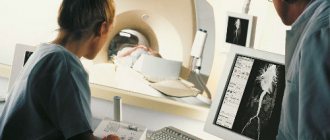
PET/CT (positron emission tomography - computed tomography) is a method for diagnosing diseases that combines the study of the structure and functional characteristics of tissues. This technology is most in demand in oncology for diagnosing and determining the extent of spread of malignant tumors.
- Description of PET/CT technology
- Advantages and disadvantages of PET
- Types of drugs for PET
- When is PET/CT indicated?
- Contraindications to PET/CT
- Preparing for PET
- Passing PET/CT diagnostics
- Complications and side effects of PET/CT
- Radiation exposure to the patient during PET scanning
Description of PET/CT technology
PET technology is based on the study of both structural and functional characteristics of tissues. Tissue function is assessed through metabolism. For example, a universal substance is selected that is necessary for all cells of the body. It is labeled with a radioactive label, injected into the body, and the places of its maximum accumulation are observed.
One of the most versatile substances in the human body is glucose. It is necessary to nourish almost all cells and tissues. But its greatest consumption is in malignant neoplasms, since a lot of energy is spent on the growth and reproduction of the tumor.
In PET/CT studies, glucose is labeled with radioactive atoms with a short half-life, such as fluorine-18. And after introduction into the body, it accumulates in large quantities in tissues with the most intense metabolism, i.e. in malignant neoplasms.
The radioactive tag decays, emitting energy in the form of gamma rays. The radiation is recorded by the device, and based on the data obtained, a visual model is built that shows the location of the tumor, its size and metastases.
Radioactive tracers accumulate only in pathological cells, while healthy tissues are not visualized. When the doctor wants to see both healthy and changed structures, a computed tomography scan is performed. It allows you to obtain a detailed image with millimeter accuracy.
After receiving data from both scanning systems, the software overlays them to create an image that gives the doctor a clear picture of where the pathological lesions are located.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Recipes
The pre-PET-CT diet is actually a low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet that offers a slight restriction of fat and a diet primarily based on animal products. Many diets designed for weight loss or athletic performance (for example, “cutting”) fall under this description.
Despite the limited range of products, the menu can be composed of complete, hearty dishes that at the same time have a pleasant taste. This will completely eliminate the feeling of hunger that sometimes occurs during forced dietary restrictions.
Chicken breast with butter in the air fryer
Bone-in chicken breast soaked in buttermilk and seasoned with a blend of herbs and spices is perfectly juicy.
To prepare it you will need:
- 1 large chicken breast without skin but with bones (700-800g);
- 1 tbsp. 1% buttermilk;
- 1.5 tsp. dried parsley;
- 1.5 tsp. fresh or dried garlic;
- 0.75 tsp. kosher salt;
- 0.5 tsp. dried dill;
- 0.5 tsp. onion powder;
- 0.25 tsp garlic powder;
- non-stick olive oil spray.
To bake a flavorful chicken breast in an air fryer, you will need to follow these steps:
- Place chicken in a bowl and cover completely with buttermilk, leave at room temperature for at least 20 minutes, or place in refrigerator for 4 hours.
- In another bowl, combine remaining spices.
- Remove the chicken from the buttermilk, allowing excess liquid to drain, then place it in the air fryer, skin side up, sprinkle the seasoning mixture on top and leave for 5 minutes so that all the additives are absorbed into the meat.
- After this time, spray it with oil and place it on the air fryer rack, cook at 150°C for 10 minutes, then increase the heat to 180°C and continue cooking until an instant-read thermometer inserted into the thickest part reads 70° C, and the chicken will not be golden brown, 30 to 35 minutes.
- Transfer the breast to a cutting board and let rest for 10 minutes, then remove the meat from the bones and cut into thick slices for serving.
Salmon with fresh herbs
This simple and healthy dish is made with baked salmon, fresh lemon and lots of fresh herbs such as dill, parsley, garlic.
All you need:
- 2 lemons;
- From 8 to 10 sprigs of parsley;
- extra virgin olive oil;
- 1 half wild salmon, such as sockeye or coho salmon, with skin, about 1 kg;
- 0.5 tsp. kosher salt;
- freshly ground black pepper;
- 2 tbsp. l. chopped fresh dill;
- 1 tbsp. l. chopped fresh garlic;
- 1 tbsp. l. chopped fresh parsley.

It is very easy to prepare baked red fish:
- Cut 1 lemon into thin slices, the second into slices.
- Place the lemon slices on a large baking sheet, place the fish skin side down in the center, place parsley sprigs on top and sprinkle with 1 tsp. olive oil, rub it evenly over the surface, seasoning with salt and coarsely ground pepper.
- Preheat the oven to 220°C, place a filled baking tray in it and bake for 15 to 20 minutes, depending on the thickness of the fillet, until the thickest part of the fish is cooked in the middle.
- Sprinkle the finished salmon with fresh herbs on top and serve with lemon wedges.
Turkey fillet in an air fryer
Air fryer turkey breast comes out moist and juicy with beautiful deep golden skin. At the same time, it bakes faster than in the oven.
To prepare you need:
- 1 kg turkey breast, bone-in, skin on (ribs removed);
- 1 tbsp. l. olive oil;
- 2 tsp. kosher salt;
- 0.5 tbsp. l. all-purpose dry seasoning for turkey or chicken, no salt.
The cooking process is as follows:
- Pour 0.5 tbsp. l. oil onto turkey breast, season both sides with salt and poultry seasoning, then apply remaining 1/2 cup. l. oils on the skin.
- Preheat the air fryer to 350°F and roast the turkey, skin side down, for 20 minutes, turn and continue cooking until the meat reaches an internal temperature of 71°F using an instant-read thermometer. This will take another 30-40 minutes, depending on the size of the breast.
- Leave the cooked turkey to stand for 10 minutes. before slicing.
Baked lamb ribs
Before undergoing a PET-CT scan, the diet may include not only chicken and turkey, but also red meat. For example, oven-roasted lamb seasoned with rosemary, fresh lemon juice and garlic is perfect within the constraints and still tastes great.

To prepare it, you will need the following:
- 4 cloves garlic, crushed;
- 1 tsp. chopped fresh rosemary leaves;
- 2 strips of lamb ribs (1 kg each);
- quarter of a lemon;
- 1.5 tsp each kosher salt and coarsely ground pepper.
To prepare this delicious dish, you will need to follow these steps:
- Season the ribs with lemon juice, kosher salt and coarse pepper on both sides, then rub with garlic and sprinkle with rosemary.
- Place a metal rack on a large rimmed baking sheet lined with foil, brush the surface with oil, add the seasoned lamb and let sit for about 1 hour.
- Preheat the oven to 220°C.
- Roast the lamb in the upper third of the oven for about 25 minutes, or until a food thermometer reads 54°C for medium-rare meat, or longer for deep-rare. To check for doneness, simply insert the tip of the thermometer into the thickest part of the meat, being careful not to touch the bone. When the temperature at this point reaches 54°C, you're done.
- Remove ribs from grill to cutting board and let rest, covered with foil, 10 minutes.
- To serve, cut the lamb along the valleys between the rib bones and place on plates, trimming off excess fat if desired.
Spicy Baked Salmon with Brussels Sprouts
This simple recipe offers a delicious and original dish that is high in protein and low in carbohydrates.
It will require:
- 120 g salmon fillet;
- 1 head of Brussels sprouts;
- light soy sauce;
- Sesame oil;
- lemon juice;
- rice wine vinegar;
- sriracha sauce;
- grape seed oil;
- smoked paprika;
- kosher salt;
- coarsely ground black pepper.

This delicious dish is very easy to prepare:
- Marinate salmon fillets by volume in a mixture of soy sauce, sesame oil, lemon juice, rice wine vinegar and Sriracha for 1 hour or more in the refrigerator.
- Toss halved Brussels sprouts with grapeseed oil, smoked paprika and coarsely ground black pepper and salt.
- Wrap the seasoned fish and vegetables in a thick sheet of parchment paper (making it look like an envelope) and bake at 180°C for 15-20 minutes.
Turkey meatballs with zucchini noodles
When reducing your carbohydrate intake, you should add more non-starchy, fiber-rich vegetables to your menu. For example, zucchini makes excellent noodles, suitable as a side dish for all meat dishes, including turkey meatballs. To make this delicious combination, you will need the following.
For the meatballs:
- 450 g lean minced turkey;
- 0.3 tbsp. zucchini puree; 0.3 tbsp. finely chopped onion;
- 2 tbsp. l. grated parmesan;
- 1 egg;
- a pinch of onion powder;
- a pinch of garlic powder.
For the zucchini noodles:
- 2-3 small young zucchini;
- olive oil;
- a pinch of onion powder;
- a pinch of garlic powder.
This dietary dish is prepared as follows:
- The oven needs to be preheated to 180°C.
- Mix all the ingredients for the meatballs until completely homogeneous, roll the resulting mixture into balls of the same size and place on a baking sheet, bake for 20-25 minutes.
- Slice the zucchini very thinly in a spiral using a vegetable slicer or vegetable peeler (the slices should resemble noodles or spaghetti) and fry in a frying pan with olive oil, season with garlic and onion powder.
- When serving, you can add sauce containing no more than 5 g of carbohydrates per serving.
Baked cod with fried asparagus
Fish dishes should be eaten at least 2 times a week, regardless of any diet. This is because it contains unique nutrients, including omega-3 fats, which are good for the brain and heart. One suitable option is baked cod with cheese and tomatoes and a side dish of asparagus.

For this dish you will need:
- 500 g cod fillet without skin;
- 0.25 tbsp. grated cheese;
- 200 g diced tomatoes;
- 0.25 tbsp. chopped fresh parsley;
- 1 bunch fresh asparagus plus oil for frying.
It's really easy to prepare:
- Preheat the oven to 200°C.
- Place half a kilogram of skinless cod in a baking dish, top with grated cheese, diced tomatoes and chopped fresh parsley and bake for about 20 minutes, or until the fish is very soft and crumbly in the middle.
- For garnish, fry blanched asparagus in butter.
This recipe makes 4 servings, so you can reduce the ingredients based on your needs. It is also worth noting that many dishes created for other high-protein and low-carbohydrate nutrition systems (Atkis, South Beach diet and the like) are suitable for the diet menu before PET-CT. The main thing is to pay attention to their composition and choose options that do not contain strictly prohibited products.
Advantages and disadvantages of PET
Advantages:
- The ability to combine several types of diagnostics in one study, which allows you to obtain highly accurate data.
- The examination is painless and does not cause discomfort.
- Possibility of diagnosing cancer at an early, pre-symptomatic stage.
- Possibility of studying all organs at once.
- The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require hospitalization.
The disadvantages of the method include the need to use radioactive drugs. To reduce risks, the study is carried out in strict accordance with radiation safety standards. In general, the side effects of PET scans are not commensurate with the valuable information this research method provides. In this case, three rules apply:
- The research must be justified. The benefits of diagnostics must outweigh the harm from exposure.
- Optimization. Medical staff are obliged to take all measures that will minimize radiation exposure to the body.
- Rationing. All radiation safety standards and regulations must be strictly observed.

Where is the diagnosis carried out?
Screening requires special equipment, which is not available in every district clinic. The examination is carried out in specialized diagnostic institutions with trained personnel. You can find the nearest medical organization on the website of the Unified Recording Center. Click on the name of the service, use the search filters, compare prices, select a suitable institution, sign up for a study with a special discount by calling the consulting service at the top of the page.
Types of drugs for PET
The potential of PET studies is determined by the arsenal of radiopharmaceuticals used—pharmaceuticals that are labeled with unstable isotopes that make the substances radioactive.
Currently, isotopes of the following elements are widely used in PET studies:
- carbon-11;
- nitrogen-13;
- oxygen-15;
- fluorine-18.
Fluorine is most widely used in oncological practice because it has the longest half-life and the lowest radiation energy. This, firstly, allows you to obtain images of high quality and spatial resolution. And secondly, the relatively long half-life (109.8 min) makes it possible to transport the drug from the production site to scanning centers.
The most common radiopharmaceutical in oncology is fluorodeoxyglucose FDG. This is an analogue of glucose, which is a universal substance absorbed by all cells of the body. Cancer cells absorb it faster, so they accumulate the drug in a higher dosage, which is clearly visible during scanning. The disadvantage of this substance is that it accumulates in slightly larger quantities in brain tissue and nephrons, which can cause illumination of these organs even in normal conditions. Therefore, the question arises of searching for other, more specific radiopharmaceuticals.
For the brain, such a drug is 18F-FET. It contains the amino acid tyrosine, labeled with the fluorine-18 isotope. Tyrosine has a very high selective accumulation in brain tissue, which is used for imaging neurotumors. In addition, 18F-FET is used for the diagnosis of oropharyngeal tumors, in the search for metastases and for the diagnosis of lesions of the lymph nodes of the neck.
In addition, there are a number of specific radiopharmaceuticals for the diagnosis of individual tumors:
- 68GaPSMA - used in the diagnosis of prostate cancer.
- 68Ga-DOTA-TATE, -NOC, TOC, -LAN, etc. are used for the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors.
- 18 FCH - used to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma.
The choice of radiopharmaceutical is made by a specialist doctor at the PET center based on the histological type of cancer, sensitivity and specificity of the tracer.
When is PET/CT indicated?
- Search for the primary tumor site when metastases are detected.
- Staging of an already identified malignant process.
- Differential diagnosis of relapse and post-therapeutic or post-surgical changes.
- Monitoring the course of the disease, detecting relapse (for example, with an increase in the level of tumor markers).
- Planning for radiotherapy and surgery.
- Planning a biopsy of the tumor and determining its most “aggressive” area.
Contraindications to PET/CT
There are absolute and relative contraindications to PET/CT. The following states are considered absolute:
- Pregnancy. The study is not carried out when a diagnosis is established, and in the case when a woman suspects its presence.
- Lactation. It is recommended to stop breastfeeding 6 hours before the intended examination. The timing of resumption of feeding is determined by the tracer used.
A relative contraindication to the study is decompensated diabetes mellitus when planning to use fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) as a radiopharmaceutical. In this case, consultation with an endocrinologist is required and stabilization of blood glucose levels below 7.7 mmol/l.
The study is carried out with caution in cases of impaired renal function, since the data obtained may be distorted due to retention of the radiopharmaceutical in the tissues.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Preparing for PET
The day before the scheduled date of the study, it is necessary to avoid physical activity. If you plan to use FDG, you should also avoid foods rich in carbohydrates. This includes not only sweets and sugary drinks, but also fruits, vegetables, baked goods, legumes, etc. On the day of the procedure, eating is strictly prohibited. You can only drink clean water.
The patient should arrive at the clinic wearing comfortable clothing. It is advisable that it does not contain metal fittings and decorations (zippers, buttons, buttons, fasteners, etc.). But if necessary, staff can provide a disposable gown.
If the patient has diabetes, glucose levels should be measured before the test. If it is above 7 mmol/l, you need to take half the dose of insulin. The minimum time between insulin injection and radiopharmaceutical administration is 5 hours. If the patient is taking tablets to lower glucose levels, it is necessary to discuss with the endocrinologist the possibility of discontinuing them on the day of the study.
What you can eat:
- Meat: beef and pork.
- Any green vegetables (zucchini, broccoli, asparagus, green beans).
- Chicken.
- Fish and tuna.
- Eggs.
- Cauliflower and mushrooms.
- Eggs.
For drinks, give preference to pure still water, unsweetened tea, and black coffee. It is also better not to drink compotes and fruit drinks. If a tomography with choline is planned, then the patient will have to exclude all foods containing choline from the diet for 2-3 days: cabbage, nuts, eggs, legumes, organ meats and B vitamins.
Passing PET/CT diagnostics
The patient must arrive at the clinic exactly at the appointed time. In this case, it is necessary to take all medical documents that are of interest within the framework of the disease - data from previous CT scans, histology data, laboratory tests, a statement of treatment, as well as data on concomitant pathology that may affect the diagnostic results (diabetes mellitus, kidney disease) .
After completing the paperwork, the patient is taken to the treatment room. There they take a blood test for glucose and measure anthropometric data. If everything is in order, the patient is taken to a relaxation room. There he is comfortably positioned, and a peripheral intravenous catheter is installed, through which the radiopharmaceutical is administered. To ensure it is evenly distributed, you need to drink a glass of water (or a contrast agent that the nurse will suggest) every 15 minutes. After administration of the radiopharmaceutical, you must be in a relaxed state and not talk. Any physical activity can lead to uneven distribution of the tracer and distort the results.
After 60–90 minutes, the patient is invited for a scan. First, a CT scan is performed, and then a PET scan. A CT scan takes a matter of minutes, while a PET scan takes up to half an hour. In this case, it is important to lie still so as not to provoke the formation of artifacts in the photographs that can distort the image. Both studies are carried out in the same tomograph and do not cause pain. After the procedure is completed, the patient must remain in the clinic for another hour, as a repeat scan may be necessary to clarify the data.
After a PET examination, the patient should not be in crowded places or have contact with children and pregnant women for 24 hours. In a family circle, you should keep a distance of at least 1 m from each other. Such restrictions apply for 24 hours after administration of the radiopharmaceutical.
In addition, during this period it is necessary to take a sufficient amount of liquid, at least 2.5 liters. This will help remove the contrast and radiopharmaceuticals faster and safer. You can drink more than just water. You can consume any caffeine-free products - juices, sparkling water, fruit drinks, mineral water, etc.
Bring with you
- Passport.
- Referral for research.
- Discharge summaries, results of ultrasound, scintigraphy, CT and MRI along with disks (preferably for the last three months) and their copies
, as well as other data that allows you to study the history of your disease in more detail. - The results of our research along with illustrations (if you visit us again).
- Creatinine blood test results (only if contrast-enhanced PET/CT is planned).
- Antihyperglycemic drugs ( for patients with diabetes
). Immediately after the test you will be able to eat and take pills. - Painkillers ( if there is severe pain
). - If you are undergoing a study at the expense of the compulsory health insurance fund (CHI), you must additionally provide a referral and a medical insurance policy (more details in the “CHI” section).
Complications and side effects of PET/CT
Complications during PET/CT are mainly related to the administration of CT contrast. As a rule, these are allergic reactions and complications associated with vein puncture - vascular damage, hematoma, pain, neuritis, etc. Renal dysfunction occurs extremely rarely. If contrast is taken orally, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea may occur.
Dizziness and weakness may occur after a PET scan due to the need for the test on an empty stomach. Therefore, it is recommended to bring a snack with you that can be eaten after all procedures related to the study are completed.
List of clinical and biochemical tests
- General blood analysis
- General urine analysis
- Blood sugar
- Bilirubin
- AlT, AsT
- Urea
- Creatinine
- Express tests for hepatitis B, C, RW.
The examination takes approximately 2 hours and requires your presence at New Life Medical.
- Of these, about 30 minutes are spent waiting for the procedure for administering the FDG drug, with which the PET study is performed.
- It takes 1 hour (sometimes a little more) to wait for the drug to completely accumulate in all tumor cells.
- The entire body scanning procedure inside the PET machine takes about 20 minutes (in complex cases up to 30 minutes.)
- After the scanning procedure is completed, you can go home. The research results will be ready within 48 hours.
Radiation exposure to the patient during PET scanning
Radiation exposure during PET/CT depends on the radiopharmaceutical used and the scope of the study. For example, scanning the head will expose you to less radiation than scanning the whole body. To minimize harm from PET/CT, the following standards are used:
- The research is carried out using ultra-short-lived isotopes, the half-life of which is several minutes or hours.
- An individual dose calculation is used for each patient, taking into account weight, height and age.
- The scanners use special filters and programs that reduce X-ray doses.
- Applying the required amount of liquid not only improves the quality of the resulting image, but also helps to remove the radiopharmaceutical faster.
In general, PET/CT is a fairly safe procedure, but it is performed only for strict indications when other studies do not provide the necessary information.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Useful tips
The diet before PET-CT has a very significant list of products recommended for consumption.
Types of food you should eat before your scan include:
- Sources of protein (unbreaded chicken, beef, turkey, pork, lamb, ham, lean sausage, fish, seafood, most nuts, seeds, eggs and unsweetened peanut butter).
- Vegetables (green beans, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, celery, asparagus, cucumber, lettuce, mushrooms and spinach).
- Dairy products (low-fat cottage cheese, hard cheese, sour cream, eggs, butter and light yogurt).
- Condiments (mayonnaise, oil-vinegar salad dressing, vegetable oil, vinegar, mustard, olives, pickles and barbecue sauce if it contains no more than 3 grams of carbohydrates).
- Drinks (sugar-free soda, drinking or mineral water).
It is worth noting that this diet does not involve the consumption of strictly healthy foods. The restrictions apply only to sugar and carbohydrates.

| Sources of carbohydrates (mostly fast) and sugar are prohibited | High-protein and high-fat foods prepared by boiling, stewing or frying in oil (but not on a charcoal grill or barbecue) are recommended |
| bread, toast, crackers, bagels, cookies, crackers, muffins, crispbreads and cereals | chicken, turkey, fish, beef, pork |
| milk, cheese | meat and sausage products without additives |
| pasta, granola | eggs and omelettes without milk |
| sweetened peanut and other nut butters | bacon |
| potatoes, legumes, corn | steaks and kebabs without additives |
| fruits and fruit juices | diet sodas |
| rice | tea and coffee without milk and sugar |
| caramel, candies, bars | mineral and drinking water |
| sugar, fructose, sucrose, Splenda and other similar sweeteners | |
| alcoholic drinks | |
| sweet soda |