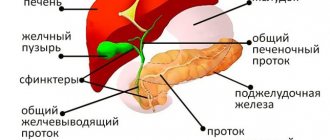
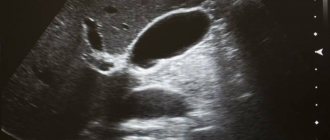
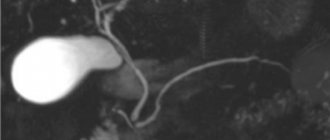
Appearance and position of the gallbladder in the abdominal cavity
Computed tomography of the gallbladder is a non-invasive, highly informative method for diagnosing pathologies of the biliary system organs; it is performed to determine the cause of the problem or to exclude alternative diagnoses.
The study involves the use of X-rays and special computer programs; the resulting images have high detail, a minimal amount of distortion and artifacts compared to previously used methods. Before the improvement of radiological diagnostics, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) was used. The method is still considered the “gold standard” in diagnosing stones blocking the bile ducts; it has its own indications. Due to high invasiveness, risk of complications, severe discomfort and high radiation exposure, RCCP is currently performed much less frequently, mainly if it is planned to remove small stones that obstruct the outflow of bile. The reliability of the method cannot be disputed.
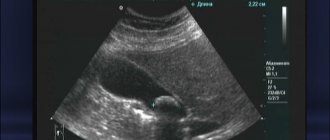
Which is better - CT scan of the gallbladder, MRI or ultrasound - is determined by the doctor based on the expected diagnosis. Ultrasound sonography is used at the initial stage of diagnosis, especially if there is a suspicion of loose stones or small stones that are not visualized on a computer scan.
The capabilities of ultrasound examination are limited by the technical parameters of the device, the specialist’s training and the patient’s obesity. On a sonogram it is impossible to differentiate the structure of the stone and the pathology of the intrahepatic biliary tract.
CT of the biliary system is not an alternative method, but can be used as an adjunct.
Why do you need radiography?
The contrast agent used to visualize the gallbladder and ducts, bilitrast, is iodine-containing. The scanning machine concentrates and directs x-rays, which pass through the soft tissue and the injected substance in different ways. A contrast agent is administered intravenously immediately before the procedure after a tolerance test.
From the blood, the contrast agent enters the liver, gallbladder and its ducts. The results of cholecystocholangiography are based on photographs taken that record the passage of the contrast agent. With its help, it is possible to assess the degree of damage to the bladder and ducts, see tumors, stones, as well as other formations and anomalies that are not visible during other research methods. Images are taken after 20 minutes, 30 minutes and 40 minutes after the administration of contrast, for a step-by-step assessment of the function of the entire biliary system.
The gallbladder is not visualized. Why is the gallbladder not visible on ultrasound?
Why is the gallbladder not visible on ultrasound? — this question comes up quite often in your letters, dear readers and subscribers. Since there are many reasons for the invisibility of the gallbladder, I decided to answer it by writing an article about it.
It is quite natural that the gallbladder cannot be seen after cholecystectomy. That is, after the gallbladder has been removed. This position seems quite natural and self-evident. But in life there are various oddities, and I decided to write about this too.
Often the gallbladder cannot be seen if the patient has not properly prepared for the examination. For example, he ate heavily (or even not very heavily) shortly before the study. At the same time, the gallbladder contracts, releasing bile into the duodenum, sharply decreases in size and often becomes very difficult to see.
Experts believe that its main reasons are:
- cholelithiasis (cholelithiasis);
- gallbladder sclerosis;
- obstruction of the cystic duct;
- organ wrinkling.
When cholelithiasis is not treated for a long time, the disease progresses so much that the bladder literally becomes filled with stones and there is no free space left for bile. The formation of a large number of stones is not the only consequence of the development of gallstone disease.
It may be complicated by sclerosis of the bladder. The muscles of the organ lose the ability to contract, and it gradually atrophies.
The most dangerous thing is when pus accumulates in the bladder.
There are several factors due to which the gallbladder is not visible during an ultrasound examination:
- violation of preparation for the examination; the patient was eating. It is necessary to conduct the examination again 6 hours after the last intake of liquid or food;
- there are anomalies in the location of the bile organ;
- hypoplasia or agenesis of a congenital organ is present;
- the organ was removed, it is necessary to ask the patient about the operation or look for scars from sutures on the skin;
- the bubble is wrinkled due to the filling of the cavity with stones that provide an acoustic type of shadow;
- insufficient qualifications of the specialist performing ultrasound.
Making a diagnosis in the absence of an image of the gallbladder is prohibited, especially if it is not visible in different positions. Various pathologies other than agenesis and organ removal are possible, leading to problems with visualization.
Contraindications to the procedure
The main contraindications to this contrast X-ray examination are intolerance to iodine-containing drugs, severe damage to the liver and kidneys.
The procedure is not performed on pregnant women in the first trimester unless absolutely necessary. For children, cholecystocholangiography is prescribed in cases where the benefits of the information obtained during the study outweigh the risks of radiation exposure. During the examination, additional protective aprons are used (protect the chest, thyroid gland and genitals).
Features of the event
During the study, additional pain or symptoms of malaise may be observed. Before prescribing the procedure, the attending physician assesses the risks and prescribes additional studies. Complications after cholecystocholangiography in rare cases may include:
- prolonged headaches;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- nausea and vomiting (symptoms of body intoxication).
Cholecystocholangiography is performed only in cases where standard research methods do not help establish an accurate diagnosis (biochemical blood tests, ultrasound). The dose of X-ray radiation received during the study should be summed up with the total dose received during the year.
Also, cholecystocholangiography is performed before liver surgery, when it is necessary to assess the condition of the excretory ducts. This research method is a mandatory part of preoperative preparation. The results (images) show neoplasms that may be a contraindication to surgery.
Advantages of fistulography at the CELT clinic
In order to eliminate pain or discomfort during the procedure, and also to obtain all the data that is necessary for a full diagnosis, contact the CELT multidisciplinary clinic. We employ radiologists with over 15 years of experience who are well acquainted with all the features of fistulography. By contacting us, you can count on:
- European quality of service;
- Possibility of pre-registration and no queues;
- High diagnostic accuracy;
- The procedure is carried out by experienced diagnosticians.
You can find out the cost of fistulography in our clinic by reading the price lists or calling us: +7 (495) 788-33-88.
Carrying out the procedure
The contrast agent is administered in two ways - orally or intravenously. In the second method, the substance is administered immediately before the procedure. After installing the catheter, the patient is positioned on the table (images are taken standing and lying down). The medical worker takes several pictures by changing the direction of the main scanner of the device.
The procedure is carried out in two opposite positions. The patient must remain still while the scan and target image testing is performed. After taking the yolks (an hour later), pictures of the emptied organ are taken. The images show shadows of the bile ducts. If the liver clears the contrast agent, the gallbladder will be visible on images without interference. If the passages are obstructed, the contrast agent will begin to accumulate, which will appear on the resulting images.
After the procedure, the patient can consume food and water.
Nutrition for a sick bladder
Diet therapy is the foundation of therapeutic measures. Only if you follow a therapeutic diet can you get the maximum therapeutic effect. For gallbladder diseases, it is recommended to eat in small portions. Food should be eaten warm; eating cold food causes a sharp spasm in the biliary system. The following should be excluded from the menu:
- foods high in animal fat;
- broths, offal, fatty fish and meats;
- plant foods that increase bile secretion;
- sweets, confectionery, chocolate;
- carbonated, alcoholic drinks, coffee.

Steaming, boiling and baking are allowed. Fried, smoked, canned, salty foods are strictly prohibited. Dietary food for gallbladder damage should consist of cereals, fermented milk products, dietary fish, meat, vegetables and fruits, mainly boiled or baked. You need to drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid per day - drinking water, rosehip decoction, weak green tea.
It is impossible to ignore pain and not seek medical help. The sooner the motive for the deterioration of the condition is identified and treatment is started, the less likely it is to detect undesirable complications and consequences.
Modern cholecystocholangiography
Currently, percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography is used. A laparoscope is used to administer an iodine-containing substance. In this study, contrast is injected directly into the bile ducts during percutaneous liver puncture.
This method is suitable for examining the biliary tract for the presence of fistulas or neoplasms. The choice of contrast injection method depends on the area being examined. Cholecystocholangiography is performed in a special room protected from background radiation. Image recording is carried out by medical workers from a designated protected room, using protective aprons and plates.
Results of the procedure
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Cholecystography is prescribed to study the anatomical structure and functional activity of the gallbladder and bile ducts. On the resulting image, you can evaluate the shape and position of the area under study, the displacement of its position, which is deviated from the norm. The size of tumors and stones is assessed from several photographs taken in different planes. The two-dimensional image allows you to evaluate large abnormal formations, tumors and polyps that interfere with the functioning of the gallbladder or ducts.
Cholecystocholangiography provides a clear image of the internal organ: the gallbladder is pear-shaped with smooth outlines and a thin contour. Any deviations from the norm are recorded by a radiologist and are the reason for prescribing additional research methods. The shape of the gallbladder may differ from the norm due to the design features of the body. In hypersthenics, the bladder is round in shape, while in asthenics it is elongated upward: the structural features and position of the organ are assessed by a doctor who writes a conclusion on the cholecystocholangiography performed.
Dangerous sizes of gallstones. Cholelithiasis
Gallbladder
This is one of the most common human diseases. Very often, the formation of gallstones is observed in adolescents and children of primary school age.
The causes of the disease are:
- congenital or acquired metabolic disorders;
- dyskinesia of the bile ducts, which is accompanied by stagnation of bile, while the content of cholesterol and bilirubin in it increases several tens of times;
- anatomical disorders of the structure of the bile ducts.
Predisposing factors include:
- obesity;
- excessive consumption of foods containing a lot of cholesterol;
- diabetes;
- taking certain medications (for example, hormonal drugs containing estrogen, antibiotics);
- pregnancy.
Some scientists believe that infectious processes play a certain role in the formation of gallstones.
What types of stones are there? Their composition is different. They can be cholesterol, bilirubin or mixed.
Obesity
Cholesterol metabolism disorders occur as a result of obesity, poor nutrition, pregnancy, and taking hormonal medications.
In the gallbladder, cholesterol gradually crystallizes and stones begin to form.
Black pigmented bilirubin stones are formed as a result of increased production of water-insoluble bilirubin.
This is typical for elderly people, patients with liver cirrhosis and hemolytic diseases.
The presence and size of gallstones can be determined by ultrasound examination. CT scans are done less frequently.
The results of a biochemical blood test show an increase in the level of bilirubin, cholestasis enzymes and serum transaminases.
By size, stones are conventionally divided into small (up to 1 cm), medium (1 to 2 cm) and large.
Very large ones are rare, since due to the small size of the gallbladder, the first symptoms of the disease appear very quickly.