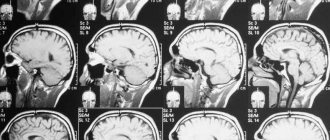
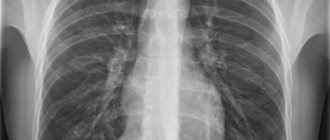
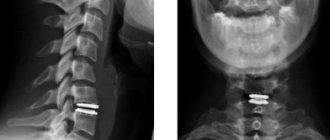
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a radiation research method. It is based on capturing the radiation that is emitted when a magnetic field is applied to hydrogen atoms found in water molecules in the body. This is an informative method that makes it possible to study individual parts of the spine and the soft tissues around it.
After complex computer processing, several layer-by-layer images are obtained; they can be viewed from any angle and even in 3D format. In many cases, X-rays and CT scans do not provide reliable information about the condition of the spinal trunk, so the doctor prescribes an MRI.
What does an MRI of the spine show?
This method allows better examination of soft tissues, because the method is based on the effect of a magnetic field on hydrogen atoms, which are found in the liquid of soft tissues. Examination of low-water bones allows one to determine the location, contours and boundaries.
The spinal column consists of the following sections: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx.
When performing an MRI, you can examine:
- structure of bone joints;
- tissues near the spine;
- discs between vertebrae;
- nerve endings;
- vessels;
- ligaments
How is the procedure tolerated?
- The examination will not cause pain.
- Some people feel nervous inside a CT scanner.
- The contrast may cause the patient to feel warm and red and have a metallic taste in the mouth. Some people feel nauseous or have a headache.
- If a patient is receiving contrast injection into the spinal canal, the patient may feel a burning or pinching sensation when the needle is inserted.
- After a CT scan with contrast, the patient is advised to keep his head up and not bend over or lie flat. This will help prevent headaches and cramps.
Indications for MRI of the spine
It's no secret that timely studies guarantee an accurate diagnosis and complete cure. An MRI is prescribed by the attending physician, this can be a neurologist, surgeon, or traumatologist. The patient himself can also undergo examination and, after receiving the results, consult a doctor.
Patient complaints and indications for MRI:
- Cervical region. For loss of consciousness, dizziness, surges in blood pressure, noise in the ears and head, numbness of the neck and upper limbs, pain when turning the head, frequent migraine attacks.
- Thoracic department. For pain in the shoulder blades and behind the sternum, if you hear a crunching sound in the vertebrae when moving, if the pain intensifies with exercise.
- Lumbar and sacrum. Restricted turns of the body, pain increases with physical activity, numbness in the lower extremities, difficulty urinating, a feeling of fullness in the intestines and rectum, and urinary incontinence.
- Coccyx. Pain and fistulas, the shape changes, when pressing with fingers, swelling is felt.
Once the diagnosis is established, MRI is indicated for the following diseases:
- for acute or chronic osteochondrosis;
- disc herniation or protrusion;
- spondyloarthrosis or spondyloarthritis, deformation of the joints of the vertebrae;
- myelitis, inflammation of the spinal cord;
- multiple sclerosis;
- for cancer, stage identification;
- congenital or acquired vertebral displacements;
- to monitor the dynamics of disease development.
MRI of the back: indications and contraindications
Indications for magnetic resonance imaging of the spine:
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs - spinal osteochondrosis;
- Herniated intervertebral discs (protrusion, Schmorl's hernia);
- Discitis;
- Radiculitis (lumbago, sciatica);
- Inflammation of the intervertebral joints - spondyloarthritis, spondylitis (Bechterew's disease, other rheumatic diseases);
- Neoplasms;
- Spina bifida, spina bifida, spina bifida;
- Spinal tuberculosis, spinal osteomyelitis;
- Cauda equina syndrome;
- Congenital or acquired narrowing of the spinal canal;
- Radicular syndrome;
- Meningitis, arachnoiditis;
- Myelitis;
- Syringomyelia, tabes dorsalis, multiple sclerosis, autoimmune and demyelinating diseases.
Symptoms for which an MRI of the spinal cord and spine is prescribed:
- Backache;
- Back muscle tension;
- Causalgic pain radiating to the shoulder, elbow, neck, torso, perineum, thigh, lower leg, dorsum of the foot, characteristic of pinched spinal cord roots (radicular syndrome);
- Impaired pain and tactile sensitivity of the skin, burning, numbness, crawling sensations;
- Weakness of the muscles of the limbs, partial or complete paralysis;
- Lack of reflexes;
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs (urinary and fecal incontinence);
- Lack of mobility and flexibility of the spine;
- Curvature of the spine, poor posture with neurological symptoms.
Contraindications to MR imaging of the spine
During MRI diagnostics, the unit generates a magnetic field. For this reason, all existing contraindications are associated with the presence of metal foreign bodies in the patient’s body. The procedure is contraindicated if the patient has:
- various implants - hearing aids, speech processors, artificial heart pacemakers, neurostimulators, insulin pumps, vascular ports and defibrillators;
- steel clips, which are often used for clipping (ligation) of the arteries of the brain, steel shavings in the eyes (for patients working in the field of metal processing - mechanics, turners);
- other metal foreign bodies - fragments, shrapnel.
MRI is also contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy, despite the absence of teratogenic and mutagenic effects of magnetic fields. Magnetic resonance imaging without sedation is not performed in children under 5 years of age (in younger children, MRI is performed in a specialized hospital). Excess weight may hinder the examination - MRI equipment is designed to accommodate patients weighing up to 130 kg and a body girth of up to 150 cm. Severe claustrophobia can also make magnetic resonance imaging difficult or impossible due to a strong fear of confined spaces.
Contraindications for MRI examination of the spine
The following contraindications do not make it possible to do an MRI of the spine:
- presence of metal implants, pacemakers;
- the patient is heavy, tomographs are used for patients weighing no more than 150 kg;
- fear of confined spaces, schizophrenia, mental illness;
- if the client is under the influence of drugs and alcohol;
- tattoos using metal in paints;
- kidney disease in the acute phase;
- curvatures in the spine that make it difficult to remain still during the study.
Myelography and its differences from MRI of three parts of the spine
For some problems, conventional tomography is not enough. Then an additional procedure is used - myelography. Its essence is that a contrast agent is injected into the subarachnoid space of the spine, after which a scan is performed.
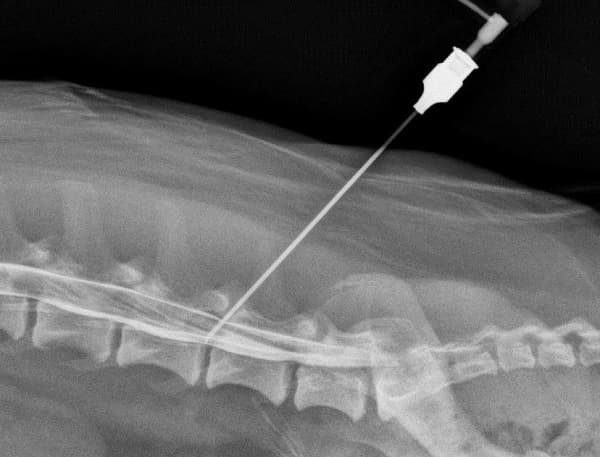
Next, a standard MRI of three parts of the spine is performed, which allows you to see how the contrast agent spreads.
Advantages of myelography:
- the procedure allows you to see the contours and nerve roots (conventional scanning does not provide this information);
- myelography reveals neurological problems, arachnoiditis, damage to the processes of the spinal nerves;
- helps to identify the causes of disturbances in the movement of cerebrospinal fluid;
- makes it possible to see spinal stenosis;
- accurately determines the presence of osteochondrosis, hernia;
- indicates the cause of compression of the spinal canal.
Myelography using Povidone-Iodine or Lipiodol makes it possible to see a three-dimensional image of the spinal cord. The picture displays the smallest parts of tissue structures, thanks to which you can recognize any violation and understand its cause. This procedure is completely harmless to the body. However, the method has contraindications: severe arthritis, previous spinal surgery, disorders in its structure.
Also, myelography followed by MRI of three parts of the spine is contraindicated in case of high body temperature, pregnancy, kidney disease, heart disease in the stage of decompensation, etc. 6 hours before the procedure, you should refuse to eat. If the patient is prescribed a lumbar puncture, a cleansing enema is used before therapy. In some cases, side effects from the administration of a contrast agent are observed. To get rid of its traces in the body, you need to drink as much water as possible.
Simple MRI and tomography with a contrast agent are effective ways to analyze the spinal cord and its pathologies. Scanning is necessary to correctly identify the problem and make a diagnosis. MRI is subsequently used to monitor treatment results. The spine is one of the main structures in the body; the proper functioning of many organs depends on it. If there are abnormalities, it is better to do a tomography as soon as possible in order to identify the pathology as early as possible and begin treatment.
Read material on the topic: Physical therapy for spinal hernia
MRI of the spine with contrast
Sometimes, in order to obtain a more informative result, an MRI with contrast is prescribed . A solution based on the element gadolinium is used for staining. Unlike iodine used in CT scans, it is non-toxic, there are no allergic reactions, this contrast is well tolerated and quickly excreted from the body. A contrast agent is introduced to improve the clarity of the images and the information content of the study.
High-definition images show all structures and foci of the disease. Most often, safe drugs are used for MRI with contrast: Omniscan and Prohans; Magnevist and Dotarem are also used. The drug is administered intravenously, very rarely through a catheter into the spine. Preparations with gadolinium are safe; during the entire period of their use, there are no known cases of harmful effects on the body. Their administration is well tolerated and no side effects are observed.
If side effects occur, they go away on their own after some time and no additional treatment is required. Nausea may occur, intensify to vomiting, a feeling of a rush of blood, and heat may be felt in the lower back. Such side effects usually develop in the patient within an hour after administration, and during this time it is necessary to remain in the facility and leave it after being fully convinced that there is no reaction to the study.
Contraindications to the use of a contrast agent during MRI of the spine are:
- early pregnancy;
- kidney disease;
- allergies in the development stage.
Approximate prices in Russia and Ukraine for CT scan of the spine
Before signing up for an examination, patients are interested in how much they will have to pay for the diagnosis.
In the capital of Russia, the cost of diagnostics for one department is 3200–5300 rubles . depending on the pricing policy of the clinic. In cities of regional significance, you can undergo such an examination for 1700-2000 rubles . An examination with contrast will cost 2 times more.
In Ukraine, you will have to pay 650–1000 UAH . When scanning the entire spine to look for metastases, you will have to pay 1,750 UAH . For a computed tomography with contrast you will have to pay about 1,700 UAH .
Separately, you should find out how much it costs to record the examination results on disk or film. In some clinics, these services are included in the total price, in others, payment is made separately.
Preparing for an MRI
There is no need to prepare in advance for an MRI of the spine. You must come to the procedure with a referral from a doctor, a medical insurance policy, a passport, and the results of previous studies. A contraindication to MRI is the presence in the patient’s body of pacemakers, ear implants, large metal products, or clips in the blood vessels of the brain.
It is necessary to remove all objects containing metals from yourself. Women should wear a bralette. Cell phones, plastic and magnetic cards must also be left at the reception.
The most important
When the first problems with the spine appear, you should seek medical help. Such a highly informative study as magnetic resonance imaging will detect even the slightest pathological changes in the bone structure, as well as the surrounding tissues. To obtain reliable research results, you need to prepare for it and behave correctly during it. Ask your doctor in advance about possible contraindications to avoid negative reactions. MRI has a high advantage over x-rays in identifying spinal pathologies. However, the decision to choose the appropriate procedure is made by a specialist, taking into account the characteristics of the course of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
Carrying out an MRI procedure
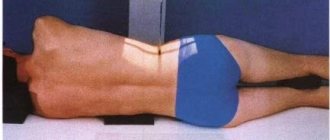
The patient being examined lies on his back on a couch in a separate room where there is a tomograph. He is asked to wear headphones against the noise of the tomograph to protect his hearing in order to prevent panic from being in a closed room.
If the study is done with contrast, then a catheter is installed nearby to supply the drug. During the MRI, the staff is in an adjacent room, but the patient can talk to them.
When conducting the study, you must lie still for 25-30 minutes ; in special cases, when conducting a study of all parts of the spine, the time is increased to an hour.
It takes up to 40-50 minutes to decrypt data, diagnose and write to a magnetic disk. The results are delivered to the client.
How is a lumbar MRI done?
To undergo an MRI of the spine, the patient must prepare: notify the doctor about existing diseases and contraindications for the study, remove jewelry, metal accessories, and piercings before scanning.
The patient takes a horizontal position, face up, on a mobile tomograph table. His body is secured with restraints, and headphones are used to protect him from the noise of the operating apparatus. The table is rolled into the wide annular part of the device, which is a tube in which a magnetic field generator and sensors are attached that read the response of the tissues being studied.
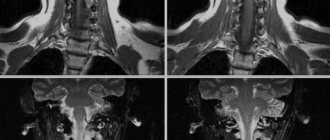
As an MRI of the spine is taken, the tomograph provides scanning of a given area in axial, sagittal and coronal projections. Based on the photos obtained, the doctor, if necessary, reconstructs a 3D model of the lumbosacral region.
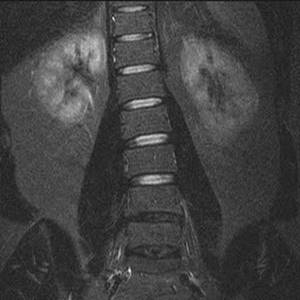
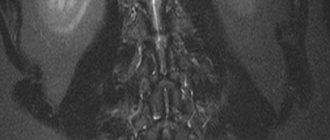
Scoliosis on an MRI image of the lumbar spine in the coronal projection (STIR mode)
To increase the information content, tomography of the spine is done with contrast enhancement. After several native images, the scanning is stopped, and the patient is injected with a gadolinium solution intravenously, using a syringe or catheter. The drug fills the vascular bed in the area of interest, then penetrates the tissue and provides visualization of pathological changes in the structures under study. The scanning continues, recording in the images the features of the diffusion of gadolinium chelates (soluble salts).
During an MRI, the radiologist and technicians are behind a partition and use an intercom to communicate with the patient. The examinee holds a special button in his hand, pressing which serves as a signal for medical personnel. If you feel negative, you can stop scanning.
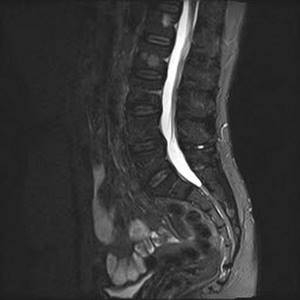
Hemangiomas on MRI of the lumbar spine (STIR)
Decoding the results
Only the radiologist who performed the diagnosis is responsible for describing the obtained MRI images of the back. Complete decryption may take from several hours to two days. The time depends on how busy the clinic is. To reassure the patient, the doctor may, at his discretion, say a few words about the results of the examination.
The results of MRI of the spine are provided in the form of a report with an accurate diagnosis, printed images, and also on electronic media. They can be received personally by the patient or one of the relatives. All information must be provided to the attending physician to determine treatment tactics and adjust the therapy performed.
Computed tomography data analysis algorithm
During the processing of CT scans of the spine, much attention is paid to multiplane reformation, which makes it possible to interpret frontal, sagittal, axial and oblique projections. This is the most complete image of the vertebrae, which can rotate around an axis and allows you to view the condition of the organs from different angles.
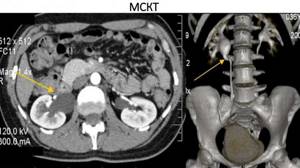
MSCT with multiplanar reformation
Important. If examinations need to be done at the acute stage of pain syndromes, then cushions are placed to reduce them. They are located in different places, the selection criterion is maximum pain reduction when the patient is lying down. In these cases, the angle of inclination of the “Gentry” frame is selected individually, and the lateral projections of the tomogram are taken into account. It is necessary to maintain a parallel position of the scanning plane with the planes of the disks.

Basic design of a computed tomograph
The number of tomography zones is determined by the doctor, taking into account the required number of scanning areas, the complexity of the pathology and the actual condition of the patient. Medical practice most often uses a tomographic slice thickness of 3 mm; 12 programs are sufficient to examine one vertebra. The reconstruction line should pass through the spine with maximum pathology in the axial projection.