Determination of abnormal processes occurring in the internal region of the cranium is possible in several ways.
The most well-studied and long-used method is traditional radiography. However, even she is not always able to recognize the causes of the disease.
The nuclear resonance scanning method has been used for more than thirty years, but it is constantly being improved over time.
Modern devices are capable of not only determining the localization of pathology with high accuracy, but also identifying the causes of its occurrence. One of the most popular types of MRI of the brain is MR angiography of the brain.
Initially, in order for the doctor to see the affected area of the vessel in the internal zone of the organ, it was necessary to introduce a coloring substance into this particular channel, as well as the presence of an X-ray machine. The method was quite painful and had complications. With the introduction of devices operating on the principle of generating magnetic fields, the traumatic method faded into the background.
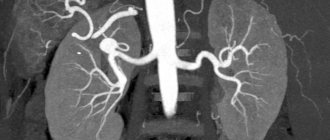
What is visible on MR angiography of cerebral vessels
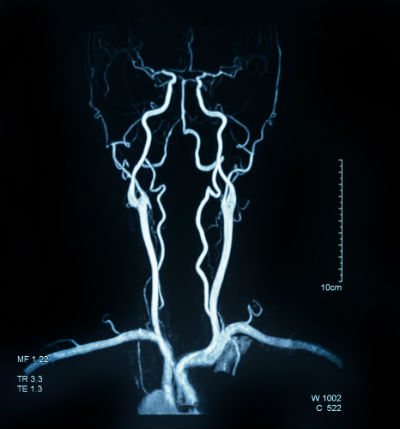
In the images produced by the machine, both normal zones of the vascular network and abnormal processes occurring in them are clearly defined.
Healthy vascular channels are characterized by smooth contours and configuration, a gradual decrease in diameter towards microscopic capillaries, the absence of bends and constrictions, and an even and smooth wall structure.
If any of the listed criteria does not match, both the specialist and the computer program will notice this and pay close attention to the “suspicious” area. In addition, the exact places of injury, the smallest tumor neoplasms, post-infarction and post-stroke changes, multiple sclerosis, etc. are clearly visible.
Types of research
The methodology for performing the procedure determines two types of examinations:
- puncture (the contrast is poured exactly into the vessel using a puncture needle);
- catheterization (the agent is injected using a catheter connected to the local vascular bed).
Based on the area examined, brain scans with contrast can be presented as:
- general angiography (visualization of vessels of different calibers is performed);
- selective angiography (means scanning of the vertebrobasilar, carotid region);
- superselective technique (a vessel with a caliber that does not correspond to any blood pool is examined).
The vascular system imaging pathway determines the following scan types:
- classical angiography - taking x-rays with preliminary introduction of contrast into the vessels of the head;
- CT angiography - scanning of the vascular system in the brain using an x-ray method with preliminary contrast and further 3D modeling of the display of the blood supply system;
- MR angiography involves examination using magnetic resonance imaging, often without prior contrast.
Computed tomography (MSCT) MRI
Indications for MR angiography of the brain
Hardware diagnostics are indicated in the following cases:
- post-stroke condition;
- symptoms of impaired blood circulation in the cranial area;
- bruises and injuries of varying severity, possible hemorrhages;
- the presence of blood clots in the vascular network;
- congenital anomalies of canal configuration;
- loss of visual function, hearing loss, “interference” in the eyes, dizziness;
- painful sensations in the head of unknown nature;
- epileptic syndrome, frequent seizures;
- development of mental disorders, behavioral changes without external influence.

Progress of the examination
The event begins with the administration of contrast medication (if necessary). The drug enters a vein in the elbow or forearm. No more than 100 ml of the drug is used.
Medical actions do not cause pain to the person; some people being scanned experience a slight sensation of heat.
At the next stage, the person being scanned changes into disposable clothes and lies down on an equipped table, which will move into the ring part of the device during the examination. During the procedure, the person must lie still.
Injection of contrast agent
The diagnostic process does not cause discomfort to the patient. Oxygen enters the tomograph, the machine makes noise, and a cracking sound may appear; if necessary, the patient is asked to use earplugs or headphones.
If the patient needs help, he can always contact a specialist using the built-in microphone or a button inside the equipment.
The examination takes on average about half an hour. After the table is outside the cylinder, the subject can get up, get dressed and leave the room. The results of the study are given to the patient.
The examination being carried out is not a traditional surgical intervention; it is a rather difficult procedure that puts a strain on the patient’s organs. This statement is especially relevant in relation to contrast research.
Therefore, after diagnosis, the patient is under the supervision of specialists to prevent undesirable consequences.
Mandatory rehabilitation appointments include regular monitoring of the patient’s body temperature and inspection of the puncture area.
When is MR angiography of cerebral vessels prohibited?
The main prohibition on diagnostics is the presence of ferromagnetic substances or electronic objects and devices in the patient’s body. Since the tomograph produces high-power magnetic fields, they are able to interact with ferromagnets. In the first case, the metal implants will heat up and displace them in healthy tissues. In the second case, electronic devices, often vital for a person (for example, pacemakers), will simply fail, which can lead to serious consequences.
What could be the consequences?
Frequently encountered negative results of angiography include edema and hematomas that form at the sites of administration of contrast or installation of vascular catheters. They often cause vascular injury.
Allergies to contrasts are less common. To eliminate it, it is recommended to take antihistamines. Anticoagulants can cause bleeding. It is recommended to apply a bandage in these areas.
In isolated cases, heart failure occurs if diagnostic rules are violated. After angiography, bed rest is recommended that day. Sports, heavy physical labor, and especially heavy lifting are not allowed for several days.
Stages of MR angiography of the brain
At the initial preparatory stage of diagnosis, the patient undergoes preliminary registration. The diagnostician gets acquainted with his medical history and determines the task of the study. After the preparatory manipulations, the person sits on the retractable part of the apparatus, the laboratory assistant helps him take a comfortable position and fixes the patient in this position.
The patient’s body is “introduced” into the tomograph, where numerous probes and sensors are located. The screening process begins, which lasts from 15 minutes to an hour and a half, depending on the complexity of the diagnosis and the power of the equipment.
During diagnostics, the installation displays a series of images of the studied area on the computer monitor. The diagnostician already has the opportunity to examine pathological areas. Often, additional enhancement—contrast—is required to study the vascular network. The price of MR angiography of cerebral vessels will increase if a dye is used.
Where to conduct the examination
If there is a need for diagnosis, you can scour the entire Internet in search of the necessary information. Or you can do it easier. If you call the phone number listed on the website, our operators will provide a complete free consultation on the issue that interests you. Consultants will tell you the exact addresses of diagnostic centers, information about the price of MR angiography of cerebral vessels, current discounts and advantageous offers. You can also sign up for diagnostics remotely by phone. Choose the most suitable time to register or submit an application online in a form that can be easily found on the portal.
The text was checked by the doctor Mikhail Mikhailovich Motov
Therapist
How to prepare properly
No special preparation is required for MR angiography. On the day of the procedure, it is recommended to refrain from taking any medications that can affect the condition of the blood vessels. If magnetic resonance imaging is being performed using contrast agents for the first time, a test for the substances used may be performed.

After an MRI with contrast, you need to drink a lot
Your doctor may then recommend drinking more fluids after the angiography to speed up the removal of the contrast agents.
A question of cost
The cost of an MRI or CT scan of the brain veins varies depending on the specifics of the scan. The average price of a CT scan in Russia is 2,500 rubles, and an MRI diagnostic is 3,000 rubles.
Angiography of the vessels of the head and neck is a reliable and fairly safe diagnostic method and reveals many local undesirable processes. Based on the method of tissue visualization, classical, CT and MR diagnostics are distinguished.
In the first two cases, the direct examination is necessarily preceded by the administration of a contrast drug; with MR angiography, contrast is often excluded. There are a number of contraindications to each type of diagnostic procedure.
The examination takes about 30 minutes. Possible complications include: renal failure, tissue inflammation (necrosis), allergic reaction to contrast. The cost of the study is determined by the specifics of the event.
Possible complications
Despite the relative safety of angiography, scanning can lead to a number of undesirable reactions, including:
- the appearance of an allergy to the administered contrast agent, leading to anaphylactic shock;
- the formation of an inflammatory process (neurosis) of tissues surrounding the vessel, which develops due to the penetration of contrast into it;
- development of acute renal failure.
An allergic reaction is the most common of the rare unwanted deviations. The reaction to iodine-containing drugs appears unexpectedly and progresses sharply. Possible manifestations of this adverse reaction include:
- swelling;
- redness of the skin;
- itching;
- low blood pressure;
- lethargy;
- fainting.

The use of non-ionic contrast agents will help prevent the occurrence of anaphylactic shock.
Extravasation is the result of poor technique for puncturing the arterial wall. Under such circumstances, the artery is punctured through - the contrast drug enters the soft tissue near the artery, provoking an inflammatory process or, less commonly, necrosis syndrome.
Acute renal failure manifests itself with previously diagnosed malfunctions in the functioning of the renal apparatus. This adverse reaction occurs when contrast is used.
Since the kidneys are responsible for removing the auxiliary agent, the organs undergo significant stress. The result of this is parenchymal ischemia and renal dysfunction.
To reduce the intensity of the load on the excretory organ and speed up the process of removing contrast from the body, after diagnosis the patient is advised to drink a lot.
Assessing the condition of the urinary system is a mandatory technique that precedes angiography of the cerebral vascular system.