MRI of the spine in the cervical region, assessment of disc height (indicated by red lines) Among all diseases of the musculoskeletal system, pathologies of the spinal column lead. The variability of manifestations makes diagnosis difficult. To correctly determine the disease, doctors need to study the structure of the bones and soft tissues of the spine. Often, for this purpose, visualization diagnostic methods are used - radiography and MRI scanning. However, the studies cannot be said to be interchangeable. What is better, an X-ray or an MRI of the spine, is determined by the doctor, based on the clinical situation and the goals set for the diagnosis. For the reason described above, you cannot conduct any research on your own initiative or independently replace the procedure prescribed by the doctor.
The principle of operation of magnetic resonance imaging
During an MRI procedure, the body is exposed to a strong electromagnetic field, causing tissues to either absorb energy or emit it.
The information obtained through the scanner is processed by a computer program, and the result is an image in 3D format, in which the slightest changes in the structure of tissues and organs are clearly visible. Despite the fact that this diagnostic method is most suitable for assessing the condition of soft tissues, MRI is also well suited for examining the spine.
During the MRI procedure, the patient lies down on a special table, which is located in a closed chamber. The examination lasts about half an hour, and throughout this time it is necessary to remain motionless.
MRI, CT, ultrasound and X-ray: is there a difference?
All people undergo many diagnostic tests throughout their lives. Since childhood, we have been tested, undergo medical examinations and immunizations. However, if everything is more or less clear with blood tests, then when it comes to MRI, CT, ultrasound and radiography, many people do not understand what is the difference between these studies? Why do doctors in some cases prefer a particular research method? Let's figure it out.
First of all, you need to understand the definitions and physical basis of each method. Let's start, perhaps, with what we have all encountered - with radiography. The principle of operation in this case is that high-frequency electromagnetic rays, or X-rays, pass through different structures of the body and are retained in them differently. The rays are most retained in those tissues where the content of chemical elements with a high atomic number is high. The atomic number of calcium, which is so abundant in our bones, is 20, which is why we can distinguish bones so well in the picture. Soft tissues mainly consist of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, the atomic numbers of which are much lower than those of calcium, so the rays are retained in them to a much lesser extent. As a result, unevenly attenuated rays fall on the sensitive film, and we get the usual X-ray picture.
X-ray examination allows you to determine the anatomical parameters (shape, size, structure) of the body part being examined, as well as identify structural abnormalities. The greatest risk of the study used to be that during it the patient received a dose of radiation, but in modern devices the radiation dose is minimal. This is why radiography is so popular now. It is used to study diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diagnose injuries, bruises, fractures, pathologies of the lungs, kidneys, heart and blood vessels; radiography is widely used in dentistry.

Ultrasound is widely used to examine soft tissues, solid tumors and identify cystic inclusions; in addition, it is with the help of ultrasound that the condition of the fetus is monitored during pregnancy. In some cases, special types of devices are used: transvaginal for a more detailed examination of the organs of the female reproductive system and transrectal for examination of the organs of the male reproductive system. Ultrasound is also used when taking biopsies for control. Unlike an X-ray machine, an ultrasound machine does not pose any danger to pregnant women. However, organs containing air (intestines, stomach, lungs), as well as bone tissue, remain inaccessible to ultrasound.

Computed tomography is essentially a modernized radiography. It is also based on the irradiation of the body with X-rays, which are weakened differently by different tissues. However, due to the fact that CT is the production of layer-by-layer images, in the end we receive not one image, as is the case with conventional radiography, but a whole set of them, which we can combine using a computer into a volumetric projection. This is the greatest advantage of CT over radiography.
Typically, the examination lasts about 5-20 minutes (depending on the urgency, since CT machines are often found even in emergency departments), during which the doctor receives a 360-degree image of the patient’s body using transverse “cuts” with beams. Using CT, you can simultaneously visualize bones, soft tissues, and blood vessels. It provides the radiologist with detailed information about the structure of bone tissue, injuries, and can be used to diagnose many diseases of the chest organs and detect cancer.
Although a CT scan is completely painless, there is a certain disadvantage in the form of radiation. Modern devices are certainly safer and more effective than the very first ones, but CT scanning is not recommended for pregnant women. It is permitted only in the most extreme cases, when such risks are justified. In addition, CT scanning is permitted for patients who have metal objects in their bodies, such as metal pins.
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on a different principle. The thing is that there are a lot of hydrogen atoms in our body. The tomograph itself is a huge magnet. After the tomograph is turned on, the nuclei of atoms fall into its magnetic field, as a result, the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance is observed: the absorption of electromagnetic waves by atomic nuclei under resonance conditions with a change in the spins (angular momentum) of the nuclei. As a result, electromagnetic waves are re-emitted by the nuclei of atoms, and then captured by a special tomograph sensor, and we receive a digital image.
This research method is absolutely harmless and safe for human health. MRI can be taken an unlimited number of times. In addition, it is not contraindicated for pregnant women and is safe for children. Using MRI, you can visualize organs, soft tissues, and diagnose the difference between normal and abnormal tissues.
There is another type of MRI - functional MRI, or fMRI . Using this research, it is possible to determine the characteristics of certain areas of the brain and their location, for example those responsible for hearing, movement or speech. The principle is based on the fact that in the areas of the brain that are currently activated to the greatest extent, increased blood flow is observed, which can be recorded using a tomograph.
What then is better to use? A definite answer can only be obtained for each specific case. Thus, CT is more informative in the case of pathology of the chest organs, skull bones, brain injuries, various diseases of the spine and blood vessels. MRI is more informative if it is necessary to study tissue damage or study tumors. X-ray is the simplest diagnostic method, which, in fact, is a reflection of the general condition of the body area. Ultrasound reflects changes in the structure of internal organs.
MRI, among other things, cannot be done on patients with iron prostheses, unlike CT, but it can be done on pregnant women and is more informative in determining tumors and their malignancy or benignity. Therefore, studies must be selected separately for each patient, taking into account all his characteristics and what we ultimately want to get.
Which diagnostic method to choose: MRI or X-ray?
Most often, when doctors admit a patient with suspected injuries or fractures, they prescribe conventional radiography as an examination method. An X-ray of the spine gives a good image, which shows the condition of the bone tissue. This is a simple and fairly cheap diagnostic method, and in the opinion of some practicing doctors, there is no point in prescribing magnetic resonance imaging as a research method.
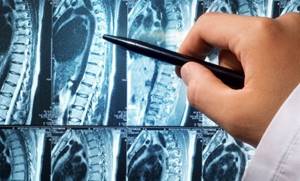
But do not forget that when performing radiography, the person being examined receives a fair share of radiation exposure. Therefore, X-ray examinations can be carried out no more than once every six months to a year. In contrast, MRI can be performed as many times as required, unless there are contraindications. This makes it possible to timely monitor the slightest changes in the structure of the spine and nearby tissues, evaluate the course of the disease and the effectiveness of the therapy used.
In addition, when choosing an MRI or X-ray of the spine as a diagnostic technique, you need to understand how detailed the examination results should be. The undeniable advantage of MRI over radiography is its high information content, as well as the digital format of the results, which are very convenient to work with in the future.
How does an MRI differ from an X-ray of the spine?
The main difference between the methods lies in the essence of the impact on the area under study. X-rays rely on the ability of X-rays to pass through body tissue and be retained in areas of high density. The described conditions determine the good information content of the procedure regarding the condition of the bone elements of the spine.
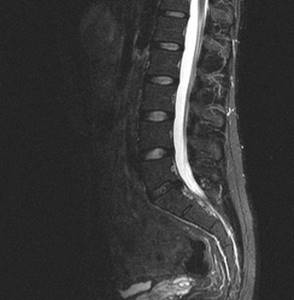
Disc herniation between the bodies of the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebrae on MRI
MRI scanning is based on the influence of a magnetic field. The latter changes the behavior of hydrogen atoms in the structure of water molecules, which are present in varying quantities in all tissues. The device captures the impulses and, based on the strength of the latter, builds a picture (called a snapshot or slice).
The main area of application of radiography is the diagnosis of vertebral pathologies. X-rays are often used as an express method for identifying injuries and associated pathological changes when other methods are unavailable. MRI well reflects the condition of soft tissues (intervertebral discs, spinal cord, blood vessels, muscles, nerves, ligaments).
X-rays are usually prescribed as a routine method for diagnosing a number of diseases and when performing certain surgical procedures. Indications for the procedure are:
- back injuries;
- Ankylosing spondylitis (if there are no other imaging methods);
- preoperative markings for interventions for disc herniations;
- tumors of the bone tissue of the spine when CT or MRI are not available;
- control of placement of transpedicular screws;
- Fluoroscopy is indicated when performing a lumbar puncture against the background of spinal diseases.
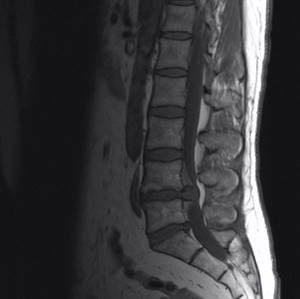
MRI is actively used to clarify the nature of the disease and detect changes in the spinal canal. The method allows you to identify tumors, disc herniations, sequestration formation, compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots. Indications for an MRI scan are:
- osteocondritis of the spine;
- suspicion of damage to the spinal cord, membranes and roots of the latter;
- inflammatory changes;
- congenital anomalies of the development of spinal structures;
- tumor diseases;
- myeloischemia;
- injuries of intervertebral joints, ligaments and nerve structures.
The difference between the procedures is the specifics of their implementation. X-rays can be done at any clinic. This is an economical and fast diagnostic method. Pictures are usually taken in two projections (if necessary, in others).
MRI requires specialized, expensive equipment, which is not available in all medical institutions. The scan takes about half an hour, during which the patient lies motionless in the tomograph tunnel.
Which is better, an x-ray or a tomography of the spine, cannot be answered unequivocally. Each method has its pros and cons.
| Diagnostic type | X-ray | MRI |
| pros |
|
|
| Minuses |
|
|
Differences between CT and MRI
If there are internal bleedings, then the most suitable technique for identifying them is computed tomography. This method is also suitable in all cases associated with spinal curvature or injuries. If you need to pay more attention to soft tissues (for example, the spinal cord), then it is best to choose MRI.
At its core, computed tomography is very similar to traditional radiography, especially since both of these diagnostic methods use x-rays during the examination, although CT has a much lower radiation dose. Therefore, the contraindications for CT will be similar to those for conventional X-rays, and you cannot undergo frequent computed tomography.
MRI and CT of the spine provide a picture that is similar in its information content: accurate, detailed, three-dimensional. Information about the state of the surveyed area is presented in digital form, which makes it possible for its further analysis and processing. For example, it can be used to predict the development of a disease or evaluate the effect of a course of treatment. The big advantage of CT over MRI is that the CT scan procedure takes significantly less time.
MRI and CT can be performed either conventionally or with the use of a contrast agent, which allows for a clearer image of the desired area. The contrast used in both of these techniques is different, but as with any medical drug, you should be careful with it, as some people may experience an allergic reaction.
Why does it hurt under the shoulder blade?
The appearance of pain in the interscapular area, under the right or left shoulder blade, is a fairly common reason for patients to consult a neurologist or traumatologist. Most often, such unpleasant sensations in the back occur during sleep or in the morning. Then during the day the pain may disappear and return again after rest.
The main cause of such pain in the scapula is osteochondrosis of the spine and poor posture. Typically, these pathologies occur in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle or work during the day in a sitting position and experience overstrain of the back muscles (accountants, system administrators, seamstresses). Rarely, pain under the scapula is associated with pulmonary pathology of inflammatory or destructive origin. If there is sharp pain in the left shoulder blade, heart disease should always be ruled out.
In any case, pain in the shoulder blade and back requires seeing a doctor and conducting a quality diagnosis. Indeed, such a seemingly insignificant symptom may hide more serious pathologies: a herniated intervertebral disc, spondylitis or a neoplasm.
Indications for the procedure
The main indications for MRI of the spine are:
- tumors and various neoplasms;
- hernias;
- pathologies of spinal cord development;
- nerve inflammation;
- the presence of infections in the tissues of the spine;
- pathologies of development and location of tissues in the spine.
MRI allows you to see how correctly the bones and soft tissues of the spine are located, what deviations there are, and whether there are inflammatory processes or not.
Causes of back pain
The most common causes of pain in the back and lower back are diseases of the spine itself and the tissues surrounding it, and, less commonly, pathologies of internal organs.
The pathologies that cause back pain are the following:
- osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, spondyloarthrosis, spondylolisthesis;
- curvature of the spine and poor posture (scoliosis, increased kyphosis or lordosis);
- back injuries, especially those accompanied by fractures or displacement of the vertebrae;
- muscle pathology (myositis);
- oncological process, including metastatic ones;
- congenital developmental pathologies (sacralization, lumbarization, cleft arches, etc.);
- inflammatory, including autoimmune diseases (spondylitis, ankylosing spondylitis).
Pain can also be caused by diseases of the chest or abdominal organs. In some cases, cardiac pathology is manifested by pain in the left half of the back or under the scapula, and changes in the lungs are characterized by symptoms in the interscapular region or the right half of the back.
Contraindications for the use of MRI
Since an electromagnetic field is used during the MRI procedure, the main contraindication for undergoing such an examination is the presence of metal objects in the body: heart pacemaker, pins, plates, hearing aids, etc.
Another contraindication is the patient’s condition in which he cannot remain in a confined space for a long time, remaining motionless. If the subject has claustrophobia, epilepsy and other diseases of a psychoneurological nature, then he should undergo magnetic resonance imaging under anesthesia. This will allow you to get high-quality images without artifacts (that is, errors) caused by
X-ray or MRI of the spine – which is better?
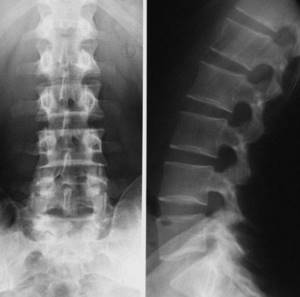
Compared to MRI, x-rays are a more economical and accessible type of examination. Thanks to the effects of radiation, it better visualizes bone tissue, which is why it is successfully used in the diagnosis of vertebral fractures and other consequences of injuries, anomalies in the development of vertebrae, tumors of bone structures, hematomas in the area of the vertebral bodies and the accumulation of fluid in them. If it is not possible to perform an MRI, x-rays can diagnose osteochondrosis, especially if it occurs without complications in the soft tissues. X-ray reveals infectious lesions of the spine in syphilis and tuberculosis, and also helps to detect unstable variants of osteochondrosis (radiography with functional tests is performed).
The main and significant disadvantages of x-rays are the low information content in the study of intervertebral discs, soft tissues, vessels, spinal cord and the presence of radiation exposure.
Advantages and disadvantages of radiography
The advantages of performing radiography are:
- High speed of detection of pathologies of bones, vertebrae, their displacement, growth, etc.
- Possibility of emergency diagnosis of spinal injuries.
- Simplicity of the procedure, no preparation required.
- Cost-effectiveness and accessibility - radiography can be done in any clinic or emergency room.
X-rays also have many disadvantages:
- The procedure is definitely more harmful than MRI; it uses radiation. Radiation exposure in modern devices is reduced, but is still present.
- X-rays should not be taken frequently.
- X-rays are prohibited for use in pregnant and lactating women.
- The method is ineffective for diagnosing diseases of paravertebral tissues and does not allow accurately determining the type of tumors.
What is CT (computed tomography)
To understand which is better - CT or MRI of the spine, you need to find out what these procedures are, how they are similar and how they differ.
CT is the same X-ray, only improved and modified. Its feature is the minimum radiation load. The rays here are directed only at a certain area of the human body. Their source makes revolutions around the body and sends information to the receiver, which is located opposite.
A full rotation of the tube around the body occurs in just a couple of seconds. And in this short time, 1,000 X-ray signals are emitted from the device. In total, 30 revolutions occur in one scanning procedure. This allows you to get a high-quality picture of the small bone structures of the spine on the operator’s screen, for example, his lumbar region or neck.
A CT scan of the spine is most often prescribed for fractures of any part of the spine or for injuries to the vertebral arches. But this study is not able to detect diseases of soft tissues or intervertebral discs, for example, a hernia.
Another option is MSCT. This is a multislice computed tomography that allows you to see every millimeter of a bone or internal organ. Moreover, you can get a picture on the screen from different angles and perspectives.
The main advantages of CT over MRI
Many doctors recommend CT scanning to their patients to identify back diseases. First of all, this study is good at identifying any pathologies of the bone structure of the vertebra at a very early stage of the disease. This means that pathology can be identified and treated even when there are no manifestations yet.
CT is an examination that is ideal for patients with artificial joint surfaces or metal structures in the body.
CT scanning takes minimal time and is somewhat cheaper. If you have claustrophobia, you can choose an open device, which is specially designed for those who are afraid of confined spaces.
X-ray and MRI - basic operating principles
When considering the question of which is better - MRI or X-ray, it is worth considering the purpose of each technique. An X-ray is now the most accessible way to diagnose spinal pathologies; it is indispensable for:
- Detection of problems of the vertebrae, intervertebral discs and spinous processes
- Detection of spinal injuries due to trauma
Obtaining an image is based on the passage of high-frequency X-ray radiation through tissue, which is delayed in areas of high density. That is why bone tissue will be clearly visible in such a picture. What will be the difference in the image if an MRI is done? Since the MRI procedure uses a magnetic field that interacts with the hydrogen atoms of the organ being examined, the image will allow you to distinguish any pathological tissue from healthy tissue. Magnetic resonance imaging does not use ionizing radiation, so it is considered safer than x-rays.
What are the advantages of x-ray
The advantages of this type of examination are low cost, speed and the ability to perform on non-transportable patients, as well as patients for whom MRI is contraindicated. Computed tomography is also based on the use of x-rays. But the images are processed on a computer and this type of examination makes it possible to obtain a three-dimensional image. Modern tomographs are the latest devices that allow you to reduce radiation exposure without losing the quality of the resulting image.
Indications
CT differs from MRI not only in the examination method, but also in the indications for use.
| When to do a CT scan | When to do an MRI |
| Spinal osteomyelitis | Intervertebral hernia |
| Chronic back pain | Spondylitis |
| Limited mobility | Spondyloarthrosis |
| Scoliosis of various stages | Tumors (malignant and benign) |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | Spinal vascular diseases |
| Fractures of various parts of the back | Coccyx cysts |
| Osteochondrosis | Narrowing of the spinal canal |
| Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine | Traumatic soft tissue injuries |
| The presence of metal structures for spinal alignment and monitoring their condition | Congenital or acquired developmental anomalies |
| Detection of bone metastases | Monitoring the condition of the spine after surgery |
| Bone Density Analysis | Detection of metastases in soft tissues |
| Determining the cause of spinal cord compression | Spinal cord infarction |
The difference between CT and MRI in the indications for performing it is clearly expressed. Therefore, it should not be surprising that the same doctor can prescribe a CT scan for one patient and an MRI for another.
No ads 1
Mistakes that patients make when choosing
Only the doctor, not the patient, should choose between CT and MRI. Both procedures are performed when there is a suspicion of a serious illness or when diagnosis is difficult. Otherwise, for a good neurologist or neurosurgeon it is enough just to examine the patient, his complaints and x-rays.
Therefore, these procedures should not be performed without reason or need. If after a CT scan the patient does not plan to visit a doctor and does it only out of curiosity, this is the biggest mistake. As for MRI, it is most often prescribed before surgery, as well as after it, in order to monitor the condition over time.
Indeed, the difference between these studies is large, and it is not recommended to carry them out unless necessary. But if the doctor has prescribed an MRI or CT scan, you should not be afraid of this. In most cases, this allows the disease to be identified at an early stage. This means that the disease can be completely cured even before it begins to manifest itself.
Main advantages of MRI over CT
But MRI also has its advantages, so it cannot be said that this method is worse or better than X-ray or CT.
Which doctor should you go to if your tailbone hurts?
The main advantage of MRI of the spine is that during the procedure the patient does not receive a dose of X-ray radiation, since the apparatus for carrying out the procedure uses a magnet. Therefore, if necessary, the procedure can be repeated several times a year or even several times a month.
This method can be considered ideal if the doctor needs to obtain images of cartilage, ligaments, intervertebral discs or nerves of the cervical, thoracic or lumbar back.
If you suspect a tumor of a malignant or benign nature, it is best to use this technique. The resulting images can reveal even formations of minimal size, which do not yet give any symptoms.
There is no need to use iodinated contrast during the procedure in order to better identify the desired areas. MRI uses a different type of contrast agent that only causes an allergic reaction in very rare cases.