Ultrasound examination is considered one of the leading methods for assessing the condition of the female reproductive system. In the modern world, almost every woman has the opportunity to undergo an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. Ultrasound is highly informative and has no contraindications. But ultrasound examination of the female reproductive system has a number of features. The results obtained strongly depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle and the examination technique. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed using two complementary techniques - transabdominal (external) and transvaginal (internal) access.
Let's figure out what transabdominal ultrasound diagnostics of the reproductive system organs is, what its pros and cons are, and how it differs from the transvaginal examination method.
Indications for ultrasound of the uterus
The content of the article
Ultrasound of the uterus
is a diagnostic examination performed to determine the anatomy, size, structure and condition of a woman's reproductive system. This procedure is usually carried out as a screening test during pregnancy and outside pregnancy to identify diseases and monitor treatment results. Ultrasound is completely painless and has no age restrictions.
Ultrasound of the uterus is prescribed for the following problems with women's health:
- irregular menstrual cycle;
- amenorrhea – complete absence of menstruation;
- prolonged menstruation;
- bleeding outside the cycle;
- copious mucous or purulent discharge with a pungent odor;
- discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- confirmation/denial of pregnancy;
- the course of pregnancy;
- inability to conceive or bear a child;
- treatment of infertility using hydrotubation;
- installation/removal of the spiral;
- pain, stinging, burning when urinating;
- suspicion of inflammatory processes;
- examination of the uterus after surgery;
- prolonged nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- after removal of the cervix and its part;
- monitoring the postpartum condition;
- suspicion of the presence of neoplasms and clarification of their characteristics.
The procedure is also performed when the uterus has a non-standard structure and the doctor is unable to see all the features using mirrors.
Interpretation of ultrasound OMT results
Pelvic ultrasound clearly visualizes the structure of the uterus, ovaries and appendages in women and the structure of the prostate gland and adjacent organs in men.
Based on the results of the study, the following pathologies can be identified in women:
- congenital anomalies of the uterus;
- endometriosis – growth of the endometrium outside the uterus;
- fibroids - tumor-like formations in the body of the uterus;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- presence of neoplasms;
- ovarian cysts.
Ultrasound also easily establishes the diagnosis of “small pregnancy”.
In men, ultrasound reveals neoplasms, prostate adenoma, inflammatory processes in the tissues of the prostate gland, pathologies of the seminal vesicles and ducts.
Bladder and kidney diseases can be detected in patients of both sexes.
A qualified doctor interprets the results of the ultrasound protocol. If necessary, he will prescribe other diagnostic procedures, give referrals to specialists, or independently draw up a treatment regimen.
Types of ultrasound of the uterus: how they are performed, features, advantages
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages can be performed in 4 ways. It is imperative that you check with your doctor which method will be used in order to take this into account when preparing for the procedure. It happens that a gynecologist recommends examination using two methods at once. Do not refuse - given the effectiveness, harmlessness and low cost of the study, this is the best option.
Transabdominal ultrasound of the uterus
The most comfortable procedure, but less informative when clarifying the nuances than other methods. Therefore, this technique is prescribed as a primary examination.
A huge advantage of the method is that with transabdominal ultrasound, a gynecologist can examine the entire genitourinary system and understand how the pathology is connected to other organs.
During a transabdominal examination of the uterus, the woman needs to lie on her back and expose her abdomen. The gynecologist applies a special gel to the area under study for better contact with the sensor and conducts the study with a special sensor. This method is ideal for pregnant women and girls who have not had sexual intercourse.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus (TVU)
This technique is considered the standard for examining the uterus and appendages.
The advantage of transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus is that the examination is aimed specifically at the desired organ, and the sensor is located in close proximity to the uterus.
A woman needs to expose her lower body and take a lying position on a couch or gynecological chair. The doctor inserts a special vaginal sensor into the vagina to a depth of 5-7 cm, scanning the uterus. A condom is put on it, which completely protects the patient from infection. Contraindications to this type of ultrasound are virginity and pregnancy.
Transrectal ultrasound
This procedure is used less frequently and only when indicated. Using rectal ultrasound, it is possible to identify neoplasms associated with neighboring organs, etc.
The patient also exposes the lower part of the body, but lies on her side. During this test, a probe is inserted into the anus, scanning the uterus through the intestinal wall. The procedure does not cause discomfort, since the gynecologist uses a narrower probe than for TVU. The doctor also puts on a condom and lubricates it with gel to improve glide and reduce discomfort.
Contraindications: anal fissures, hemorrhoids, inflammation in the intestines, neoplasms of the colon.
Intrauterine ultrasound
This method is the most informative, but it differs from the others and has some difficulties in execution, so it is used in special cases.
Intrauterine ultrasound is performed as follows:
- The woman undresses and lies down in the gynecological chair.
- The gynecologist opens the cervix using a speculum, then inserts a catheter for saline, which will help straighten the endometrial folds and provide a better examination. After the fluid is injected and the uterus is filled, the speculum is removed and the sensor is inserted directly into the uterine cavity.
- To assess the patency of the fallopian tubes, a saline solution with air is injected into the uterus and the movement of the bubbles is monitored.
The duration of the procedure is about 30 minutes. Intrauterine ultrasound is rarely prescribed, mainly when uterine fibroids and endometrial changes are suspected.
Benefits of transabdominal ultrasound
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Transabdominal ultrasound is a primary diagnostic method, along with laboratory tests. With its help, you can study the structure and functional state of the pelvic organs at any period of the menstrual cycle. The advantage of the method is the possibility of a general overview of the pelvic organs, obtaining an idea of the topography of normal and pathological formations of the pelvis and abdominal cavity. In some cases, transabdominal ultrasound is sufficient to make the correct diagnosis. The advantages of this method include non-invasiveness and painlessness. Thus, the transabdominal ultrasound method can be used at any age. The efficiency of the method is important - the procedure takes no more than 15-20 minutes, and the patient receives the results immediately upon completion of the examination. Transabdominal ultrasound has no restrictions for use during pregnancy: diagnostic ultrasound is safe for the fetus and the expectant mother at any stage. Volumetric scanning makes it possible to assess the condition of several organs at once and obtain complete information about the structure of the uterus and ovaries. Transabdominal ultrasound examination using modern ultrasound equipment provides accuracy and information content and allows you to identify tumors of the uterus and appendages even of small sizes. In case of detection of large formations, the transabdominal method has advantages over transvaginal ultrasound, since it makes it possible to completely visualize them.
How to prepare for a uterine ultrasound procedure
Preparing for a uterine examination is simple and does not require much effort. By following the recommendations of the gynecologist, you can protect yourself as much as possible from discomfort and unpleasant sensations. Features of preparation for ultrasound examination depend on the method in which it will be carried out.
Preparing for a transabdominal ultrasound
The day before the procedure, you need to change your diet to reduce gas exchange as much as possible: cabbage, beans, carbonated drinks, nuts, black bread and other gas-forming foods should be excluded.
The bladder should be full. The patient is offered the choice of either drinking 1 liter 1 hour before the examination. liquids without gas, or do not urinate for 2-3 hours.
A full bladder will help make the picture clearer and provide a convenient location for the organs to be examined.
Preparing for a transvaginal ultrasound
Preparatory measures include emptying the bladder immediately before the procedure. To improve the quality of the examination, it is recommended to empty the intestines of gases the day before using special medications (Smecta, Espumisan, etc.).
Preparing for transrectal ultrasound
A woman needs to empty her rectum 6-8 hours before the examination using one of the following methods:
- small enema with cool water;
- microenema - quick-acting rectal suppository (sold in a pharmacy);
- inserting a glycerin suppository into the anus (can also be purchased at a pharmacy);
- laxative.
It is better to use modern drugs, for example, guttalax. Do not use products containing senna and other components that promote the formation of spasms.
Preparing for intrauterine ultrasound
This type of examination does not imply any preparatory procedures. Immediately before the ultrasound, you need to empty your bladder so that the organ does not put pressure on the uterus
Procedure
Transabdominal ultrasound scanning requires minimal preparation . It consists only of filling the bladder. This must be done by drinking about a liter of water an hour before the procedure. In this way, a full bladder displaces the intestines from the field of view, which improves visualization during the examination.
Transabdominal ultrasound, regardless of the patient’s gender, is performed according to the standard procedure :
- The subject takes a horizontal position, lying on his back or turning on his side.
- The skin on the abdomen is lubricated with a special gel to remove the air gap between it and the sensor, which will make the signal clearer. For the same purpose, the patient is asked not to move.
- The doctor runs a sensor along the anterior abdominal wall and examines the organs located behind it, observing their image on the monitor screen.
- Based on the results of the examination, the patient receives a detailed transcript of the data obtained.
What does an ultrasound of the uterus show?
Ultrasound examination of the uterus is a very effective procedure that detects dozens of diseases and pathologies. With its help, you can diagnose in a timely manner:
- leiomyoma – benign smooth muscle tumor;
- uterine cancer is a malignant tumor;
- adenomyosis - a benign formation (germination of the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) into the thickness of the uterus itself);
- endometrial polyps are benign neoplasms inside the uterine cavity;
- cervical polyps - benign neoplasms in the cervical canal (warts);
- cysts - tumors with blood or other fluid inside;
- synechia - fusion of individual sections of the uterine mucosa with each other. In girls, this disease often manifests itself in the form of adhesions of the labia minora, less often - minor and major;
- separation of surgical scars;
- uterine rupture during pregnancy;
- trophoblastic disease is a generalized concept of benign and malignant pathologies of placental tissues;
- pathological abnormalities in the development of the uterus, causing infertility and miscarriage;
- pregnancy - duration, number of embryos, etc.;
- frozen pregnancy;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- pathological development of the fetus.
What does this type of diagnosis reveal?
Indicators of the size of the uterus with appendages and prostate indicate the presence or absence of pathologies in the reproductive organs. Being the most reliable way to determine these parameters, transabdominal ultrasound allows:
- identify a number of problems in the reproductive system (endometriosis, ectopic pregnancy, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, the presence of adhesions, polyps, malfunction of the appendages and ovaries, chronic infectious diseases);
- detect cysts, tumors, fibroids, cancer at an early stage;
- diagnose pregnancy and monitor fetal development.
Ultrasound examination is especially necessary for expectant mothers to identify severe genetic pathologies in the child (hydrocephalus of the brain, Down syndrome, etc.). From the 12th week of fetal development, ultrasound can only be done transabdominally, so as not to cause premature birth or miscarriage. For women experiencing difficulty conceiving, such diagnostics help clarify the presence or absence of ovulation.
For men, ultrasound diagnostics will help:
- establish the cause, make an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment of chronic pathologies of the reproductive system, pain, discomfort in the groin, scrotum and bladder, discharge from the urethra and blood in the urine;
- identify the cause, source of problems with potency and inability to conceive a child;
- prevent the development of age-related prostate diseases.
When is the best time to perform an ultrasound of the uterus?
Unlike ultrasound examination of any other organs, ultrasound examination of the uterus must focus on the menstrual cycle. Ideally, it should be carried out 5-7 days after the end of menstruation.
At the very beginning of the cycle, the endometrium is thinnest, which will provide the most accurate assessment of the condition. In the second half of the cycle, the growing endometrium can distort the result, hiding the tumor or the affected area. In case of acute disease, an ultrasound of the uterus is performed on the day pathological symptoms are detected.
To check the functionality of the ovaries, examinations are prescribed three times during the cycle on days 8-10, 14-16 and 23-24. If the rectal temperature does not drop for more than 2 weeks and the hCG test result is negative, then an ultrasound is performed to rule out a cyst.
During pregnancy, three mandatory ultrasounds are performed to monitor the condition of the uterus and fetus. An ultrasound examination is prescribed at the following stages of pregnancy: 10-14, 20-24, 32-34 weeks.
What organs are examined by ultrasound OMT?
The Renovatio Aesthetic Medicine Center offers men and women to undergo a pelvic ultrasound procedure in Krasnoyarsk.
Women are seen by a gynecologist. He checks the condition of the following organs:
- walls and cavity of the uterus;
- cervical canal;
- fallopian tubes;
- ovaries;
- Bladder;
- kidney
The doctor is also interested in the presence of fluid in the pelvis and neoplasms. It is mandatory to describe the structure of the endometrium in the ultrasound protocol. It depends on the period of the menstrual cycle.
Pelvic ultrasound in men is performed by a urologist. During the examination the following are visualized:
- bladder;
- prostate;
- seminal vesicles;
- kidneys
The doctor records the results of the study in the ultrasound protocol.
Why do an ultrasound of the uterus during pregnancy?
Using an ultrasound of the uterus, the gynecologist monitors the condition of the amniotic fluid, umbilical cord, placenta and fetal development in general throughout the patient’s pregnancy. Carrying out early ultrasound diagnostics provides the specialist with the following information:
- condition of the uterus - absence or presence of deformities, tumors, polyps that can lead to miscarriage
- estimated date of conception, gestational age;
- diagnosis of multiple pregnancy.
With the help of the new device installed in our clinic, you can hear the heartbeat of the unborn child already at the first ultrasound session. The heart rate of the fetus is higher than that of a child who has already been born; the rate depends on the stage of pregnancy. For example, at 6-8 weeks the norm is 110-130 beats per minute, while at 9-12 it is already 170-190. Heart rate is one of the most important characteristics of the embryo’s condition; if the indicators exceed the norm, it allows timely diagnosis of the development of pathology and the taking of measures.
First ultrasound
10-14 weeks are the optimal period for ultrasound examination. During the first session, the gynecologist records the most important indicators (biparietal size, coccygeal-parietal size of the head), measures and controls the main characteristics of pregnancy. In addition, the thickness of the collar space is measured (allows us to determine the likelihood of the unborn child developing Down syndrome), and the size of the nasal bone is determined.
The nuchal translucency is measured in the neck area of the fetus; this is a dark stripe between the soft tissues and skin of the unborn child. The norm is the thickness of the space not exceeding 3 mm. The information is processed in the process of a comprehensive study, which allows us to determine the risk of having a baby with chromosomal abnormalities. In addition, ultrasound diagnostics allows a thorough examination of the structure of the fetal brain.
If indicated, the doctor may send the patient for an unscheduled ultrasound examination, regardless of the stage of pregnancy.
Second ultrasound
At 20-24 weeks, the expectant mother can see the arms and legs of her grown baby and examine his movements. The doctor carries out a full examination of the fetal organs, which have already formed, and carefully examines the vital organs - kidneys, heart, and so on.
During the second scheduled ultrasound diagnostic session, the embryo is measured, the amount of water and the condition of the placenta are studied. The results of the second ultrasound are certainly compared with the results of the first examination, which makes it possible to assess the intensity of development of the unborn child. And finally, the second examination allows the specialist to make sure that the fetus does not have obvious signs of chromosomal diseases. And the mother does not have any problems with the uterus and nearby organs
In most cases, a second planned ultrasound allows the doctor to find out the sex of the unborn baby. At 20-24 weeks, you can already independently see signs of gender on printouts or a monitor.
Third ultrasound
The main task of the third ultrasound during pregnancy is to check the position and condition of the unborn child before its birth. An ultrasound examination is performed at 28-32 weeks of pregnancy. The doctor determines whether the baby is breech or cephalic and makes sure there is no entanglement in the umbilical cord. This ultrasound diagnostic session makes it possible to calculate malformations, the signs of which appear only in the third trimester of pregnancy.
The last planned ultrasound for parents is no less interesting than the first, as it allows you to see the face of the unborn baby on the monitor; this is almost a newborn baby. Expert class equipment broadcasts the face of the unborn child in a three-dimensional image; parents, if desired, can film this joyful moment on video.
As a rule, the third ultrasound is combined with Doppler ultrasound; during this study, blood flow in the vessels of the embryo, uterus and umbilical cord is studied.
During pregnancy, there may be a need for additional ultrasound diagnostics, regardless of the period - an unscheduled ultrasound of the uterus is absolutely safe for the mother and child.
Three-dimensional ultrasound and 4D ultrasound
3D ultrasound of the uterus is a standard ultrasound, during which you can see an image of the unborn baby from all sides; a special program simultaneously processes the results. As a result, you can get a video recording with a three-dimensional image of the fetus in the uterus. 3D ultrasound increases the accuracy of medical diagnostics and gives parents the opportunity to “get to know” their baby before birth. 4D ultrasound differs in that the ultrasound image is broadcast in real time.
From the point of view of the emotional state, an ultrasound scan is very useful for a pregnant mother, since the study makes it possible to visually verify that the baby is okay. Often, it is the image of the baby that is displayed on the device’s monitor that becomes the moment when future parents realize the role ahead of them.
For a specialist, 3D and 4D ultrasound are important in the process of studying the fetal heart, because genetic abnormalities cannot always be identified at the prenatal stage. The heart is constantly in motion, which makes it difficult to examine. It is the combination of time study and obtaining a three-dimensional image that simplifies the diagnosis of fetal pathologies. This study also improves the quality of blood flow studies.
Terms of pregnancy: embryonic and obstetric
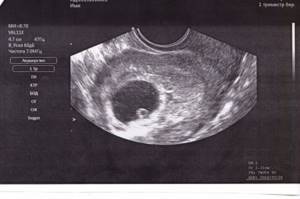
The gestational age indicated in the maternal card, filled out when registering at the antenatal clinic, differs slightly from the actual time elapsed from the day of fertilization by about 2 weeks.
But there may be other options, for 1-1.5 weeks, depending on the length of the menstrual cycle. This is considered the norm, because we are talking about different periods: embryonic and obstetric:
- Embryonic - counted from the actual day of conception, which coincides with the date of ovulation. For women, it is not difficult to calculate the day of conception only if they keep an ovulation calendar.
- Obstetric period is the period that has passed since the last menstrual period, after which conception occurred.
It is this period, which is easier for a woman to determine than the embryonic period, that is considered a reference point for scheduling routine examinations and establishing the upcoming date of birth.
Sometimes, women wonder “can an ultrasound not show pregnancy”? - yes, maybe, in the case when the doctor cannot see the fertilized egg, a repeat examination is prescribed due to the probable risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
Advantages of detecting pregnancy in the early stages:
- Timely detection of ectopic pregnancy;
- Establishing the fact of successful conception and its duration;
- Determining the cause of delayed menstruation in the absence of a positive pregnancy test;
- Determination of the number of conceived embryos;
- Recording possible threats to pregnancy.