Authors of the article
Olga Aleksandrovna Sargsyan, obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Evgenia Vladimirovna Marchuk, head of the gynecological department of the Central Medical Center on Titov, obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of the highest category
Lyudmila Vladimirovna Buko, obstetrician-gynecologist
Major gynecological operations are one of the methods of treating diseases of the female reproductive system. Such operations eliminate pathologies and preserve to the maximum the possibility of successfully conceiving a child.
Depending on the surgical access, operations in gynecology are divided into several types:
- laparoscopic: entry into the abdominal cavity through three small incisions in the navel and iliac regions
- laparotomy: through a transverse or longitudinal incision
- vaginal: do not require an incision in the anterior abdominal wall
We carry out all these operations at the Center for New Medical Technologies.
Laparoscopic operations
Laparoscopy is a modern method of surgical gynecology. During the operation, manipulators equipped with lighting, micro-cameras and micro-instruments are inserted into the abdominal cavity through several punctures. To prevent the abdominal wall from interfering with the examination and operation, it is lifted and air is forced into the abdominal cavity. Indications for laparoscopy:
- infertility of unknown cause
- ineffectiveness of hormonal therapy for infertility
- operations on the ovaries (cysts and tumors, sclerocystosis)
- suspected adhesive disease, endometriosis
- chronic pelvic pain
- uterine fibroids
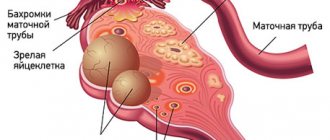
- ectopic pregnancy, tubal rupture, tubal ligation
- ovarian torsion, cysts, ovarian apoplexy
- internal bleeding
- pelvic examination
Like any surgical intervention, laparoscopy has contraindications: severe cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases; coma; state of shock; severe exhaustion of the body; disorders in the blood coagulation system; hernia of the white line of the abdomen, anterior abdominal wall, diaphragm.
Laparoscopic operations can be emergency or planned. In the first case, if we are talking about saving the patient’s life, preparation may be minimal. But during a planned operation, you need to undergo tests (general blood count, biochemistry, coagulation, HIV, syphilis and hepatitis, urine test, blood glucose, blood type, Rh factor) and examinations (gynecological smear, ECG, fluorography, gynecological ultrasound ). If you have chronic diseases, you will also need a therapist’s opinion on the safety of anesthesia.
A few days before laparoscopy, a light diet is prescribed, and in the evening before the operation, the intestines are cleansed.
Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. Depending on the volume or location, 3 or 4 punctures are used. After disinfection of the skin of the anterior abdominal wall, trocars (devices for puncturing the abdominal cavity and inserting instruments) are introduced.
Carbon dioxide is injected into the abdominal cavity, the volume and technique of the operation are determined, the abdominal cavity is carefully examined and manipulations begin. The operation lasts from 15-30 minutes to several hours. At the end of the operation, the abdominal cavity is inspected again, gas is removed, and instruments are removed.
Advantages of laparoscopic surgery
- short hospitalization period
- low trauma, therefore, minimal postoperative pain
- cosmetic effect - puncture marks on the skin leave almost no traces
- quick recovery after surgery
- less risk of postoperative complications and adhesions
Indications for routine laparoscopy in gynecology are:
- removal of ovarian cysts and tumors
- removal of uterine fibroids
- removal of the uterus (hysterectomy)
- restoration of functional patency of the fallopian tubes
- diagnosis and treatment of external endometriosis
- diagnosis and treatment of chronic pelvic pain
- diagnosis and treatment of congenital anomalies of the reproductive system
- diagnosis and treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome (wedge resection and coagulation)
- correction of genital prolapse and prolapse
- diagnosis and treatment of causes of infertility
- preparation for IVF
- sterilization procedure (tubal ligation)
Laparotomy operations
Laparotomy is an invasive surgical operation, dissecting the anterior wall of the abdomen to gain access to the abdominal and pelvic organs. Indications for laparotomy are:
- large benign tumors
- large uterine fibroids
- uterine fibroids, if a woman plans to give birth in the future
- endometriosis
- ovarian rupture accompanied by internal bleeding
- torsion of the uterus
- ectopic pregnancy
- severe inflammation and suppuration of the reproductive system organs
- congenital abnormalities of organ development
Contraindications to laparotomy: blood pathologies that affect coagulation; severe kidney, liver and cardiovascular diseases; coma or shock; severe exhaustion of the body.
Laparotomy is an open surgical procedure and therefore requires adequate preparation. If the operation is planned, then the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination: general and biochemical blood test, urine test, coagulogram, ultrasound of the pelvic organs. Immediately before the operation, the anesthesiologist talks with the patient. 12 hours before laparotomy, food and water intake is excluded, and bowel cleansing is indicated.
If the operation is emergency, the preparation time is reduced to 30 minutes - 2 hours (depending on the pathology). During this time, blood and urine tests are taken from the patient, coagulability is examined, and the blood type and Rh factor are determined.
In gynecology, the following types of laparotomy are mainly found:
- Inferomedian - the incision is made along the line between the navel and the pubic bone.
- Pfannenstiel laparotomy is a key method in operative gynecology. Used for caesarean section and some pathologies of the ovaries and uterus. The incision goes in the transverse direction along the suprapubic skin fold, retreating from the symphysis pubis by 3-4 cm. Such an incision along the lower line of the abdomen turns into a small, hard-to-notice scar.
When performing a Pfannenstiel laparotomy, surgeon, Professor Igor Olegovich Marinkin performs a transverse incision as low as possible, so that after healing the suture is not visible under clothing
Advantages of laparotomy
- technical simplicity of the operation
- no complex tools required
- this type of surgery is convenient for the surgeon
- the method has no restrictions on the volume of intervention
Rehabilitation period after laparoscopy
After the operation, 3-4 incisions of 5 mm in length remain on the skin of the abdomen. Patients begin to get out of bed a few hours after surgery. Discharge from the hospital is carried out the next day, after 24 hours. Pain therapy is minimal. For 1 week – a gentle diet.
You should wait 1 month for physical activity. Abstinence from sexual intercourse is necessary for two to three weeks. Restoration of working capacity, as a rule, occurs on the 10-14th day after surgery.
Laparoscopy is performed under high-quality anesthesia using modern equipment from KARL STORZ by experienced medical doctors
Make an appointment
Vaginal surgeries
Vaginal access is used to perform vaginal hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) and vaginal plastic surgery (treatment of prolapse of the vaginal walls).
In a vaginal hysterectomy, an incision is made at the apex of the vagina. Through this approach, the surgeon crosses the ligaments that hold the uterus and blood vessels, and the uterus is removed through the vagina.
Some operations are performed simultaneously using two approaches. For example, laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy or vaginal plastic surgery with ventrofixation of the uterus.
To treat stress urinary incontinence, which often accompanies genital prolapse, our Center uses an original surgery using a free synthetic loop (TVT-O). The method was developed at the University Hospital (Sweden) and today is the “gold standard” in the surgical treatment of urinary incontinence.
TVT-O operations in our Center are performed by surgeon, obstetrician-gynecologist, professor Igor Olegovich Marinkin
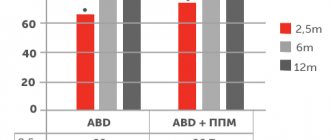
Advantages of the TVT operation: low trauma, ability to control the tension of the loop (prolene tape). The operation is performed under endotracheal anesthesia and lasts about 30 minutes. The confirmed effectiveness of the method is 97%.
Reviews from patients after laser and radiofrequency treatment of varicose veins at Dr. Semenov’s clinic
I am writing with the hope that my review will help other people decide on laser treatment for varicose veins.
I am 74 years old. In addition to varicose veins of the lower extremities, she is burdened with a bunch of other serious ailments. Varicose veins have haunted me for decades. But in Sakhalin we did not have the opportunity to treat varicose veins with a laser. And now no one would undertake a complex operation due to health, or rather, lack thereof. I learned about new technologies at the City Center for Laser Surgery in Moscow, about doctors Letunovsky, ... Read more Lyudmila Maksimovna, 74 years old, Sakhalin
A huge thank you to the surgeon-phlebologist Artem Yuryevich Semenov for the brilliant operation that was performed on me on December 20!!! The operation was large - three trunks were removed at once: RFO of the GSV on both legs + RFO of the SSV on the left leg + miniphlebectomy on the legs. Previously, in medical institutions I had never been told about RFO as an alternative method to classical phlebectomy and laser, especially since the laser was not suitable for me at all due to the large diameter of the trunks of the large saphenous veins (about 20...More
Larisa Filimonova
No matter how good and unique the technology is, for treatment it is better to contact experienced specialists who have been involved in laser treatment of varicose veins for a long time.
Careful approach
We can perform laparoscopy and hysteroscopy simultaneously, under the same anesthesia - this approach significantly reduces the time of examination, recovery and the patient’s expenses for surgery. We also perform simultaneous operations—simultaneously on two or more organs.
After gynecological surgery at the Center for New Medical Technologies, recovery is very fast. You will only have to spend 1-3 days in the hospital, then the patient can be discharged. Depending on the scope of the operation, a sick leave certificate is issued for the period necessary for the patient’s recovery.
Please note that our surgeons are focused on organ-preserving operations.
Dear patients! If you are scheduled for surgery, but you do not agree with its scope, or if other clinics refuse to accept you due to the complexity of the surgical intervention, take advantage of a free consultation with our experienced surgeons. Specialists will conduct an examination, study the results of examinations and give recommendations on surgical intervention, optimal timing and volume of surgery, techniques and recovery period.
- there is no point in arguing!
I believe that a professional phlebologist must be fluent in both methods and offer the patient the most optimal innovative treatment in each specific case. Leading European specialists successfully use both methods, since they both comply with the best government standards adopted in European countries.
Master class performed by Semenov A.Yu. on laser coagulation of veins for phlebologists from Ufa
In some city phlebological centers in Moscow, laser coagulation is still performed using end-mounted light guides on old hemoglobin (wavelength 980 nm) laser units. Most good European clinics have long used high-energy lasers (wavelength 1470 nm) and radial light guides in their work, which are not inferior in their characteristics to the radiofrequency procedure. In the best clinics in Europe and Russia, in addition to radial light guides, they have almost completely switched to a new generation of endovenous lasers with a wavelength of 1940 nm.
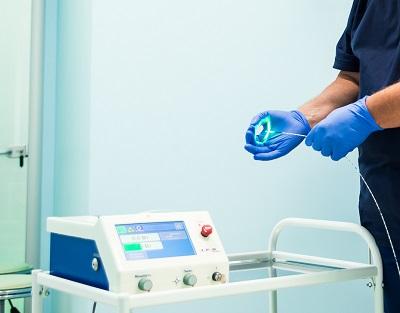
The latest laser generator with a wavelength of 1940 nm in our clinic
The principle of operation of the laser installation is to transmit laser radiation through fiberglass, which has a damaging effect on the vein wall, obliterating the lumen of the vessel, essentially gluing it together. Subsequently, the varicose vein undergoes lysis and, after a few months, completely resolves without a trace.

Radial light guide with wavelength 1940 nm
The operation at the Moscow City Phlebological Center takes place under constant modern ultrasound control. Therefore, complications with innovative procedures are practically nonsense.
Ultrasound control when performing any procedures on veins
TREATMENT OF DIAPHRAGMAL HERNIA
Who needs surgical treatment for hiatal hernia? Elimination of a hiatal hernia is necessary for patients with a paraesophageal (paraesophageal) hernia due to the risk of strangulation, regardless of the severity of existing symptoms, as well as for patients with a sliding hiatal hernia, which has pronounced clinical manifestations in the form of heartburn, regurgitation (regurgitation) of food and requiring constant drug treatment.
Patients with extraesophageal symptoms of a diaphragmatic hernia (recurrences of pneumonia and bronchitis, night cough, chronic laryngitis), Barrett's metaplasia, side effects from therapy with acid-lowering drugs are also candidates for surgical treatment.
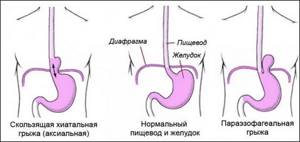
Figure - Main types of hiatal hernia