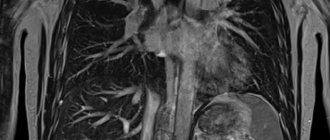
Computed tomography of the chest is the most accurate and most informative study in this area. If diseases of the chest organs are suspected, patients are first prescribed an X-ray examination, but the information content of this method is quite limited and in complex, controversial cases, computed tomography is prescribed. Computed tomography of the chest is also based on the use of X-rays, but has greater resolution. This becomes possible due to the fact that this method does not create general photographs of the body, in which the shadows of organs are layered on top of each other, but sequential “slices” of tissue.
This technique allows you to visualize elements of the chest skeleton (vertebrae, ribs), lungs and respiratory tract, as well as mediastinal organs, which include the heart, large vessels, lymph nodes, thoracic esophagus and thymus.
MSCT of the chest organs will allow you to diagnose inflammatory processes, specific changes (tuberculosis), malignant and benign processes in this area. Damage, developmental anomalies and other changes that cannot be determined by other methods will also be visible in the photographs.
MSCT of the chest
Computed tomography (MSCT; CT) of the chest is prescribed for the purpose of diagnosing diseases and pathological conditions of the chest, lungs, heart and mediastinal organs.Indications for chest CT:
Diseases that can be diagnosed using a chest CT scan:
Computed tomography of the lungs is very often used as a screening method during clinical examinations. MSCT of the lungs allows you to detect the smallest nodules characteristic of the initial stage of lung cancer. Computed tomography of the chest is prescribed to study the pathology of large great vessels: aorta, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins. In this case, the method is called CT angiography of blood vessels using a contrast agent. Based on the results of a computed tomography scan of the chest (lungs), the patient receives images or a CD and a detailed report from a radiologist (radiologist). |
Features and advantages of CT diagnostics
Computed tomography is a method of layer-by-layer scanning using x-rays. Body tissues have different densities and absorb X-rays differently. After processing the received data, a clear image is built on the monitor, which shows any disturbances in the functioning of the chest organs.
The main advantages of the method:
- computed tomography, unlike MRI, can be done in the presence of pacemakers, vascular stents, implants;
- CT makes it possible to obtain clearer images of organs that are in constant motion (heart, lungs, etc.) than with MRI;
- the high resolution of tomographic equipment makes it possible to study blood vessels, internal organs, the lymphatic system and neoplasms in the smallest detail (radiography and ultrasound are inferior to this method in terms of information content);
- Thoracic CT is performed very quickly, which is important in situations that threaten the patient’s life: heart attack, trauma, pulmonary embolism.
Preparation
No special training required
General requirements for contrast-enhanced CT:
To perform the test, you must have the result of a blood test with you.
for creatinine, the statute of limitations is no more than 30 days from the date of submission of the biomaterial.
Be sure to tell the radiologist before the examination with contrast:
- Do you have allergies to iodine, medications or food?
- whether you have diabetes, asthma, heart or thyroid disease
Preparation for MSCT of the kidneys and adrenal glands with contrast
When MSCT of the chest organs is planned with contrast, you should not eat food for 4 hours before the study. The patient must remove all metal objects from himself before the procedure. You should wear light, comfortable clothing for the session.
Preparation for MSCT of the brain with contrast:
Patients with an increased risk of allergic reactions and reduced renal function should be pre-treated with antihistamines and should not take diuretics or nephrotoxic drugs on the day of the study.
Benefits and risks of CT
Advantages
The results of computed tomography allow doctors to make the most accurate, correct diagnosis and timely prescribe treatment. Computed tomography is a non-invasive, painless diagnostic method. Carrying out CT scans very often reduces the required number of studies to a minimum and eliminates the advisability of using invasive techniques.
CT scan:
— allows you to study the state of the bone structure, soft tissues, blood vessels and individual organs layer by layer; - often used in emergency situations, for post-traumatic disorders, for suspected damage to internal organs, bleeding; — can be used if the patient has implanted medical devices of any kind; — used for control during biopsy of organs and pathological areas of the human body. X-rays from a CT scan have no immediate side effects.
Estimated risks and contraindications
The effective dose of radiation from computed tomography is minimal, however, it is always present. The radiation dose is usually specified in the study protocol. In the interests of accurate diagnosis, especially in acute cases, this risk is mitigated. Women are required to inform the referring physician and radiologist about the possibility of pregnancy. Because of the potential risk to the baby, CT scans are not recommended for pregnant women unless there are specific medical indications. It is extremely rare, but allergic reactions to a contrast agent that contains iodine do occur. In such cases, PATERO CLINIC has all the necessary means to stop such reactions.
Manufacturers of intravenous contrast media do not recommend that mothers breastfeed for 24 to 48 hours after receiving or administering contrast media.
Indications for examination
CT scans are performed on patients with complaints of breathing problems, stiffness of movement, pain in the thoracic region, numbness and tingling in the upper extremities. Such symptoms can be a sign of various diseases. To find out the cause of the discomfort, they are sent to a CT scan.
Tomography is done if pathology is suspected:
- hearts;
- respiratory system;
- esophagus;
- mammary glands;
- bone structures;
- blood vessels.
During diagnosis, doctors are able to differentiate tuberculosis foci, identify intervertebral hernias, assess the severity of lung diseases, detect tumors and accurately determine their location.
Indications
- A more detailed study of pathological processes detected during standard chest radiography;
- Diagnosis of the causes of symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, long-term high body temperature, etc.;
- The need to exclude oncological diseases, such as a primary tumor of the lungs and mediastinal organs, secondary damage to the lungs in the presence of a tumor of another location, damage to the lymph nodes of the chest and mediastinum;
- Assessing the effectiveness of cancer treatment results, including after radiation or chemotherapy; determining the presence of free fluid in the pleural cavity;
- Assessment of the condition of the lungs, blood vessels, bone structure (ribs, spine) for injuries of varying severity;
Contraindications for CT (MSCT or SCT) of the chest organs
Carrying out without contrast enhancement:
- Pregnancy and early childhood, which is associated with radiation exposure
- Body weight exceeds the maximum for the device (up to 200 kg)
Carrying out with contrast enhancement:
- History of severe reactions to contrast agents (shock, respiratory or cardiac arrest, seizures)
- Bronchial asthma or severe allergic disease
- Hyperthyroidism
- Severe renal or liver failure
- Pregnancy and lactation period.
How is a CT scan performed?
The examination is usually performed lying on your back, rarely - lying on your side or stomach. To maintain correct or still body position during the examination, you may be asked to place your arms under your body or raise your arms above your head.
If it is necessary to use a contrast agent, it is administered either orally (orally - swallowed) or administered intravenously, depending on the type of study being performed.
You may be asked to hold your breath during the scan. Any slightest movement of the body can lead to artifacts in the images. After the test is completed, you may be asked to wait a short time while the radiologist checks the quality of the image.
Typically, a CT scan takes about 30 minutes. The administration of a contrast agent during the study lasts from 10 to 30 seconds.
What sensations arise during the study.
A CT scan is a painless and quick procedure that is easily tolerated by the patient. Although the scan itself is not painful, there may be some discomfort from having to remain still for several minutes. If you have pain and find it difficult to lie still, your doctor may suggest painkillers. When a contrast agent is administered intravenously, you will feel a rush of warmth and a slight metallic taste in your mouth. These sensations last no more than two minutes.
The contrast agent may taste unpleasant when administered orally, but almost all patients tolerate the procedure well.
After the CT scan, the patient can immediately return to his normal routine.
What pathologies does MSCT of the OGK detect?
At the EuroMed clinic, multislice computed tomography of organs and tissues of the chest is performed according to the indications of a specialist.
The main goal of diagnosing OGK is to identify pathological abnormalities with a predisposition to their development or with signs of the development of diseases of organs located in this area. When performing MSCT of the chest, the following are examined:
- organs of the respiratory system;
- vessels;
- pleura;
- sternum and ribs;
- esophagus;
- lymphatic system;
- mammary gland.
Indications for examination may include signs of pathologies of the chest organs:
- infectious lesion;
- tumor formations;
- systemic diseases;
- aortic aneurysms;
- abnormalities of large vessels;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- thromboembolism.
MSCT of the breast may be recommended in preparation for surgery, in order to monitor the treatment or to clarify the diagnosis (differential diagnosis).
Detailed description
Multislice computed tomography is a modern research method. The procedure differs from standard CT of the chest organs in the quality of equipment and higher speed.
The MSCT tomograph is equipped with several X-ray tubes and sensitive sensors. This improves the clarity and detail of your photos. Image viewing is also available in several projections with volumetric visualization.
When examining the esophagus and lungs, MSCT of the chest organs is performed only with contrast. This will allow not only to identify anomalies, but also to establish their type and boundaries. During the study, it is possible to detect the following pathologies:
- neoplasms of any etymology in the lungs, bronchi, esophagus;
- peristalsis disorders, including esophagospasm;
- hiatal hernia;
- inflammatory and infectious processes.
Also during the procedure, the condition of other structures located in the chest is studied. This allows you to recognize even hidden defects and concomitant diseases.
MSCT of the chest with bolus contrast reveals
Multislice computed tomography is leading in the diagnosis of tumor processes, as well as in the diagnosis of traumatic injuries and diseases of the thoracic cavity. Multislice computed tomography with bolus contrast enhancement makes it possible to diagnose lung cancer at the earliest stages. Using bolus intravenous contrast, the brain, pulmonary arteries, aorta and arteries of the lower extremities are examined. Tumor or inflammatory diseases of the thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, kidneys and retroperitoneal space, and the presence of metastases are excluded.
How are lungs diagnosed?
MSCT of the breast does not require preparation, with the exception of diagnostics with a contrast agent. When using contrast liquid, the specialist will give all the necessary recommendations in advance. The procedure takes on average about 30 minutes, but depending on the purpose of the procedure and the area being examined, the examination may take longer.
The patient comes to the clinic at the appointed time. In the diagnostic room, he changes clothes, removes all objects containing metal from his body, then goes into the room where the MSCT machine is located.
Diagnostics of OGK is performed in a special apparatus with a retractable table on which the patient lies. After the patient takes the desired position, the couch slides into the tube, and the specialist leaves the room and turns on the device. The scanning process begins.
The results of MSCT of the lungs are prepared within 24 hours. Then the patient can contact the clinic specialists or another doctor to evaluate the results. You can sign up for diagnostics and consultation at the EuroMed clinic directly on the medical center’s website or by calling the contact number, using the help of consultants.