X-ray of the leg bones: what is it, what is it done for?
An X-ray of the shin is a radiation-based, non-invasive diagnostic method used to identify pathologies of bone tissue. Most often, the need for an x-ray occurs in cases of fracture of the lower leg bones - tibia and fibula.
This diagnostic procedure is highly informative, accurate, and is performed quickly - preparing, shooting and decoding images will take no more than 15-20 minutes. This is very important, especially for such a field of medicine as traumatology, where most often it is necessary to make operational decisions to restore the patient’s health.
Clinical example.
Patient G., 56 years old, fell from a stepladder at the dacha, received a closed fracture of both bones of the right leg with displacement, and was hospitalized at K+31 by the insurance company. On the day of admission, a complete preoperative examination of the patient was performed, skeletal traction was applied, and he was hospitalized in the department.
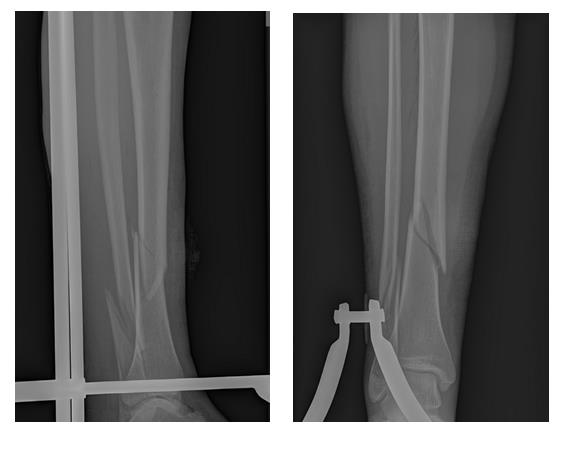
On the same day, osteosynthesis of the tibia fracture was performed with a pin with locking, and the fibula with a plate and screws. Activated on the second day. On the third day he was discharged in satisfactory condition for outpatient follow-up treatment.
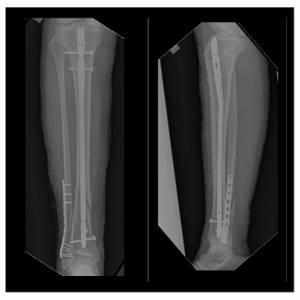
6 weeks after surgery, axial load on the limb is allowed. The fracture healed 12 weeks after surgery in a satisfactory position.
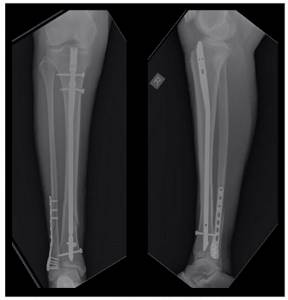
The patient is fully activated, walks without additional support without limping, and is not bothered by pain. The attentive reader will be able to notice
Indications for testing
X-ray of the lower leg
can be carried out in the presence of various indications and can be prescribed by different specialists.
In traumatology
Fractures of the leg and foot can have a very diverse location, size, and complexity. An x-ray will help identify the features of the fracture, see if there are bone fragments and how they are located. X-rays are also used after the broken bones have been connected and cast. In this case, it is important to observe in dynamics how the fusion of bone tissue occurs.
In oncology
Oncological foci, as is known, can arise not only in internal organs or soft tissues, but also in bone tissue. Bone cancer most often affects areas near the knee joint, such as the lower leg. It is worth clarifying that we are talking about primary cancer, that is, cases when cancer cells first originate in the bone, and are not a consequence of metastasis of a soft tissue tumor. There are three main types of cancer that can affect the ankle joint:
- Osteosarcoma. This pathology is the most common, and the risk group includes mainly adolescents who are in the stage of active growth and physical development. Osteosarcoma begins in new, developing bone tissue.
- Chondrosarcoma. This pathology most often originates in the cartilage of the joints and affects people aged 40 to 60 years.
- Ewing's sarcoma. This disease mostly affects young children. It is characterized by the appearance of small cancerous foci in the child’s bone marrow. If such a pathology is detected in the early stages, then it responds quite well to treatment.
In purulent surgery
The bones of the lower leg can also be affected by purulent diseases. The most common of these is osteomyelitis. This pathology can affect all elements of the bone: bone marrow, periosteum and bone tissue itself.
Osteomyelitis can be acute, that is, occurring for the first time, or chronic. In both cases, an x-ray of the leg helps to accurately determine the focus of the pathology, assess its size, and the degree of bone damage. An x-ray is also necessary if surgery on the lower leg is planned to eliminate foci of osteomyelitis.
What is the way out? What's new in the treatment and rehabilitation of fractures?
As it turns out, he is! Recently, an effective solution to this problem has emerged - shock wave therapy, a truly unique method of treating non-united fractures and pseudarthrosis. Over 10 years of treating PCP, specialists at Avatage MC have developed their own method for treating delayed consolidation of fractures and pseudarthrosis using Storz Medical equipment, which was patented. According to our data, the effectiveness of such treatment is 100%. All patients who came to our center were discharged with recovery - the formation of bone callus.
What is unique about shock wave therapy for bone nonunion?
The shock wave acting on tissue leads to stimulation of angiogenesis (the only method in medicine!). The flow of nutrients and oxygen increases to the area of injury. Tissue healing is accelerated. When exposed to bone, osteoblasts are activated, which begin the synthesis of bone tissue. As a result of the impact of shock wave therapy on the fracture area, callus formation and bone fusion occur. We also use the shock wave therapy method as a method of preventing delayed consolidation of fractures. Metal structures are not a contraindication for shock wave therapy procedures. More than 200 people were treated at the Avatage MC with a diagnosis of delayed consolidation of fractures or pseudarthrosis. All of them received bone fusion. 12 years of our own experience in the treatment of fractures and cooperation with leading departments of traumatology and orthopedics in Ukraine allowed us to create our own methods for the treatment and prevention of delayed consolidation of fractures and pseudarthrosis.
What will an X-ray of the shin bones show?

An X-ray of the shin, like a black and white photo, shows the location of the bones of the ankle joint. Their connection, cartilage tissue, is also visualized. Joint fractures will be visualized as shadows on the white background of the bone. Tumor-like malignant neoplasms are also defined as opacities, but have unclear boundaries.
Sometimes, in order to get a clearer picture of the pathology, pictures of the lower leg are taken of two legs at once, even if only one is affected. When comparing images and their symmetry, it can be easier to find a deviation and make a diagnosis. Osteomyelitis of the leg has special signs on x-ray:
- Thickening of the bone at the site of inflammation.
- Foci of necrosis may be visualized on bones and muscles. They look like dark circles on bones or light circles on soft tissues that have an irregular shape.
- In osteomyelitis, the bone marrow canal is not visualized in the image.
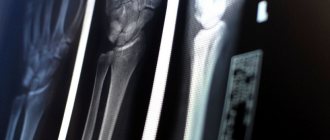
Tibia fracture
A fracture of the tibia occurs due to the impact of great force on the body of the bone and occurs at different levels. This often happens during road traffic accidents. Of all fractures of the musculoskeletal system, tibial fractures account for 23% of the total number of musculoskeletal injuries.
Classification of tibial fractures
Fractures of the bone diaphysis are classified into transverse, oblique, comminuted, fragmentary and intra-articular. Intra-articular fractures of the tibia include fractures of the tibial condyles and fractures of the medial (inner malleolus). The medial malleolus is the medial bony stabilizer of the ankle joint and fractures occur during twisting (rotation) of the leg with a fixed foot. Also often, a fracture of the inner (medial) malleolus occurs with a sharp, non-physiological rotation of the foot.
How is the procedure done?
X-ray of the ankle takes little time and does not require special preparation. The patient's body, with the exception of the area being studied, must be protected at the time of filming with a special apron that shields ionizing radiation.
An x-ray of the lower leg is taken in two projections: direct and lateral. If these projections are not enough to make a diagnosis, an x-ray is taken in oblique projections (at different angles), as well as an x-ray of the foot with a load
.
How is shock wave therapy performed to treat delayed fracture consolidation?
In case of delayed consolidation of the fracture (non-union of the bone), the procedure is performed once every 7-10 days. At the Avatage Medical Center, doctors use special attachments that stimulate the formation of callus (stimulate osteogenesis). The impact is applied to the fracture area. Doctors at the Avatage Medical Center use their own patented methods for treating and preventing delayed fracture consolidation, based on the use of Storz Medical equipment. As the famous scientist Professor G. Ilizarov said: “Tensile tension is a powerful factor that activates tissue growth. According to this pattern, it is possible to stimulate the formation of new structural units of fibrous tissue, blood vessels, skin, and bones.” Taking this into account, we force muscles to contract and stretch using biomechanical stimulation (directed local vibration therapy), which trains the muscles and makes them work without making movements. This effect complements shock wave therapy and accelerates the process of bone healing.
Decoding the results
After development, the images need to be decrypted. For this, certain indicators are used and compared with standard values:
- The arrangement of bones in relation to each other, as well as their shape and size. In cases where the bones increase when receiving load, a diagnosis of hyperostosis is made, that is, an increase in bone substance. Reduced bone size occurs with atrophy due to limited physical activity and nerve diseases.
- Condition of the surface of the shin bones. In case of oncological diseases in the lower leg area, foci of destruction of the upper layer of bone tissue are observed. The opposite situation may also occur, that is, there is ossification of the periosteum tissue, detachment.
- Structure of the bones of the lower leg. When images show shadowed areas in the white areas of bone structures, osteoporosis may be diagnosed. At the same time, the outer layer of bone is thinner, and the medullary canal is expanded. With increased bone density, osteosclerosis is diagnosed.
- The size of the gap between the joints. Uneven narrowing of this gap indicates the presence of arthritis or arthrosis.
- Foot angle. Normally it should be 130˚. Deviation from the norm is a sign of flat feet, the degree of which will be determined by the doctor.
Delayed fracture consolidation - what is it?
What is delayed consolidation of fractures (bone non-union). Most bone fractures heal (consolidate) within 3-6 months. If the fracture has not healed by this time, then doctors talk about delayed consolidation of the fracture or delayed healing of the fracture. Pseudoarthrosis (false joint, non-union fracture) is a complication of a bone fracture when the healing process of the fracture is interrupted. Fibrous or cartilaginous tissue forms between the main fragments of the fracture and therefore, even after 6-8 months, the formation of bone callus and healing of the fracture does not occur.
Causes of injury
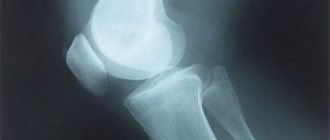
Let us first consider the mechanism of injury to the medial collateral ligament. As already mentioned, she gets injured quite often. The situation in which this occurs is a blow just below the knee from the outside of the shin. In this case, the leg is usually in an extended position and is more susceptible to injury (happens more often in football players). Otherwise, this can happen during falls, when the lower leg is fixed, and the body moves relative to it to the side with torsion on the leg (injuries of skiers and snowboarders). When the external collateral ligamentous fibers are torn, on the contrary, the blow should fall on the inner surface of the lower leg, and also excessive extension of the knee or internal rotation of the body on the supporting leg should occur.
Degrees of ligament damage
Different degrees of damage produce both differences in the clinical picture and require different treatment tactics. Highlight:
- First degree- This is a partial rupture of the surface fibers. Pain occurs at the site of deformation, and swelling is possible.
- The second is damage to most ligamentous fibers. The pain is more widespread, swelling of the joint increases quickly, may be associated with hemarthrosis, and a hematoma occurs on the lateral surface of the joint.
- The third is a complete break. In addition to the above symptoms, joint dysfunction and instability appear.
Treatment of collateral ligament ruptures
Treatment of isolated deformities of the external and internal ligaments is usually carried out using conservative methods. Here it is important to provide fixation to the joint in the first time after injury by using an orthosis. It is better to avoid stress. A course of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will relieve inflammation and relieve pain. For rapid regeneration, injections of platelet-rich plasma are used. The rehabilitation period is aimed at gradually increasing the load with strengthening the muscles and without additional injury to the lateral ligaments. Kinesiotherapy, mechanotherapy, taping and physiotherapeutic procedures are used.
Arthroscopy for ligament rupture
It happens, especially with extensive damage, that after the injury instability occurs, which worries during exercise (for athletes and other patients with an active lifestyle). In such cases, reconstruction is performed surgically. Arthroscopy is the most gentle type of surgery. In addition, recovery after it is quick and easy. Sometimes the ligament can be sutured (with fresh partial ruptures); in other cases, fixators are used to the bone if the rupture occurred at the site of attachment of the ligament to it. Another method of reconstruction is ligament plastic surgery using autografts (own tissue). The tendons of the muscles of the popliteal region are used. In the vast majority of cases, the prognosis after such operations is favorable. Patients quickly undergo rehabilitation and return to sports and normal life. When damage to the collateral ligament is combined with injuries to other structures of the knee, their arthroscopic restoration and all necessary surgical procedures are usually carried out in one operation.