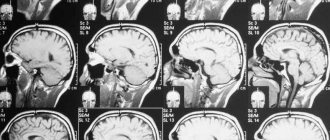
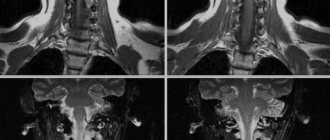
MRI of the lumbosacral region is a diagnostic method that allows you to obtain a comprehensive picture of the area under study with detailed visualization of anatomical structures.
Back diseases have become a real problem in the modern world, where many people lead a sedentary lifestyle. According to some studies, about 80% of the adult population suffers from periodic or constant back pain.
Factors influencing the development of diseases of the lumbar spine are:
- passive lifestyle;
- incorrect posture;
- insufficient physical activity;
- improper exercise in the gym;
- making a careless, sudden movement. For example, lifting weights while twisting the body;
- stress;
- injuries;
- excess weight;
- infectious diseases.
The lower back takes the hit first. It is in this area that hernias, protrusions and osteochondrosis often occur. As a rule, if acute or long-term persistent pain occurs, the patient turns to a neurologist, who may prescribe an MRI of the lumbosacral spine to clarify a possible diagnosis.
What is MRI?
Magnetic resonance scanning is a progressive visual diagnostic method that allows you to obtain many layer-by-layer images of the area under study at one time.
Modern high-field tomograph
Magnetic waves are completely harmless to humans, unlike X-rays. As they pass through the body, they interact with the nuclei of hydrogen atoms in the human body, causing them to move. The tomograph measures the energy emitted by the nuclei and converts it into an image.
The resulting scans form a detailed picture on the computer monitor screen. At the same time, a layer-by-layer image allows you to examine in detail all areas of the organ or structure under study.
For MRI of the lumbosacral region, the slice thickness is usually set to about 3 mm. This is enough to view the structure of the vertebrae, identify the presence of intervertebral hernias and protrusions, and determine the possibility of finding tumors in the bones or substance of the spinal cord.
MRI diagnostics is the only way today to obtain a full-fledged detailed image of the soft tissues of the lumbar and sacral region. The magnetic radiation used for research is capable of scanning and displaying an image of the organs of the lumbar region, such as the spinal cord, intervertebral discs, nerve processes, and soft tissues surrounding the spine, with the utmost precision.
When using radiography and its more advanced analogue - CT - it is impossible to obtain images of soft tissues. Visualization of bone structures may be sufficient to identify dystrophic changes, injuries and deformities of the vertebrae, but radiography-based techniques are not suitable for diagnosing soft tissue pathologies.
A CT scan allows you to see the gap between the vertebrae, from which the doctor can make an assumption about the presence of a hernia and its size. The intervertebral disc itself cannot be visualized by radiography.
The advantages of magnetic resonance diagnostics also include:
- harmlessness of magnetic radiation to humans;
- no pain;
- speed of obtaining diagnostic data;
- the ability to detect diseases at the earliest stages.
MRI of the lumbosacral region allows you to visualize even the slightest pathological lesions in the spine. This is especially important when diagnosing cancer tumors and metastases to the area under study from other organs.
Coccyx fracture – MRI or CT
Coccyx fractures often occur from falls on the gluteal region. Conventional radiography in most cases turns out to be uninformative, and therefore such injuries occur hidden. The resulting chronic pain syndrome can significantly limit physical activity and worsen the patient’s quality of life.
Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography are fairly accurate methods that allow us to detect violations of the bone structure of the coccyx. Whether it is better to undergo an MRI or CT scan of the coccyx is determined by the clinical tasks facing the doctor.
An MRI of the coccyx in this case allows us to identify hidden cracks, fractures, and the degree of displacement of bone fragments. Also, traumatic changes in the surrounding soft tissues are simultaneously diagnosed. MRI for a coccyx fracture makes it possible to choose the most optimal treatment method and, if necessary, perform surgery with the most accurate reposition of the fragments.
Computed tomography also visualizes bone tissue quite well. However, its implementation is associated with radiation exposure to the body, which limits its use in certain categories of patients.
Indications for MRI of the lumbosacral region
The presence of pathologies of the spine in the lumbar and sacral regions and damage to the intervertebral discs can be manifested by the following symptoms:
- the occurrence of sharp pain in the lumbar region;
- chronic or periodically occurring lower back pain of varying intensity and nature: nagging, sharp, dull, aching, shooting, etc.;
- shooting or aching pain radiating to the thigh, buttock, lower leg, groin, ankle or even collarbone;
- pinching, loss of mobility, inability to straighten after bending or sudden movement;
- urinary and fecal incontinence;
- erection problems;
- weakness in the lower extremities or sensory disturbances.
If the symptoms described above occur, patients in most cases turn to a neurologist, who can prescribe an MRI diagnosis, based on the results of which a further treatment plan will be drawn up. If serious spinal cord lesions or neoplasms are detected, the patient may be referred to a neurosurgeon or oncologist for further consultation.
Indications
Symptoms that may be signs of pathologies in the coccygeal part of the spine:
- Pain in the lower back and legs when walking, sitting, changing body position, pressing on or straining the buttocks.
- Impaired leg reflexes, impaired sensitivity of the legs and perineum, numbness, “goosebumps.”
- Gait changes.
- Swelling, redness of the skin on the lower back.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Urinary, fecal incontinence and other disorders of the excretory system.
Without timely treatment of injuries and pathologies of the sacrococcygeal spine, complications such as improper fusion of the vertebrae, inflammation of the nerve roots, and disturbances in the functioning of the pelvic organs and legs are possible.
Contraindications to MRI of the lumbosacral region
Despite the fact that MRI diagnostics is a modern, painless and harmless procedure for patients, there are still contraindications for its implementation.
The absolute contraindications under which MRI examination cannot be performed are as follows:
- a pacemaker installed in the patient. Magnetic waves can disrupt its operation, which can lead to serious health consequences;
- the presence in the body of structures made of metal that reacts to magnetic radiation. These could be: dentures, dental bridges, vascular clips, etc.;
Modern dentures and implants are often made from inert materials such as titanium. If you doubt that you can undergo MRI diagnostics, show the doctor the passport of the implant or prosthesis, which indicates the material of manufacture.
- first trimester of pregnancy;
Although magnetic waves are harmless to humans, there is not enough data on their effects on the developing fetus. Therefore, it is permissible to conduct MRI in late pregnancy if indicated. Diagnosis in the 1st trimester is carried out only in cases of life-threatening situations for the mother.
- patient weight 130 kg or more, maximum body girth more than 150 cm;
- the patient's inability to maintain a long-term immobile position.
This category of people includes small children and mentally unstable people. Patients suffering from severe pain or severe fear of confined spaces should take painkillers or sedatives before the test. Any movements during the procedure will make the resulting images unclear due to the appearance of multiple artifacts.
The essence of the method
This diagnostic method is unique because it makes it possible not to shift or change the position of the patient, if it is necessary to examine not only the coccyx, but also the upper parts of the spine, which is ensured using special tomograph sensors. MRI of the coccyx is a safe diagnostic method, since X-ray ionizing radiation is not used during the examination, and thanks to this, this examination can be carried out many times without causing harm to the human body.
MRI of the coccyx is performed in three projections: transverse, longitudinal and sagittal. After conducting the study, the results are usually printed on film, or they can be entered into a computer or saved on disk.
Content:
- The essence of the method
- What is the tailbone?
- Indications for MRI
- Contraindications to the procedure
- Preparation for the procedure
- What happens during an MRI?
- Benefits of MRI of the coccyx
What does an MRI of the lumbosacral region show?
Many patients are interested in what an MRI of the lumbosacral region shows. The high detail of images obtained using MRI diagnostics makes it possible to accurately identify the following diseases localized in the lumbar spine:
- protrusion and herniation of intervertebral discs;
- degenerative diseases: osteochondrosis, spondylosis;
- consequences of previous injuries, such as compression fractures, subluxations and vertebral displacements;
- multiple sclerosis;
- neoplasms of primary and metastatic origin;
- osteomyelitis;
- myelitis (inflammation of the spinal cord).
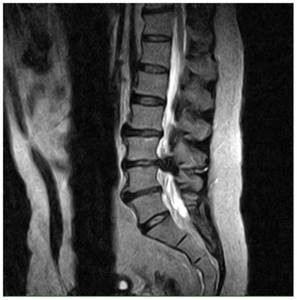
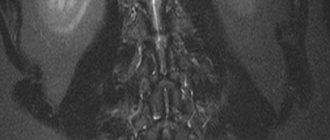
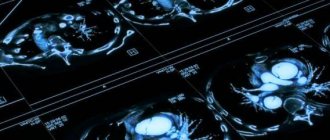
Intervertebral hernia
On MRI you can clearly see:
- thickness and density of intervertebral discs;
- dystrophic changes in the vertebral body;
- narrowing of the spinal canal;
- the condition of the soft tissues in the area under study.
Based on these data, it is possible to draw a clear picture of the course of diseases of the lumbosacral spine.
The most common indication for an MRI examination of the lumbosacral region is suspicion of osteochondrosis, protrusion and herniated intervertebral discs.
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease in which deformation of the vertebral bodies occurs, erasure and flattening of the intervertebral discs.
Typical manifestations of lumbar osteochondrosis are periodic aching and nagging pain, numbness and loss of mobility. People who lead a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle are at risk for the incidence of osteochondrosis.
Timely detection of the disease makes it possible to stop degenerative processes and the occurrence of complications. Diagnosis using MR scanning will give an idea of the stage of the disease and the extent of the affected area.
Protrusion is a bulging of the intervertebral disc without rupture of the surrounding fibrous ring.
The disease occurs when degenerative-dystrophic disorders in the lumbar region are advanced. The appearance of protrusions can also be preceded by sudden movement or heavy lifting.
A common symptom of the disease is lower back pain of varying intensity, numbness in the legs and groin area.
MRI of the lumbar region helps to identify even small protrusions in the early stages of occurrence. Further treatment of the disease is usually conservative. The patient is prescribed painkillers, physiotherapy and massage. An important factor in preventing protrusions is physical activity adequate for age and health status.
A herniated disc occurs when the annulus fibrosus ruptures and the disc moves into the spinal canal, compressing the spinal cord.
The disease is characterized by severe pain, which may subside over time and return again. Depending on the location of the hernia and possible compression of the spinal cord roots in a certain area, the patient may experience shooting pains in various areas of the lower extremities, urinary incontinence and severe pain in the lower back, buttocks and thighs.
Timely diagnosis of hernias helps relieve the patient from discomfort and pain. MRI gives a detailed picture of the course of the disease. In the pictures you can see the location of the hernia, its size and the degree of compression of the spinal cord, and determine the inflammation of the surrounding tissues.
Treatment of hernias can be conservative and include therapeutic blockade, avoidance of excessive tension and stress, physical therapy and yoga, and massage. In severe cases of the disease and when the pain syndrome does not subside over time, surgical intervention is performed.
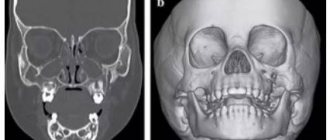
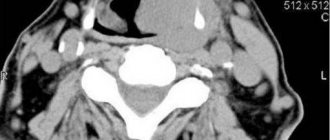
Computed tomogram of the coccygeal-sacral region
The bones are visualized quite well on a CT scan, but sometimes the patient is recommended to undergo a contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan. The administration of an iodine-containing drug makes it possible to better examine the architecture of blood vessels, confirm or exclude the oncological process and metastases.
The radiopharmaceutical accumulates in pathological areas, which helps to carry out differential diagnosis, identify the disease in the early stages and prescribe appropriate treatment.
There are situations when, during diagnosis, tomograms reveal areas suspicious of a tumor or its secondary manifestations. Their nature can be clarified using a series of photographs after the introduction of contrast. Considering the systematic nature of the process, in these cases, not only a CT scan of the coccyx is performed, but also a study of all the bones of the skeleton (scintigraphy).
The administration of contrast is unacceptable if the functional capacity of the kidneys is impaired (increased blood creatinine levels), allergies to iodine, overproduction of thyroid hormones, or while taking Metformin. If the endocrinologist allows you to stop the drug for several days, diagnosis is possible.
The appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth, fever, nausea are common reactions to the administration of contrast; after a short period of time, these sensations pass.
Patient position during diagnosis
The progress of the procedure must be monitored: sometimes side effects develop during contrast. The doctor carefully monitors the patient's condition, if there is a suspicion of an allergy: shortness of breath, redness, palpitations, rash, swelling, drop in pressure - appropriate medications are immediately administered.
During the procedure, you can report all alarming symptoms to the doctor: there is a special button for communication.
Computed tomography is performed only for vital indications of the following categories of persons:
- nursing women;
- children under 5 years of age (CT with contrast is not performed until 12 years of age).
In these situations, functional diagnostic specialists recommend using other methods that do not involve radiation exposure.
The study involves keeping the patient in a motionless horizontal state for up to 20 minutes. Some people may experience autonomic reactions: dizziness, weakness, sweating, etc. A light meal will help minimize the likelihood of these effects developing.
Before the examination, you need to choose loose clothing without metal parts, remove jewelry, and empty your pockets.
The radiologist should be warned about existing implants and allergies to iodine.
The doctor will give the patient a conclusion and a disk 2 hours after completion of the diagnosis. If desired, and for an additional fee, you can order the study to be printed on film. This can be done as needed; the results are stored in the database of the Magnit diagnostic center.
The patient must take into account that in most cases the final diagnosis is established based on the results of all studies. Thus, a CT scan of the coccyx will show a metastatic lesion, but will not be able to answer the questions: where is the primary tumor located, what is it like.
To verify the diagnosis, MRI of the pelvic organs, ultrasound, biopsy, etc. are additionally prescribed.
If you already have conclusions from previous studies, take them with you.
It is better to come to the Magnit diagnostic center with a referral from a doctor, which indicates a preliminary diagnosis and a specific method of examination suitable for your case.
If contrast is to be administered, the result of a blood test for creatinine is required; express diagnostics can be carried out in our center. The test will take about 10-15 minutes, so you must come for a CT scan of the tailbone with contrast with plenty of time.
Is it necessary to use a contrast agent when performing MRI of the lumbosacral region?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbar spine usually does not require additional use of contrast; they are well visualized on images without the use of contrast agents.
If the indication for an MR examination is the suspicion of the possible presence of a tumor or metastatic screenings, the use of a contrast agent is justified. The staining substance helps to assess the size of the formation and its possible growth into the spinal cord tissue
How to prepare for a tomography of the coccyx and sacrum
No special preparation is required to study the coccygeal region. A person may not change his eating habits and lifestyle. Special instructions can be set by the doctor only if contrast is administered to the patient. As a rule, restrictions include refusing food 2 hours before the procedure.
- MRI
- Ultrasound
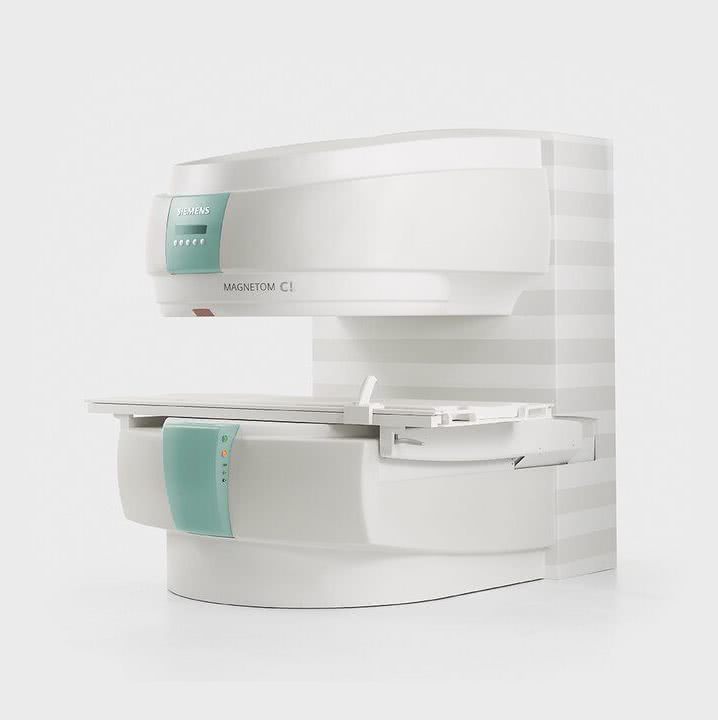
MRI tomograph:
Siemens Magnetom C
Type:
Open (expert class)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written report from a radiologist, recording of tomograms on CD + free consultation with a neurologist or orthopedist after an MRI of the spine or joint
Ultrasound machine
HITACHI HI VISION Avius
Class:
Expert (installation year 2019)
What's included in the price:
Diagnostics, interpretation of images, written diagnostic report
How is an MRI of the lumbosacral region performed?
If it is planned to conduct a magnetic resonance scan of the lumbar region using contrast, it is recommended to follow a rational diet on the day of the procedure.
In other cases, no preliminary preparation for the study is required.
Before the scan, the patient will be asked to remove all metal items. This could be: accessories, jewelry, clothing containing metal fittings, glasses, removable hearing aids.
You must bring with you to your appointment your previously taken photographs, if available. The radiologist questions the patient about the presence of contraindications to the study and concerning symptoms.
The patient lies down on a couch, which is placed in the tomograph tube.
You cannot move during the procedure, so the area being examined can be additionally secured with straps, although this is usually not required. The device produces quite loud sounds, but at the DiMagnit medical center they take care of the comfort of patients and provide special headphones to minimize the unpleasant sensations from the sounds of the operating device.

The radiologist carefully studies the images before making a conclusion
Once the scan is completed, results can be obtained in as little as 30 minutes. The radiologist draws up a detailed report in which he describes all the anatomical structures of the area under study, including those in which no abnormalities were detected. Possible pathologies are also described in detail, indicating their size and location in relation to other organs. The images are recorded on disk and sent to the patient along with a paper report.
Advantages
To diagnose spinal structures, different methods can be used: X-ray, MRI and CT.
Advantages of MRI:
- There is no need for preliminary preparation - the examination is possible on the day of your visit to the doctor.
- The examination will take only 15-30 minutes, depending on the type of procedure - with contrast or not.
- The method is highly safe - there is no radiation exposure, no skin damage, the contrast agent provides a minimum risk of side effects.
- The images allow you to evaluate both the vertebrae and soft tissues: nerve endings, cartilage tissue, blood vessels.
How long does an MRI of the lumbosacral spine take?
MRI diagnostics of the lower back and sacrum will last no more than 20 minutes. If you need to administer contrast, the duration of the procedure will increase by another 15 minutes.
MRI of the lumbosacral region makes it possible to identify frequently diagnosed spinal pathologies such as intervertebral hernias, protrusions and osteochondrosis, as well as other, less common diseases. The study helps determine the exact location of the lesion and its size. MRI of the lumbosacral region is safe and painless, and the results of the study can be obtained immediately upon completion of the procedure.
| MRI of the spine, what does it show? |
| What does an MRI show? |
| What does an MRI of the cervical spine show? |
| MRI of the sacroiliac joints, which shows |
| MRI of the sacroiliac joints |
| MRI of the coccyx |
What will a tomography of the coccyx show?
During an MRI examination, you can obtain accurate information on the condition of the coccygeal region and:
- Identify congenital or acquired anomalies;
- Detect tissue destruction in the coccygeal region;
- Identify possible post-traumatic changes;
- Find out the condition of the coccyx. When healthy, it represents an inverted pyramid;
- Find out the number of vertebrae that form the coccygeal bone;
- Determine the position of the coccyx, the presence of injuries, fractures, displacements;
- Consider the condition of the vessels that are located in the pericoccygeal region;
- Determine the presence of fistulas, abscesses, as well as tumors and cysts;
- Examine the articulation of the patient’s coccygeal bone and the sacrum;
- Note changes in connective tissue or bones;
- See the presence of degenerative changes.
Coccyx on MRI image
| MRI of the coccyx | MRI of the coccyx with coccydynia |
Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
Preparing for the study
There is no need for any special preparation for an MRI scan of the tailbone. Experts recommend adhering to only a few rules:
- If the diagnosis is carried out with the introduction of a contrast agent, refrain from eating a few hours before the examination.
- Clothing during the study should be as comfortable as possible. It should not have metal fasteners and zippers, as well as other elements.
- Before the examination, it is necessary to remove all implants and prostheses, jewelry and watches, empty your pockets of keys, bank cards, small change, flash drives, telephone and other items that cannot be carried with you during the tomography.
- For greater comfort during the procedure, before scanning, you should use earplugs or special headphones suggested by your doctor.
- If you are very nervous and worried that you will not be able to remain still during the entire examination, then warn your doctor about this. You may be advised to take a sedative.
This article contains general information only, is not scientific material and should not be construed as a substitute for medical advice.
Preparation for diagnosis and contraindications
MRI of the coccyx and sacrum does not require preliminary preparation. An exception is contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, which is performed on an empty stomach. Immediately before the procedure, it is necessary to free the body from metal objects: jewelry, hairpins, watches, clothes with rivets. Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging are standard:
- overweight (more than 125 kg);
- the presence of a pacemaker and metal implants in the body;
- mental illness.
The procedure with contrast is not prescribed for patients with allergies to the components of the drug, as well as for renal and liver failure. For claustrophobia and mild neurotic conditions, MRI is performed under sedation.