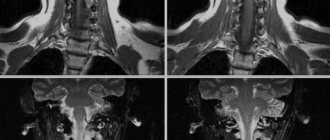
Various pathologies in the spine are always accompanied by discomfort in the chest or back. Sometimes problems in this part of the body are indicated by shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, rapid fatigue, pain in the heart area. To correctly diagnose this condition, X-rays of the thoracic spine are used. This method of radiation examination has been helping doctors and patients for more than 100 years. Despite the development of other diagnostic methods, conventional x-rays have still not lost their popularity. With its help, the condition of the vertebrae is examined, curvatures and pathologies of internal organs are determined.
Why are spinal x-rays prescribed?
X-ray is a radiation-based, non-invasive method of examining any part of the body. His invention is considered a huge step in world medicine: it allows you to see the structure of bones and pathologies of organs without surgical intervention. Advanced examination methods such as computed tomography are based on the same idea. The radiography method is used to diagnose many diseases; in case of bone tissue pathologies, it remains mandatory.
Content:
- Why are spinal x-rays prescribed?
- In what cases is it necessary to undergo examination?
- When X-rays are contraindicated
- Where is the best place to take pictures of the spine?
- How to prepare for the examination
- How does this happen
- How to reduce the harm from examination
Radiation examination of the thoracic spine is prescribed in order to study in detail its condition in the specified area. The reason for prescribing the procedure is the patient’s complaints, injuries, or the doctor’s suspicions of disc displacement, hernia or other problems.
The thoracic region is considered the most protected from the influence of the external environment, but even the slightest malfunction in this system immediately affects well-being.
The thoracic region consists of 12 vertebrae and is the largest area of the spine. The ribs are attached to the vertebrae, thus forming the rib cage.
This part of the body performs several vital functions: it protects internal organs and the spinal cord, provides support and balance, and participates in the movements of the whole body. Curvatures, illnesses or injuries in this area may be subtle but life-threatening.
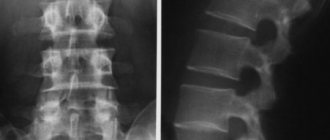
X-ray examination shows cracks, displacements, and neoplasms. If the procedure is performed correctly, the doctor can see the pathology of the heart and respiratory system. Images are needed not only for diagnosis, they also help determine the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment and change it if necessary.
A patient can be assigned up to 7 diagnostic tests per year; the limitation is related to the radiation dose the patient receives. However, such a process does not pose any particular danger, since the dosage is clearly calculated and the person does not suffer in any way.
Effective treatment of symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
You can often cope with the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis at home. Many people “save” themselves, without doctors, with over-the-counter painkillers and painkillers, and by applying heat.
However, self-medication is only a temporary reduction in symptoms, and if done incorrectly, the problem can only worsen. During an exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, gymnastics and massage are contraindicated. On the contrary, at this time you should try to unload the spinal muscles as much as possible.
An experienced neurologist will correctly assess your condition and prescribe treatment that will help. The symptoms described in this article do not always indicate thoracic osteochondrosis; competent differential diagnosis is often necessary.
Visit a specialist. The neurological center of the multidisciplinary international clinic Medica24 employs experienced neurologists, uses modern diagnostic equipment, and treats diseases in accordance with the principles of evidence-based medicine. Clinic administrators are on duty at the telephone around the clock, call at any time.
We will call you back, leave your phone number
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The causes of thoracic osteochondrosis are not fully understood, and in general, this disease raises a large number of questions for many doctors. Some even argue that such a disease does not actually exist, and its manifestations are usually caused by completely different pathologies. By the way, in English-speaking medicine this term refers to completely different diseases.
In what cases is it necessary to undergo examination?
X-rays are prescribed to determine obstructive changes in the lungs; at the same time, they identify pathologies of the vertebrae and heart. This method is also used to diagnose cancer tumors in the chest area.
The examination is carried out as part of routine examinations and as prescribed by the treating doctor. A cardiologist, neurologist, therapist or vertebrologist - a doctor who treats the spine - can direct you to take pictures.
In addition, you can undergo this procedure at will if you have the following symptoms:
- impaired posture and gait, chest deformation;
- constant pain in the back or chest;
- breathing problems: temporary stoppage, difficulty in inhaling, pain, feeling of lack of air, etc.;
- frequent swelling of the legs;
- bleeding during coughing - hemoptysis;
- fast fatiguability;
- prolonged fever for no apparent reason.
In case of such problems, you need to contact a general practitioner, who will prescribe an examination and refer you to another specialized specialist, for example a cardiologist, if the complications are caused by malfunctions of the heart. To determine the exact cause of pain or other symptoms, a series of X-rays are necessarily taken to evaluate the patient’s condition.
Indications for X-rays of the thoracic spine:
- curvature of the spine;
- injuries in the chest area, fractures and dislocations of the ribs, collarbones, displacement of the vertebrae;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system: increased heart size, aortic aneurysm, cardiomegaly, congenital defects;
- fluid between the lungs and the outer wall of the sternum;
- all types of kyphosis - acquired or congenital deformation of the spinal column, in which part of the vertebrae protrudes forward. Expressed in stooping, sometimes hunchbackedness;
- calcification of the aorta or heart valve;
- accumulation of air in the pleural cavity, lungs and other tissues.
Images of the internal structure of the chest are also needed to monitor the operation of the catheter, pacemaker, and defibrillator. In the images, the doctor can see other diseases, such as tuberculosis, dysplasia, pneumonia, pleurisy, and so on.
For examining soft tissues, a conventional X-ray is of little information and is inferior to a computed tomography scan, therefore, as a rule, after obtaining images, the doctor may refer you to a CT scan to confirm or refute suspicions.
Radiation diagnostics can show changes in the lymphatic system, which also signals a serious problem in the body. In this case, lymphangiography is considered more informative.
When X-rays are contraindicated
Because the imaging process relies on radiation exposure, not every patient can undergo this procedure. Although the dose of X-ray radiation is small and does not cause damage when used correctly, such a study is carried out only when there are no contraindications.
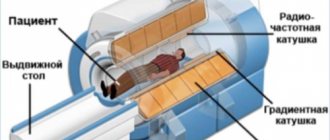
During pregnancy, X-rays of the thoracic spine are not taken. Radiation exposure can cause irreparable damage to the development of the fetus. This procedure is avoided even in later stages, replacing it with alternative methods, for example, MRI of the thoracic spine.
To obtain clear images, the patient during the diagnostic process must not move for some time and follow the radiologist’s commands, for example, hold his breath. With severe mental disabilities and mental changes, a person cannot fulfill this requirement, so this may become a contraindication for the study.
A barium examination is considered a temporary contraindication. X-rays can be taken after such a procedure only after 4 hours.
In most cases, the examination is postponed to the next day. For people for whom this technique is contraindicated, other examination methods are recommended - MRI, CT, angiography, etc. In extreme cases, doctors are forced to examine the problem area only during surgery.
Where is the best place to take pictures of the spine?
The radiography procedure is considered the most accessible and easiest to use. Compared to other diagnostic methods, this can be done in any clinic. Similar devices are available in public clinics and hospitals, as well as large diagnostic centers. The process will be the same in both a private clinic and a public one.
The only differences are the price and waiting time for results. Thus, the state X-ray room will take pictures in a few minutes, but decoding may take several days. By law, this service in a government agency must be free.
Private diagnostic centers provide examination results within an hour. In addition, the X-ray machine can be digital, and such a device transmits the image to a computer monitor. The doctor can examine the condition of the organs and spine immediately during the diagnostic process; this is very important when identifying dangerous pathological conditions.
The results of this technology are transferred, at the patient’s request, to an electronic medium - a flash card or DVD. The health worker can also send them by email, which is much more convenient.
Feedback from those surveyed shows that there is not much difference between having an X-ray done in a public clinic or in a private one. If comfort and level of service are important, you need a private one. The price for one photo will be from 10 to 40 dollars. Before your appointment, it is important to ask if transcription is included in the price. As a rule, in private centers you have to pay an additional 10-15 dollars for this.
However, modern equipment makes it possible to view the examined area with multiple magnification. The doctor can examine in detail even small cracks or tumors. Old-style equipment takes pictures only on a film matrix, which narrows diagnostic possibilities.
Why CELT?
If you want the diagnosis to be successful the first time and not have to go through it twice, contact the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. We are chosen by many patients who want to receive an optimal price-quality ratio and European-quality service.
We have a powerful diagnostic base and can conduct research not only in the X-ray office, but also in the ward or at home. Our radiologists have over 15 years of experience, which speaks for itself. You can sign up for diagnostics through our website online or by calling.
How does this happen
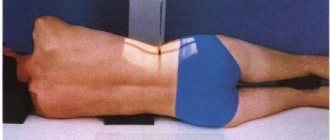
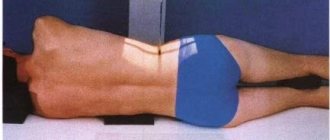
After this preparation, the patient is given a lead apron - a special covering that protects other parts of the body from the harmful effects of X-rays. The device can be of two types: for horizontal shots or vertical ones. In most cases, the examinee stands in the booth; sometimes he is asked to lie down on a special table. In any case, the process takes a few minutes and is completely painless.
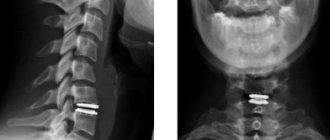
During radiography, pictures are taken in two projections: frontal and lateral. This is necessary to obtain more information.
The subject first stands straight, then turns one side and the other. The x-ray technician will monitor the correct position of the subject, control the entire process, and tell what to do. The success of such a process largely depends on how accurately the patient follows the instructions. Each of the resulting projections shows separate areas:
- Straight line - identifies the body of each vertebra, its processes, intervertebral discs. Such images clearly show the deformation of the ribs and spinal column. However, they are not enough for a complete picture.
- Lateral – done on both sides. Shows middle and lower thoracic vertebrae, endplates, rib deformity.
Sometimes x-rays of the thoracic region are not enough, since some areas may be “shaded” by internal organs, shoulder joints, etc. In such situations, the patient is prescribed additional examination, for example, CT or MRI.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
After receiving the data, the doctor examines it in detail, compares it with the previous ones (if any), draws up a description and conclusion. He will not give recommendations regarding treatment; with the results obtained, you need to contact the doctor who sent you to the X-ray room.
How to reduce the harm from examination
Radiation exposure certainly does not benefit the human body, but not all doses are dangerous to health. We receive small amounts of radiation every day, for example when sunbathing. Radiation is measured in sieverts (Sv), the daily background norm is 10 μSv for each inhabitant of the planet. During a chest x-ray, a person receives approximately 20 µSv. That is, such a procedure does not pose a direct threat, but it is still better not to accumulate the amount of radiation.
To reduce harm from this procedure, advice from doctors recommends making sure that after each session, the radiologist writes down in a report how much radiation the patient received. Based on these data, the next level of exposure will be calculated: decrease or increase. It is also useful to adjust the menu, introduce more seafood, dairy products, carrots, and walnuts. Such a diet will remove some of the radionuclides faster, and there will be no negative consequences from the diagnosis.
More fresh and relevant information about health on our Telegram channel. Subscribe: https://t.me/foodandhealthru
We will be grateful if you use the buttons:
Contraindications
X-rays have several relative contraindications related to potential harm from radiation:
- The patient's age is less than 15 years.
- Pregnancy and lactation.
However, with digital devices the level of radiation is so low that you shouldn’t worry too much about it, and the possibility of examination and the need to do an x-ray (and not an ultrasound or MRI) is determined by the doctor.
The usefulness of x-rays may be questionable if the patient weighs more than 130 kg - the images may be unclear.