The mandibular joint is a combined joint that connects the bones of the lower jaw with the temporal bone; it is responsible for the proper functioning of the lower jaw. The temporal bone is the load-bearing part of the skull, protecting the inner ear and vestibular apparatus. It also ensures the chewing function, and is an attachment for the human hearing system, nerve fibers and arteries. As you can see, the temporal bone performs a number of very important functions and any pathologies associated with it can lead to disruption of the vital functions of the body.
Anatomy of the temporomandibular joint
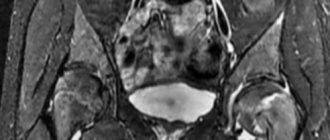
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a combined paired joint formed by the heads of the lower jaw and the articular tubercles (pits) located on the temporal bone. In the cavity of the TMJ there are menisci - cartilaginous plates that act as pads and shock absorbers, and also provide articulation function. Thanks to this, the temporomandibular joint is able to withstand significant loads that occur when chewing food. For the same reason, the TMJ has a powerful ligamentous apparatus that strengthens and stabilizes the joint.
The complex structure of the temporomandibular joint and intense loads are the reason why degenerative processes and diseases often occur in the joint. Magnetic resonance imaging, unlike other diagnostic methods, “sees” not only bones, but also cartilage, ligaments and menisci. This is why MRI is the best method for diagnosing diseases of the maxillofacial joints.
Indications for MRI of the maxillofacial (temporomandibular) joints
The temporomandibular joint, like any other joint in the human body, is susceptible to rheumatic and degenerative diseases. The outcome of these pathologies depends on timely diagnosis and treatment. In severe cases, the disease can cause complete loss of TMJ function, leading to the inability to eat solid foods and other negative consequences.
In complex and controversial cases, MRI of the TMJ can be performed with contrast. To do this, a special contrast agent is injected into the patient’s ulnar vein, which is absorbed by diseased tissues, facilitating diagnosis. The contrast is safe and only occasionally can cause mild allergic reactions in the form of a rash or itching on the skin.
TMJ diseases that can be seen on MRI images:
- Inflammatory diseases (arthritis);
- Degenerative-dystrophic pathologies (arthrosis, deforming osteoarthritis);
- Ankylosis (fusion) of the TMJ;
- Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint;
- TMJ dislocations and other injuries;
- Neoplasms;
- Aseptic necrosis, bone osteomyelitis;
- Congenital anomalies of the TMJ.
Alarming symptoms, in the presence of which it is recommended to do an MRI of the TMJ:
- Pain in the area of the maxillofacial joint, intensifying with movement of the lower jaw (when chewing) and radiating to the face and temple;
- Swelling and redness of the maxillofacial joints;
- Nodules, dense or soft formations, bumps that are identified in the TMJ area visually or by palpation;
- Impaired mobility of the TMJ, stiffness, limited mouth opening;
- Spasm of the masticatory muscles;
- Clicking in the joints that occurs when chewing and moving the lower jaw;
- Discomfort that occurs when the mouth is opened wide (it is difficult for the patient to close the mouth, which may cause clicking and pain in the TMJ area).
Diseases of the soft tissues of the face
The doctor selects the type of MRI and the area of examination, taking into account complaints, anamnesis, examination data, palpation tests, ultrasound
The same symptoms - facial asymmetry, pain, numbness of the skin - can occur in diseases of various natures. Magnetic resonance scans show changes not only in soft tissues, but also in structures located inside the skull. In difficult cases, the doctor will prescribe an MRI of the brain, neck, and face in one diagnostic procedure. If bone damage is suspected (tumor, arthrosis, ankylosis), computer scanning is preferred to evaluate fractures of the jaw, orbits, and calvarium.
MRI of soft tissues of the face shows:
- Tumors. Neoplasms can be benign or malignant. MRI scans are used to differentiate lipomas, neuromas, angiomas from sarcomas and carcinomas. The latter, due to rapid uncontrolled growth, often cause paresis of the facial nerve and deformation.
- Inflammatory processes. The pathology develops against the background of direct tissue trauma or the penetration of microorganisms from a painful focus located in the mouth, pharynx, ear, jaw. Late diagnosis and lack of treatment cause complications:
- phlegmon;
- abscess;
- purulent lymphadenitis.
- Infections. Cervical-maxillofacial actinomycosis is initiated by radiant fungi, the disease is characterized by the formation of specific granulomas, fistulous tracts, and abscesses. Similar changes are detected in tuberculous lesions of the lymph nodes. Infection of the soft tissues of the face can manifest itself after medical procedures in patients with a weakened immune status or when aseptic rules are not observed. MRI shows the localization of the lesion; based on the results of the study, the following is diagnosed:
- cellulite (inflammation of subcutaneous fat);
- fasciitis (damage to connective tissue membranes);
- myositis (involvement of muscle fibers).
- Injuries. Damage to the soft tissues of the face is recorded in road traffic accidents, direct impacts, industrial accidents, etc. As a result of severe injuries (including animal bites), rough scars are formed, the duct of the parotid/salivary gland is deformed, and compression of the nervous structures occurs.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging of the maxillofacial joint is contraindicated:
- Patients with pacemakers, neurostimulators, cochlear hearing prosthetic systems, defibrillators implanted in the patient’s body (magnetic fields used for MRI can disable the devices);
- Patients who have metal foreign bodies in their bodies (steel or iron shavings in the eyes, vascular clips on the main arteries, fragments and fragments of ammunition);
- Children under 5 years old;
- Pregnant women up to 12 weeks of pregnancy;
- Persons with excess weight of more than 130 kg and body girth of more than 150 cm (there is no physical ability to place the patient in the tomograph).
What is included in an MRI of soft tissues of the face?
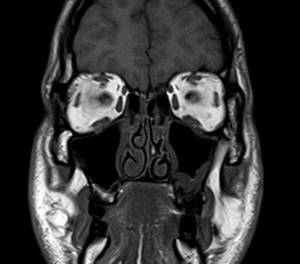
Magnetic resonance scan
MRI allows you to examine the superficial and deep muscular aponeurotic systems of the face. The first is represented by the dermis, fatty tissue, fascia, subcutaneous muscle, the second - by facial and masticatory muscles, facial nerve, large vessels, Bichat's lumps, ducts of the salivary glands. The layers of the face are fixed by connective tissue ligaments, the main task of which is to prevent sagging and deformation.
Pathological processes can affect any of the structures, the genesis is variable. Unexplained facial asymmetry, atony, atrophy, paresis of facial and masticatory muscles require a magnetic resonance scan.
Indications for the study:
- infections of the soft tissues of the face, bones, joints;
- suspicion of abscess, phlegmon, osteomyelitis, etc.;
- facial injuries, presence of a foreign body;
- palpable neoplasm, etc.
MRI of soft tissues of the face and neck is performed for:
- diagnosis of diseases;
- determining the stage of a malignant tumor of the parotid gland, orbit;
- planning radiation therapy;
- assessment of anatomical features before surgery, the effectiveness of therapy.
Preparing for MRI of the temporomandibular joint
The procedure does not require any preparation. The study is carried out at any time convenient for the patient, is not accompanied by pain and does not require complex medical procedures. All that is required of the patient is to remain motionless until the examination is completed.
MRI of the TMJ is a safe procedure, provided that safety regulations are followed. It is prohibited to carry metal objects, accessories, jewelry, wearable electronics and gadgets on the body or in pockets or on clothing. Magnetic fields can cause metal to heat up, causing burns. Massive metal objects attracted to the scanner's magnet can cause injury or equipment failure. Any excess can be left in the storage room.
How to do an MRI of the temporomandibular joint
There are special installations for carrying out MR tomography - MR tomographs. They look like a large cylindrical block, weighing several thousand kilograms, in which a superconducting magnet is located, generating a magnetic field, receivers and transmitters of radio waves. In the center of the tomograph there is a tunnel, about 60 cm long and wide. A narrow movable table passes through the tunnel, on which the patient lies during the examination.
The procedure begins with placing the patient on the table. After the patient is laid down, he is asked to put on headphones - they muffle the noise that comes from the equipment and are used to communicate with the operator and even listen to music. The table is then moved so that the patient's head is in the center of the installation tunnel. This is why some patients who suffer from claustrophobia may experience discomfort during the examination.
During the procedure, you must follow all the operator’s recommendations, remain calm and still. The noise the equipment makes may sound like banging, whistling, or trumpet sounds. It is not a sign of a breakdown and indicates normal operation of the tomograph. After completing the procedure, the patient needs to wait a little - 15-30 minutes until the decoding of the images is completed. For storage, they are recorded on a CD (free of charge), or, at the patient’s request, on a flash drive, or printed on film (for a fee). After completing the examination, the radiologist talks in detail about the results of the study.
Interpretation of MRI of soft tissues of the face
The doctor will definitely reflect the identified changes in the report
The interpretation of the results is carried out by the doctor who conducted the study. Normally, minor facial asymmetry is allowed within 2-3 mm. The parotid and submandibular salivary glands are of a homogeneous structure and have clear boundaries. Muscles, fiber, vessels without visible pathology, lymph nodes are not enlarged. There are no space-occupying formations, foci of necrotization, or inflammation.
You can get an MRI of the soft tissues of the face in St. Petersburg at the Magnit diagnostic center. Research is carried out on a Siemens closed expert-class tomograph with a power of 1.5 Tesla. The characteristics of the equipment make it possible to determine the diagnosis in the most difficult cases; a “Second Opinion” service is available for an additional fee. The recording disc, conclusion and conversation with the doctor are included in the total price. For the convenience of patients, the medical center operates around the clock; at night, the price of facial MRI is lower. Make an appointment by phone and come - with timely assistance, the success of treatment is higher!
What will magnetic resonance imaging of the maxillofacial joint show?
MRI, unlike CT, perfectly “sees” tissues of all types. Computed tomography, unlike magnetic resonance imaging, is not capable of providing clear and legible images of cartilage, ligaments and tendons, but is better suited for examining bones. Therefore, to diagnose TMJ diseases, it is better to do an MRI.
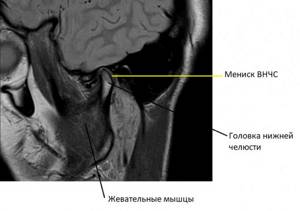
In a series of such images, taken layer by layer in the form of thin sections in several planes, it is easy to recognize the articular cartilages covering the heads of the lower jaw and the articular tubercle, forming the temporomandibular joint, the TMJ meniscus. Individual ligaments and tendons and masticatory muscles are visible. Any possible pathological change, such as joint inflammation or neoplasm, will immediately be visible on the MRI.
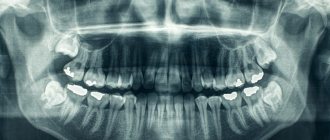
CT scan of the jaw: what it shows, how it is done, radiation doses
Dental computed tomography is an important part of diagnostic procedures in the dental field. This is a very informative method that allows you to see the structural features of the jaw, dentition, and also identify pathological processes. Previously, X-rays were used for this, but CT is a more advanced diagnostic method that allows you to get the most accurate picture.
3D dental diagnostics are carried out using a tomograph. In one procedure, you can obtain detailed information regarding the condition of the dentition. The main feature of this method is a three-dimensional image that allows you to see the object under study in full. This is extremely important for making an accurate diagnosis and drawing up a detailed treatment plan.
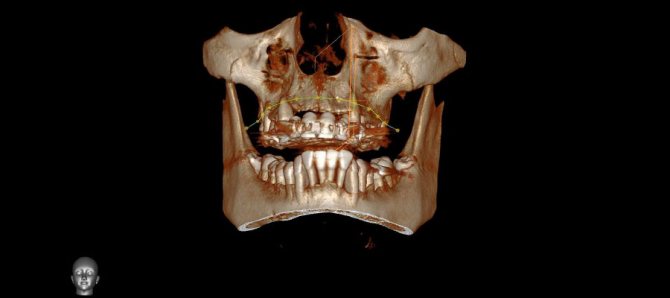
Content
- The main advantages of dental tomography
- Indications for CT scanning
- Main contraindications
- Is it harmful to have a dental CT scan?
- How often can a dental CT scan be done without harm to health?
- Basic rules of preparation
- How are dental CT scans done in specialized clinics?
- What does this procedure show?
- Computed tomography after implant installation
- Which is better - CT or X-ray?
- Computed tomography of the jaw in St. Petersburg
The main advantages of dental tomography
Compared to other diagnostic methods, computed tomography has the following advantages:
- The entire procedure lasts no longer than 1 minute.
- High level of information content.
- CT is safe for the patient’s health, so it can be performed repeatedly if necessary.
- The high quality of the image in the image allows you to clearly see the structural features of bone tissue.
- The radiation dose received is minimal.
At the end of the procedure, the resulting 3D image is recorded on a CD with universal software, which is installed automatically on the attending physician’s computer for the purpose of further diagnosis.
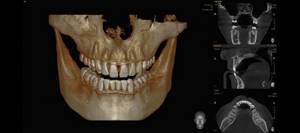
Indications for CT scanning
The information obtained after a CT scan is necessary to solve a number of problems in the field of dentistry.
The procedure is carried out in the following cases:
- Damage to the jaw after minor injuries. It is with the help of CT that dislocations and fractures can be determined.
- Detection of pathologies in the structure of the dentition. This procedure is commonly used before any type of orthodontic correction.
- Drawing up a computer model of the jaw for the manufacture of an individual brace system.
- As a preparatory procedure before the upcoming operation.
- Presence of neoplasms in the jaw.
- Diagnosis of hidden caries.
- Complications in the dental canals.
- Monitoring the success of previous treatment.
A CT scan is performed before dental implantation, because based on a 3D image, a suitable implant is selected, its installation is carried out and the quality of the procedure is checked.
Main contraindications
During the procedure, the body is exposed to a certain dose of radiation, so computed tomography is not performed during pregnancy. As for women during lactation, the procedure is possible, but after its completion it is forbidden to breastfeed the baby for 24-48 hours.
It is prohibited to perform dental CT scans on preschool children. In this case, alternative diagnostic methods are used. The same applies to patients with a pacemaker.
Is it harmful to have a dental CT scan?
Computed tomography is based on the principle of passing x-rays, with the help of which a series of layer-by-layer images are produced. Accordingly, a certain radiation dose is present during a CT scan of the jaw. It depends on the number of images and the total area of study.
When examining the chest and abdominal cavity, this figure is 11-14 mSv. The critical level for one procedure is 50 mSv (the maximum permissible annual dose is 150 mSv). If this figure is exceeded, there is a high risk of developing cancer.
So is it harmful to have a CT scan of your teeth? The study of this area is considered the most gentle, because the radioactive dose during the procedure is only 0.1-0.3 mSv. Therefore, computed tomography is absolutely safe for the health of patients (except in cases of contraindications).
How often can a dental CT scan be done without harm to health?
Despite the fact that a dental CT scan exposes the body to a minimal dose of radiation, there is no need to overuse this procedure. The frequency of the procedure depends on the degree of need for this, but it must be taken into account that radiation can accumulate in the human body. Therefore, the standard frequency of procedures is no more than 2 times a year.
But there are times when it is necessary to exceed the permissible limit. Based on the permissible radiation exposure, CT scans of the face and jaw should be performed no more than once every 2-3 months.
Basic rules of preparation
There are no special requirements that must be strictly observed before tomography of the dental jaw. It is better not to eat for three hours before the procedure.
The remaining requirements are standard, as in the case of x-rays. You will need to remove all jewelry and objects containing metal. This is necessary to obtain the most accurate research results.
How are dental CT scans done in specialized clinics?
Compared to the old X-ray machine, the tomograph is much more compact. A CT scan can be performed lying down, standing, or sitting. The choice depends on the physiological characteristics of the person, his age, as well as the type of pathology itself.
In cone beam computed tomography, the patient's head is placed between two scanners. To ensure maximum immobility, clamps are provided for the jaw, chin and temples. To understand how a dental CT scan is done, we will describe the procedure in stages:
- The procedure is carried out standing, the platform for fixing the jaw, chin and temples is set in accordance with the patient’s height, and a protective lead vest is put on before the procedure. The head is placed on a special tomograph stand and pressed against the equipment rack. And in this position it is fixed by means of stabilization.
- After preparing the patient, the specialist turns on the tomograph. The moving part of the device rotates around the patient's head. During the entire procedure, about 200-300 images are obtained, which are immediately displayed on the monitor.
- During the procedure, the patient may hear noise - this is quite normal and there is no need to be afraid of it. When it subsides, you do not need to immediately remove your head from the platform or make other movements; you must wait until the x-ray technician reports the end of the study and asks you to leave the scanning area.
During the procedure, the patient does not experience pain or any discomfort. The only discomfort is the forced need to remain immobile. Also, for 10-20 seconds during the image, the patient can feel the heat emanating from the moving scanners.
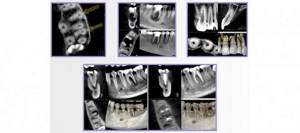
CT scan of the jaw: what does this procedure show?
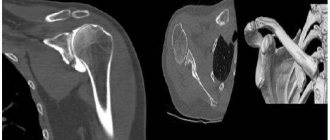
The resulting CT image of the teeth is a three-dimensional image of the jaw, which is obtained using hardware positioning and the use of a three-point fixation system.
Computed tomography of teeth allows you to clearly see all pathological processes and disorders in the structure of bone tissue. With this study you can see:
- Crowns and fillings.
- Condition of the paranasal sinuses.
- Location of canals, roots and unerupted molars.
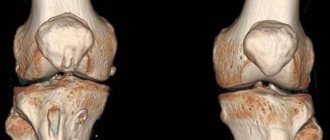
- TMJ condition.
- Various pathologies of the jaw.
The high accuracy of the results obtained allows us to accurately determine the nature of the pathology. If a CT scan is performed for dental implantation, then layer-by-layer images allow you to get the clearest picture of the condition of the maxillofacial area in different projections. The specialist sees the maxillary sinuses, canals, TMJ and blood vessels.
This type of research is the most accurate source of information about the dental system. Only with the help of CT can you correctly plan the upcoming implantation procedure. If you do not use CT, there is a high risk of installing a smaller implant, which will lead to unnecessary stress on the bone tissue.
Computed tomography after implant installation
Quite often the question arises: is it possible to do a CT scan with dental implants? Unlike magnetic resonance imaging, when foreign bodies can produce a “phonic effect,” there is no such problem with computed tomography. Moreover, it is not only allowed, but recommended after implantation.
CT is necessary in the following cases:
- Identification of the reasons for the instability of the installed structure.
- If you need to determine whether the artificial root has taken root or not.
- Determination of the quality of implantation performed. This is especially necessary if computer modeling of the jaw was not carried out at the preliminary stage.
- Identification of complications hidden during visual examination.
If the patient has metal crowns installed, then preliminary consultation with a specialist is necessary. The fact is that metal elements can create unwanted optical effects in images, which will complicate diagnosis and diagnosis.
Which is better - CT or X-ray?
Computed tomography is considered one of the most informative diagnostic methods used in dentistry. Using this method, it is possible to obtain a multilayer image of the area under study. A 3D image is much more informative compared to a conventional X-ray, which only provides a planar image.
From the point of view of affordability, x-rays are preferable, but they do not always provide an accurate picture of the condition of the dental-maxillary system. As practice shows, if a CT scan is performed, then in 99% of cases it is possible to accurately determine the cause of toothache and other symptoms.
Computed tomography of the jaw in St. Petersburg
If the doctor has prescribed a CT scan for you, but you don’t want to wait and sit in lines, then X-ray will offer you to undergo this study on their newest tomographs. The procedure takes no more than a minute, is absolutely painless and effective.
Today we told you how a CT scan of the jaw and teeth is done without negative consequences for your health. You can also record the examination results on a CD, send them by e-mail and make an online appointment. You can find out more detailed information by phone.
Sign up for a study by phone
+7 (812) 332-52-54