Ultrasound examination is a safe and informative procedure intended for diagnosis and monitoring of treatment of various diseases. Hepatitis, tumor formations, gallbladder diseases, cirrhosis of the liver are determined by ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system (HBS) with high accuracy and efficiency. One of the common diseases of GBS is cirrhosis of the liver. The clinical picture at the initial stage of the disease is quite unclear.
It is not possible to make a correct diagnosis based on symptoms alone. The patient is prescribed a series of laboratory tests to identify changes in the composition of the blood and a hardware examination. Is it possible to determine cirrhosis of the liver using ultrasound and trust the ultrasound results? According to statistics, it is possible to detect the disease in the initial period of development in 70% of cases. At the second and third stages of pathology, ultrasound diagnostics provides a 100% guarantee of results.
Reasons for examination
Cirrhosis is a gradual transformation of living hepatocytes (liver cells), which ensure the functioning of the liver, into connective tissue that does not carry a functional load. Since the process of degeneration occurs slowly, the signs of the disease at the initial stage are weakly expressed. The main symptoms are:
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- chronic drowsiness and weakness;
- heaviness in the epigastric region and right hypochondrium;
- indigestion and intense gas formation;
- bitter taste in the mouth.
Many potential patients do not pay attention to the listed signs and seek medical help only at the stage of yellowing of the eyeballs and skin. Early diagnosis of cirrhosis can increase the patient's life expectancy to 10–12 years. Detection of liver pathology at the second stage reduces this period by half. Before performing an ultrasound examination of the organs of the hepatobiliary system, the patient is prescribed blood microscopy, including general clinical and biochemical tests.
In the presence of cirrhosis of the exocrine gland (liver), the following changes in blood composition are determined:
- elevated levels of liver enzymes AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase), Alpha-Amylase, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bilirubin (the main component of bile);
- high concentration of gamma globulins and IgM immunoglobulins (moderate IgG and IgA immunoglobulins);
- decreased level of platelets and protein fractions;
- high ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and leukocytosis;
- significantly increased levels of lipids and cholesterol (hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia).
Depending on the stage of the disease, pathological changes in the blood progress.
Symptoms of liver fibrosis in adults
Scarring from liver fibrosis can affect the liver's ability to function effectively.
However, fibrosis itself does not cause any symptoms. You may have it and not know it. If fibrosis progresses to cirrhosis, the main symptoms may include:
- constant bruises on the body and bleeding;
- fatigue, confusion and weakness;
- itching;
- poor appetite, nausea and weight loss;
- swelling of the abdomen (ascites) and legs (pasty);
- yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
Liver cirrhosis is a serious disease that can lead to life-threatening complications. Seek medical help immediately if you experience the above symptoms.
Hardware examination
The main diagnostic procedure is liver ultrasound. According to the decision of the attending physician, in the future, computer or magnetic resonance imaging (CT or MRI) may be prescribed. The technical side of ultrasound diagnostics involves passing ultrasonic waves through the liver tissue. The intensity and speed of their back reflection are recorded by a sensor.
A special program converts the results into a visual image on the monitor. The ultrasound specialist takes measurements of the necessary parameters, evaluates the vascular pattern, conductivity of ultrasound waves, and the overall picture of changes. The results are assessed by comparison with normal values for a healthy organ.
General assessment parameters and normative values for the gland (in general)
| Length (mm) | Cross parameter size (mm) | Thickness or size of the liver in the sagittal plane (mm) |
| 140–180 | 190–230 | 100–120 |
Norms for the right and left lobes in millimeters
| Fullness (thickness) | Vertical oblique size | Length | Angle of the right lobe | |
| Right lobe | 110–130 | 150 | 110–150 | 75 degrees |
| Craniocaudal size (height) | Anteroposterior size (thickness) | — | Angle of the left lobe | |
| Left lobe | 100 | ≈ 70 | 45 degrees |
Norms for hepatic arteries, veins and ducts (in millimeters):
| Portal vein | vena cava | Splenic artery | Hepatic artery | Common bile duct |
| 13 | 15 | ≈ 10 | ≈ 7 | ≈ 7,5 |
The structure of a healthy gland should be homogeneous (uniform), consisting of small grains. The outline (contour) of the organ has clear, even boundaries (without depressions or bulges). One of the main evaluation criteria is echogenicity - the degree and rate of ultrasound absorption by hepatocytes. The examination shows how capable the liver tissue is of reflecting and transmitting ultrasonic waves. Increased absorption (hyperechogenicity) indicates pathological compaction of the gland or an increase in the amount of fluid; decreased absorption (hypoechogenicity) indicates replacement of cells with scars and a low amount of fluid.
Discrepancies with the norms mean the presence of pathological changes in the liver.
Preparation and carrying out diagnostics
Whether the presence of pathology will be visible on ultrasound depends on proper preparation for the procedure. The basic rules concern changes in eating behavior three days before the study. It is necessary to eliminate foods that cause intense gas formation from the diet:
Ascites in liver cirrhosis
- cabbage of all varieties and legumes;
- products containing lactose, in particular fresh milk;
- sweet pastries and brown bread;
- fruits (apples, pears, grapes);
- vegetables (radish, radish, cucumbers);
- confectionery and carbonated drinks.
The consumption of alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited. If you are prone to flatulence, the patient is recommended to take carminative medications (Espumizan, activated carbon) two days before the examination. Ultrasound diagnostics are performed strictly on an empty stomach, otherwise, due to the remains of undigested food, the doctor will not be able to see all the changes in the liver and ducts.
Preliminary preparation is necessary to optimize results as much as possible. Neglecting recommendations greatly distorts the picture of the study. As a result, the doctor may make an incorrect diagnosis.
The ultrasound is performed in the patient’s standard position (lying on his back). If necessary, the doctor may ask you to turn over to your left side or raise your arms. In some cases, this increases the visibility of the area being surveyed. The doctor sequentially moves the sensor, treated with gel, over the patient’s body and monitors the projection of the internal organs on the monitor. A description of the pathological changes in the organ is recorded in the examination protocol, which is given to the patient immediately after the examination.
Based on the conclusion of the ultrasound specialist, the final diagnosis is made by a gastroenterologist or hepatologist. To assess the speed of blood circulation in the vessels, standard ultrasound is combined with Doppler ultrasound (USD). The examination procedure takes from a quarter of an hour to 30 minutes, depending on the extent of the lesion.
Duration
In 10-20 minutes, the doctor examines in detail the condition of the liver and its lobes, adjacent tissue and vascular structures. The scanning time will depend on the type of installation, the qualifications of the diagnostician and the person’s body weight. In overweight patients, the fat layer is large, and the doctor will need 20 minutes to perform a high-quality liver scan. To examine people with a thin body structure, the research time will be required in half.
| Ultrasound service | Price according to Price, rub | Promotion price, rub |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, stomach) | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of one organ (liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas, bladder, adrenal glands) | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the bladder | 2000 rub. | |
| Kidney ultrasound | 800 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland) | 2400 rub. | 1999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidney + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + pelvic ultrasound with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
| Comprehensive body diagnostics (MRI of the thoracic spine, MRI of the lumbar spine, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, ultrasound of the kidneys, ultrasound of the bladder, consultation with a neurologist, consultation with a therapist) | 11700 rub. | 7000 rub. |
Signs of cirrhosis on ultrasound
During the study, all digital parameters of the liver, qualitative changes in structure, contour, echogenicity, a description of the condition of veins, arteries, and possible anomalies in adjacent organs of the hepatobiliary system are entered into the protocol. The ultrasound image changes depending on the stage of the disease, severity, and the presence of complications.
Transformation of sizes
At the initial stage of development of the disease, the gland grows in volume. As the pathology progresses, the right lobe decreases; in the stage of decompensation, the entire organ contracts. Cirrhosis can be diagnosed at a ratio of 1:3. The tail part of the liver also thickens.
Change in conductivity (echogenicity)
In the initial and subcompensated stages, hyperechogenicity (increased ability to absorb ultrasound) is recorded, which indicates compaction of the gland. In the stage of decompensation - hypoechogenicity (or lack of echogenicity), since atrophied hepatocytes are not able to reflect ultrasound.
Outline deformation
In the presence of cirrhotic changes, ultrasound will show a clear deformation of the outlines of the organ (discontinuous contour, the presence of depressions and bulges). The lower edge is characteristically rounded (the angles of the left and right lobes exceed the norm, turning from sharp to obtuse). The surface of the liver is covered with tubercles - a characteristic sign of cirrhosis when differentiating from hepatitis.
Morphological changes in tissue
Due to the formed scars of connective tissue in place of hepatocytes, the structure of the liver tissue looks like a heterogeneous nodular structure. There are three types of damage:
- micronodular (nodules up to 0.3 cm in size);
- macronodular (the size of the nodes doubles);
- mixed (presence of different-sized lesions).
In the fourth stage of the disease, ultrasound may show a complete absence of healthy areas. The entire parenchyma is replaced by scar tissue.
Vascular system
The vascular pattern is not clearly visible. Varicose dilation of the portal vein and other vessels of the portal system is observed. Capillaries are not verified.
About the disease
The liver is one of the most important organs of the human body, ensuring the purification of toxins from the blood. The organ also takes an active part in digestion, carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism. It is not surprising that any malfunction of the liver negatively affects the entire body and the patient’s quality of life.
Liver cirrhosis is a serious disease, as a result of which liver tissue is replaced by connective tissue and the organ ceases to perform its function. Cirrhosis is a chronic, progressive disease that can lead to very serious, life-threatening consequences.
Sign up for a consultation
Additionally
Relative (relative) signs of cirrhosis include:
- splenomegaly, that is, an increase in the size of the spleen (length -> 120 mm, thickness -> 60 mm);
- increased diameter of the splenic vein (> 9mm);
- change in shape and increase in volume of inguinal lymph nodes.
In later stages, ultrasound reveals:
- hepatorenal syndrome (damage to the renal apparatus);
- hepatogenic duodenal ulcer;
- accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites);
- liver failure;
- presence of oncological processes;
- bleeding of internal organs.
On ultrasound with Doppler sonography, a biphasic diastolic component is observed in the splenic artery. Slow blood circulation is noted (in the terminal stage, blood circulation may not function or blood flow is in the opposite direction). Ultrasound examination most accurately determines cirrhosis, starting from the stage of subcompensation. At earlier stages, the diagnosis is made based on a comparison of laboratory blood microscopy and hardware examination (ultrasound + tomography).
With liver cirrhosis in the decompensated stage, the picture will be clearly expressed. In order to confirm the presence of pathology with 100% probability, a biopsy is performed in all cases.
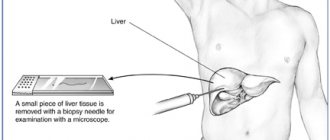
Biopsy
The procedure involves taking organ tissue for histological analysis. It is carried out under mandatory ultrasound control in two ways: through an incision in the anterior wall of the peritoneum (laparoscopic biopsy), by introducing a special needle into the area of the right hypochondrium (puncture method). Based on the results of the biopsy, the following is diagnosed: destruction of the bile ducts, proliferation of bile canaliculi, degenerative changes in tissue, activity of cancer cells, necrosis of hepatocytes and the presence of nodes and scars. The patient receives the biopsy results after 5–7 days.
Prerogative aspects of ultrasound diagnostics
Ultrasound is the most important test in diagnosing cirrhosis. The advantages of ultrasound diagnostics include:
- safety;
- no contraindications;
- availability;
- sufficiently high information content;
- low cost (compared to alternative examinations);
- efficiency of obtaining results.
Cirrhosis of the liver is an irreversible process. The disease is classified as incurable. The patient's lifespan is largely determined by the timely diagnosis of the pathology. Ignoring an ultrasound examination means hastening death.