Content
- What does a TRG image show?
- Types of teleradiogram
- How is diagnostics carried out?
Teleroentgenogram (TRG)
is an innovative x-ray examination used in dentistry, most often before orthodontic treatment or before surgery. With the help of TRG, the doctor can conduct a diagnosis before complex dental treatment, look in detail at all parts of the skull, the location of the upper and lower jaw, the position of the teeth, and occlusion anomalies. TRG is conducted for adults and children.
Advantages of teleradiography:
- Safe examination with minimal radiation exposure
- Accurate and comprehensive examination (bone and soft tissue)
- Instant ready results
- The further treatment plan can be calculated using a special computer program.
Diagnostics in orthodontics: what does it include and why?
Orthodontics is a rather isolated specialty in dentistry. When planning treatment, the orthodontist must have maximum information about the pathology he wants to treat. Often, orthotherapy begins without a thoughtful analysis of the problems, and the results of such treatment are quite disastrous. High-quality treatment is not possible without analysis, and analysis without the necessary diagnostic data. Which ones exactly?
A good orthodontist can tell a patient little at the first consultation other than a general introduction to his orthodontic problem and the general mechanisms for getting rid of it. If the patient is ready for treatment, then at the first meeting it is also possible to collect all the necessary diagnostic information:
1. Orthopantomogram (OPTG)
2. Teleroentgenogram (TRG) in the lateral projection (additionally in the direct projection - according to indications)
3. Dental scan or regular impression to obtain jaw models
4. Photography (portrait and intraoral photographs)
5. Computed tomogram (CT) according to indications
6. Sometimes video recording to record functional malocclusion.
Quite a lot, right? Moreover, the first 4 points are the bare minimum for any situation. If the doctor does not do any of this, he deprives himself of important information strictly necessary for analysis.
There are many ways to move teeth, and a doctor can do almost anything while a patient has braces, aligners, or other means of moving teeth on their teeth. But the question is where and how to move them. This is precisely what the results of in-depth diagnostics answer. Orthodontic treatment is a clearly planned sequence of actions, and not an action “where the curve leads.” Even before fixing the equipment, the doctor must imagine the result of the treatment and the path that will lead him and the patient to success. There may be changes in plan during the treatment process, because medicine has never been measured in absolute terms. But there must be a general line. Unfortunately, we have to see how patients are treated by braces, and not by doctors. Just thoughtlessly pasted equipment will not only not give any result (at best), but can also aggravate the problem or cause new ones (at worst). Therefore, the doctor must have an action plan... where to go:
Panoramic photograph of teeth (OPTG)
For many doctors, this photograph has already become mandatory when “getting to know” a patient; it is necessary for a therapist, a surgeon, and an orthodontist. A panoramic photograph gives the doctor a lot of information about the condition of the roots of the teeth, the presence of wisdom teeth, impacted teeth, the absence of teeth, the presence of supernumerary teeth, and the condition of the bone tissue. Taking into account the OPTG data, the doctor can draw up a competent treatment plan.
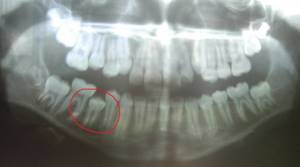
In this case, during the initial examination, one may suspect the absence of a permanent tooth germ. However, on OPTG it is visualized in bone tissue. And the reason for the delay in eruption is even visible - lack of space in the dentition.
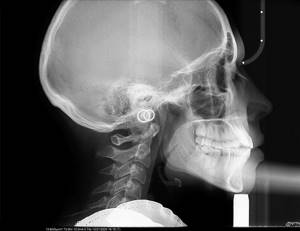
TRG in lateral projection
This is an X-ray "photograph" of the head in profile.
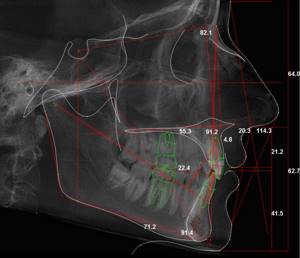
This is the second required photograph for the orthodontist. No competent doctor will allow himself to do without it. Unless for the treatment of a small child. Why is it needed? To carry out a number of calculations, distances and angles are measured, parameters are calculated using formulas, which determine the plan for further treatment. Of course, I will not go into details of the calculations, because the purpose of the article is to clearly convey to the patient the need to undergo orthodontic diagnostics, and not to teach them to make orthodontic diagnoses on their own;).
I will allow myself just a small educational program... Not every bite pathology can be cured by an orthodontist alone. There are patients who need orthognathic surgery. What does it mean? This means that the orthodontist has a limit to what he can do. And the lateral TRG gives him a chance to understand where the pathology is - within the range of his capabilities or beyond... Imagine that the upper jaw in the skull is located too anteriorly, and the lower one posteriorly.
In this case, the orthodontist must push the upper teeth back and push the lower teeth forward, but he can only do this a certain distance, which is always limited by the size of the jaws. At the diagnostic stage, it is important to calculate how much distance the teeth need to travel. In the calculation of TRG there are certain indicators that clearly limit the doctor in solving such a problem. If the value N is greater than the standard value, then STOP!!!! This cannot be done without surgery; the position of the jaws must be corrected at the skeletal level. This means you can’t expect good treatment without surgery. The doctor should warn the patient about this before starting treatment.
TRG in forward projection
This is a “photograph” of the patient in X-rays, but from the front.
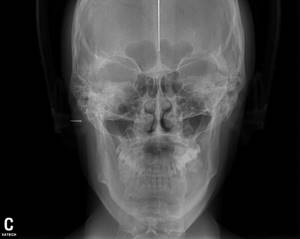
With facial asymmetry, it is important to determine the cause: it may lie in the incorrect position of the teeth, which “do not allow” the lower jaw to stand correctly. But the situation may be more serious, when facial asymmetry is dictated by the incorrect position of the upper jaw in the skull or different sizes of the right and left halves of the lower jaw.
In this picture we clearly see the asymmetry of the jaw bones:
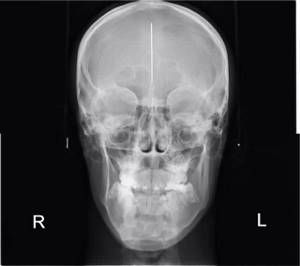
It is important to carry out a diagnosis and promptly (even before the start of treatment) warn the patient about what the orthodontist can correct and what is not within his competence. For example, only a maxillofacial surgeon can change the position of the jaws in the skull or their asymmetry. And if the doctor does not carry out some stages of diagnosis, then he will never be able to overcome the problem without knowing it in person. We get an unexpected result... and this is just a lack of diagnostic material and our Russian “maybe it will somehow resolve itself.”
Calculation of diagnostic jaw models.
To plan orthodontic treatment, it is necessary to take impressions of the dentition. I do this using a modern 3D scanner. Next, the models are calculated in a special computer program.
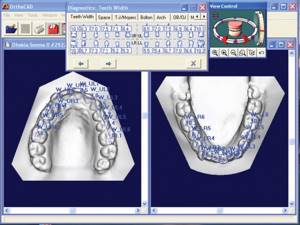
I will talk separately about the conveniences and advantages of computer analysis of virtual models, virtual treatment planning and its visualization. Today, it is important to understand why an orthodontist studies jaw models at all.
If an impression is taken from the teeth using the traditional method, then a technician in the laboratory casts plaster models, and after that they are calculated.
The doctor identifies the true size of the jaws (whether there is potentially enough space for all the teeth, or whether teeth will have to be removed to free up space). At this stage, it is important to compare the size of the front teeth on the upper and lower jaws. To help the doctor, there are special formulas that can be used to calculate the size of the teeth. If the situation does not correspond to normal sizes, then the width of the teeth is corrected, and the doctor should also talk about this during a follow-up consultation.
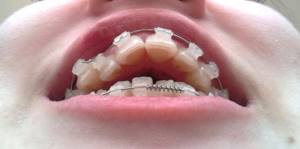
Photos
The most common motivation for ortho treatment is to improve the appearance of your smile. And only a few can guess that the shape of the lips, profile, severity of nasolabial folds and even the presence of a double chin can depend on the bite. By analyzing portrait photographs, the doctor can and should predict changes in his appearance after treatment.
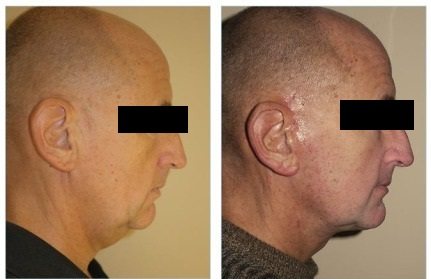
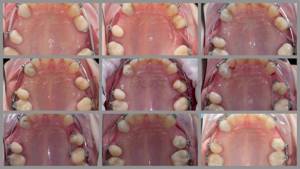
Intraoral photographs are necessary at each stage of treatment to track its progress. At an appointment, it is not always possible to assess the progress of tooth movement in all details. A static photograph allows the doctor, in a calm environment, to thoughtfully analyze the progress of treatment and notice even minor nuances in order to eliminate them in time. For example, in this photoset the progress of the movement of premolars is clearly visible.
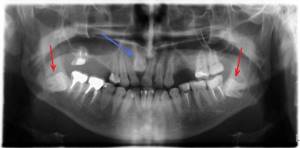
Computed tomogram (CT)
In some cases, the doctor may need a CT scan. Only in this image will we be able to assess the spatial arrangement of the teeth relative to each other; this is necessary when planning the movement of impacted teeth, when it is extremely important to understand which tooth lies more superficially and to choose the correct vector of movement so as not to touch the roots of other teeth. On OPTG, it is possible to assess the position of the tooth only in one, frontal plane.
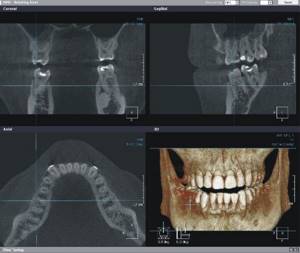
Another common indication for CT is moderate to severe periodontitis. A CT scan can reveal the periodontal condition of an individual tooth, which will help the doctor determine whether the tooth can be moved and in which direction. On a CT scan it is possible to see the inclination of the tooth: it happens that the teeth are already at their maximum inclination, and its further increase can lead to tooth loss.
Video shooting
To record dysfunctions of swallowing and chewing, the doctor needs video recording; video material at the end of treatment can be compared with the situation before treatment.
So, the first thing a potential orthodontic patient needs to remember is that the diagnosis and treatment plan on the day of treatment is bad manners. That is, in addition to complaints, the doctor must study your pathology inside and out... and only then start thinking about a solution. Not frantically on the first day of meeting, but some time later, after assessing the OPTG, calculating the TRG and aesthetic analysis of photographs, at a minimum. Only by bringing together the data from these studies can a competent treatment plan be drawn up. In this case, the virtuosity and speed of decision-making does not depend at all on the doctor’s experience: he has already been working for 100 years or 1 year. Nowadays, in times of fierce competition, some clinics have a policy of “tying the patient” on the day of the initial appointment. And doctors are forced to fulfill the working conditions dictated by the employer: a ready-made diagnosis and treatment plan, immediate prepayment for the hardware and off they go. Just to leave the patient... Don't get hooked!

Author of the article: orthodontist Daria Kostina
What does a TRG image show?
- Structure of the maxillofacial region
- Ratio of bone and soft tissue sizes
- Bone structure, defects
- Position of the upper and lower jaws relative to each other and the base of the skull
- Jaw angle
- Absence or presence of bite pathologies
- The location of the teeth, their inclination, the degree of tooth displacement
- The presence or absence of asymmetries of the facial part of the skull
- Detection of inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues, sinuses, jaw joints.
- Detection of hidden injuries of the dental system
The use of TRG diagnostics is carried out to determine an accurate diagnosis, formulate a further treatment plan, using the most suitable orthodontic structures, and the ability to control how the treatment proceeds.
Indications
Pathologies of the structure of the jaws and teeth
- Bite correction
- Determining or clarifying the diagnosis
Contraindications
- Bleeding
Types of teleradiogram
- Frontal or direct projection
, the picture is taken from the front, from the side of the face and the back of the head. Based on the results, the doctor will be able to determine the symmetry of the face, the structure of the dentition, the relationship of the upper and lower jaw, the presence of inflammatory processes, injuries - A lateral view
is a profile shot of the skull. Based on the results, the doctor will be able to determine the proportionality of the structure of the jaw and other bones of the skull, the direction of growth of the jaw structures, and the angle of inclination of the jaws and teeth.
Projections in X-ray diagnostics
A radiographic projection is an image on a plane obtained when X-rays pass through a given body onto a plane (for example, onto a film in a cassette).
There are many different projections in X-ray diagnostics, but the following standard and additional projections remain the main and frequently used projections. In this case, standard projections are mainly performed in a lying position.
Standard projections:
- Right lateral projection.
- Left lateral projection.
- Ventrodorsal projection.
- Dorso-ventral projection.
Additional projections:
- Oblique projections.
- With a horizontal course of rays - lateral, straight.
Now let's take a closer look.
The right lateral projection (RLP) is performed with the animal lying on its right side, and if the area of study is the thoracic region, abdominal cavity or survey image, then the thoracic limbs should be retracted strictly forward so that they do not block the chest and spine and the sternum should lie parallel to the table, and the ribs should be in superposition.
The left lateral projection (LLP) is performed similarly to the right lateral one, but with this projection the animal lies on its left side.
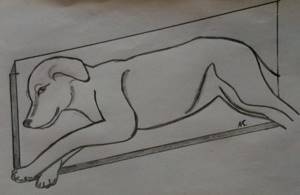
The position of the animal when performing the lateral projection.
Ventro-dorsal projection (VDP) is the position of the animal lying on its back, while the sternum and spine should be in superposition throughout, and the pelvic limbs should be retracted evenly back.
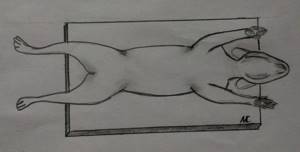
The position of the animal when performing the ventro-dorsal projection.
The dorsoventral projection (DVP) is similar to the ventrodorsal one, but the animal lies on its stomach.
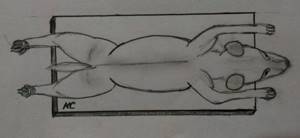
The position of the animal when performing a dorsoventral projection.
Oblique projections are projections when the animal lies on its side at an angle of 45º to the table surface (see figure). Such projections can be performed both on the right side and on the left. And other variations are also possible depending on the area being studied.
The position of the animal when performing oblique projections.
With horizontal ray path - with this projection, X-rays pass horizontally (from the side). These projections can be performed both in a lying and standing position, and can be lateral and straight.
The position of the animal when performing direct projections with horizontal rays.
The position of the animal when performing lateral projections with horizontal rays.
The position of the animal during lateral projections with horizontal rays.
Projections in X-ray diagnostics are selected based on the area of study and preliminary diagnosis.
It should be borne in mind that if the area of interest is the chest, then only the chest is imaged. From a survey image, it is impossible to evaluate any indicators for examining the chest due to the fact that, firstly, the image is distorted due to the inclination of the X-rays passing along the periphery (the further the object is from the center to the edge, the greater the distortion). Secondly, we will not see small details that should be taken into account when describing the chest and making a correct diagnosis. The same situation occurs when examining the abdominal cavity, head, etc. Therefore, survey photographs should be used very rarely and only in emergency cases.
Therefore, before the owner and the animal go for X-ray diagnostics, it is necessary that the doctor, at a minimum, conduct a full clinical examination, make a preliminary diagnosis and, only on this basis, determine the area of study and the necessary projections.
To identify pulmonary pathology, the following are necessarily used: right lateral and ventro-dorsal projections.
To identify metastases: right lateral, left lateral and ventro-dorsal projections.
For cardiology: right lateral and dorsoventral projections.
To examine the trachea (including to identify collapse): lateral during inhalation and exhalation, straight, oblique cranio-caudal tangentially.
To examine the abdominal cavity: right lateral and ventro-dorsal.
However, do not think that for the same pathology there will be a standard number of images, this is not the case. For each specific case there will be a different number of projections due to the pathophysiology of the ongoing process and the anatomical structure of the animal. In some cases, in order to identify and correctly make an x-ray diagnosis, 2 projections are enough, but in some cases, 4 projections are completely insufficient. Therefore, the main standard projections are initially performed, and then additional projections are made as necessary.
It should also be taken into account that in order for the image to be obtained qualitatively, a well-positioned and fixed animal is important; for this it is necessary that at least 2 people come with the animal for X-ray diagnostics.
I would also like to note that when you come for X-ray diagnostics, you must have a referral for X-ray diagnostics with you, which you can read and print on our website or in the VKontakte group.
You can take an x-ray in Tver at our veterinary clinic “Doctor Ay and Oy” at the address: Tver, T. Ilyina St. 1 B. If you have any questions, please call; (4822)737-077
Source of the VK article “Doctor Ay and Oy” - 2015
radiologist Alexandrova Maria Sergeevna
How is diagnostics carried out?
- TRG diagnostics are performed on modern high-precision equipment MyRay Hyperon X9, this new generation device is absolutely safe and provides a reduced radiation dose.
- The patient is wearing a protective apron
- The patient approaches the center of the device, the head is fixed in one stable position for an accurate image
- Diagnosis takes 3-5 minutes, the patient does not experience any pain or discomfort
- The resulting image is saved and can be seen on the computer monitor