Call the clinic +7 928 828 4001
Prices for services
| Service | Price |
| Phlebologist consultation | 1350* ք |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of the veins of the lower (upper) extremities | 1900 ք |
| Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the lower (upper) extremities | 3800 ք |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of the arteries of the lower extremities | 1900 ք |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of extracranial brachiocephalic arteries | 1900 ք |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of the arteries of the upper extremities | 1900 ք |
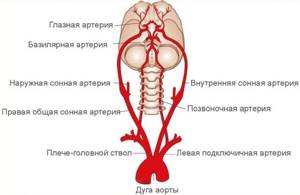
Using this method, blood supply disorders in the brain and neck vessels are determined. The bracheocephalic arteries consist of vessels responsible for supplying blood to the head, brain, shoulders and arms. The aorta is the largest vessel in the body. Large arteries branch off from it. On the right is the brachiocephalic or bracheocephalic trunk. It divides into the carotid and subclavian arteries. And they are already divided into small vessels. On the left are the carotid and subclavian arteries. They extend directly from the aorta and form the brachiocephalic trunk. Next, they divide into small vessels. The internal carotid and basilar arteries, as well as their branches, supply blood to the brain. They are arranged in a circle so that in case of obstruction in some areas, blood flows from other vessels in this circle.
Norm and interpretation of research results
As a rule, the results are ready on the same day, immediately after the examination.
The obtained indicators are compared with normal data. Separately, the doctor examines the results of each artery, assesses the condition of its walls and the speed of blood movement. For any pathological change, the doctor notes the data obtained. If the vessels are in good condition, then there will be no narrowing in them, and there will also be no atherosclerotic plaques blocking blood flow. Blood should flow freely to the brain, tissues of the head and upper extremities. Thanks to the blood flow, the organs receive oxygen and all the necessary nutritional components.
For young patients, the norm is considered to be a condition in which the vessels are characterized by increased elasticity. Thanks to this quality, the risk of stroke and other pathologies is reduced. However, with age, the vessels lose their elasticity, and the clinical picture also changes, which can be easily determined thanks to BCA ultrasound.
In a normal state, the vessels have clear contours, their connecting walls have the same structure. Paired vessels must have the same diameter.
Moreover, this indicator may differ depending on the name of the artery:
- General carotid - the permissible diameter of paired vessels is 4.2-6.9 mm;
- The external carotid artery should contain vessels with a diameter of 3.0-6.0 mm;
- The norm for the internal carotid artery is 3.0-6.3 mm;
- The diameter of the vertebral arteries should be 3.0-4.0 mm.
However, these are not the only indicators that Doppler sonography determines. The doctor determines the speed of blood flow during tension (systolic speed) and relaxation (diastolic speed). In each artery, blood moves at different speeds, and the difference can be quite large.
For example, in the common carotid artery, the systolic velocity can be 50-104 cm/sec. Only a doctor can say exactly which parameter is normal. The results depend on many other factors, tests, the person’s age, and medical history. Therefore, you should not try to independently diagnose a particular disease based on the results of Doppler sonography.
Even medical education may not be enough to decipher the data. The doctor must have experience in performing ultrasound examination of the BCA.
In addition to the ability to compare results and identify deviations from the norm, a specialist must be able to evaluate a set of parameters. For example, a neurologist examines the external state of blood vessels and determines all layers of the carotid and other arteries.
Typically, treatment tactics and final analysis are determined by a neurologist and therapist.
Anatomy of the brachiocephalic arteries
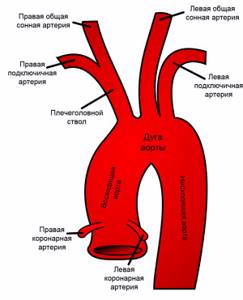
Brachiocephalic vessels are represented by:
- Brachiocephalic trunk and its branches;
- Left subclavian artery;
- Left common carotid artery (CCA).
All of these vessels originate from the aortic arch. The brachiocephalic trunk is a short vessel up to five centimeters long, which at the junction of the clavicle with the sternum on the right gives two large branches - the right subclavian and the right CCA. The left CCA is directed from the aorta upward, to the left sternoclavicular joint.
The common carotid arteries have a lumen width of about 6-8 mm, but not less than 4 mm. Having reached the upper edge of the thyroid cartilage, they branch into the right and left internal and external carotid arteries. The bifurcation can also be located at the level of the hyoid bone or the angle of the lower jaw. To this place, the CCA goes with one trunk, “without sending” a single arterial branch to the tissues.
The external carotid artery (ECA), almost immediately after its origin at the common artery, gives rise to nine arterial vessels supplying blood to the soft tissues and structures of the head.
The internal carotid artery (ICA) goes to the cranial cavity, and there, in the suprasphenoid part, it participates in the formation of the circle of Willis and gives off large cerebral arteries - the anterior and middle cerebral.
The first branch of the ICA is the orbital branch, which supplies blood to the eyes and anastomoses with vessels - branches of the ECA. Blood flow occurs through these communication pathways when the ICA is damaged.
The left subclavian artery arises from the aortic arch and leaves the chest cavity at the level of the middle third of the clavicle, then both subclavian arteries run parallel to this bone and go to the axillary region, where the vessels supplying the upper limbs begin. The diameter of the subclavian arteries reaches 9 mm.
The important arterial branches starting from the subclavian are the vertebral ones, going into the cranial cavity and, connecting, forming the main (basilar) artery, which gives off the posterior cerebral arteries, which are included in the circle of Willis.
Thus, going up and entering the cranium, blood flows from the ICA, ECA and subclavian arteries are connected into a large anastomosis - the Circle of Willis, which redirects blood in conditions of impaired patency of one or another arterial system.
In contrast to the variant anatomy of the Circle of Willis, which is important for brain nutrition, the BCAs have a fairly constant structure. Therefore, branching anomalies of the brachiocephalic arteries are diagnosed quite rarely. Among them:
- Complete absence of the brachiocephalic trunk, when the CCA and subclavian arteries begin directly from the aorta, like similar vessels on the left;
- The origin of the left vertebral artery is from the aorta, the right - not from the subclavian, but from the CCA;
- Asymmetry of the lumens of the vertebral arteries - often the left one is larger, their minimum diameter is 2 mm, maximum - 5.5 mm.
Video: anatomy of the brachiocephalic arteries
How to prepare for this procedure
Blood test for cholesterol: preparation and interpretation of results
In order for the examination results to be as correct as possible, it is necessary to properly prepare for an ultrasound scan of the BCA.
It is necessary to begin preparatory measures by adjusting the patient’s nutrition plan. Approximately 7-10 days before a referral for Doppler sonography was received, it is recommended to exclude from the subject’s diet those foods that may affect changes in cerebral vascular tone.
The products presented include:
- tea;
- coffee;
- alcoholic drinks;
- energy;
- fatty and salty foods, smoked foods.
Particular attention must be paid to the arrangement of the room in which the subject will arrive as part of the preparatory stage. The patient should avoid stuffy or smoky rooms
Prolonged stay in rooms with limited access to oxygen can lead to changes in vascular tone.
You also need to be careful when choosing medications. It is recommended to temporarily exclude any drugs that stimulate or suppress brain activity.
Shortly before ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels, it is necessary to stop taking vitamin and support complexes.
For patients taking any medications to support the cardiovascular system, this condition must be met with extreme caution. The advisability of temporarily stopping the medication before ultrasound of the BCA should be discussed with your doctor.
It is strictly forbidden to make such a decision on your own, since illiterate correction of the therapeutic course can cause irreparable harm to health.
Atherosclerosis of BCA is a disease, the need for treatment of which is considered a priority
It is important to remember that if you suspect a cerebral vascular disease, you should contact a medical facility immediately. On an outpatient basis, doctors will be able to perform ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries and form a clearer clinical picture
Based on the results obtained, an experienced doctor will be able to correctly assess your condition, as well as establish and describe symptoms and treatment.
Carrying out examination of cerebral vessels for children
Quantitative analysis for hepatitis C virus: interpretation of results
A young child often undergoes a comprehensive brain examination called neurosonography. To be more precise, this term combines different methods for studying the state of the central nervous system: examination of the spinal column, brain and spinal cord, blood vessels, and head tissues. But it is customary to call neurosonography an ultrasound examination of the brain.
Using ultrasound techniques, a doctor can identify tissue pathologies, cysts, tumor formations, diagnose intracranial increased pressure and other disorders.
Today, neurosonography is performed in three different ways:
- The simplest is transfontanelle. The name speaks for itself: the sensor is brought to the child’s fontanel and the brain is examined. The disadvantage is that the study of the brain is done in one projection.
- The second is transcranial neurosonography. It requires more serious equipment. The brain of adults is also studied in this way.
- The third method combines the other two. Transcranial-transfontanelle neurosonography is performed on young patients. Advantages – the brain is viewed in different projections. Requires more time to carry out and serious equipment.
Main indications for the study:
- Hypoxia;
- Prematurity;
- Suspicions of CNS pathology;
- Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system.
No special preparation is needed for the examination. The procedure is absolutely safe and painless.
Ultrasound diagnostics
The study of the main arteries using ultrasound is by far the most informative diagnostic method, allowing to identify not only physiological changes (wall deformations, width of the vascular bed, bends, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques), but also qualitative and quantitative indicators of blood flow.
Ultrasound scanning used to diagnose pathologies of the brachiocephalic arteries can be divided into 2 types:
- Doppler ultrasound (USDG);
- duplex scanning.
Both methods are based on the Doppler effect, the essence of which is to capture the reflected ultrasonic wave from moving objects. In the case of blood flow studies, red blood cells act as moving objects that reflect ultrasound. The change in the frequency emitted by the sensor (Doppler shift) occurs in direct proportion to the speed of red blood cells moving along the bloodstream, and if the red blood cells move towards the sensor, the frequency increases and the sensor records a positive shift, and if away from the sensor, the frequency decreases and a negative shift is recorded.
On the ultrasound monitor this is reflected in the form of a color image of multidirectional blood flows - red (positive shift) and blue (negative shift). The BCA ultrasound method has both positive and negative sides. A positive feature is the possibility of examining the transcarnial parts of the brain, that is, the arteries located inside the cranium, while for classical ultrasound examination (β-mode) this area is inaccessible.
The negative side is the inability to accurately determine the position of the vessel, and therefore diagnostics are carried out based on its probable location and changes in scanning depth. In rare cases, with an anatomically uncharacteristic location of the arteries, USDG cannot reflect blood flow, but this is not an unambiguous sign of its actual absence.
Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries is performed using the latest generation ultrasound scanners, combining classical β-mode ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound. The condition of the arteries and the quality of blood flow are assessed based on a two-dimensional (duplex scanning) or three-dimensional (triplex scanning) image. In this case, the vessel can be displayed in the transverse plane and in length.
The use of extracranial ultrasound (examination of vessels located outside the cranium) in duplex mode allows one to obtain the following detailed information:
- condition of the vessel wall;
- thickness, structure and number of atherosclerotic plaques;
- size of the vascular lumen;
- blood flow speed.
Important! Color Doppler mode reflects information about the quality of blood flow, and spectral mode is used to obtain quantitative information.
Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries (BCA) is their main pathology
Atherosclerosis is considered one of the most common pathological processes occurring in the arteries supplying blood to the brain and limbs. Vasoconstriction inevitably affects the functioning of the brain, which experiences a lack of arterial blood supply and hypoxia.
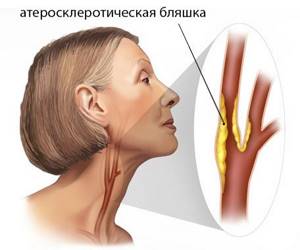
Atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries develops for the same reasons as similar damage to the aorta, arteries of the heart, kidneys, and limbs. Mature and old age, excess weight, lack of physical activity, poor nutrition, bad habits, and fat metabolism disorders predispose people to it.
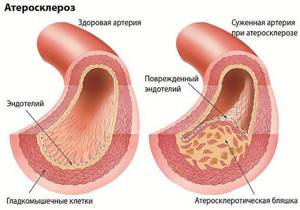
The prerequisites for the appearance of a plaque are damage to the inner layer of the arterial walls, which occurs as a result of active blood flow, high intravascular pressure, and turbulent blood flow in places where vessels branch. A growing plaque can go unnoticed for a long time, because the lumen of the arteries is quite wide, but the progression of atherosclerosis sooner or later leads to disruption of blood supply to the brain.
Atherosclerosis of the BCA can be:
- Stenotic;
- Non-stenotic.
Non-stenotic atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries is said to occur when the plaque grows predominantly along the length of the artery, without causing significant narrowing. It is clear that blood flow will still be disrupted, but complete blockage usually does not occur. As such a flat plaque grows, the circulatory system of the brain is rebuilt to accommodate new conditions - collaterals are turned on, blood is redirected along the components of the circle of Willis, and the brain receives the amount of nutrition it needs.
Atherosclerosis is also considered non-stenotic when the plaque does not cover half the lumen of the artery. As the disease progresses, a non-stenotic lesion can become stenotic - the growing plaque will cover half or even more of the diameter of the vessel.
The situation of stenosing atherosclerosis of the brachiocephalic arteries seems much more serious. In this case, the atherosclerotic plaque protrudes into the lumen of the vessel and leads to severe stenosis, and its rupture or damage to the outer cover threatens local thrombus formation and complete obstruction of the artery.
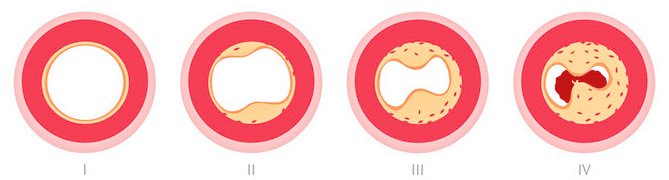
stages of development of complete artery stenosis
Against the background of stenosing atherosclerosis of the BCA, blood flow is also restructured, and its functionality depends on the structure of the circle of Willis. Considering that the classic branching of the arteries of the base of the brain is much less common than various types of variations, most patients with atherosclerosis experience a lack of collateral circulation, and therefore the risk of adverse consequences (stroke, for example) increases significantly.
The favorite zones for the formation of atherosclerotic plaques are considered to be those areas of vessels where they divide or change the direction of their course, which leads to turbulence in the blood flow and damage to the intima, and the most common localization of atherosclerosis of the BCA is the zone of division of the common carotid artery into external and internal branches.
Due to damage to the brachiocephalic arteries, blood flow in the brain suffers, the latter experiences ischemia (dyscirculatory encephalopathy) or necrosis occurs (stroke). The mechanism of development of these complications is associated with hemodynamic reasons, when partial or complete occlusion of the artery occurs, as well as with emboli, when particles of carotid artery plaque and microthrombi from areas of atherosclerotic lesions become emboli.
Hemodynamic preconditions and, in fact, atherosclerosis are much more common in the extracranial parts of the BCA, while blockage of intracranial arterial segments is usually caused by thromboembolism from larger underlying trunks.
The risk of stroke against the background of atherosclerosis of the BCA increases significantly with thrombus formation, the presence of a loose plaque with hemorrhage into its thickness or ulceration of the surface, as well as with severe arterial stenosis (70-80% or more).
In addition to atherosclerosis, other pathological processes are possible in the system of brachiocephalic arteries, leading to their narrowing and disruption of blood flow. Thus, frequent changes in blood vessels include kinks and looping, which are usually eliminated surgically. Aneurysms of these arteries also occur, but are relatively rare.
Video: about carotid artery stenosis - “Live Healthy” program
What does the ultrasound scan of the BCA show?
First of all, a duplex examination of the head is prescribed for those patients who have suspicions of atherosclerotic processes, aneurysms and deformations and other pathologies, and is aimed at identifying functional and structural arteriovenous disorders. During the examination, a specialist can recognize the presence of plaques, blood clots, thickening or reduction of vascular walls, a violation of the normal anatomical integrity of the walls, see tortuosity, surrounding tissue, and the speed of blood flow.
Ultrasonic scanning of the BCA shows:
- lumen of blood vessels;
- blood clots, plaques, detachments;
- stenosis, wall expansion;
- ruptures, aneurysms, deformations.
Using ultrasound scanning of the BCA, you can diagnose:
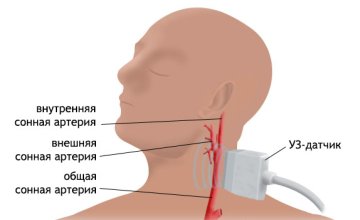
- vascular pathologies;
- vascular hypoplasia;
- violation of wall tone during VSD;
- atherosclerosis;
- arterial aneurysms;
- fistulas between vessels;
- angiopathy;
- thrombosis;
- vascular injuries;
- varicose veins.
The cerebral vessels are a complex system that is capable of self-regulation and maintaining cerebral blood flow. Only comprehensive diagnostics, which includes ultrasound scanning, CT, MRI, allows you to accurately and timely choose treatment, and then evaluate its effectiveness.
Ultrasound scanning helps to assess the anatomy of the vessels of the neck and head, determine the characteristics of blood flow, and assess the condition of the walls and lumen. This way, atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, tortuosity of arteries and their dissection can be diagnosed at an early stage.
What are the differences from ultrasound?
An ultrasound examination primarily measures the patency of blood vessels, responding to the movement of red blood cells in the blood. The image on the screen is one-dimensional; based on the state of patency, one can judge the presence or absence of vasoconstriction, atherosclerosis and other causes of stenosis. The examination is usually cheaper than ultrasound.
Duplex scanning of the vessels of the head and neck, together with conventional Doppler sonography, visualizes the vessels in B-mode, shows the localization of atherosclerotic plaques and thrombotic masses on the inner walls of the veins, their morphological features and the extent of the process. The picture is two-dimensional, in combination with color Doppler mapping (color Doppler mapping) - color.
Such capabilities of ultrasound scanning are its undeniable advantage, because the method not only saves time on diagnosing the disease, but also gives a broader picture of changes in the vessels. However, such research is correspondingly more expensive.
Duplex scanning, ultrasound of the brachiocephalic arteries and other examination methods
Atherosclerosis of the vessels of the neck, abnormal branching of the brachiocephalic arteries can be asymptomatic for a long time, so examinations are not carried out or changes are detected as an accidental finding in connection with the search for another pathology. Patients who have complaints related to obstruction of blood flow in the brain are usually prescribed a study of BCAs, the defeat of which can cause ischemic changes in the nervous tissue.
The main methods for diagnosing vascular lesions are:
- Ultrasound examination (color duplex scanning);
- MR angiography;
- MSCT with contrast;
- X-ray contrast angiography.
Duplex ultrasound scanning using Doppler (USDG)
Doppler ultrasound can be considered one of the most accessible studies, which does not require large material costs, is safe and, at the same time, quite informative. Through ultrasound examination, a specialist can establish not only anatomical features and structural changes in the walls of the brachiocephalic arteries, but also determine blood flow parameters using duplex color mapping.
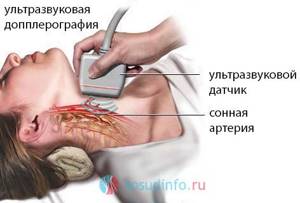
Ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck is indicated for patients who have certain symptoms of obstruction of blood supply to the brain:
- Headache, dizziness;
- Feeling of noise in the ears or head;
- Visual or hearing impairment;
- Decreased memory, attention, intellectual performance;
- Insomnia;
- Symptoms of speech impairment;
- Numbness of the limbs, weakness in them;
- Pulsation of the cervical arteries.
For patients at risk of vascular lesions of the brain, it is also advisable to undergo ultrasound scanning for the purpose of early diagnosis of changes and prevention of severe complications (stroke). The risk group includes persons:
- With diagnosed atherosclerosis of another location (vessels of the legs, aorta, coronary arteries, etc.);
- Suffering from diabetes and other metabolic disorders;
- People over 40 years of age;
- Patients with cervical osteochondrosis;
- Patients who have had a stroke or myocardial infarction.
Ultrasound of the vessels of the head and neck does not require any specific preparation, but the specialist will still recommend giving up strong tea, coffee and, of course, alcohol on the day of the examination. You should not smoke at least two hours before the procedure - this can cause vasospasm and lead to an incorrect conclusion about the condition of the arteries.
During ultrasound examination of the brachiocephalic arteries, the subject lies on his back, the neck is freed from clothing and jewelry, and the head is turned in the direction opposite to the vessels being examined. The sensor is treated with a special gel and moves along the front surface of the neck from the edge of the lower jaw to the collarbone. The study lasts about 15-20 minutes. The main advantage of ultrasound scanning is its harmlessness, and, therefore, the absence of contraindications, that is, children, pregnant women, and elderly people with a number of severe concomitant diseases can be studied.
Using a standard ultrasound mode, the doctor assesses the width of the lumen of the vessels, the presence of stenosis in them, and the nature of branching. Supplementing the method with color Doppler mapping provides information about the characteristics and direction of blood flow.
If pathology of the brachiocephalic arteries and their branches is suspected, it is advisable to begin the diagnosis by examining the peripheral parts - the common carotid arteries, their bifurcation zone, since it is in this place that atherosclerotic plaques are most often located, causing chronic cerebral ischemia. If nothing is found in the underlying sections during Doppler ultrasound, but there are symptoms of impaired cerebral blood flow, then a transcranial ultrasound examination can be performed to determine the condition of the vessels located in the cranial cavity.
Carrying out an ultrasound
Physical activity and walking can distort the result, so you should come for ultrasound examination of the brachiocephalic vessels approximately half an hour before the appointed time. This will be enough to calm down and relax. The examination is performed on an outpatient basis in an ultrasound room equipped with an ultrasound machine in a certain sequence:
- The patient lies with his back on a flat, hard surface, while turning his head to the side. A cushion is placed under the neck for better access to the arteries.
- Jewelry is removed from the neck, the examination area and the upper chest are freed from clothing.
- A special gel that conducts ultrasound waves is applied to the sensor and skin.
- The doctor applies the sensor to the neck and sequentially moves it along the surface in longitudinal and transverse planes, examining all sections and recording the parameters.
- You need to be prepared for the fact that you will need to turn on your side or stomach. This may be necessary for a comprehensive examination of the vessels of the neck.
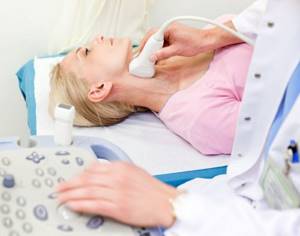
If there are anatomical features or a family history, additional functional tests are performed:
- change of body position, the patient is asked to sit down;
- holding your breath while inhaling;
- taking medications with an antianginal effect (usually nitroglycerin or anaprilin).
Attention!
Depending on the condition of the vessels and the presence of additional samples, the duration of the BUA can last between 5-45 minutes.
After completing the examination, the doctor makes a conclusion and gives a printed protocol with the information received to the patient. If necessary, a digitized image is attached to it.
Medical Center Extra
- Bratislavskaya810 m
- Maryino1.1 km
Moscow, st. Myachkovsky Blvd., 13, floor 2.3
Medical Center Extra is a modern medical institution located in the south-eastern district of Moscow, in the Maryino district.
The area of activity of the Extra medical center is obstetrics and gynecology, therapy, pediatrics, vaccination, cardiology, urology, gastroenterology, dermatology, surgery, traumatology, neurology, manual therapy, reflexology, otolaryngology, ophthalmology, X-ray diagnostics, ultrasound diagnostics, dentistry, occupational pathology, endocrinology, dietology, endoscopy, cosmetology, massage.
Ultrasound, 3D/4D ultrasound, ECG, Holter, EchoCG, Doppler studies, X-ray, gastro- and colonoscopy, hysteroscopy, fetal CTG are performed at the Extra Medical Center.
Another area of activity of the medical center is conducting prof. examinations, registration of certificates, personal medical records.
Expansion of medical services is planned.
A comfortable psychological atmosphere, professionalism of doctors and nurses, modern medical equipment, focus on results in the treatment of patients, responsibility are guaranteed in the medical center.
Preparing for the examination
When receiving a referral for examination, the patient wonders about preparation; it plays a big role. This is an important point, since by following certain rules, you can obtain the most reliable result without errors and distortions.
Due to the fact that the vessels are being examined, it is very important to exclude the intake of substances that affect their tone. Similar components are found in some medications, as well as in food (tea, coffee, energy drinks and alcohol-containing drinks, as well as foods with a high amount of salt)
The use of these substances should be avoided for 24 hours before the BCA ultrasound.
You should not take hot baths or visit saunas before an ultrasound scan of the BCS for a couple of hours, and during this period any type of smoking, including passive smoking, is excluded.
Ultrasound examination of BCS - what is it and what is it for?
First of all, you need to decide what the brachiocephalic arteries are. This is the name given to the complex of arterial vessels that are located in the neck and supply blood to the brain. This includes the branches of the aortic arch (the largest blood vessel of the human body) - the brachiocephalic trunk, common carotid (right and left), subclavian (also right and left) and the vertebral arteries extending from them.
Ultrasound Dopplerography of brachiocephalic vessels (arteries) involves studying the structure of the extracranial vessels of the neck using ultra-high frequency waves, which makes it possible to study not only the vascular wall, but also to determine the nature of the blood flow.
This means that any deviations from the norm will be identified, assessed and indicated in the conclusion, and the attending physician will determine further tactics.
Studying the structure of blood vessels and determining the speed of blood flow, as well as identifying various obstacles, contribute to a favorable prognosis for life. Rehabilitation after a stroke will be more effective if the specialist is provided with information about the dynamic state of the blood flow.
Benefits and Risks
Ultrasound scanning of brachiocephalic vessels and smaller arteries is a non-invasive, gentle, fast and affordable method for a thorough study of the structure of the vascular wall, determining the speed of blood flow and visualizing the slightest pathological changes.
The patient is not exposed to any types of radiation exposure, parenteral administration of contrast agents is not performed, and after examination and receipt of documents there is no need to limit physical activity.
For a person referred for ultrasound examination of the cervical vertebral joint, any risks are excluded, since an analysis of the effect of ultrasonic waves on adults has shown the absolute safety of the method. Even children under 5 years of age can undergo Doppler examination without the slightest concern.
In addition to the described advantages, Doppler ultrasound of the vascular system supplying the brain is characterized by high diagnostic value
It is important to know that scanning can only be performed by a suitably qualified specialist.
Indications and contraindications
Before referring a patient for a BCA scan, the doctor must determine the indications and contraindications for this study.
Main indications:
- headaches and attacks of dizziness;
- noise in the head;
- recurrent problems with movement and sensitivity;
- short-term disturbances in speech, hearing and vision;
- complaints from the patient or his relatives about forgetfulness, changes in behavioral reactions;
- history of syncope;
- family history of vascular accidents (stroke, heart attack);
- women over 45 years old, men aged 40 years and older;
- the presence of atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyscirculatory encephalopathy and metabolic syndrome;
- smokers with more than 15 years of experience (including those diagnosed with bronchial asthma);
- various angiopathy and vasculitis, including systemic and hereditary diseases;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
There are no absolute contraindications for performing ultrasound of the BCA. There are only relative ones that can delay the vascular scanning procedure.
These include:
- mechanical obstacles in the neck area - bandages, wounds;
- non-standard neck sizes or the presence of tumor formations that make it difficult to visualize blood vessels;
- calcified atherosclerotic plaques can distort the diagnostic picture.
Ultrasound examination of the BCA - what is it?
Are you looking for a research method that will provide the most reliable information about your disease?
With duplex scanning, the specialist receives accurate data on the pathologies and condition of the brachiocephalic vessels of the neck that supply the brain. Duplex scanning of the BCA also examines the dynamics of blood flow: speed of movement, nature of blood distribution. Modern Doppler ultrasound of the brachiocephalic arteries has a number of advantages, including:
- absolute harmlessness;
- painlessness;
- high information content;
- frequency of repeated examinations.
Do you feel frequent dizziness, periodic or constant numbness of the limbs, progressive deterioration of vision, dark spots and “spots” flashing in your eyes? Do you experience short-term fainting or headaches for no reason? Dopplerography of the brachiocephalic arteries is a quick way to visually examine the carotid, vertebral, and subclavian arteries and make a diagnosis. Get an ultrasound scan of the neck vessels if you suffer from diabetes. The examination will protect you from dangerous complications (hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis)!
Pros and cons of the study
Among the main advantages of BCA ultrasound, it is worth highlighting:
- Non-invasiveness of the method. This means that during the procedure the patient does not experience pain or discomfort. The person is not required to perform strenuous exercise. At the same time, preparing for the study also does not cause any problems for patients.
- Minimum list of contraindications. Since this type of diagnosis does not involve the use of instruments that can put a strain on the body’s systems, the examination process itself is permitted for most patients.
- Availability. Equipment for examination is available in almost any medical center.
- Speed of the procedure. The examination takes no more than a few minutes.
- High information content. Doppler ultrasound allows you to collect a lot of data that will help you make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Each examination method has not only advantages, but also disadvantages.
The disadvantages of Doppler ultrasound include:
- Difficulty defining data. The diagnostician must be highly qualified. A novice specialist can easily miss an important nuance. Therefore, the doctor must have extensive experience.
- Relative primitiveness of the method. Today, ultrasound examination of the BCA is considered an outdated diagnostic method, since there are more advanced methods, for example, duplex or triplex scanning of blood vessels. These diagnostic methods are much more informative, more modern and do not require high specialization of the doctor. However, duplex and triplex scanning are more expensive.
- Inability to identify certain signs of pathology. For example, with Doppler ultrasound it is impossible to determine for what reason the blood flow was disrupted, which is not part of the vessels. That is, if the patient suffers from the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, performing an ultrasound scan of the BCA will not help make the correct diagnosis. With duplex or triplex scanning, blood clots and plaques can be detected.
A little about symptoms and treatment
Symptoms of damage to the brachiocephalic arteries are associated, first of all, with impaired patency of the arterial vessels. The brain suffers from lack of nutrition, which results in numerous patient complaints:
- Dizziness;
- Headache;
- Weakness, fatigue, decreased mental performance;
- Flashing of “flies” before the eyes, feeling of a veil;
- Presyncope.

If the blood supply to the upper extremities is disrupted, then complaints will include numbness, impaired sensitivity, and weakness in the arms. Often, disruption of blood flow through the carotid arteries is accompanied by emotional disorders, neuroses, panic attacks, depression, and insomnia.
When specialists have established a diagnosis of stenosis due to atherosclerosis or congenital anomalies, they first prescribe conservative therapy - diet, proper regimen, sufficient physical activity, blood pressure control, vascular medications, vitamins, neuroprotectors.
If drug treatment is ineffective, surgery is possible. In the case of a local change in the vessel wall, the surgeon can remove this section of the artery, the atherosclerotic plaque by itself or with a fragment of the vascular wall, perform plastic surgery, and install a stent.
Carrying out
Duplex scanning of the BCA includes examination of the extracarnial sections of the main arteries in a combined mode, combining β-mode and Dopplerography, as well as examination of the transcarnial sections using the Doppler effect. Since the frequency of ultrasound used in the β-mode does not allow assessing the condition of the walls of blood vessels located inside the skull, diagnosis is carried out based on Doppler color indicators of the volume and speed of blood flow.
Examination of arteries to determine the value of IMT is performed according to standard methods. The patient, immediately before the procedure, must lie on his back for at least 15 minutes, and only then begin an ultrasound examination of the common carotid artery.
In this case, the head is moved slightly to the side from the sensor, and the sensor itself is effortlessly leaned against the side of the neck. At this moment, a clear picture should appear on the monitor, showing the anterior and distal wall of the artery, with characteristic intima-media lines. Measurement of functional parameters of the arteries can be carried out simultaneously with an ECG, which makes it possible to determine the thickness of the IMM with extremely high accuracy (up to 0.01 mm).
To assess the state of the endothelium, its ability to provide adequate resistance to blood flow, that is, to contract and stretch according to the phases of the cardiac cycle, the method of functional tests is used, the essence of which is to record data obtained as a result of the influence of various stimulants (medicinal or mechanical) on the blood flow. For example, when examining the brachial artery, a tourniquet is applied to the forearm and after 5 minutes it is quickly removed, measuring the increase in blood flow velocity and the width of the vascular bed at intervals of 15 seconds, then 1 minute, 3 minutes, and so on.
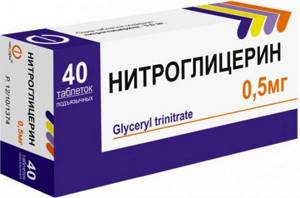
Nitroglycerin has a powerful but short-term vasodilatory effect
A functional test is carried out similarly using medications, for example, nitroglycerin. The reaction to taking the medication begins to be recorded after 15 seconds, and then at intervals of 1–3–5 minutes. A normal reaction to the use of functional tests is considered to be expansion of the vessel (dilatation) no later than 15 seconds. The absence of vessel dilation at 15 seconds is considered a pathological condition.
Duplex scanning of the BCA, despite the extremely high diagnostic value of the information obtained, is a relatively inexpensive research method, the cost of which, taking into account the use of functional tests, usually does not exceed 5,000 rubles. The main condition that determines where to do an ultrasound scan of the BCA is the presence in the selected clinic of a latest generation ultrasound scanner, the algorithm of which provides for the synchronization of all actions with the ECG.
Doppler studies of the vessels of the lower extremities
To conduct a study of the vessels of the lower extremities, two options are used: the actual ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities and duplex scanning. These procedures reveal diseases such as thromboangiitis (Buerger's disease), arterial thrombosis, atherosclerosis and others.
The main goals of studying the blood vessels of the legs:
- Diagnosis of vascular thrombosis;
- Detection of aneurysm;
- Assessment of the condition of peripheral vessels;
- Diagnosis of pulsating formations;
- Monitoring the dynamics of dilated veins;
- Determination of venous insufficiency;
- Diagnosis of postthrombophlebitis disease;
- Preoperative marking of veins.
We can safely say that ultrasound techniques are the most advanced methods for examining the vessels of the legs. For example, using duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities, you can study the vessels in detail, determine the degree of change in them, and make the correct diagnosis
It is important that these methods detect vascular disorders at a very early stage, which cannot always be done by other methods.
When to see a doctor?
It is recommended to visit a medical facility if certain symptoms bother you constantly or from time to time.
Signs of arterial pathology:
- There is often a feeling of numbness in the legs;
- There are complaints of weakness in the limbs;
- Muscle cramps occur for an unknown reason;
- There may be pain when running, walking;
- The legs become cold to the touch and pale as the temperature in them decreases;
- The person limps, although there are no inflammatory processes in the joints.
Problems with veins are indicated by:
- Swelling of the legs, worsening in the evening;
- Brownish skin of legs;
- The appearance of spider veins;
- Long-term non-healing ulcers may appear;
- Dilated veins become noticeable.
It should be noted that numbness, weakness, convulsions and other signs can appear in completely healthy people. Therefore, there is no need to immediately diagnose yourself and, even worse, prescribe treatment. Contact your doctor, tell us about your suspicions, and if necessary, you will be prescribed an examination and only then treatment.
Advantages of ultrasound examination of leg vessels:
- Absolute safety;
- Painless;
- Information content;
- Non-invasive (no damage to the skin);
- Speed of manipulation (the patient receives the result immediately);
- Can be done at any age;
- Low price.
Ultrasound of the blood vessels of the legs is performed on an outpatient basis. After applying a special gel, the doctor uses a sensor to examine the vessels. Pathological changes are clearly visible on the device monitor. With color mapping, it is easy to distinguish veins from arteries. The entire manipulation lasts less than an hour. There is also no need to prepare for the examination.
Advantages of the method
Ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries has several advantages:
- Completely non-invasive. The body is not damaged.
- No discomfort. The patient does not feel anything.
- Versatility. The method is suitable both for diagnosing diseases from scratch and for verifying (confirming) a previously established diagnosis and clarifying specialist suspicions.
- Efficiency. Diagnostics is carried out in 20-30 minutes. The patient receives the results of the examination almost immediately.
- Safety, repeatability. This allows the study to be carried out indefinitely often and makes it possible to assess the course of the pathological process over time.
And, of course, information content. This is one of the most valuable advantages of the method.