Liver biopsy is a diagnostic procedure that involves obtaining a small piece of tissue from an organ for morphological examination and making a final judgment about the diagnosis or treatment results. In all clinical situations, a biopsy is the final stage of examination when all previous diagnostic methods are not sufficiently informative.
Our expert in this field:
Allahverdyan Alexander Sergeevich
Surgeon-oncologist, professor, MD. Head of the ROH expert group. International expert
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
About the method
The problem of liver diseases is extremely relevant and, despite the development of medical technologies, improving the quality of life remains very serious in the modern world.
The liver is one of our most vulnerable organs. She is easily susceptible to various types of viral and inflammatory diseases. And if the problem of oncology arises, it is the liver that often becomes the “target” of metastases penetrating into it from other organs susceptible to the disease.
Using ultrasound and CT, it is not always possible to recognize a disease developing in the liver. And here a biopsy comes to the aid of both doctors and patients.
A liver biopsy is the removal of cellular material for the purpose of histological examination. As a diagnostic method, a biopsy is extremely informative, so its main tasks are to clarify the diagnosis, identify the characteristic features of the disease, its course, after which the doctor will be able to prescribe the optimal treatment or adjust what has already been prescribed.
In a number of cases, a biopsy is performed after other diagnostic methods, such as ultrasound, CT, and so on. If cancer is suspected, a biopsy is required. Using the procedure, the benign nature of the neoplasm is also recorded.
The procedure is quite painful and there is a risk of serious complications in case of significant changes in the structure of the liver tissue. That is why it is important for the doctor to clearly formulate the indications for it or refuse if there is a significant risk for the patient.
Lymph node biopsy
The procedure is carried out in a clinic or as part of a day hospital: the patient needs rest and observation for 4-5 hours.
The duration of the procedure itself varies from 5 minutes to an hour.
conclusions
Percutaneous TB of space-occupying formations is a technically simple and relatively safe method of obtaining material for pathomorphological examination.
Image fusion technology (CT+PET-CT, CT+MRI, ultrasound+CT, ultrasound+MRI) makes it possible to accurately plan the type and volume of intervention, the trajectory and depth of penetration of the biopsy needle.
The free hand technique and staged biopsy with constant CT control allow safe intervention even with small sizes and complex anatomical localization of the tumor. The use of coaxial needles allows to minimize surgical trauma and reduce the risk of implantation metastasis.
Indications
So, a biopsy is indicated in the following cases:
- Suspicions of liver cell pathology;
- Identification of characteristics of an already detected tumor;
- Monitoring the effectiveness of already prescribed treatment;
- Detection of rare liver diseases.
As mentioned above, a biopsy is often performed after diagnostic methods such as ultrasound, CT MRI and others and serves as a method for the final diagnosis.
There are many indications for the procedure:
- Pathological changes in the organ;
- Diagnosis of hepatitis, cirrhosis, fatty hepatosis;
- Unreasonable enlargement of the organ;
- Jaundice of unknown origin;
- Infestations of a parasitic nature;
- Bacterial infections;
- Genetic malformations;
- Neoplasms, etc.
To minimize the risks of the procedure, the patient undergoes a blood test for biochemistry, undergoes ultrasound and other examination methods.
How to prepare
During preparation you must:
— tell your doctor about pregnancy, lung and heart diseases, allergies to medications, diabetes, and problems with blood clotting;
- inform the doctor about taking anticoagulants that thin the blood;
- a week before the procedure, you must stop taking aspirin, aspirin-containing and some anti-inflammatory drugs - you should consult your doctor about this in advance.
The following laboratory tests must be performed before a liver biopsy:
- general blood analysis
- general urine analysis
- blood clotting test
- HIV test
- hepatitis test
Contraindications
The following diseases are categorical contraindications to the procedure:
- Ascites;
- Dysfunction of hemostasis;
- Hemophilia;
- Fluid formations in the liver;
- Thrombocytopenia;
- Purulent inflammation in the abdomen and liver;
- Disorder of consciousness;
- Mental illnesses;
- Subhepatic cholestasis and some others.
There are restrictions on performing a biopsy that are relative in nature, that is, those that can be eliminated or minimized before the procedure:
- General infections;
- Heart failure;
- Hypertension;
- Excess body weight;
- Cholecystitis
- Stomach ulcers are some others.
Kinds
Types of liver biopsy are classified depending on the method of sampling:
- Puncture;
- Incisional:
- Laparoscopic;
- Transvenous;
- Fine needle.
Needle biopsy
A puncture biopsy is performed using local anesthesia. It is carried out blindly or under ultrasound or CT control. The procedure is quick to perform.
To study, it is necessary to take tissue from several mm to 3 cm, and from different areas.
It is worth considering that a fragment taken for study will not give a complete picture of the condition of the liver, but only the area from which it was removed.
This technique is indicated in the following cases:
- Unspecified jaundice;
- Unreasonable enlargement of the liver or spleen;
- With a viral disease;
- Cirrhosis;
- Tumors;
- In order to control the already prescribed treatment.
The main stage of the technique is to puncture the liver with a syringe needle containing saline solution and quickly take material for research.
In most cases, after a couple of hours, the patient receives a control ultrasound, the purpose of which is to make sure that no fluid has accumulated at the puncture site.
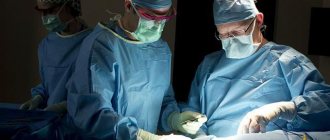
Incisional biopsy
This technique is not used as an independent method. But during surgical procedures that target tumors and metastases, it is widely practiced.
During manipulations with a scalpel or coagulator, parts of the liver are cut off, then they are sent for laboratory study.
Biopsy laparoscopic and incisional
These techniques, performed under general anesthesia, are more often used as diagnostic measures for diseases of the abdominal cavity, unexplained accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, and to determine the stage of cancer.
During the procedure, the doctor makes punctures or incisions in the abdominal wall, into which he then inserts special instruments, including loops or biopsy forceps. The manipulation is controlled using a picture displayed on the monitor.
Having taken the necessary material, the doctor cauterizes the bleeding vessels, and then sutures the incisions and applies a sterile bandage.
Contraindications are:
- Heart failure;
- Pathologies of the respiratory tract;
- Intestinal obstruction;
- Inflammatory process in the peritoneum;
- Significant obesity;
- Significant hernial protrusions.
To carry out these techniques, written consent from the patient is required.
Transvenous biopsy
Indicated in case of hemostasis disorders and in patients on hemodialysis. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, as it is quite painful, but the pain is short-lived and does not affect the patient’s general well-being.
The doctor inserts a catheter into the hepatic vein. This helps minimize the possibility of bleeding after the procedure is completed. The procedure must be carried out using ECG monitoring in order to avoid the risk of heart rhythm disturbances.
If the patient has thrombosis of the liver veins, cysts, dilated intrahepatic bile ducts and some other pathologies, this technique is not used.
Fine needle biopsy
The procedure is also quite painful, which is why an anesthetic is used. The technique, carried out under CT control, is good for clarifying the nature of neoplasms. Indicated for vascular changes, as well as hepatic echinococcosis.
After the procedure is completed, the patient requires an additional ultrasound examination, then he is placed in the ward.
Technique
The research takes place in several stages:
- The patient lies on his back, with his right hand behind his head.
- The patient should not move.
- If the patient is excessively excitable, he is prescribed sedatives that have a depressing effect on the nervous system.
- Find the 9-10 intercostal space.
- The site of the intended puncture, where there are no blood vessels, is disinfected and an anesthetic is administered.
- The doctor makes a small incision through which a puncture needle is inserted.
- Using a needle, carefully remove a piece of the liver at the height of the patient's inhalation.
- The needle is quickly removed, and the puncture site is treated with an antiseptic.
- A sterile dressing is applied.
- The patient will learn the result in a few days.
This is the main method called puncture biopsy. In addition, there are other techniques:
- laparoscopic;
- transvenous;
- histological.
The first is used in cases requiring the study of a specific parenchyma sample. During laparoscopy, an incision is made in the abdominal cavity through which a tube with a camera is inserted. It allows you to visualize the organ on the monitor. The doctor sees the entire liver and takes the required fragment.
The transvenous method is used for ascites and pathologies associated with poor blood clotting function. A thin tube with a needle is inserted through the subclavian vein to remove material. Gradually, the doctor advances the tube through the venous system to the liver, where he takes part of the parenchyma.
To carry out histological analysis, a tissue column 2 mm thick and 3 cm long is required. If three or more portal tracts can be identified in the material, the study will give results. In order to assess the severity of fibrosis, the material must have a length of at least 10 mm.
Preparation
The rules for preparing for a biopsy are not difficult to learn.
- 7 days before the procedure, we cancel anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents and systemically taken non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- For 3-5 days, we exclude from the diet foods that can cause bloating;
- 1-2 days before the procedure, we forget about the sauna, steam bath, hot bath;
- We do not engage in heavy physical labor;
- For 10 hours we forget about any food;
- We do a cleansing enema the evening before the procedure.
Already at the clinic, the patient takes a second blood test, undergoes an ultrasound, and has his pulse and blood pressure measured. To top it all off, the patient gives written consent for the biopsy.
After the biopsy
After the procedure, the patient must spend two hours lying on his right side. It is necessary to forget about hot dishes on the first day after the procedure, the diet should be gentle, and the first meal should be done only after 3 hours. Bed rest must be strictly observed.
It is important to monitor blood pressure and heart function on the first day. After 1.5 - 2 hours, and also a day later, an ultrasound is performed.
In case of mild discomfort or mild pain in the shoulder area or back, painkillers may be used.
The patient should neglect:
- Physical activity for at least 24 hours;
- Driving a car within 8 hours after the manipulation;
- Blood thinners for a week;
If your body temperature rises within three days after the procedure, chills, weakness, nausea, difficulty breathing, acute pain in the liver or in the chest, shoulder, or abdomen appear, you should not postpone your visit to the doctor.
Postoperative recovery
After the manipulation, ice is placed on the puncture site for 2 hours. No later than 6 hours and one day after the puncture, control ultrasound of the intervention area and blood tests are performed.
The likelihood of complications is minimal - less than a percent, the most common - hematoma inside the liver occurs in one out of 350 patients, bleeding - in one out of 2.5 thousand, other troubles occur in isolated cases per 10 thousand manipulations.
The main disadvantage of a biopsy is the morphological “emptiness”, when it is not possible to interpret the analysis and the question of repeated invasive diagnostics arises. The human factor can also play a negative role - “I took it the wrong way, interpreted it wrong.”
To avoid repeat biopsies in our patients, the international clinic Medica24 employs only experienced surgeons who have practiced thousands of biopsies, and the analysis is interpreted by pathomorphologists who have reviewed millions of slides.
The material was prepared by oncologist, endoscopist, chief surgeon of the international clinic Medica24, Konstantin Yuryevich Ryabov.
Bibliography:
- Technology for performing liver puncture biopsy/Recommendations of the NOGR//Clin and exp. gastroenter.; 2008; No. 5.
- Elsayes KM, Kielar AZ, Chernyak v. , et al. /LI-RADS: a conceptual and historical review from its beginning to its recent integration into AASLD clinical practice guidance// J Hepatocell Carcinoma; 2019; 6.
- Stewart CJ, Coldewey J., Stewart IS /Comparison of fine needle aspiration cytology and needle core biopsy in the diagnosis of radiologically detected abdominal lesions// J Clin Pathol; 2002.
- Vogel A., Cervantes A., Chau I. et al. /Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice. Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up // Ann Oncol; 2018; 29(Suppl 4).
results
Liver biopsy results are assessed using two methods:
- Metavir method. It is used in the case of a biopsy for hepatitis C. A classification of stages is established from 0 to 4 points. Belonging to one or another stage gives a picture of the amount of fibrous tissue and its scarring.
- Knodel method. It is applicable to assess the presence of the degree of inflammation, necrosis of the liver lobes, the degree of scarring of the organ, etc.
Clinic Onco.Rehab performs liver biopsy procedures in partner clinics. Using global experience, modern technologies, and qualified doctors, we guarantee compliance with a high quality standard of diagnostic procedures.