As one of the best methods of hardware diagnostics, which has great information content and accuracy, magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joints solves many medical problems. It helps doctors detect even the smallest changes, study pathological foci in detail in a three-dimensional image, absolutely accurately determine the localization of the process and clearly see the boundaries between it and healthy tissue.
The use of MRI of the sacroiliac joint is especially important in rheumatology, neurology and hematology, when specialists can describe in detail all pathologies at the very beginning of diseases, and thereby prevent the development of serious complications and preserve their patients’ health, mobility, and sometimes life for a long time.
Where is the sacroiliac joint located?
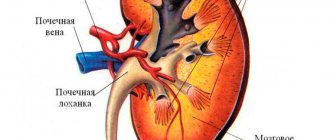
The sacroiliac joint is a large, inactive joint formed by the ear-shaped surfaces of the sacrum and ilium, covered with dense fibrous cartilage. The sacroiliac joint is the most mobile in young children. With age, due to increasing vertical loads, the joint becomes stronger - ridges and depressions form on the articular surfaces, overlapping each other. The stability of the joint is also ensured by powerful ligaments, which are stronger than the pelvic bones.
The main function of the joint is to absorb shock loads, support the spine, and rotate the belt of the lower extremities relative to the spine within 2-18 degrees. The joint is also directly involved in walking.
Diseases of the sacroiliac joint
Sacroiliitis is inflammation of the sacroiliac joint. Serves as a characteristic sign of rheumatoid arthritis and other joint pathologies, ankylosing spondylitis. Sacroiliitis is one of the diagnostic criteria for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Inflammation can also be a sign of brucellosis, degenerative-dystrophic phenomena (arthrosis, osteoarthritis). Sacroiliitis leads to pathological mobility (instability) or ankylosis (pathological fusion) of the sacroiliac joint. Dysfunction of the joint becomes a source of constant pain.
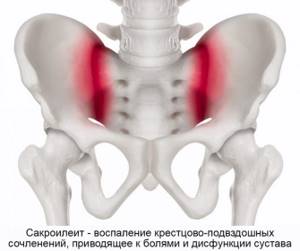
The area of the sacroiliac joint can be affected by tumors, metastases in the pelvic bones, or an infectious process (osteomyelitis).
Indications
Symptoms indicating the need for MRI diagnostics of the sacroiliac joints:
- A history of congenital structural anomalies, disseminated encephalomyelitis, sclerosis, infectious lesions of the pelvic organs.
- Decreased flexibility of the lower spine.
- Sudden attacks of lameness that occur after prolonged sitting at a desk or improper distribution of load during physical activity.
- Pain in the lower abdomen and sacral region, spreading to the legs.
The following factors are also indications for MRI:
- Injuries of the pelvis and lumbosacral spine.
- Suspicion of tumor development, penetration of metastases, inflammation of bone and soft structures.
- Analysis of pathology dynamics.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of conservative treatment.
- Determining the feasibility of surgery and preparing for surgery.
- Postoperative control.
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the sacroiliac joints
MRI of the sacroiliac joint is recommended if the patient has the following complaints:
- pain in the lower back, in the buttocks, sacrum, radiating to the thigh - a sign of sacroiliitis and instability of the SIJ;
- the pain intensifies when a person stands or sits for a long time, when turning the body, walking for a long time, when trying to change position, or get up from a chair;
- a characteristic symptom is the occurrence or intensification of pain when climbing stairs, transferring the weight of the body from one leg to the other, trying to roll over while lying in bed;
- limited mobility of the spine;
- the presence of space-occupying formations, edema, swelling, nodes and bumps, determined visually or by touch.
MRI of the sacroiliac joint is prohibited if there are contraindications:
- pacemakers, defibrillators, cochlear implants and other medical devices implanted into the patient’s body are an absolute contraindication, unless the implant is made of MRI-compatible materials;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed in patients under 5 years of age and in pregnant women in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- foreign bodies made of magnetic metal are also an absolute contraindication for MRI (this especially applies to small pieces of metal in the eyes, steel clips on brain vessels, fragments and fragments of ammunition);
- patient weight more than 130 kg and/or body circumference more than 150 cm is an obstacle to research due to inconsistency of anthropometric data and the size of MRI equipment;
- severe claustrophobia.
Contraindications
MRI is one of the safest diagnostic methods. However, despite this, there are a number of absolute contraindications that exclude MRI diagnostics:
- Functioning pacemakers.
- Metal implants of any location.
- Vascular clips of the brain.
Other contraindications, such as pregnancy, the presence of peripheral or central neurostimulators, internal hearing aids and insulin pumps, are relative, that is, the study can be performed when the expected high value of the results for the treatment process.
In addition, it is worth noting that the maximum permissible load on the tomograph installed in our clinic is 170 kg.
Preparing for MRI of the sacroiliac joints
It is very important to remember that magnetic resonance scanning, despite the lack of preparation required, has a number of requirements. Before the study, patients must leave all unnecessary items in the storage room - this especially applies to jewelry, piercings, any metal objects, phones and gadgets. The powerful magnetic fields generated during an MRI can damage electronics and heat metal, causing burns.
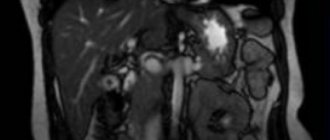
Magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joints with contrast
MR imaging of the SIJ supports the use of contrast enhancement. This technique involves the introduction of a special contrast agent into the patient’s blood, which accumulates in pathologically altered tissues due to inflammatory diseases and tumors. The use of contrast greatly facilitates the diagnosis of diseases of the sacroiliac joints and increases the information content of the study, especially in controversial cases.
The effectiveness of treatment depends entirely on the quality of diagnosis!
Indications for this examination are:
- the presence of a genetic predisposition to the occurrence of ankylosing spondylitis;
- suspicion of ankylosing spondylitis;
- partial manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis – sacroiliitis;
- long-lasting pain syndrome due to osteochondrosis, which is not relieved even by anti-inflammatory drugs;
- the presence of inflammatory diseases of the lower extremities;
- chronic back pain, which results in decreased performance;
- presence of injuries to the pelvic bones or lower back;
- decreased mobility and flexibility of the spine.
What does a magnetic resonance imaging scan show:
- expansion of the joint space;
- the location of foci of inflammation in the discs, joints, and spinal cord;
- pockets of salt deposits;
- the presence of bone growths;
- presence of tumors;
- presence of injuries.
MRT24 centers are ready to receive you at a time convenient for you and guarantee that we have an affordable price for all types of services. You will be able to do an MRI of any part of the body and receive a detailed explanation of the diagnosis. Addresses and prices are listed on our website. If a simple diagnosis is not enough, our specialists will be able to carry it out using a contrast agent. Contact us if you are interested in high-quality diagnostics and its reasonable cost.
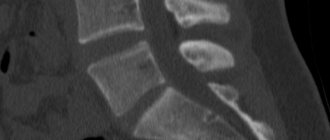
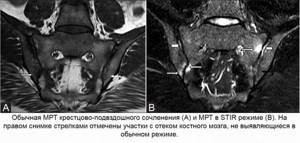
MRI of the sacroiliac joint in STIR mode
Magnetic resonance imaging is not one study, but a whole complex of algorithms, modes and programs used to diagnose diseases. The STIR mode is one such algorithm, suppressing the signal from adipose tissue and detecting sacroiliitis in the early stages, when inflammation manifests itself only as bone marrow edema. Other diagnostic methods are not able to detect sacroiliitis at the very beginning, which ultimately worsens the prognosis and prevents effective prevention of complications.
How is magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joint performed?
MRI is carried out using a tomograph - a device in the form of a cylinder lying on its side, with a short and wide tunnel in the center. This tunnel is the working part of the installation; the patient is in it during the study. For this purpose, there are guides in the tunnel along which the table for the patient moves.
Before starting the study, you need to make sure that you have left all foreign objects, especially metal objects, in the storage room. Then, after going into the room with the tomograph, with the help of the medical staff, the patient is placed on the table. It is recommended to wear headphones on your ears - they muffle the rather loud sounds of the tomograph operating. To make the examination more comfortable, they also broadcast calm music and convey the operator’s instructions.
The duration of MR imaging of the SIJ is 15 minutes. If contrast enhancement is required, the procedure lasts 30 minutes. After completing the study, you need to wait no more than 30 minutes until the doctors decipher the images.
MRI technique
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
An MRI examination is performed in a special room that houses an MRI system, or “scanner.” You will be escorted into a room by a medical professional and asked to lie down on a special retractable table that will slowly slide out of the scanner. A typical scanner is open at both ends.
In general, when preparing for an MRI exam, you may need to use earplugs or hearing protection because certain scanners may produce loud noises. These loud noises are normal and should not be a concern.
If it is necessary to study with a contrast agent during the examination, the x-ray technician controls the extension of the table from the scanner to introduce contrast.
The most important thing for the patient to do is to relax and lie still. Most MRI scans take between 15 and 45 minutes. You will be told in advance how long the scan will take. During the examination, the x-ray technician will be able to talk to you, hear you, and observe you at all times. If the patient has questions or a feeling of fear and anxiety, it is imperative to report this using a special signal bulb. Once the procedure is complete, you may be asked to wait while the images are reviewed to determine if more images are needed for an accurate and correct diagnosis. After the scan, the patient has no restrictions and can safely carry out his usual activities.
What will an MRI of the sacroiliac joints show?
Any patient wants to know what is visible on an MRI of the sacroiliac joints. Therefore, we provide a consultation with a radiologist to each of our patients - a specialist in the field of MRI diagnostics will show you your images, tell you what changes and signs were detected, what diseases they may correspond to. If you have had an MRI before, take the old images with you - this will allow you to compare them with the new ones and find out whether there are positive or negative dynamics in the development of the disease.
Interpretation of MRI of the sacroiliac joints
In a series of layer-by-layer photographs taken in several projections through the area of the sacrum and pelvis, it is easy to see the SIJs themselves, their articular surfaces and articular cartilages, the joint cavity, the surrounding ligaments and tendons, as well as the pelvic bones. An MRI diagnostic doctor, looking at the images, pays attention to deviations from the norm, signs of inflammatory changes, narrowing of the joint space, and the presence of effusion in the joint cavity. In STIR mode, signs of sacroiliitis in the form of bone marrow edema can be detected. When contrast is used, the dynamics of its accumulation and release from tissues are assessed. The presence of gross changes in the form of tumors, osteomyelitis, osteoporosis, etc. is excluded. The information received after decoding the images is included in the conclusion.