Carotid angiography is an invasive X-ray imaging procedure of the carotid arteries that is performed through a catheter inserted into a blood vessel in the arm or leg. A contrast agent is injected through the catheter, which is opaque to X-rays and therefore shows the internal lumen of the carotid arteries. This procedure is the gold standard for visualization of the carotid and cerebral vessels.
What is MR angiography of the neck?
The technique is based on nuclear magnetic resonance: hydrogen atoms release energy, which the device reads and converts into an image. MR angiography of the neck
involves using a magnetic resonance imaging scanner to obtain clear images of blood vessels. The equipment scans tissues and takes pictures of thin sections of planes to diagnose the slightest pathologies in the early stages. Using the method, the condition of the vascular walls, aneurysms, dissections, and structural disorders are examined.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
CT angiography is prescribed for:
- cerebrovascular accident;
- swelling, pain, injuries in the neck with suspected blood flow impairment;
- suspected aneurysm, vascular dysplasia;
- preparation for operations and for postoperative monitoring.
The study is contraindicated if:
- allergic reactions to drugs containing iodine;
- renal or heart failure;
- pregnancy;
- thyrotoxicosis.
When is MR angiography of the neck prescribed?
Many people ask the question: “MR angiography of neck vessels, what is it?” The procedure involves scanning the vessels of the cervical spine to visualize them. Among the indications for the study:
- frequent pressure changes;
- attacks of dizziness and headaches;
- diagnosis of thromboembolism;
- identifying possible consequences of injuries;
- impaired vascular patency, suspected narrowing;
- clarification of the location of the stenosis;
- dicirculatory encephalopathy;
- oncology;
- exclusion of vascular aneurysms and atherosclerosis.
The pictures show disturbances in blood flow in the arteries, and its direction can be determined. The method allows you to study the pathologies of the neck vessels without irradiation and obtain informative images in the shortest possible time.
If you feel dizzy or faint
MRI can help determine the causes of fainting and dizziness. The resulting layer-by-layer images provide an accurate picture of the condition of the vessels in the area under study.
For discomfort in the neck, a feeling of “tightness”
Discomfort and “tightness” in the neck can be consequences of osteochondrosis. To assess the lumen of blood vessels, MR angiography (MR arteriography and MR venography) of the neck and an ultrasound examination are prescribed.
Painful sensations in the root zone of the hairline
A symptom of vegetative-vascular dystonia is pain that occurs when touching the root zone of the hairline. The examination allows for a correct diagnosis.
What disorders can be detected using MRI of neck vessels?
The method allows:
- see the condition of a large vessel without harsh radiation and the introduction of contrast;
- identify the exact size and location of blood clots, vascular anastomosis and hematomas;
- obtain a complete picture of the vessels located in the part being examined;
- identify the physiological and anatomical state of blood vessels;
- assess the biological and physico-chemical processes that have occurred in brain tissue;
- establish a diagnosis and draw up the necessary treatment plan.
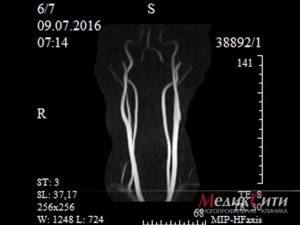
1 MRI of neck vessels
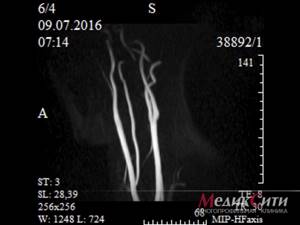
2 MRI of neck vessels
3 MRI of neck vessels
How is MR angiography of the neck performed?
The procedure lasts 30-40 minutes. During this time, the patient must lie motionless on a special table that slides into the device. In the resulting images, the doctor can see the location of the vessel structures. MR angiography of the neck
often performed without the use of a contrast agent. If the doctor recommends the introduction of contrast, the procedure takes longer and its complexity increases. In this case, a puncture will be made to introduce contrast. The patient needs observation for several hours after the procedure, sometimes for one day, to eliminate and prevent the risk of bleeding.
How is MRI of the cervical spine with angiography performed?
MRI of the cervical spine and MRA of neck vessels are performed according to a generally accepted protocol. No preparation is required before the procedure, so the patient can lead a normal lifestyle.
Immediately before scanning, the patient must remove any items or products that contain metal. It is also necessary to leave electronic gadgets, watches, pens, removable dentures and hearing aids outside the manipulation room.
Next, the radiologist assistant guides the patient into the treatment room, where the patient lies on his back on the retractable tomograph table. A specialized neck coil is worn. Patients suffering from psychomotor disorders and claustrophobia may be prescribed sedatives. After this, the table moves into the MRI tunnel.
The device starts working, taking cross-sectional images in different projections. After obtaining the initial images, if indicated, the patient is injected with a contrast solution. An additional series of images is taken, which will allow the diagnostician to identify the most minimal deviations from the norm.
Important! Contrast-enhanced MRI of the cervical spine uses a gadolinium-based solution, which does not cause an allergic reaction. The component is completely eliminated from the body naturally within 24 hours.
Contraindications for
The study is not carried out if there are metal devices in the body: a pacemaker, an insulin pump, clips on blood vessels, endoprostheses. Such elements may fail. There is a risk of movement of metal elements caused by the magnetic field, which can lead to tissue damage. When administering a contrast agent, it is necessary to exclude pregnancy in women. The procedure is not performed during breastfeeding. Renal failure is a contraindication to the examination.
Preparation for MRI of neck vessels
One of the advantages of magnetic resonance imaging is that, unlike X-rays, it does not have a harmful effect on the body and does not require special preparation.
Before starting the procedure, you need to remove clothes with metal inserts and any metal objects (pectoral cross, earrings, rings, watches, etc.). This will avoid distortion of research data.
It is important to let your doctor know if you have metal objects in your body (such as dentures, an insulin pump, a pacemaker, etc.).
The doctor warns the patient about the need to remain still during the entire period of the study.
To perform an MRI of the neck vessels with contrast, you must come for examination on an empty stomach.
During the examination, the patient does not experience any unpleasant sensations, except that the equipment makes loud noises (so you can bring earplugs from home).
Price
Without contrast: 4000 rub.
With contrast with body weight: 7000 rub.
Included in the price:
- MRI examination using expert-level tomographs with a magnetic field strength of 1.5 T, which allows reducing examination time by 15-20% (without loss of research quality);
- professional opinion, the radiologist will provide the results with brief information about the changes identified in the patient and, if necessary, recommend contacting a doctor specialized in the disease (gastroenterologist, surgeon, urologist or oncologist);
- recording research results on CD
Additionally you can order
Printing of the completed study on 25x30 cm format film - 250 rubles. Printing of the completed research on 35x43 cm format film - 400 rubles. Recording research results on a USB Flash drive (memory capacity 8 Gb) - 850 rub.
MR angiography of neck vessels is included in complex studies
Complex “Central Nervous System”: 12,000 rubles.
Complex “Advanced Oncology Search”: RUB 51,500.
| To main |
(Radiation diagnostic news 1999 1: 24-26)
MR angiography of the vertebral arteries for degenerative changes in the cervical spine: possibilities and disadvantages.
Marchuk V. P., Belyaeva E. L.
Vitebsk Diagnostic Center.
Today, the arsenal of magnetic resonance imaging uses three main types of pulse sequences that enable volumetric visualization of the bloodstream: - A sequence based on registration of an inflowing bolus of blood into the area of interest is called ToF (time of flight). — The Phase-contrast method uses the principle of encoding the speed of blood protons. — The MTC (magnetization transfer contrast) sequence allows you to improve the image of small vessels by suppressing the signal from stationary tissues.
Additional information about the state of the vascular bed is carried by the standard sequences SE, FSE, FE.
In assessing angio-vertebral abnormalities, we mainly used ToF and MTS – angiography technique. All studies were carried out on a VISTA tomograph (PICKER) with a magnetic field strength of 1.0 Tesla.
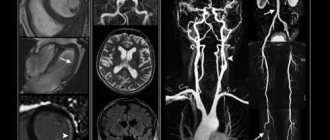
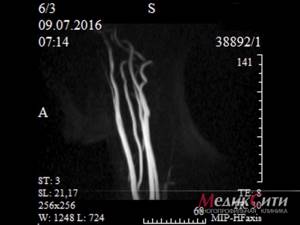
Normally, angiograms using a saturation field to the venous flow show: the upper part of the aortic arch; carotid system; proximal parts of the subclavian arteries; trunks of the vertebral, thyroid-cervical, deep cervical arteries; distal jugular veins ( Fig. 1
).
The vertebral artery (VA) was tracked along its entire length, from its mouth to its confluence with the basilar artery. The analysis of the obtained images was carried out on the basis of changes in the intensity of the PA signal, changes in the projection diameter and outer contour, as well as the degree of deviation from the rectilinear stroke.
We performed 50 MR angiographies in patients with radiological signs of degenerative changes in the cervical spine and clinical signs of hemodynamic disturbances in the vertebrobasilar region (VB).
MRI signs were distributed as follows:
| Rice. 1. MR angiogram of the neck vessels is normal. The upper part of the aortic arch, the carotid system, the proximal parts of the subclavian arteries, the trunks of the vertebral, thyroid-cervical, deep cervical arteries, and the distal parts of the jugular veins are visible. | |
| MRI sign | Number of observations |
| Reducing the projected diameter of the vessel | 40 |
| Signal intensity reduction | 12 |
| Fragmentary visualization of the vessel | 8 |
| Arc displacement | 8 |
| Roughness of the outer signal contour | 5 |
| Lack of signal at the entire study level | 2 |
In order to establish a possible connection between MR angiography data and blood flow velocity (diastolic linear velocity, LVV), 30 patients underwent Doppler ultrasound (USDG).
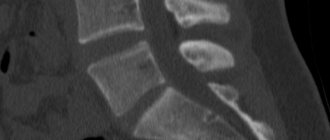
It turned out that on angiograms performed using ToF, there is no image of VA with a linear blood flow velocity of less than 3.9 cm/sec ( Fig. 2
). Visualization of vessels with LSV 4.0-6.8 cm/sec was either fragmentary or with reduced signal intensity and narrowing of the projection diameter of varying degrees. When studying PA with BFS more than 6.8 cm/sec, no changes were detected.
It should be noted that the interpretation of angiograms is complicated by factors related to the imaging technique itself.
The disadvantages of ToF and MTS sequences include the fact that they are nonspecific to blood flow. The missing signal on the angiogram (“dropped out”) can be obtained from protons with both a slow linear flow and turbulent flow (distal to an atherosclerotic plaque, thrombus), and a hyperintense signal can be produced not only by moving blood protons, but also by tissues with a short relaxation time T1w (adipose tissue, thrombus, tissue enhanced with a paramagnetic contrast agent).
Therefore, to interpret angiogram data, we performed parallel analysis of standard T1w and T2w weighted images performed in sagittal and axial sections. Analysis of tomograms (T1w and T2w) showed that in the majority of patients (28 people), against the background of a “dropped out” signal from the moving blood of the PA, areas with an inhomogeneous increase in the signal at various levels are identified. On angiograms, such areas showed a narrowing of the projection diameter and a decrease in intensity. Such changes were interpreted as intravasal.
There was a significant difference in the form of VA angiograms in the presence of extravasal pathology (8 people). These changes were clearly visible on PA images with precise topographical matches. Doppler ultrasound revealed a decrease in BFV and a disturbance in the spectral characteristics. Angiograms revealed an arcuate (sometimes angled) displacement of the VA site, a decrease in signal intensity, and a decrease in the diameter of the vessel. X-ray data indicated the presence of osteophytes and disc protrusions. We assessed this option as vascular-compression.
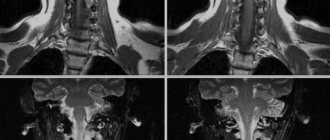
It is also significant that in the absence of obvious displacements of the VA trunk, in a number of cases a decrease in the diameter of a concentric vessel of varying length was found ( Fig. 3
). Axial T1w and T2w tomograms showed mild deformation changes in the joint capsules and disc protrusions. This option was assessed as reflex-compression.
It should be added that matrix angiographic tomograms provide additional information. They visualize small branches of the VA and vessels anastomosing with the VA.
To summarize, it should be noted that MR angiography is an informative non-invasive method that allows the assessment of both anatomical and functional disorders.
However, for assessing blood flow, the method has a number of general and specific disadvantages: - firstly, the use of MRAG is possible on tomographs with a magnetic field strength of at least 1.0 Tesla. More precisely, this possibility also exists on low-field devices, but only systems with high field strength can obtain reliable information with high-quality computer processing; -secondly, the method is quite expensive and not yet accessible; thirdly, MRAG is a nonspecific method that does not allow distinguishing between a mural thrombus and normal blood flow, turbulent flow and atherosclerotic plaque.
Meanwhile, our studies have shown that changes in the intensity of the VA signal in MRAH serves as an indirect sign of hemodynamic disorders (blood flow velocity), and local arcuate displacements of the VA trunk are an indication of the level of the lesion. Thus, MRAG data in combination with MR imaging can provide information about the state of VA, the presence or absence of compression, and its causes. This information is important when choosing a treatment method - conservative or surgical.
Indications for MRAG are conditions with long-term hemodynamic disturbances in the vertebrobasilar region that are not amenable to conservative treatment, the cause of which cannot be established using other non-invasive methods. The purpose of the study is to determine the nature of pathological disorders (extra-, intravasal), as well as to determine the level and extent of changes.
In cases where the arteries are not visualized with MRAG, or are visualized fragmentarily, and we are talking about the presence of pathology at several levels, X-ray angiography is necessary to decide on the tactics of possible surgical treatment.
Thus, only a set of diagnostic measures, including X-ray, ultrasound, and MRI studies will help identify the main cause of clinical manifestations of degenerative changes in the spine, as well as establish the nature and localization of pathological changes in the vascular bed.
Literature:
1. E. Zlotnik et al. Angiographic diagnosis of vascular lesions and brain tumors. Minsk. Belarus., 1973 2. I. Tager X-ray diagnosis of spinal diseases. Moscow. Medicine., 1983 3. Ya. Popelyansky Diseases of the peripheral nervous system. Moscow. Medicine., 1989. 4. JR Haaga, and other CT and MRI imaging of the whole body.
| Rice. 2. There is no image of the right vertebral artery (hypoplasia). Arrow—left vertebral artery. | |
| Rice. 3. Concentric narrowing of the right vertebral artery caused by protrusion of the C6-C7 disc on the right and arthrosis of the uncovertebral joint at this level (not shown). | |
What is the difference between tomographs?
The key to correct diagnosis differentiation is reliable images, which are created only through the full interaction of medical personnel and diagnostic equipment. But at the same time, one should take into account the fact that, despite the enormous practical experience of a radiologist, it is impossible to achieve high-quality visualization of pathologies on tomographs with low magnetic field induction (up to 0.5 Tesla). Thus, diseases of the brain are not displayed due to the complex structure of the organ and the lack of accuracy and clarity of the images. Read more…
Duration and quality of the study result depending on the magnetic field strength of the tomograph
Where to do it?
In order to sign up for MRA of the neck arteries in the city of Kasli, you just need to call the medical office, where the best specialists in Chelyabinsk work. Here angiography is performed on reliable and modern equipment from the world famous manufacturer Siemens. The Siemens Magnetom Harmony 1T MRI machine is distinguished by a high level of performance , as well as the presence of built-in modern software. Due to the use of reliable and high-quality equipment, after performing MR angiography of the arteries of the neck, clear and detailed images are always obtained, which provide invaluable assistance in making a diagnosis.
The result of MR angiography of the neck arteries can be recorded on a CD if necessary.