Organs of the chest schematically Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to study the structure of the internal organs. The method provides comprehensive information about the condition of soft tissues and is less indicative of bones. MRI diagnostics are prescribed to detect diseases of the chest organs. Scanning in most cases is not the method of choice for examining the lungs, but it allows for good visualization of the trachea, bronchi, pleura, heart, thymus, large blood and lymphatic vessels. What a chest MRI shows often determines the final diagnosis. The method is used as an alternative and addition to CT, radiography or ultrasound examination of the heart.
Indications
MRI of the thoracic spine is indicated in the following cases:
- pain in the back, chest area;
- feeling of numbness in the limbs;
- limited mobility in the thoracic region, stiffness of movement;
- suspicion of osteochondrosis;
- intervertebral hernia, Scheuermann's disease;
- presence of signs of cysts and tumors (osteochondroma, osteosarcoma, gliomas, neurofibromas, meningiomas);
- mechanical injuries of the spinal column, spina bifida;
- anomalies of intrauterine development of the spine.
Free diagnostic consultation
If in doubt, sign up for a free consultation. Or consult by phone
+7
Alternative methods: which is better, MRI or CT
As an alternative, the most commonly used x-ray methods include CT scan of the lungs. This is a targeted diagnosis of the respiratory system, which clearly shows any changes in the lung parenchyma, adjacent tumor processes, and the spread of metastases from neighboring and distant areas. This type of scan is part of a generalized CT scan of the chest. It shows compactions, the condition of hollow, dynamic objects, and is often used as an adjunct to MRI.
It is difficult to answer unequivocally which of these methods is better, since different types of tomography solve different diagnostic problems. Computer screening reveals microscopic foci of inflammation, well displays the vascular network, lymphatic channels, pulmonary pattern, heart walls, and diaphragm. Chest MRI focuses on the condition of all soft tissue structures and is used if there are contraindications to X-ray radiation. If the doctor needs a complete picture of the area being studied, he uses both methods as part of a general diagnosis.
What can be seen on an MRI of the thoracic spine
As the tomographic images are obtained, the radiologist conducts a detailed check of the anatomical structures of the thoracic region. When deciphering scan results, close attention is paid to the following aspects:
- Statics of the spine: thoracic kyphosis is preserved, straightened, strengthened; Are there any signs of right- or left-sided scoliosis?
- Do the vertebral relationships deviate from the norm?
- What are the indicators of the height and shape of the vertebral bodies and joint spaces.
- Are there any symptoms of bone degenerative changes of osteophytes.
- Are there pathological changes in the bone marrow?
- Do you have uncovertebral arthrosis?
- How sharp are the facets of the facet and costovertebral joints?
- Quality of tissues of the yellow ligament and paravertebral tissues.
- Location, height and hydration of intervertebral discs
- The presence of protrusions, hernial formations, prolapse by compression of nerve roots, stenosis of the intervertebral foramina.
- Signs of myelopathy and structural changes in the spinal cord
| NORM | PROTRUSION | HERNIA |
EXAMPLE OF MRI CONCLUSION - thoracic spine
On a series of MR images, weighted by T1 and T2 in three planes, degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs are determined, characterized by a decrease in the height and intensity of the MR signal from them on T2-weighted images. Kyphosis is preserved. At the level of the Th8-Th9 intervertebral disc, a left-sided paramedian dorsal hernia is determined, sagittal size up to 3 mm, compressing the anterior wall of the dural sac. The roots are intact. The median sagittal size of the spinal canal is 14 mm. There is a dorsal left-sided paramedian herniation of the intervertebral disc Th10-Th11, up to 3 mm in size, which compresses the anterior wall of the dural sac. The roots are intact. The median sagittal size of the spinal canal is 15 mm. A dorsal median herniation of the intervertebral disc Th11-Th12 is determined with a tendency of cranial migration up to 3 mm, up to 5 mm in size, which compresses the anterior wall of the dural sac. Convincing data on root compression have not been obtained. The median sagittal size of the spinal canal is 13 mm. At the level of the intervertebral disc Th12-L1, a median dorsal hernia is determined, sagittal size up to 5 mm, compressing the anterior wall of the dural sac. The roots are intact. The median sagittal size of the spinal canal is 16 mm.
Interpretation of results: norm and deviations
An MRI analysis of the mediastinal and chest organs is carried out by a doctor - he draws up a conclusion in which he indicates the structures and formations identified during the examination, then the conclusion is transferred to the treating doctor, who makes the final diagnosis.
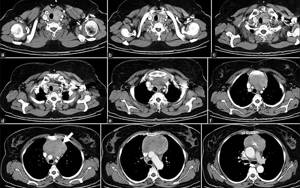
Normally, the trachea is curved inwards during exhalation, the diameter of the ascending aorta is 3.5 cm, the descending aorta is 2.5 cm, the diameter of the main pulmonary artery is up to 3 cm. The size of normal lymph nodes ranges from 0.5-1.5 cm in depending on their location. A small amount of pericardial fluid may be present in the pericardial pockets; veins and bronchovascular bundles are distinguished in the pulmonary parenchyma.
Changes in the structure of blood vessels, such as thickening, protrusion, thinning of the vascular walls, various neoplasms, traumatic injuries, foreign bodies, swelling, changes in the contours of internal organs, hemorrhages and hematomas, are not allowed on the images.
As for deviations from the norm, they all have specific signs based on which they can be identified. Malignant neoplasms are visualized as areas of increased density, dark color and uncertain shape. Benign tumors are characterized by a lighter shade and distinct contours - the surrounding soft tissues are not affected. Cysts are presented as round, light-colored formations with a thin dark outline, since they do not accumulate contrast agent and are filled with fluid. Edema tissues will also have light-colored shadows and slightly altered outlines.
Intercostal neuralgia is not visible on MRI except for swelling at the site of the lesion - with the help of such diagnostics, it is possible to roughly determine the cause that provoked compression or irritation of the nerve roots. Vascular abnormalities manifest themselves in the form of thinning, dilatation or thickening of the vascular walls. Hematomas are usually located close to the bone structures and are represented by a light stripe, the width of which is determined by the volume of blood accumulated in the tissues.
Compression and tissue deformation are characteristic of traumatic injuries; it is also possible to diagnose the presence of foreign bodies in the chest cavity in patients. MRI of the thoracic ribs allows visualization of skeletal structures, including the spine, and is most often performed as a concomitant procedure for examining the internal organs of the chest cavity.
How to prepare for the procedure
By contacting the information service of the Citywide Diagnostic Appointment Center, the patient will learn all the details of preparing for and undergoing the procedure in his specific situation. In general, for an MRI examination of the thoracic spine there is no preparatory stage, and a recovery period is also not needed - after the MRI, the patient can continue to do his usual activities.
You just need to keep in mind that if you have any implants or endoprostheses in your body, you must have documentation indicating the exact composition of the material used to make them. You will be asked to present it before the procedure begins.
How much does the examination cost?
Different clinics with MRI services have different admission conditions. The cost depends on the diagnostic mode, workload of the medical institution, and the availability of specialists with experience in interpreting MRI scans. Some organizations employ specialized doctors who can immediately advise on the results of the procedure.
Our service contains verified city MRI clinics that accept appointments for various types of examinations. The minimum prices for scanning using different methods are presented in the table. More complete data is available via links to price lists of medical institutions.
| Service name | Prices, rub. |
| MRI chest | 4115 |
| CT lungs | 2500 |
| PET-CT lungs | 31500 |
| CT scan of the chest | 2800 |
| CT scan of the chest with contrast | 4200 |
How to do a thoracic MRI
In diagnostic clinics in St. Petersburg, MRI is performed as follows:
- a person removes all metal objects from the body;
- lies on the platform of the device;
- the operator fixes a special MRI coil on the patient’s chest;
- the platform moves inside the tomograph;
- The scan is accompanied by the noise of the tomograph operating.
The duration of the study without the introduction of a contrast agent takes approximately 15-20 minutes; if a contrast agent is required, the study time increases to 40-60 minutes.
One of the limitations to the tomographic procedure is a strong form of claustrophobia. If the patient has this problem, we will help you choose a clinic where an open-type MRI machine is installed. Also, the Citywide Unified Center for Appointment for Diagnostics will indicate in which medical center you can get an MRI of the thoracic region with contrast, and where you can get an MRI of the spine using a super-powerful 3 Tesla machine.
where and how to get a high-quality MRI in St. Petersburg
- After scanning, you should receive MRI images in electronic form in DICOM format, recorded on a CD or flash drive. Printing tomographic images on X-ray film alone is not enough for a qualitative analysis of the results of magnetic resonance imaging.
- MRI diagnostics must be carried out in accordance with the technical requirements for the minimum scan slice. It should not exceed 2-4 mm depending on the tomograph model. You can clarify the thickness of the slice in the report that the radiologist will give you after completing the diagnosis. Remember, the smaller the scanning step, the more detailed and accurate the tomography results will be.
- When conducting cancer screening, it is imperative to perform MRI with bolus or dynamic contrast enhancement. In addition, there are minimum requirements for the power of the tomograph itself. If cancer is suspected, the examination should be carried out on an MRI machine with a magnetic field induction of at least 1.5 Tesla!
- If an MRI examination is repeated, the examination protocol must indicate the dynamics of changes in relation to previous images.
- The MRI images themselves should be clear without grain or blur from motion artifacts!
What does the diagnostic equipment look like?
A standard MRI machine is a large cylindrical tube surrounded by a magnet. The patient sits on a movable examination table that slides inside a magnet.
Some CT scanners (called short-tunnel systems) are designed so that the magnet does not completely surround the patient's table. Some devices are open on the sides. Such tomographs are especially suitable for examining obese patients and people who suffer from a fear of closed spaces. Modern open MRI scanners make it possible to obtain very high-quality images for various examinations. However, if an open type machine uses an old magnet, the image quality may be reduced. Some studies cannot be performed on an open tomograph. For more information, consult a specialist.
The computer working system that processes the images is located in the room next to the scanner.
Up
Magnetic resonance imaging results
Most often, upon completion of the procedure, the patient receives a written doctor’s report and a CD with images. You will need to wait for the result within an hour. After receiving the results, you need to seek advice from your attending physician, who will make a final diagnosis and prescribe treatment tactics.
Leading doctors of St. Petersburg

Pashkova Anna Alexandrovna
specialization: MRI doctor, radiologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences. Appointment - at the AMI Medical Center, Standard MRI on Ladozhskaya
medical experience - 21 years
Online registration
Khalikov Aziz Jalanovich
specialization: MRI doctor, radiologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences. Registration - at MC Scandinavia
medical experience - 20 years
Online registration
Trufanov Gennady Evgenievich
specialization MRI doctor, MD, professor. Recording - Federal State Budgetary Institution "National Medical Research Center named after. V. A. Almazova"
medical experience - 35 years
Online registration
Kholin Alexander Vasilievich
specialization MRI Doctor Professor of the Department of Radiation Diagnostics Northwestern State Medical University Appointment - CMRT Staraya Derevnya, CMRT Petrogradskaya
medical experience - 35 years
Online registration
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging compares favorably with computed tomography and radiography in its safety and harmlessness. During scanning, the human body does not receive any radiation load. However, this form of tomography also has a number of limitations. Since the tomograph is a large magnet, this procedure cannot be performed:
- persons with implanted electronic devices in the body (for example, pacemaker, neurostimulator, inner ear implants, insulin pumps);
- people with metal in the body (magnetizable fragments, plates, shunts, pins, staples, Ilizarov apparatus).
The need to lie quietly in a confined chamber may prevent individuals with claustrophobia and obsessive motion disorder from undergoing this test without the use of sedatives.
Other restrictions are relative in nature and can be resolved during consultation with a radiologist before diagnosis.
Tips on how to get an MRI inexpensively in St. Petersburg
To sign up for an MRI examination, it is better to clarify in advance all the points that may affect the quality and cost of diagnosis: class of equipment, qualifications of specialists, the need to use contrast, the cost of the service in the selected medical clinic, and what is included in this service. Here are some practical tips on how to get an MRI at an affordable price :
- The most inexpensive scanning method is ]MRI at night[/anchor], when the maximum discounts apply. Many private 24-hour clinics provide it. The biggest discounts are usually offered for examinations between 24:00 and 7:00.
- In St. Petersburg, there is a general seasonal decline in demand for medical services in January and August. Therefore, some medical centers, in order to actively attract clients, reduce the cost of MRI at this time.
- A number of clinics in St. Petersburg provide benefits for MRI to certain categories of patients: veterans, disabled people, large families, students, which allows them to save on costs. Information about such discount programs can be clarified when registering for an examination.
- MRI is included in the list of medical services that residents of St. Petersburg can receive under the compulsory health insurance policy. Free MRI under compulsory medical insurance will require the patient to receive a referral from the attending physician and is associated with waiting for a diagnostic quota. The average waiting time is 2 months. If the oncological diagnosis is in question, scanning is carried out urgently within 14 days.
Benefits and risks of the study
Advantages:
- MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique in which the patient's body is not exposed to ionizing radiation.
- MRI, compared to other imaging methods, allows you to obtain clearer and more detailed images of soft tissue formations such as the heart, liver and other organs. This property makes MRI an invaluable tool for early diagnosis and assessment of the status of many local disorders and tumors.
- MRI has proven diagnostic value for a wide range of diseases, including malignant tumors, cardiovascular pathology, and diseases of the joints and musculoskeletal system.
- MRI can detect pathological lesions hidden by bone formations and therefore invisible to other imaging methods.
- MRI allows doctors to non-invasively assess the condition of the bile ducts without the need to administer contrast.
- The contrast material used in MRI is much less likely to cause allergic reactions than the iodine-based contrast used in traditional x-rays and CT scans.
- MRI is a non-invasive alternative to X-rays, angiography and CT for diagnosing heart and blood vessel diseases.
Risks:
- If appropriate safety guidelines are followed, MRI carries virtually no risks for the average patient.
- When using sedatives, there is a risk of overdose. This is why the radiologist assistant carefully monitors the patient's vital signs.
- Despite the fact that the powerful magnet in the scanner itself is harmless, problems during MRI can arise if there are devices implanted into the patient's body that contain metals.
- When contrast material is injected, there is a very small risk of developing an allergic reaction. Such reactions are usually very mild and go away quickly when appropriate medications are prescribed. If allergy symptoms occur, a radiologist or nurse will immediately provide the necessary assistance.
- One recently described, but extremely rare, complication of MRI is nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, which develops when large doses of gadolinium-based contrast material are administered to patients with impaired renal function.
Up
Why is an MRI procedure considered safe?
Magnetic resonance imaging does not carry harmful radiation exposure, does not irradiate a person and does not have any harmful effects on the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging is completely painless. When undergoing diagnostics, there is no surgical intervention. If injection of a contrast agent is used, slight discomfort is possible since the drug is administered intravenously. Before the administration of a contrast agent, the patient must inform the doctor if he has any allergic reactions to the drugs.
Since the procedure is absolutely harmless, it can be done an unlimited number of times and combined with any other forms of diagnostics - ultrasound, CT, x-ray.
What is the basis for the research?
Unlike traditional X-rays and computed tomography (CT), MRI does not require the use of ionizing radiation. Instead, the radio waves generated by the magnet change the direction of rotation in a powerful magnetic field of protons, which are the nuclei of hydrogen atoms.
In most MRI machines, a magnetic field is generated when an electric current passes through coils. Other wires located in the machine, and in some cases placed on the area of the patient's body that needs to be examined, send and receive radio waves. This generates signals that are picked up by sensors.
The signals are processed by a computer program, resulting in a series of images, each showing a thin section of tissue. The resulting images can be examined from a variety of angles by a radiologist.
Often, MRI is the best way to distinguish pathologically altered, diseased tissue from healthy tissue than other imaging techniques, such as radiography, CT or ultrasound.
Up