- Also, an ultrasound of the kidneys allows you to determine the cause of the disturbance in the outflow of urine from the kidneys (presence of stones, enlargement of the collecting system or obstruction). Under ultrasound guidance, a kidney biopsy is performed, a kidney puncture is performed to extract fluid or pus, and a drainage tube is installed. In the presence of arterial hypertension or varicocele, Doppler ultrasound is performed. After a kidney transplant, the condition of the transplant is assessed using ultrasound. During the ultrasound examination, not only the kidneys are examined, but also the adrenal glands, as well as perinephric tissue.
How to prepare for a kidney ultrasound
In order for the procedure to be successful, the patient needs to fill the bladder. He is recommended to drink about one and a half liters of clean water two hours before the start of the study. You should not drink carbonated water, since the presence of gases in the liquid leads to their accumulation in the intestines, which interferes with the study. You should not drink sweet juices, which lead to intestinal gas pollution.
Immediately before the examination, the patient is asked to remove clothes from the upper half of the body and put on a medical gown. It is better to come to the kidney ultrasound procedure in a tracksuit; a light dress is suitable for a woman. If you plan to visit a functional diagnostics room at a municipal clinic, then bring a towel or disposable napkins with you.
Before the study, the patient must give written consent to the procedure. He needs to explain that during an ultrasound of the kidneys there is no pain, this procedure does not require anesthesia. When applying the gel, you may experience a feeling of slight coolness, which causes discomfort for some particularly sensitive people. It disappears after a few minutes.
Diagnosis of tumor and kidney cancer
1) Laboratory tests of blood and urine (anemia, accelerated ESR, hematuria are often observed). However, these symptoms are nonspecific, and their absence does not exclude the diagnosis of kidney cancer.
2) Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
is a screening diagnostic method that allows you to determine the nature of a space-occupying tumor in the kidney and differentiate it from a cystic formation and a solid tumor.
3) Multispiral computed tomography with contrast (MSCT)
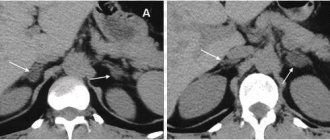
is the gold standard. This method allows you to accurately determine the boundaries of the tumor, its diameter, position, as well as tumor growth into neighboring tissues. The diagnostic accuracy is 95 percent. Multislice CT of the chest is performed if metastatic lesions are suspected on conventional radiography.
Figure 2. CT image of renal papillary cell carcinoma
4) Magnetic resonance therapy (MRI)
kidney examination is performed if there are contraindications to MSCT. Used to visualize extended liquid tubular structures, such as great vessels, which is important in patients with tumor thrombosis.
5)
Renal
scintigraphy using indirect angiography allows you to evaluate kidney function, blood supply characteristics, and visualize tumor formation.
6) Angiography
mainly performed when planning renal artery embolization.
7) Kidney tumor biopsy
carried out to clarify the nature of the tumor (malignant or benign), its histological type and gradation.
How is a kidney ultrasound performed?
The duration of a kidney ultrasound is about thirty minutes. All this time the patient lies on the couch with his back down. The duration of the procedure largely depends on how advanced the device is and how experienced the doctor who conducts the study is. A functional diagnostics doctor applies an indifferent gel to the surface of the body in the lumbar region, and then places a sensor on the skin. An image of the organ appears on the computer monitor. The specialist measures its dimensions and looks at the tissue structure. When performing a kidney ultrasound, this diagnostic method provides a lot of information. It determines the thickness of the renal parenchyma, as well as the volume of their pyelocaliceal system. The doctor can also see stones, enlargement or shrinkage of the kidney, and abnormalities in its structure. If there is an obstacle to good urine flow, ultrasound of the kidneys can show echoscopic signs of hydronephrosis.
It should be remembered that the results of a kidney ultrasound, like studies of other organs, are not a final diagnosis - this is only a medical opinion. To make a diagnosis, the doctor analyzes the data from this study, laboratory tests, fluoroscopy and computed tomography, which he prescribes if indicated.
During a kidney ultrasound, the following diseases and pathological conditions are most often detected:
- congenital anomalies of the kidneys and ureters;
- inflammatory diseases (purulent kidney damage, acute and chronic pyelonephritis);
- urolithiasis;
- kidney cancer;
- hydronephrosis;
- urinary tract obstruction;
- level of stone location.
The procedure for ultrasound examination of the kidneys is usually tolerated without complications and has no contraindications. However, difficulties may arise during the procedure for the following reasons: the presence of gas or barium in the intestines after a recent test procedure, as well as severe obesity.
Morbidity
Kidney cancer accounts for about 3 percent of all malignant tumors.
The disease is usually detected at the age of 40-70 years. The incidence of kidney cancer in St. Petersburg is currently about 20 cases per 100 thousand among men, and 15 per 100 thousand among women. The incidence among whites and blacks is the same, and among Latin Americans it is approximately 30 percent higher. Approximately 8 thousand people die from kidney cancer every year in Russia. This is approximately 2.78 percent in the structure of mortality from malignant tumors. Currently, in 30–40 percent of cases, the disease is detected by chance during a professional examination. inspection. In 25–30 percent of patients, metastases are detected during the initial examination. Ultrasound (ultrasound), computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) make it possible to detect tumors with high sensitivity (from 95.2 percent to 97.1 percent), including kidney cancer of even very small sizes - from 0.5 cm. Survival is directly related to the initial stage of the disease: 5-year survival is 60–90 percent in patients with a localized tumor process and decreases to 0–13 percent in patients with a widespread process.
Normal echoscopic characteristics on renal ultrasound
On ultrasound, the normal thickness of an adult kidney is in the range from forty to fifty millimeters, its width is from fifty to sixty millimeters, and its length can be from one hundred to one hundred and twenty millimeters. The thickness of the organ parenchyma is about twenty-three millimeters. With age, it decreases and by the age of sixty it can reach twenty-three millimeters.
On ultrasound, the kidneys have a bean-shaped shape, as well as an even, clear outer contour. The left kidney is located slightly higher than the right. The thickness of the kidney capsule is one and a half millimeters, it is hyperechoic. The echoscopic density of the kidney pyramids is slightly lower than that of the parenchyma, and the renal sinus is identical in echoscopic density to the perirenal tissue. The kidneys have the same echogenicity as the liver, or their echogenicity may be slightly lower.
Normally, the pyelocaliceal system is not visualized; it is anechoic when the bladder is full. On ultrasound, the anterior-posterior dimensions of the kidney are no more than fifteen millimeters, and the mobility of the organ during breathing is from two to three millimeters. The sizes of both kidneys can be the same or differ by no more than two centimeters.
At the conclusion of the ultrasound, the doctor indicates whether there is an abnormality in the structure of the kidneys. It emphasizes whether there is aplasia or hypoplasia, a cyst, as well as a spongy kidney. Attention is also drawn to the presence of space-occupying formations, their echogenicity and echostructure. If a kidney ultrasound reveals stones, then you need to indicate how many there are, what their diameter is, and on which side they were found. The location of the stones is also determined and whether there is an acoustic shadow near them or not.
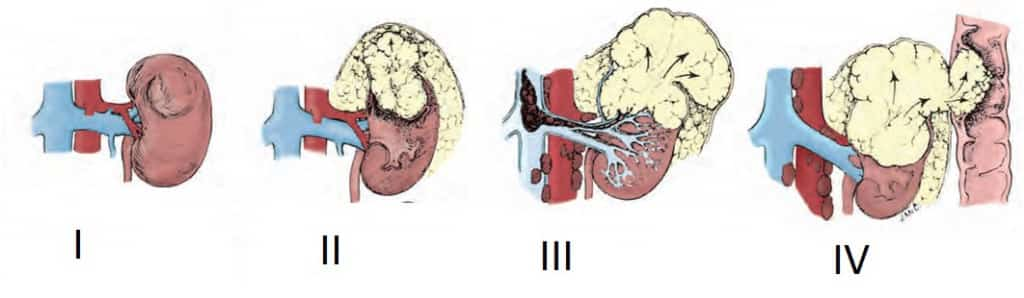
Types of kidney cancer. Classification.
Depending on the prevalence of the tumor process, treatment methods and, accordingly, prognosis, kidney cancer can be divided into three types:
- localized (limited to the kidney),
- locally advanced (spreads beyond the renal capsule to surrounding tissues and/or into the renal/inferior vena cava),
- generalized (metastatic).
As with all cancers, clinicians use the TNM classification.
Ultrasound of the kidneys in children
In childhood, ultrasound of the kidneys is done for the following purposes:
This study is performed if a child has pain or discomfort when urinating, after an injury to the lumbar region or abdomen, or if there is hyperthermia or swelling after a viral disease. Indications for ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder in newborns are as follows:
- pathological changes detected in urine analysis;
- increased bilirubin levels;
- the presence of a tumor-like formation in the abdominal cavity;
- swelling in the morning;
- visible external congenital malformations;
- kidney disease in the child’s parents;
- dysbiosis diagnosed immediately after birth;
- severe pregnancy in the mother or pathological birth;
- finding the child in the intensive care unit after birth;
- resuscitation measures performed after the birth of the baby;
- decrease in daily urine volume;
- arterial hypertension of unknown origin (with systolic blood pressure above eighty millimeters of mercury, and diastolic blood pressure above sixty-five).
Causes
The causes of kidney cancer are not fully understood. There are many different opinions about the factors that play a role in the development of a malignant tumor. Predisposing factors:
- Smoking increases the risk of development by 2 times;
- Occupational hazards (contact with asbestos and tannins);
- Obesity, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension – increases the risk by 25%;
- Uncontrolled use of certain medications (diuretics, analgesics, hormonal drugs) increases the risk by 30%;
- Hereditary predisposition - there are two variants of familial kidney cancer, inherited in an autosomal dominant manner: the first is found in Hippel-Lindau disease, the second variant is papillary clear cell carcinoma);
Variants of the norm on ultrasound of the kidneys in children
Children's normal kidneys have smooth contours and a clearly visible fibrous capsule. The size of a child’s kidneys depends not only on his age, but also on his height. If the baby’s height is between fifty and eighty centimeters, then ultrasound measures only two indicators of the kidney - its length and width.
The parameters of the left and right kidneys are recorded separately. The length of the left kidney can vary from forty-eight to sixty-two millimeters, and the length - from forty-five to fifty-nine millimeters. The left kidney should be from forty-eight to sixty-two millimeters wide, and the length should be from forty-five to fifty-nine millimeters. The width of the left kidney can be from twenty-two to twenty-five millimeters, and the right one - from twenty-two to twenty-four millimeters. At the same time, in children from one to two meters tall, the thickness of the kidney parenchyma is measured. Its dimensions range from nine to eighteen millimeters for the left kidney, and in the right kidney it can reach from ten to seventeen millimeters.
If you need to perform an ultrasound of the kidneys, contact the IVF Center clinic in Smolensk. We conduct research using modern equipment, which allows us to see minimal changes in the structure of the organ. Our specialists are always happy to help you.
Prognosis for kidney cancer
- With adequate treatment of localized kidney cancer, the 5-year cancer-specific survival rate of patients exceeds 90-95 percent, for locally advanced ones - 60-80 percent. Metastatic kidney cancer has a significantly worse prognosis - depending on the number and location of metastases, survival can range from 10 to 30 percent.
- Thus, today kidney cancer (if detected early) is a completely curable disease. Moreover, it is not always necessary to remove the affected kidney.
- All you need to do for timely diagnosis of neoplasms (kidney tumors) is to undergo an ultrasound scan of the abdominal organs and kidneys once a year.
Be healthy!