Radiography is a medical diagnostic method based on the use of x-rays. Radiation exposure during radiography does not pose any danger to human health, but implies a limitation in the frequency of use of studies (x-rays, radiography, fluorography, etc.).
X-rays are divided into overview, which gives an idea of any area of the body (most often, a survey X-ray of the chest organs is performed - fluorography), and targeted, which gives more detailed information about the work of a particular organ and its structure.
The image obtained as a result of radiography is called a radiograph. The results of X-ray diagnostics are necessary for making a diagnosis in all branches of clinical medicine; X-ray diagnostics is included in the basic level of medical diagnostics in children and adults.
Preparing patients for radiography:
Special preparation of patients for x-ray examination is generally not required, however, the following preparation methods are available for examination of the digestive organs:
- Previously, special diets were carried out, foods that contributed to flatulence were excluded from the diet, and a cleansing enema was performed, but now it is generally accepted that RI of the stomach and duodenum of patients with normal intestinal function does not require any preparation. However, in case of severe flatulence and persistent constipation, a cleansing enema is performed 2 hours before the test. If there is a large amount of liquid, mucus, or food debris in the patient’s stomach, gastric lavage is performed 3 hours before the test.
- Before cholecystography, the possibility of flatulence is also excluded and a radiopaque iodine-containing drug is used (cholevid, iopagnost 1 g per 20 kg of live weight). The drug enters the liver and accumulates in the gallbladder. To determine the contractility of the gallbladder, the patient is also given a choleretic agent - 2 raw egg yolks or 20 g of sorbitol.
- Before cholegraphy, the patient is injected intravenously with a contrast agent (bilignost, bilitrast, etc.), which contrasts the bile ducts.
- Before irrigography, it is carried out using a contrast enema (BaSO4 at the rate of 400 g per 1600 ml of water). On the eve of the study, the patient is given 30 g of castor oil, and in the evening a cleansing enema is given. The patient does not eat dinner, the next day a light breakfast, two cleansing enemas, a contrast enema.
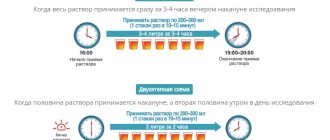
If preparation is carried out using the drug FORTRANS
- For effective preparation, you need to purchase 4 packets of the drug at the pharmacy.
- Dissolve the contents of each FORTRANS packet in drinking water at room temperature at the rate of 1 packet per 1 liter of water per day on the eve of the study.
- The resulting solution (4 liters) must be drunk from 18.00 to 22.00. The solution is drunk gradually in small sips of 1 liter per hour.
- Some patients note that after the second liter of the product, nausea may occur, which is caused by drinking large amounts of liquid. Regular lemon will help combat this symptom. To overcome nausea, simply bite a slice of lemon after drinking the solution. It is also recommended to drink the drug chilled, which reduces discomfort. You can no longer eat after you start taking Fortrans.
- Approximately 1.5-2 hours after taking the first liter of Fortrans solution, loose stools will appear, which is a natural consequence of taking this drug. Liquid stool will appear periodically several more times. The preparation is considered complete if, instead of stool, liquid is released that does not contain formal impurities.
X-ray and fluoroscopy in the Volyn hospital
Digital X-ray equipment used in the Volyn hospital is highly sensitive and allows you to reduce the radiation dose by 5-10 times for radiography and 2 times for fluoroscopy, i.e. make the procedure as safe as possible for humans.
In X-ray rooms, radiographic and fluoroscopic examinations of any degree of complexity are carried out:
- Examination of the chest organs (fluorography);
- Examination of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Retrograde cholangiopancreatography;
- Examination of the genitourinary system;
- Mammography;
- Fistulography;
- Radiography and fluoroscopy of skeletal bones;
- X-ray of the paranasal sinuses;
- X-ray of the nasopharynx, etc.
State Budgetary Healthcare Institution "Regional Children's Clinical Hospital No. 1"
List of diagnostic studies performed in the clinic:
- clinical and laboratory studies
- X-ray examinations
- MRI and CT examinations
- ultrasound and functional diagnostics
- ECG
- FGDS
Preparation for laboratory tests:
Blood: It is recommended to donate blood for laboratory tests in the morning, on an empty stomach, after an 8-12 hour fast. It is advisable to adhere to a standard diet for 1-2 days. On the eve of the study, avoid physical and emotional stress.
Urine: Before collecting urine for clinical analysis, careful toileting of the external genitalia is necessary. The morning urine sample collected immediately after sleep is collected for testing. Only a sterile, disposable container should be used to collect and transport urine.
Feces: Feces for examination are collected after natural bowel movements, without sudden changes in diet, before instrumental methods of examination and treatment with antimicrobial and chemotherapeutic drugs. A sterile disposable container is used to collect and transport stool.
Urine and stool samples should be delivered for analysis within 2 hours of collection.
Types of X-ray examinations that require preliminary preparation.
| 1 | Excretory urography | Preliminary preparation is necessary, the specifics of which should definitely be clarified with the radiologist who issued the referral. |
| 2 | X-ray of the stomach, duodenum, esophagus | The study is carried out in the morning. On an empty stomach, do not smoke, do not drink water, take medications only for health reasons. Last meal before 18:00, light dinner. |
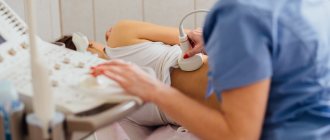
Preparing for an ultrasound:
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) is a study of the human body using ultrasonic waves. There are no age restrictions for performing an ultrasound scan.
If the child is overly emotional or restless in a new environment, a few days before the test it is necessary to begin preparing the child - explain that the procedure is painless and does not last long. During the ultrasound, try to distract the child from the examination as much as possible, this will enable the doctor to quickly and efficiently conduct the examination, and it will be easier for the child to tolerate the procedure.
There are certain rules for conducting ultrasound, the observance of which ensures a complete diagnosis.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, thymus gland, hip joints, scrotal organs, heart, superficial skin formations, superficial lymph nodes, kidneys, spleen and neurosonography are performed without preparation.
Ultrasound of the bladder, pelvic organs: prostate, uterus, ovaries is performed with a full bladder. To prepare for an ultrasound in 30-40 minutes. the child needs to drink any non-carbonated liquid at the rate of 5-10 ml per 1 kg of the child’s weight.
Ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas is performed on an empty stomach (the child should not be fed for at least 4 hours, the optimal period is 12 hours). To reduce the amount of gas in the intestines, it is recommended to exclude foods containing coarse fiber from the child’s diet one day before the test: cabbage, beets, legumes, chocolate, coffee, milk, rye bread.
Preparing for an MRI:
To optimize MRI and CT diagnostics, it is NECESSARY to refer a specialist with a preliminary diagnosis, the purpose and objectives of the study.
When applying to assess the dynamics of a previously identified disease, or to clarify data from other diagnostic methods (ultrasound, CT, MRI, angiography, scintiography, PET, etc.), you MUST bring with you the results (images, conclusions, CD\DVD) of the above methods.
Most MRI exams do not require special preparation.
Absolute contraindications for MRI:
Pacemaker and its electrodes; neurostimulants; insulin or others; infusion pump; claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces); heart valves; vascular clips; intravascular coils, filters; hearing prostheses, pregnancy first trimester; ocular prostheses; orthopedic metal structures (plates, pins, screws, nails); bullets, shot or shrapnel.
Relative contraindications for MRI:
Orthopedic joints (if certified); dental crowns, dentures, bridges; piercing; epilepsy; 2nd half of pregnancy; cardiac stents, if certified, after 6 months; the patient's serious condition (requiring constant monitoring, artificial ventilation); after abdominal surgery up to 6 months; eye tattoo
Preliminary preparation
To undergo an MRI examination of the brain, pituitary gland, paranasal sinuses, joints and spine, no prior preparation is required.
To undergo an MRI examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs, preliminary preparation is required, the specifics of which should definitely be clarified with the radiologist who issued the referral.
Some MR examinations require the administration of a contrast agent, in which case an allergic reaction is a contraindication. In case of polyvalent allergies, consultation with an allergist is required, and recommendations must be followed.
Preparing for an ECG:
Electrocardiography is a method of studying the heart muscle by recording the bioelectric potentials of the beating heart. There are no age restrictions for performing an ECG.
It is necessary to prepare the child for the examination in advance, explaining its painlessness, and, if possible, showing how the examination is carried out on another child. It is recommended to dress your child in such a way that it is easy to remove clothes. If the baby is restless, there may be distortion in the recording.
Preparation for FGDS
The study is performed strictly on an empty stomach. The evening before the study (before 20:00) - light dinner. Before the study, if possible, refrain from smoking. Before the test, you can drink small amounts of plain still water, but be sure to tell your doctor about this. After the examination, you should not drink or eat food for 30 minutes. If you had a biopsy, the food you eat on the day of the test should not be hot. It is possible to perform gastroscopy in the afternoon. In this case, a light breakfast is possible, but at least 5 hours must pass before the study.
Rules for conducting video-EEG monitoring for patients: These rules were formulated based on our experience and global standards for conducting video-EEG monitoring. Compliance with them during the study allows you to obtain maximum information about the disease. 1. Patients and their accompanying person (1 person) must arrive 15-20 minutes before the start of the study and actively cooperate with the doctors of the department, ensuring the most comfortable position for the patient in the ward, as well as assistance in conducting functional tests, participating in patient testing, etc. d. 2. Concealment of anamnesis (medical history) data is unacceptable. It is imperative to inform the department’s doctors about possible factors that provoke attacks - photostimulation, watching TV, reading, etc. A complete picture of the medical history will allow the department doctor to optimally choose the research scenario. 3. The patient’s head must be clean – the use of varnishes and gels before the examination is unacceptable. 4. During the study, patients and relatives must inform the department doctor about all paroxysmal events, indicating the time and their exact description (attacks or conditions, movements, sensations suspicious in relation to attacks). 5. Accompanying persons must not block the view of the video camera. 6. The patient must be within the operating radius of the video camera. 7. The level of lighting in the ward is regulated by the department doctor, not by the patients. 8. The patient and his accompanying persons must be informed that pronounced movements (both of the patient himself and relatives in relation to patients - rocking, patting, etc.) cause artifacts (interference) on the electroencephalogram, which significantly complicate the analysis of the bioelectric activity of the brain . 9. The patient should not remove the electrode cap until the end of the study. When the cap is removed by the patient (or their accompanying persons), the study can be stopped. When reapplying electrodes, technical problems may arise that will make it impossible to continue the study. Termination of the study in this case is not a reason for returning the cost of the study. Parents should, if possible, explain this rule to the patient; if contact is difficult (in the case of an early age or behavioral disorder of the patient), it is recommended to distract the patient and watch his hands. 10. Research conducted in the wards of the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution “KDKB No. 1” begins and ends at strictly established times. If patients are late for the study, the end time of the study remains the same. 11. It is unacceptable for patients and their accompanying persons to be under the influence of alcohol or drugs during the study. If intoxication or the smell of alcohol is detected, the test is stopped immediately. Termination of the study in this case is not a reason for returning the cost of the study. 12. GBUZ "KDKB No. 1" is a medical institution. Smoking is strictly prohibited in all areas of the Center. If this rule is violated, the study is terminated. Termination of the study in this case is not a reason for returning the cost of the study. If this rule is violated by medical personnel, the doctor may be dismissed in accordance with the Internal Regulations. 13. During the study, patients and their parents should not distract the department doctor from performing their direct duties.
Patients should be informed that failure to comply with the rules may significantly reduce the quality of the study or completely invalidate the data obtained. In this case, a decrease in the quality of the video-EEG monitoring study, which arose due to the fault of the patient and his accompanying persons, is not a reason for returning the cost of the study. Failure to follow the rules may not provide the necessary information about the disease to the attending physicians and lead to erroneous diagnosis or incorrect therapeutic tactics. Refusal to comply with the conditions of the rules described above should not come from the department staff, but only from patients or their parents when using the principle of informed consent!
Preparation for Video-EEG monitoring.
It is best if a specific type of study is recommended to you by your supervising epileptologist. Depending on the clinical situation (relationship of attacks with a certain time of day, with the phase of falling asleep and waking up, etc.), the type of monitoring is selected. Over the years of work in our center, several general recommendations have been developed for parents whose children undergo VEM. These recommendations mainly concern preparing the child for monitoring and are designed to make the study as informative as possible.
So: Sleep deprivation. As a rule, both daytime and nighttime studies involve recording EEG sleep. However, a well-slept and rested person finds it difficult to fall asleep in an unfamiliar environment - and a child is no exception. You will greatly help both the doctors and the child if, on the eve of the test, you put the child to bed 2 hours later, and wake him up earlier - so that by the time the monitoring begins, he will already be yawning. Those who are familiar with the generally accepted recommendations for a regimen for children suffering from epilepsy should not be surprised: indeed, strict adherence to the sleep-wake regimen is exactly what epileptologists recommend their patients to strictly observe. However, the most informative EEG study becomes precisely in a situation of controlled stress. For this purpose, during the course of the study, functional tests with hyperventilation, rhythmic photostimulation and, in the same series, with sleep deprivation are used.
Psychological preparation. It is highly desirable that the child knows about the upcoming study and is not afraid of a stranger. The examination is completely painless and the child’s fear of doctors usually disappears after getting acquainted with VEM, but the first examination can look quite dramatic in excitable children. The classical requirements for recording an EEG of quiet wakefulness require that a person remain completely still, in silence, and darkness with his eyes closed for as long as possible. Even for calm children, these requirements are fully fulfilled only immediately before falling asleep, and for restless children (for example, with hyperactivity and attention deficit syndrome), these moments are completely fleeting. Nevertheless, it is our duty to strive for the ideal, and success is achievable only with the help of parents.
Entertainment. Consider activities for your child during periods of quiet wakefulness. Ideal conditions for recording are when the child sits in one place and does not make any movements. The devices used in our center make it possible to make high-quality recordings even during the child’s leisurely movements, but the baby’s freedom is limited by the boundaries of the bed on which he is located. The parents' task is to prepare something that would attract the child's attention for a sufficiently long period and would help him withstand the restriction of motor freedom (watching cartoons, reading, quiet play). The child's head should be clean. This is not only a matter of general hygiene: the fact is that fat released with sweat is a fairly powerful dielectric, and increases the amount of interference during the study.