What are the differences between contraindications for CT and MRI?
Among the differences between CT and MRI, there are a number of contraindications that should be taken into account when choosing certain options for influencing the human body.
There are several main contraindications when performing MRI. These include:
- The presence of foreign metal products in the body. These can be various fragments, staples, artificial joints, plates and much more. The main condition is that such elements should not be subject to magnetic influence. Otherwise, due to magnetization, there is a risk of severe heating, burns, and internal bleeding.
- Patient use of various types of electronic devices. These include varieties such as pacemakers, insulin pumps, hearing aids and more. But it is also worth paying attention to the fact that many modern devices are initially created taking into account the likelihood of performing an MRI and their presence does not become a contraindication. To clarify such information, it is worth reviewing the accompanying documentation or directly to the manufacturers.
There are also a number of relative contraindications. These include fear of confined spaces, nervous tics, mental illness, and large body weight. A person who is unable to remain motionless throughout the entire procedure will not be able to undergo an MRI.
The only way out is to use anesthesia in especially important cases, when magnetic resonance imaging simply cannot be done without.
As noted above, when performing computed tomography, X-rays are used. Therefore, there are a number of contraindications that apply to this method:
- Pregnancy.
- Age up to five years.
- Frequent exposure of the body to radiation.
Despite the fact that modern CT machines use special methods to reduce radiation exposure, it is worth considering what impact your body was exposed to over the course of the month.
If your doctor recommends using a contrast enhancement method to increase the accuracy of your images, you need to pay attention to whether you have any contraindications to the use of contrast. These include personal severe intolerance to the components of the drug, as well as diseases such as renal failure.
As you can see, the difference between CT and MRI of the abdominal cavity, when it comes to contraindications, is not so great. But MRI is safer for the body and therefore is more often recommended for examining the abdominal cavity if various types of diseases are suspected.
What can be seen on a tomogram?
As in the case, complex computer processing of images obtained on MRI is performed. The result is a very clear picture of pathologies affecting the abdominal wall, intraperitoneal space and further body structures.
The doctor immediately sees which organs are affected and can clearly show it to the patient or relatives. The image from MRI is much clearer to non-specialists than CT, or, moreover, obtained from ultrasound.
Visualization helps to better justify the need for surgical intervention and obtain consent for surgical treatment. MRI images are transferred to the patient in digital form, say, as files recorded on a flash drive. Subsequently, they can be printed on a home printer and viewed on a computer screen.
In our clinic, MRIs are performed in strict accordance with standards, obtaining high-quality results that are easy to interpret for any specialist.
If there are contraindications, you can undergo a CT or ultrasound. An experienced doctor will examine you, identify indications and refer you to tests that will give the best results. Rate this article: (1 rated 5 out of 5)
Advantages of the methods
The best option is the flexible use of one or another method, taking into account their strengths and weaknesses, indications and contraindications.
MRI has several important advantages:
- Excellent fabric contrast. This helps to obtain information about the structure and other features of internal organs.
- No radiation exposure to the body. The procedure can be performed for children and pregnant women.
- Low risk of allergies. The drug used when checking the condition of the abdominal cavity rarely causes allergies.
If we talk about what is more informative, CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity, we can clearly talk about the high level of information content of magnetic resonance imaging in searching for foci of inflammation, as well as neoplasms and metastases.
CT also has a number of important advantages:
- High speed. The examination is much faster than an MRI. This is more convenient for those patients who, for some reason, cannot remain still.
- Low interference. The device itself does not depend so much on whether a person can remain still. The examination should be carried out when the patient is completely relaxed and calm, but movement does not create such disturbances as is the case with an MRI.
- Large diagnostic coverage. The image clearly shows not only the abdominal cavity itself with the organs located in it, but also the retroperitoneal space in the human body.
Despite all the differences between CT and MRI of the abdominal cavity, computed tomography also provides a very high level of reliability of the final result.
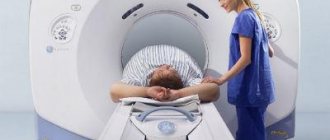
How is magnetic resonance imaging performed?
The patient is placed on a retractable table of a huge device, the inside of which resembles a tank. Lie on your back so that the abdominal wall is on top. If a different position is indicated by the attending physician, the attendants fix the patient as prescribed. Then the table slides inside the device.
There is an emergency button on the wall, by pressing which the patient can urgently call for help. You should lie still while the MRI is taking place and you should not make any movements. The operator transmits instructions over the speakerphone. Sometimes you need to hold your breath, for a few seconds at most. This allows you to obtain clear tomograms that are not blurred by breathing movements.
When the diagnostic procedure is completed, the table moves out again, the patient stands up independently or is transferred to a stretcher (gurney). Everything is absolutely painless, there are no unpleasant sensations.
Differences in MRI and CT scanning of the abdominal cavity with contrast
Contrast enhancement is used in both procedures to make images clearer and to be able to track even the smallest changes in the condition of internal organs. The main difference is the type of drug used.
MRI uses a substance based on gadolinium salts. During a CT scan, the patient receives a drug with a high level of iodine.
As described above, for some patients an allergic reaction may be a contraindication. And here, CT with contrast shows itself worse than MRI, because a person is allergic to iodine more often than to gadolinium salts.
The difference is impressive - in medicine, cases of allergic reactions to this type of substance are recorded 15 times more often.
When is a CT scan indicated?
On X-ray tomograms made using a computer, hollow organs are clearly visualized. Especially with the use of contrast agents. This is an excellent alternative to endoscopic examination of the stomach, intestines, and especially the gallbladder, which is unattainable with an endoscope.
CT scans clearly visualize the bones, which provides surgeons with guidance when surgery is to be performed. CT makes it possible to prepare based on the individual characteristics of the body, for example, to find out at what level the appendix of the cecum is located.
Important diagnostic differences
For the initial examination of the human body, none of the described methods are usually used. Ultrasound is more in demand in diagnostics because it is much cheaper and more convenient.
Doctors use CT scans when they urgently need to examine a patient and quickly assess the condition of organs in both the abdominal cavity and the retroperitoneal space. Without contrast, such a study can be performed in just 20 seconds.
This allows you to quickly navigate and perform the operation when minutes count.
At the same time, computed tomography usually gives a more complete picture of the state of the human stomach and intestines.
The reason is that the dependence on pulsation is much less than that of MRI. This way it is possible to track even minor changes in the condition of these organs.
MRI is much more often used when it is necessary to obtain the most detailed and informative conclusion to make a diagnosis.
It should be borne in mind that MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space are two different procedures. A detailed check of one organ can take up to 20 minutes.
An important advantage of using MRI is that the device makes it possible to conduct diffusion-weighted diagnostics of the bile ducts. In this way, the patient’s lymph nodes begin to be very clearly visible.
Even changes up to 2 mm will be noticeable very clearly - this gives an idea of the early stage of cancer.
Also on the list of advantages of MRI is the availability of color contrast. In this way, doctors can superimpose several images on top of each other at once and obtain complete data on the condition of organs and the presence of tumors.
What is diagnosed by magnetic resonance?
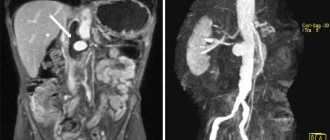
Since the abdominal cavity is vast and consists of several sections, the tomograph reveals diseases of many systems: digestive, genitourinary, endocrine. Also, MRI can be useful in cases of damage to large vessels, although CT in this case is informative (with contrast).
A separate category of research is the use of a magnetic field to diagnose tumors. MRI effectively detects cancer of the stomach, liver, kidneys, and metastases of tumors with a primary source outside the abdominal cavity. Many tumor processes are extremely difficult or practically impossible to detect on CT, so it is obvious which diagnostic method should be used.
Let's sum it up
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. So the question of what is more harmful, CT or MRI of the abdominal cavity can be answered unequivocally - computed tomography. Moreover, this method is faster and allows you to clearly view the stomach and intestines.
If you have enough time and there are no contraindications, we recommend using MRI. It is very informative, has few restrictions, and allows doctors to make a clear diagnosis and begin treatment.
Our center uses expert class MRI equipment. We quickly prepare the images - the radiologist draws up an informative, detailed report in just 30 minutes.
We offer affordable prices and favorable social discounts. To find out more details about the procedure or sign up for a session at a convenient time, simply leave a request on the website or call us.
Patient preparation
When an MRI or CT scan of the abdominal cavity is performed, preparation for the examination is necessary. When contrasting, a contrast agent is injected inside or into the vessels. You should also prepare the digestive tract for examination of the abdominal cavity so that feces and excess volumes of gases do not interfere with the diagnosis of pathological changes.
When contacting medical centers, patients are explained in detail what diet to follow. Typically, in 2-3 days you should reduce the amount of food you eat and eat foods that do not lead to flatulence or constipation. The medical staff will provide you with a detailed plan for preparing for the MRI, and the same applies to CT.
Comparison
What's better? Let's summarize.
| CT | MRI | |
| What is the method based on? | Exposure to ionizing radiation | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| Evaluation of results | Informative (better visualizes hollow organs and various injuries) | Informative (reliably identifies the tumor process, allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels and soft tissues) |
| Tolerability of the procedure | Possible complications | Well tolerated, but some patients find it difficult to remain motionless for long periods of time |
| Its duration | Up to 10 minutes | 30-40 minutes |
| Safety | Radiation exposure; side effects associated with contrast administration | Safe |
| Price | High | 1.5-2 times higher |