In this article we will look at the difference between CT and MRI, and also find out for which studies this diagnosis can be used.
When diagnosing a particular disease, many different methods and technologies are used. CT and MRI are among the most progressive and basic modern methods of computer examination. With their help, specialists can detect pathologies of the body, as well as the presence of tumors in it. However, these methods have different methods of influence, as well as costs. We'll look at which one is best, when to use MRI versus CT, and what the benefits of each are.
What is the difference between CT and MRI, what is their difference?
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging examinations have a number of distinctive features. To understand the differences, what they show and what the difference is in using these methods, it is necessary to highlight the main characteristics of each of them. CT has the following features:
- X-rays are used for research
- During the examination, the patient receives a moderate degree of radiation exposure
- Several microdevices are simultaneously directed at the body, which influence without stopping during the entire inspection process
- The use of CT is similar to the principle of using an x-ray machine
The MRI method has the following characteristics:
- Applications of electromagnetic waves
- Anesthesia is sometimes used to examine pediatric patients.
- The effect of the device takes longer
- Exposure to electromagnetic waves is variable
- When examining a patient, movement is prohibited for the entire period of the procedure.
Which is better, more informative, more effective, more accurate, safer – CT or MRI diagnostics: comparison
When choosing a study, many patients think about the question: “What is better and what are the advantages of using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging?” In order to give an answer, it is important to familiarize yourself with the consequences, indications and stages of the procedure that accompany the examination. In general, MRI and CT are characterized by the following features.
- A similar examination method (the patient lies down on a special couch, which is placed in a spherical apparatus, where the body is examined for abnormalities and tumors).
- There are open and closed MRI (when using the first type of device, a person has the opportunity to see the entire room, so this technology is often used to diagnose patients who are afraid of closed spaces).
- CT and MRI have high image quality, so both methods can be used to diagnose almost all diseases. However, computed tomography is more effective in examining bones and large organs (stomach, lungs, kidneys).
- When examining the whole body, CT takes about 10-15 minutes, while using magnetic resonance imaging requires 20 to 60 minutes.

- To diagnose a patient using MRI, it is necessary to purchase additional one-time equipment.
- The cost of examination using computed tomography is slightly lower.
- During the diagnostic process, the patient is not allowed to move, but it is easier to undergo a CT scan because the procedure does not require much time.
- For patients with physical abnormalities, as well as large body weight, it is not always possible to perform a computed tomography scan due to the design of the device.
- Due to the use of X-rays, CT is not suitable for examining hypersensitive patients.
- It is prohibited to conduct MRI examinations on people whose bodies contain elements of any iron alloys, as well as electronic devices.
- Based on the data obtained through an MRI or CT examination, the specialist can make the same prognosis, as well as make a single diagnosis, since the information about the patient’s body will be identical.
Therefore, to answer the question: “What is better to choose?” – it is necessary to consult with your doctor and also inform him about the presence of contraindications or other concomitant diseases and injuries.
What is more harmful: MRI, CT or X-ray
In the case of MRI, there is no talk of harm at all. When undergoing radiography and CT scanning, the human body receives a certain dose of x-ray radiation.
The x-ray lasts for several minutes, the x-ray is ready in a split second. Computed tomography is accompanied by the reproduction of a series of images; the more slices, the longer the scan and the higher the load - this is the price for the high quality of the final images.
To reduce possible harm from radiation examination, special protective equipment is used (lead aprons, plates, collars).
It is possible to do an X-ray on the same day as an MRI, this is explained by the harmlessness of the second procedure. The situation is different with a combination of radiography and CT.
Since we are talking about studies that involve radiation exposure, diagnostics in a short period of time are not recommended.
Under such circumstances, it is necessary to take a break of at least 1-2 months. Conducting research in a short period of time is justified only if the benefits of diagnostics exceed the possible harm.
Advantages of MRI over CT: list
In order to determine which method is better to use for adults and children, it is necessary to understand the advantages of both methods. The main advantages are considered:
- MRI analysis data shows better images of the brain, as well as the presence of pathologies and dysfunctions in it.
- When using magnetic resonance imaging, the patient is not subject to repeated exposure to x-rays.
- MRI data better shows the nerve endings, as well as their inactive areas.
- Before using an MRI examination, the patient may be given a number of drugs intravenously to improve contrast and image quality.
Benefits of the study
- With the use of open magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to diagnose diseases in the disabled and seriously ill, as well as people who are psychologically unstable to closed, cramped spaces.
- The use of MRI makes it possible to identify bone pathologies, as well as the presence of cracks and osteochondrosis in them in the early stages.
- The use of magnetic resonance imaging has virtually no contraindications. Therefore, it can be used for diagnostic purposes for most patients, including children.
What is more expensive: CT or MRI?
It's no secret that the cost of quality medical services is not universally accessible. However, if you suspect any disease, you should not skimp on a professional examination, because further treatment and progression of pathological processes will depend on the diagnosis. When choosing between CT and MRI, it is important to consider the following factors:
- When using magnetic resonance imaging, a number of medications are often used that act on the body in such a way that the image of the results looks brighter and clearer.
- When using an MRI machine, the body is not affected by harmful X-rays, but unlike them, electromagnetic waves periodically need to be changed and repaired, which increases the cost of providing services.
- Since the MRI method requires a longer time to process the results, for young patients drugs are used to calm or induce sleep during the examination period.
Thus, we can summarize:
- Using an MRI machine is more expensive
- Exposure to electromagnetic waves is safe
- Examination using an MRI device is more informative
- The magnetic resonance imaging machine is suitable for most patients: including children, women at all stages of pregnancy (if necessary) and people with disabilities
Can MRI be replaced by CT?
Many patients are reluctant to undergo MRI examinations for many reasons, the main ones being cost and availability of the machine. After all, this device is not always available in clinics in small cities and towns. To determine whether magnetic resonance imaging can be replaced by computed tomography, the following factors must be considered:
- Exposure to X-rays can lead to more serious complications of pathologies. Therefore, CT is prescribed only if the patient has no prerequisites for cancer
- Pregnant women and children are strictly prohibited from using computed tomography
- For the diagnosis of nerve endings, brain and soft tissues, CT results will not have sufficient information
- If the patient has previously had cancer, computed tomography may trigger a relapse
- For the diagnosis of soft tissues and small vessels, the use of CT results will not be sufficient to make a diagnosis
- Due to the design features of the device, computed tomography is not possible for patients suffering from a fear of closed spaces, mental disorders, and those suffering from morbid obesity
Therefore, in order to find out about the possibility of changing the examination method, you need to consult a doctor, and also tell about the presence of concomitant diseases or attacks of claustrophobia.
The essence of MRI, computed tomography and x-rays: distinctive features
The operating principle of a computed tomograph (CT) scanner is based on X-ray radiation. The rays pass through tissues and are absorbed by the latter with varying intensities. The information processed by the computer program is translated into a layer-by-layer 3D image.
MRI uses electromagnetic radiation that passes through organs, stimulating the reaction of hydrogen compounds. The observed changes are recorded, and on their basis a three-dimensional image of the anatomical structure is formed.
Radiography (x-ray) and fluorography are based on the action of x-rays. Ionizing radiation passes through the human body until it reaches the receiving matrix.
Due to the different throughput of tissues, the output is an image (not three-dimensional) with darkened and lightened areas.
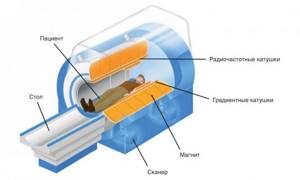
MRI
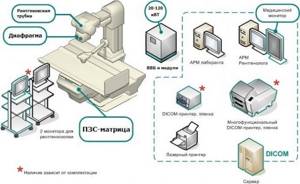
X-ray Fluorography
The difference between radiography and MRI and X-ray and CT lies in the principle of operation of the equipment and other diagnostic features:
- a few seconds are enough to carry out radiography; magnetic and computed tomography will require 10-60 minutes (depending on the examination area and type of diagnosis);
- Each of the methods is applicable for certain diagnostic purposes. X-ray radiation helps in identifying pathologies of the musculoskeletal system and bone injuries. Magnetic tomography is powerful in diagnosing infectious zones, diseases of the spinal cord, digestive system, etc.;
- X-rays and computed tomography have an adverse effect on the patient’s body, MRI does not.
Is it possible to do a CT and MRI on the same day and how long after a CT scan can an MRI be done?
To understand whether it is possible to undergo an MRI and CT examination on the same day, you need to rely on the rules for the general use of these devices:
- Magnetic resonance examination several times a year is permissible upon the direction of a doctor after heart disease, brain disease or surgery.
- CT scanning is not recommended for children. Therefore, after the initial examination, as a rule, the use of an MRI machine is prescribed.
- To conduct additional diagnostics, the interval between examinations with a computed tomography device must be at least 1 month.
- After using CT, magnetic resonance imaging is allowed, even if the studies are carried out on the same day.
Most people ask the question: “How often can an adult and a child have an MRI or a CT scan?” In order to answer this question, it is important to consider the following factors:
- Do not carry out diagnostics without a doctor's order
- The use of computed tomography more than 3 times a year is not permitted
- At the age of 3, magnetic resonance imaging is not recommended
- For early pregnant patients, using MRI with developer medications can be dangerous. However, this method is permissible in the second and third trimesters if there are prerequisites for a threat to the woman’s life
- In order to prevent diseases in adults, it is enough to conduct an MRI and CT examination once a year, if the attending physician considers this method appropriate
- Regular diagnosis using magnetic resonance imaging is acceptable if there are prerequisites for relapse of the disease, and there are no contraindications or hypersensitivity to developing drugs
Is it possible to do an MRI after surgery?
When is a tomography prescribed? Both for the diagnosis of “global” processes (study of organs and systems), and specific ones (carrying out ultra-fine diagnostics of diseases of each organ). The method is used in preoperative and postoperative diagnostics.
Tomography before and after surgery
The main form of using the achievements of modern tomographic diagnostics is preoperative diagnostics (if we are talking about diseases that require active influence on the patient in order to cure him). However, postoperative studies are increasingly being used in clinical practice, especially where the problem of choosing a tactic – conservative or active surgical – is fundamentally solved.
MSCT - what kind of examination is this? Advantages and disadvantages
What can be said about modern MSCT systems? Speed, reliability, high spatial and temporal resolution, high throughput of rooms, ease of burden for the patient, no feeling of enclosed space.
The only drawback – “no matter how you look at it” – is that the study is based on the X-ray principle, which means it involves ionizing radiation. Therefore, it is not recommended to use it for a short time.
But there are life situations when diagnostics are indispensable, and everyone understands this, and then they consciously decide to perform an X-ray tomographic examination. Such decisions are made collectively, by a council.
There are also inevitable conditions when, even if there is a very strong desire to use magnetic resonance imaging, one has to perform a CT scan. For what reasons? First of all, this:
— known limitations of the MRI method;
- second - restrictions that appeared as a result of surgical intervention (application of clips, special allografts), which can cause artifacts during an MRI examination, or even threaten the patient’s health (leading to local heating of tissues);
— the third limitation is the serious condition of the patient and the not always available auxiliary equipment made of special materials that allow the use of this equipment directly next to the tomograph (for example, anesthesia machines, devices for monitoring the patient’s vital functions, trolley beds, etc.). Iron structures are not acceptable for use inside MRI treatment rooms.
MRI or MSCT: which is better?
With MSCT, you can quickly and reliably contrast the gastrointestinal tract and see the movement of the contrast agent along it. This study is not informative with MRI.
When performing multislice computed tomography, isotropic image reformation is possible, and this is a post-processing function of working with the image. With MRI, images that are not similar to axial ones must be obtained during the examination (if the doctor did not think of performing the sequence in a certain plane, there will be no images).
The phases of contrast enhancement during dynamic scanning with MSCT are clearer. With MRI, the arterial phase is not always comparable with the arterial phase with MSCT.
MCT allows you to make three-dimensional reconstructions, very different and with greater effect than with MRI, in which this is still a very limited scope of application - only three-dimensional scanning is possible (that is, the initial collection of “volumetric data”). And with MSCT, reformation is done post-processor, as desired and necessary.
MSCT also wins when assessing the duration of the study.
The disadvantage of MRI is the “interposition” of fluid structures when constructing MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography) images. At the same time, this factor has no significance with CT.
Angiography of the distal bed and studies of the whole body are an advantage (for now) over CT. At the same time, MRI has additional capabilities - for example, the use of diffusion-weighted images. Magnetic resonance imaging can produce non-contrast angiography images, but CT cannot.
In fact, postoperative examination questions require almost the same answers as in the preoperative period. The difference is that in the postoperative period, on CT, residual tumor tissue, for example in the liver, may not be differentiated from the area of inflammation (and with MRI such differentiation is possible).
So what should you do: what to choose - MRI or CT? Where to begin?
If possible, you need to start with an MRI (and, preferably, complete the diagnostic process). There is no such possibility - we will follow the principle known from childhood: “The nut of knowledge is hard, but still we are not used to retreating! The newsreel “I Want to Know Everything!” will help us split it. (Igor Razdorsky)." And in our case, we will call on the good old method of computed tomography, proven over the years, to help.
Author: Karmazanovsky Grigory
What is better to do for adults and children: MRI or CT?
To determine which of the two diagnostic methods will be most effective, it is important to first consult with your doctor. Indeed, in the case of each individual disease and the rate of progression of the disease, the specialist independently decides on the advisability of using one or another method. To summarize, the following factors can be identified:
- CT scans are not permitted for children under 3 years of age
- For women with a pregnancy of 2 trimesters or more, the use of MRI is more effective and safer
- When examining the body for pathologies of bone tissue and internal organs, it is recommended to carry out CT diagnostics
- Magnetic resonance imaging is more expensive, but it is more effective and safe
- CT and MRI can be done on the same day
- The use of computed tomography is not allowed more than 3 times a year
Thus, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- MRI is safer for health because it does not use X-rays
- Examinations using computed tomography are faster
- MRI can be used for both children and adults
As you can see, both CT and MRI are necessary studies that are carried out quite often nowadays. Both CT and MRI have their advantages and disadvantages, so before going for an examination, consult your doctor, tell him about your health status and get a referral from him.
Combination of X-ray and CT: is there a danger?
It is undesirable to do a CT scan after radiography, since both methods are based on X-ray radiation, which is harmful to the patient’s health.
It is necessary to delay diagnosis for 1-2 months. If it is impossible to organize a break, resort to CT immediately after an x-ray only if the diagnostic benefit outweighs the harm.
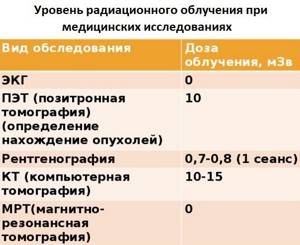
If it is necessary to perform repeated diagnostic procedures based on X-ray radiation, they rely on the maximum permissible annual exposure for the population - 5 mSV. Use the “Dosimeter” to determine the examination dose.
In general, X-ray scans are performed once a year. If there are grounds for an additional procedure, the diagnosis is carried out as many times as is permissible in a particular case.
Important! The radiation dose received depends on the equipment used, the organ being examined and the number of images taken.