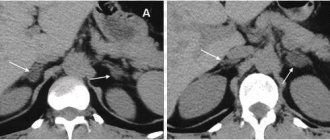
Author: Strokina O.A., therapist, functional diagnostics doctor. December, 2021.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a very common diagnostic method for diseases of the cardiovascular system. The examination allows you to obtain the most accurate data on the condition of tissues, organs and blood vessels, as well as establish a diagnosis, predict the further development of the disease and develop an effective treatment regimen.
MRI of the heart, with a competent and timely approach, can significantly facilitate diagnosis, and therefore increase the patient’s chances for a speedy recovery.
The main and important advantages of this study are:
- non-invasiveness – the ability to obtain accurate data without surgical or other external influences;
- the ability to visualize the heart in various planes using computer processing of the received information;
- simultaneous analysis of moving blood with assessment of speed and other functional features;
- obtaining high contrast and clarity images.
MRI diagnostics is based on the interaction of a magnetic field, high-frequency radio waves and hydrogen atoms in the human body, and the use of modern computer technologies makes it possible to create a 3D model of the heart and determine the exact location of the pathology. A minimal list of contraindications and a short duration of the procedure make MRI the most popular type of examination.
The ability to diagnose heart disease using MRI is impressive.
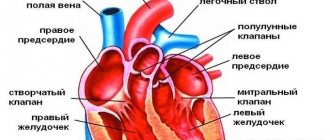
- Using "gradient echo" you can quickly assess the condition of the coronary arteries, valves and ventricles of the heart.
- The spin echo method is indispensable when studying large vessels and cardiac chambers.
- Cine-MR tomography allows you to combine and arrange all phases of the cardiac cycle into a single picture.
- Cardiac MRI with contrast can be used to predict heart attacks and assess post-infarction changes.
- The phase-contrast MRI technique allows you to measure the speed of blood flow.
- Magnetic resonance angiography provides a three-dimensional image of the heart and allows assessment of damage to large vessels.
Indications for cardiac MRI
Only a qualified specialist can tell you whether an MRI is necessary. A cardiologist will insist on this study in the following cases:
- the presence of acquired (after previous diseases - rheumatism, atherosclerosis, endocarditis) or congenital heart defects;
- suspicion of diseases of the coronary vessels and aorta;
- inflammatory heart diseases (pericarditis, myocarditis);
- coronary heart disease (CHD);
- diagnosis of tumors and other space-occupying formations in the heart;
- cardiomyopathy;
- pathology of the right ventricle (poorly visualized on ultrasound of the heart);
- storage diseases and other myocardial pathologies (hemochromatosis, amyloidosis,)
- examination of the pulmonary arteries;
- examination after heart surgery.
It is worth noting that MRI is an absolutely safe (in the absence of contraindications) procedure, which makes it stand out among X-ray examinations (computed tomography, coronary angiography) and has no age restrictions. It can also be performed on children from 5 years of age. Moreover, the possibility of MRI diagnostics often depends not on the patient’s age, but on his ability to lie still during the examination.
Types of equipment
There are several types of equipment on which diagnostics are carried out. There are open and closed devices. Tomographs are also divided into:
- low-floor - power up to 1 Tesla, usually 0.3 - 0.4 T;
- high-field - power 1.5 - 3 Tesla.
Some experts also highlight 1 Tesla mid-field devices.
The higher the magnetic field strength, the better the quality of the resulting images. Open devices have low voltage, so choosing such a tomograph is not always advisable. Always consult your doctor before going for an examination so as not to waste extra money and time redoing the tomography using other equipment.
Contraindications
The examination procedure itself is usually well tolerated by patients and does not cause much discomfort. However, there are a number of contraindications, absolute and relative, that may interfere with its implementation.
The first group of contraindications makes the procedure impossible. These include:
- the presence in the patient’s body of various devices and metal products for medical purposes (pacemakers, intracardiac catheters, insulin pumps, vascular stents, clips, steel endoprostheses, etc.) - the magnetic field can lead to heating of individual elements, causing device failure or displacement, which will cause injury to surrounding tissues;
- increased body weight (over 120 kg) – the patient’s waist is incommensurate with the diameter of the device.
The second group of contraindications makes the procedure possible subject to strict adherence to a number of conditions and recommendations of the attending physician:
- fear of confined spaces;
- pregnancy (first trimester);
- nervous and mental disorders;
- serious condition due to any illness;
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation (usually III, IV functional classes);
- the patient's inability to remain completely still;
- the presence of tattoos with metal-containing dyes.
List of tests (laboratory diagnostics)
| Clinical blood test | |
| Complete blood count with leukocyte formula |
| Biochemical blood test (advanced) | |
| Glucose | |
| Bilirubin total | |
| AST (AST, aspartate aminotransferase, AST, SGOT, Aspartate aminotransferase) | |
| ALT (ALT, Alanine aminotransferase, alanine transaminase, SGPT, Alanine aminotransferase) | |
| Creatinine | |
| Urea (Urea) | |
| Uric acid | |
| Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT, glutamyl transpeptidase, GGT, Gamma-glutamyl transferase) | |
| Total cholesterol (Cholesterol, Cholesterol total) | |
| Triglycerides | |
| HDL Cholesterol (High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol, HDL Cholesterol, α-cholesterol) | |
| Cholesterol-LDL (Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL, Cholesterol LDL, β-cholesterol) | |
| Total protein (Protein total) | |
| Iron (Fe, Iron) | |
| Alkaline phoshatase | |
| Potassium (K+, Potassium), Sodium (Na+, Sodium), Chlorine (Cl-, Chloride) | |
| Homocysteine | |
| C-reactive protein (CRP, CRP) | |
| Magnesium (Mg, Magnesium) | |
| Total calcium (Ca, Calcium total) | |
| Creatine kinase (Creatine phosphokinase, KK, KFK, CK, Creatine kinaze) |
| Thyroid function | |
| Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH, thyrotropin, Thyroid Stimulating Hormone, TSH) | |
| Free thyroxine (free T4, Free Thyroxine, FT4) | |
| Free thyroxine Antibodies to thyroglobulin (AT-TG, anti-thyroglobulin autoantibodies) | |
| Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (AT-TPO, microsomal antibodies, anti-thyroid peroxidase autoantibodies) |
| Blood coagulogram | |
| APTT (APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time, cephalin-kaolin time, Activated Partial thromboplastin time, APTT) | |
| Fibrinogen | |
| Prothrombin, INR (prothrombin time, PT, Prothrombin, INR) |
| Clinical urine analysis | |
| General urine analysis | |
Preparation
No special preparatory procedures are required for cardiac MRI. Only tomography with contrast is performed strictly on an empty stomach.
Before the examination, the patient removes all jewelry, watches and other metal objects that may affect the operation of the device. Also, the doctor conducting the examination must make sure that the patient does not have implants containing steel (prostheses, catheters, etc.).
The subject will be asked to wear a special uniform made of cotton fabric and use earplugs or headphones to protect their hearing from the various noises of the operating device.
Patients suffering from fear of confined spaces or other nervous disorders should take a mild sedative before the procedure, and patients with acute pain should take a painkiller.
Methodology
The person lies on the MRI capsule transport table on his back. Special electrodes are attached to the patient's chest, and if necessary, an intravenous catheter is installed in the ulnar or subclavian vein to administer a contrast agent. The procedure requires complete immobility of the patient, so the patient’s limbs and chest are fixed with special fasteners.
The procedure is completely painless and safe. However, people with very serious diagnoses are usually examined, and excessive anxiety before and during the examination can worsen their condition. In this case, the patient can always report his health to the doctor using the two-way communication system built into the MRI scanner.
The duration of cardiac MRI depends on the complexity of the examination and can range from 10 minutes to 1 hour.
Detectable changes on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the chest
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the chest may show the following abnormalities in the heart, lungs, or chest:
- developmental anomaly and acquired pathology of the pulmonary vessels (arteries, veins);
- developmental anomaly and acquired pathology of the lymph nodes of the chest;
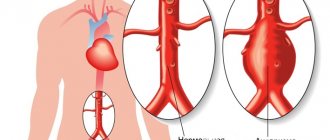
- dissection of the aortic walls;
- stenosis (narrowing) of the aorta;
- myxoma (tumor) of the atrium;
- defect in the atrial septum;
- developmental anomaly and acquired pathology of the bronchi;
- cardiac tamponade (blood or effusion in the pericardial cavity);
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD, COPD);
- caorctation (narrowing of the lumen) of the aorta;
- constrictive pericarditis (“shell heart”);
- cystic lung disease;
- esophageal tumors;
- ischemic cardiomyopathy;
- lung tumor (lung cancer);
- mitral regurgitation (acute and chronic);
- mitral valve prolapse;
- pathological masses and tumors in the chest cavity;
- pericardial effusion (fluid in the pericardial cavity);
- pericarditis (inflammation of the heart sac);
- pathological changes in the pleura - thickening of its petals during pleurisy and effusion in the pleural cavity;
- pulmonary edema;
- restrictive cardiomyopathy;
- obstruction (blockage of the lumen) of the superior vena cava;
- thoracic aortic aneurysm;
- thymoma or tumor of the thymus gland (cancer of the thymus gland);
- sternum tumors.
The obtained data from the results of MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the chest organs are further analyzed by the patient’s attending physician, who develops a plan for the necessary additional examination and treatment.
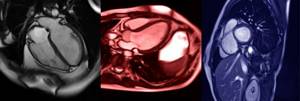
Cardiac MRI in T2W and DWI mode.
MRI of the heart, showing the three phases of the heart.
Possible complications after MRI
The MRI procedure in most cases does not cause discomfort or side effects, with the exception of:
- slight physical discomfort in a state of immobility during a particularly long examination;
- fear and fear of loneliness in the patient (occurs in 1 out of 20 cases);
- unpleasant sensation from the installation of an intravenous catheter;
- allergic reaction to a contrast agent (occurs extremely rarely, less than 1% of all subjects react);
- an increase in the temperature of the scanned body area (considered normal).
Important! Breastfeeding women are advised to wean their baby for 2 days after an MRI with contrast.
How is the procedure done?
A CT examination of the heart and coronary vessels lasts about 5-15 minutes, depending on whether contrast was used. If a contrast agent was injected, the doctor will take longer to examine the heart and adjacent blood vessels. During the examination, the mobile table of the tomograph slides into the ring of the device, the device produces X-ray radiation and makes a slight noise. The patient will not experience any discomfort, since the method does not require surgical intervention in the body.
CT scan of cardiac vessels with contrast
CT scan of blood vessels and heart with contrast agent is needed in rare cases, usually these include suspected cancer. The contrast accumulates in the affected tissues and makes it possible to assess the presence, size and location of the tumor. The procedure will be useful if it is necessary to find out whether the neoplasms are primary or grow from another organ. If there is no suspicion of a tumor, CT does not require contrast, since the procedure is already very informative.
Cardiac MRI results
After the examination is completed, the results are given to the patient, who hands them over to the doctor who ordered the MRI.
The doctor, by analyzing layer-by-layer images of the heart and blood vessels, can assess the state of coronary blood flow, study the functional characteristics of cardiac activity and note changes in the functioning of the heart chambers. In addition, MRI of the heart allows you to identify defects of the interventricular and interatrial septa, various space-occupying formations and congenital malformations, as well as assess the localization and degree of development of atherosclerosis.
Alternative methods for examining the heart
The MRI technique has much in common with ultrasound (US) and X-ray computed tomography (CT) in terms of the principle of scanning tissues and internal organs, processing and obtaining their images. However, the MRI method has some advantages. This:
- safety of the procedure for all groups of patients, including pregnant women and children;
- increased image contrast, available thanks to the special “sensitivity” of the device;
- the ability to examine even small objects (less than 1 centimeter);
- the ability to study in detail both longitudinal and transverse sections and create a three-dimensional model of organs.
That is why today MRI is the “gold” standard, the most informative and health-safe diagnostic method. However, due to the much higher cost of the examination, MRI is still only the second line in diagnosing the disease after echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart).
Sources:
- Bacca M.S. MRI is the “gold standard” in assessing the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels. — Remedium Privolzhye, 2021.
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology Ed. A.J. Camm, T.F. Lyushera, P.V. Serrius. Translation from English / Ed. E.V. Shlyakhto “GEOTAR-Media” 2011