based on the anatomical features of the hernia. Here they highlight:
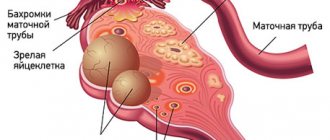
- Indirect hernias - the entrance gate is the internal inguinal ring. In this case, the hernial sac is located next to the spermatic cord.
- Direct hernias - the hernial orifice is the medial fossa located opposite the external inguinal ring. Neither the inguinal canal nor the spermatic cord are affected.
- Combined hernias. This is a complex formation, which includes both oblique and direct hernias, but they do not communicate with each other.
Application of mesh endoprostheses
Inguinal hernia
An inguinal hernia is a protrusion of internal organs outside the abdominal cavity. It appears when the abdominal muscles weaken. More often, this disease occurs in men due to anatomical features that lead to expansion of the inguinal ring. The insides descend, creating a hernial sac, which puts even more pressure on the abdominal cavity from below and a hernia appears.
Up to 10 years of age, a hernia appears due to defective formation of the ligament that closes the inguinal canal. In adulthood, the appearance of an inguinal hernia in men is facilitated by genetics, body structure, excessive or insufficient physical activity, abdominal trauma and a sharp decrease in body weight.
Meshes for the treatment of a hernia are used after surgery to remove it, after which a mesh endoprosthesis of the required size is selected, which replaces weakened muscle tissue, which will subsequently melt into the endoprosthesis as it grows larger.
When selecting a mesh endoprosthesis for the treatment of an inguinal hernia, it is necessary to choose its size correctly. If you use a larger endoprosthesis, the patient will have folds in the groin that will cause discomfort, and if it is smaller, the tissues will separate, the endoprosthesis will not be able to hold the internal organs and the hernia may occur again.
If the hernia is minor and the abdominal muscles are in good condition, the hernia mesh is installed without stitches, after which it naturally grows into the tissue and protects against the recurrence of the hernia.
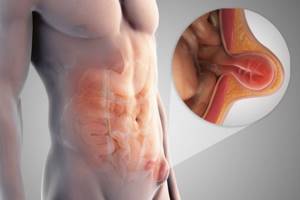
Umbilical hernia
An umbilical hernia is characterized by a condition in which the intestines and omentum extend beyond the anterior abdominal wall at the umbilicus. The protrusion increases when a person is in an upright position and decreases in a horizontal position.
It is most common in newborns with delayed formation of the umbilical ring and in women over 40 years of age after pregnancy.
The formation of an umbilical hernia is promoted by: frequent crying in infancy, constipation, prolonged cough, pregnancy, ascites, physical overexertion, obesity, postoperative scars.
During laparoscopic surgery to treat an umbilical hernia, a three-dimensional endoprosthesis is used, consisting of two flaps connected by a third flap rolled into a tube. Two flaps are fixed on different sides of the abdominal cavity, and the third occupies the hole.
In a conventional operation, conventional non-absorbable mesh endoprostheses are more often used, which are secured with special medical staples.
For small hernias and good condition of the abdominal cavity, absorbable meshes are used to prevent the occurrence of cicatricial fibrosis.
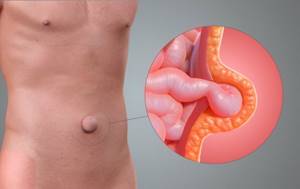
Ventral hernia
This is a hernia that can form at the site of a postoperative scar when the wound heals slowly or the patient violates the established recovery regimen. A hernia can form at the site of a postoperative scar due to an infection, non-compliance with the recovery regimen prescribed by the doctor, diabetes mellitus, heart and kidney failure, obesity, or mistakes made during surgery. The larger the scar, the larger the hernia.
Depending on the location, condition of the patient and the size of the ventral hernia, 2 types of surgery are performed:
- Elimination of a hernia by stretching the patient’s own tissues.
- Closing the hernia using mesh endoprostheses.
When using hernia meshes, laparoscopic or open surgery is performed. A mesh endoprosthesis is installed and sutured. If the operation is done correctly, then the hernia will not form again.
Method with installation of a mesh endoprosthesis:
- allows you to eliminate hernias of any size;
- eliminates the recurrence of a hernia;
- reduces the rehabilitation period.
Other hernias
There are many hernias, which are classified depending on the location of their appearance:
- Femoral;
- Hernia of the white line of the abdomen;
- Spigelian line;
- Douglas Line;
- Lumbar;
- Perineal;
- Ischial;
- Hernia of the xiphoid process.
To treat them, mesh endoprostheses can be installed during surgery. The surgeon selects the size of the endoprosthesis, its thickness and ability to dissolve based on the location of the hernia, its size and the patient’s condition.
With the correct choice of medical mesh for a hernia and its installation, the prognosis for recovery is favorable. The mesh endoprosthesis does not cause discomfort and prevents the secondary appearance of a hernia. After recovery, the patient returns to normal life and lives with a mesh endoprosthesis.
Causes of inguinal hernia in men
In adult men, the formation of inguinal hernias is facilitated by the anatomical features of the inguinal canal - it is wider, shorter and not as well strengthened by muscles and tendons as in women. However, anatomical features alone are not enough; provoking factors are also needed:
- Age-related changes that lead to weakening of muscle tone and connective tissue structures.
- Systemic diseases leading to disruption of muscle function.
- Frequent increase in intra-abdominal pressure. This condition is typical for constipation, chronic cough, obesity, etc.
Prices for hernia meshes
On average, mesh endoprostheses can cost:
- Absorbable - 5,000 - 17,000 rubles;
- Partially absorbable - 3000 - 10,000 rubles;
- Non-absorbable - 1000 - 5000 rubles;
- Three-dimensional - from 10,000 rubles.
You can purchase from us non-absorbable Endoprol mesh endoprostheses in the following options:
- Lungs;
- Classic;
- Heavy;
- Super heavy.
These are our products, which have long been successfully used in many Russian medical institutions.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease is made on the basis of complaints, physical examination data and instrumental research methods.
Complaints
The main complaint with an inguinal hernia is a tumor-like formation in the inguinal fold, which increases with straining and disappears (or at least decreases) in the supine position. Periodically, a dull aching pain of varying degrees of intensity occurs in this place, which can radiate to the sacrum.
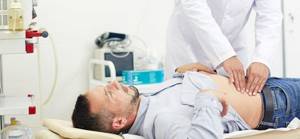
Physical examination
Physical examination is carried out in two positions - horizontal and vertical. At the same time, the size of the formation, its pain, shape, as well as the possibility of reduction are assessed.
Instrumental diagnostics
For differential diagnosis, herniography and ultrasound examination are performed. If necessary, additional research methods are prescribed.
How is implantation carried out?
There are 4 ways to install a mesh in the hernial orifice:
- Onlay . The mesh is sewn onto the aponeurosis of the rectus or external oblique abdominal muscles, directly contacting the subcutaneous fatty tissue.
- Inlay . The mesh is installed on the rectus or external oblique muscle, separated from the subcutaneous fat layer by the same aponeuroses.
- Underlay . The mesh is placed behind the muscle layer, usually separated from the abdominal cavity by the transversus abdominis muscle and transversalis fascia.
- Sublay . The mesh is located in the preperitoneal tissue, separated by the peritoneum from the abdominal organs.
The surgeon individually selects the appropriate implantation method for each patient.
In this case, it is necessary to follow the rules for installing mesh endoprostheses:
- the hernia mesh is installed only within the aponeurotic and muscle tissues;
- multifilament threads cannot be used to secure the endoprosthesis;
- For mixed truncation, a non-absorbable type of mesh endoprosthesis cannot be used.
How to prepare for inguinal hernia removal
To prepare for inguinal hernia repair, it is necessary to undergo a standard examination, which is carried out for all surgical interventions. This includes:
- General clinical tests - blood, urine, biochemistry.
- Blood test for infections - syphilis, HIV, hepatitis B and C.
- Coagulogram is an analysis that reflects the functioning of the blood clotting system.
- Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
- Blood pressure measurement.
- Chest fluorography (not older than one year).
- ECG.
In addition, as part of the preoperative examination, irrigoscopy, examination by a gynecologist, cystoscopy, and computed tomography may be prescribed according to indications. As a rule, such an extensive diagnosis is required for large hernias involving the internal organs of the small pelvis.

Preparation immediately before surgery
In patients with large hernias, displacement of internal organs is often observed. When they are adjusted, the level of intra-abdominal pressure changes, which can affect the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. To prepare the patient for such changes in advance, it is recommended to reduce the hernia (if possible) with the application of a compression bandage for several hours. This will allow it to adapt to changing conditions.
On the eve of the operation, it is necessary to shave the hair in the groin and pubic area. Colon cleansing is also carried out. On the day of surgery, you should not drink or eat.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Indications and contraindications for surgery
The indication for planned removal of inguinal hernias is an uncomplicated disease. When choosing a surgical technique, the patient’s condition, age and medical history are taken into account. Risks must be assessed.
Planned surgery may be denied in the following cases:
- Giant inguinal hernias in patients over 70 years of age with decompensated disorders of the cardiovascular system.
- Liver cirrhosis, complicated by ascites, enlarged spleen, dilated esophageal veins.
- Decompensated diabetes mellitus.
- Inguinal hernias that occurred after palliative operations, for example, in the treatment of malignant neoplasms.
Emergency operations are performed when there is a threat to the patient's life. For example, if a hernia is strangulated or intestinal obstruction occurs as a result of it. There are no contraindications as such in this case, even if the patient’s condition is serious or he is very advanced in age, when the risk of complications is quite high.
Complications
Possible complications when using meshes for surgical treatment of a hernia can arise in cases where the operation was performed incorrectly - an infection got into the wound, the endoprosthesis was poorly installed, the mesh was chosen of the wrong size.
If the operation is performed incorrectly, the following complications may occur:
- possible occurrence of extrusion and adhesions when the mesh is displaced;
- development of infections, suppuration and fistulas when germs or bacteria enter during surgery;
- discomfort when installing a larger mesh than necessary;
- relapse when installing a mesh that is smaller than necessary;
- bleeding due to insufficient wound suturing and improper installation of the endoprosthesis.
If the mesh endoprosthesis was installed correctly, then there should be no complications after the operation.
Despite the fact that the mesh endoprosthesis is hypoallergenic, in very rare cases the patient’s body may not accept the mesh and react to it with inflammatory and allergic reactions. In this case, the patient may experience vomiting and general intoxication of the body.
Information about the types of operations to remove hernias and their features
All currently available methods for removing hernias involve the following steps:
- An incision is made at the site of protrusion of the hernial sac.
- Repositioning of internal organs into the abdominal cavity.
- Plastic surgery of hernial orifices.
The last point is key, since it is what should prevent relapse of the disease. All types of hernia repair are divided into two large groups:
Tension hernioplasty - the hernia gate is sutured with its own tissues. In this case, the inguinal canal narrows to a normal size - 0.6-0.8 cm. The disadvantage of this operation is the high risk of relapses, long-term pain in the postoperative period and rather long rehabilitation. In this regard, in economically developed countries this method is practically not used, with the exception of the treatment of children under 16 years of age.
Tension-free hernioplasty - artificial implants are used to strengthen the hernial orifice (as a rule, they have the form of a mesh made of inert synthetic materials). The implant not only takes on the load that occurs when pressure increases, but also strengthens the tissues, preventing them from stretching and the reverse formation of a hernial protrusion. The use of implants allows you to preserve the anatomy of the inguinal canal and avoid tissue tension. This will ensure an easier recovery period.
Types of mesh for hernia
According to the degree of resorption, medical meshes for hernia treatment are:
- Absorbable . Over a certain period of time they dissolve in the human body. When using these endoprostheses, it is necessary to take into account that the time for complete wound healing and patient recovery is less than the time for resorption of the mesh endoprosthesis. There is a risk of relapse after complex operations.
- Non-absorbable . They do not dissolve in the human body at all. Such an endoprosthesis stays in the human body all his life and does not interfere with it in any way. Over time, they become overgrown with muscle tissue, as they have sufficient porosity. Most commonly used in medicine. The most reliable, with minimal risk of re-development of the hernia. They are produced, for example, by the Volot company.
- Partially absorbable . After muscle tissue builds up, it is partially resorbed in the body.
By form:
- Simple one-dimensional ones . They represent a grid that is in the same plane.
- Complex three-dimensional . A mesh consisting of 3 flaps located in different planes. The structure of the three-dimensional mesh is such that one flap is applied on the inside of the hernial orifice, and the other on the outside, and they are connected by a flap rolled into a cylinder, which fills the hole itself.
By coverage:
- Drug coated . Coated with a substance that prevents infection and promotes rapid wound healing.
- No drug coverage . No drug coverage.
By thickness:
- Lungs . Meshes with a thickness of 0.32-0.44 mm with a monofilament diameter of 0.09±0.01 mm. Intended for reconstructive surgical plastic surgery after removal of hernias of various locations, in cases where the tissues do not experience increased stress and/or their own tissues are in satisfactory condition, as well as for strengthening wounds.
- Classic . Meshes with a thickness of 0.45-0.70 mm with a monofilament diameter of 0.12±0.01 mm. Intended for reconstructive plastic surgery of the anterior abdominal wall after removal of a hernia, for damage to the diaphragm and chest wall, for soft tissue defects, as well as for strengthening traumatic and surgical wounds.
- Heavy . Meshes with a thickness of 0.65-0.99 mm with a monofilament diameter of 0.14±0.02 mm. Used to treat giant ventral hernias. They are used on areas of soft tissue that have greater mobility and are subject to increased stress.
- Superheavy . Meshes with a thickness of 0.65-0.99 mm with a monofilament diameter of 0.16±0.02 mm. Used in the most severe cases when the highest strength is required.

Laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a relatively new, minimally invasive method for removing an inguinal hernia. All manipulations are performed through several small punctures. This minimizes tissue damage. Accordingly, the patient experiences less pain and discomfort in the postoperative period. Working capacity is restored literally within a couple of days. During this intervention, a special technique is used: a laparoscope, which provides an overview of the surgical field, and trocars with miniature instruments, with the help of which the hernial protrusion is eliminated, a mesh implant is installed and fixed.
Advantages and disadvantages of hernia meshes
Advantages of mesh endoprostheses:
- are not rejected by the body;
- low probability of recurrence of a hernia;
- does not interfere with the patient after surgery and does not cause discomfort;
- short rehabilitation period;
- fuses with connective tissue and reliably fixes the hernial orifice.
Disadvantages of mesh endoprostheses:
- slight inflammation, as the body’s reaction to a foreign body, which quickly passes.
Postoperative period
Features of the operating period will vary for each type of hernioplasty. The longest and most painful stage of recovery after removal using the tension method. The period of incapacity for work can reach several weeks. Laparoscopic surgery is the easiest to tolerate because it involves a minimum of tissue intervention. Recovery after it occurs within several days.
Regardless of how the operation is performed, at first it is necessary to refrain from physical activity, especially those that lead to increased pressure in the abdominal cavity. It is also recommended to adjust your diet to avoid constipation. You can return to work and resume physical activity only after consulting a doctor.
Questions patients often ask
Do you need any special preparation for hernia surgery?
If you are planning surgical treatment for a hernia of the anterior abdominal wall, please carefully study the preoperative preparation section.
If you would like to learn in more detail about the methods of pain relief used during the surgical treatment of a hernia of the anterior abdominal wall, please read carefully the information specifically posted on the website.
Is it possible to simultaneously perform an operation to treat a hernia and, for example, for cholelithiasis?
The minimally invasive surgery techniques I use make it possible to perform two and sometimes three operations simultaneously during one anesthesia by a team of several surgeons. The issue of simultaneous operations, including for hernia of the anterior abdominal wall in combination with cholelithiasis, is discussed in more detail in a special section of the site. Simultaneous performance of several surgical interventions will reduce the load on the body, reduce hospitalization time, and speed up the body’s recovery compared to performing several operations with an interval of 5-6 weeks.
Where can I have surgery for a hernia?
I conduct an initial consultation with all patients, including patients with a hernia of the anterior abdominal wall, postoperative hernia, in Moscow at the Swiss University Clinic. Get acquainted in more detail with my main clinical sites in Moscow and Switzerland.
Forecast
If left untreated, an inguinal hernia will inevitably progress and become more complicated. Therefore, it is recommended to undergo surgery, and the earlier the operation is performed (there are no pronounced changes in the soft tissues yet), the greater the chances of a radical cure without subsequent relapses.
However, in any case, to avoid the problem returning, it is recommended to follow simple recommendations:
- Maintain a normal weight.
- Avoid heavy lifting.
- It is also necessary, if possible, to cure diseases that lead to a constant increase in intra-abdominal pressure, for example, chronic cough, impaired urine outflow, constipation, etc.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78