Ultrasound – what is it and why is it needed?
Ultrasound examination of the endocrine gland is a simple and safe procedure for the patient
. It is necessary to determine the presence (or absence) of pathologies, inflammation, neoplasms or other problems in this organ.
The study helps to identify:
- Enlargement or reduction of an organ
- Presence of nodes, cysts and tumors
- General inflammation or tissue damage
- Obstruction of blood flow
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes
- Impossibility of pregnancy
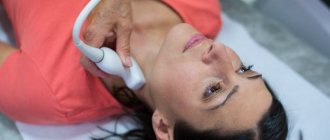
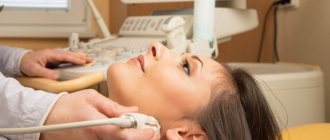
The examination mechanism is quite simple and painless:
- The patient is placed on a chair or couch in such a way as to provide access to the neck
- The doctor applies a special composition to the patient's throat
- Then the doctor picks up the sensor and moves it from different sides over the part of the body being examined.
- During the process, signals about the state of this endocrine organ are transmitted to the monitor and are also recorded on magnetic media
- The result is an image and data on the condition of the organ, which the doctor compares with normal
If any signs of abnormalities are found in the tissues or structure of the thyroid gland, the doctor prescribes other tests to clarify, confirm or refute the diagnosis.
What pathologies can a doctor detect on an ultrasound?
Developmental anomalies
Most of the anomalies are congenital, the cause of which lies in a violation of embryogenesis, that is, intrauterine development.
Rare anomalies include agnesia - the absence of the thyroid gland, hemignesia, in which one of the lobes is missing.
Hypoplasia occurs - underdevelopment of the organ, which is clinically manifested by hypothyroidism.
When the organ is located in an atypical place, for example, behind the sternum or under the tongue, they speak of ectopia.
Ultrasound examination helps to identify cysts formed during embryogenesis.
Diffuse lesions
Refers to non-tumor diseases of the organ. The cause of the development of pathology is a lack of iodine in the body or a violation of iodine excretion associated with taking certain medications.
Diffuse pathologies include:
- thyroiditis is an inflammatory disease;
- hyperthyroidism without the formation of nodes - hyperfunction of the gland with increased biosynthesis of hormones;
- hypothyroidism - hypofunction of the gland with insufficient biosynthesis of thyroid hormones.
Focal lesions
This group of pathologies includes benign formations:
- non-follicular and follicular adenomas - proliferation of glandular tissue;
- nodular or multinodular goiter - benign nodes;
- cyst - a cavity filled with fluid.
Dopplerography of blood vessels will show the most complete and informative results. Based on its results, you can get a complete picture of the changes occurring in the gland.
Thyroid cancer
A dangerous disease that occurs asymptomatically in the initial stages and does not manifest itself for a long time. Medical statistics show that malignant neoplasms occur in 20% of cases in patients with nodular goiter. Therefore, it is so important to identify malignant changes at an early stage of the disease, even before the cancerous node grows into the gland tissue.
Ultrasound examination of the organ in dynamics allows you to determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
specialist
Our doctors will answer any questions you may have
Chikov Sergey Vladimirovich Ultrasound Doctor
Ask a Question
When should you get tested?
The frequency of ultrasound examination of the endocrine gland depends on individual characteristics such as age, medical indications, and the presence or absence of ailments. Individual parameters:
- Age up to 50 years: preventive examination every five years
- For older people over 50: prophylaxis every two to three years
- During pregnancy and its planning: to eliminate negative effects on the fetus
For some medical indications and ailments, you need to be examined as soon as possible:
- In the presence of already established endocrine problems
- To monitor treatment or its results
- If there is a risk of recurrence of endocrine gland dysfunction
- With a noticeable enlargement of the thyroid organ, palpable seals and nodes
- Sudden weight loss or weight gain
- In case of unstable emotional state – apathy, nervousness
In what cases does a doctor prescribe an ultrasound?
Studies of the thyroid gland are carried out if the attending physician or endocrinologist suspects diseases of the gland, and when palpation reveals formations that are not characteristic of a healthy organ.
Diagnosis of pathologies is based on the following symptoms:
- feeling of a lump or sore throat;
- cough of unknown etiology;
- sudden loss or gain of body weight;
- difficulty swallowing;
- emotional instability;
- hair loss;
- hoarseness of voice;
- swelling;
- hand tremors;
- rapid pulse, arrhythmia;
- insomnia, other sleep disorders;
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- profuse sweating.
Emotional lability in diseases of the thyroid gland can manifest itself with symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, nervousness, and sudden changes in mood.
Ultrasound is prescribed for preventive purposes to people working with harmful production factors or a hereditary predisposition to the disease. The procedure is necessary for patients after a course of hormonal medications, patients with diabetes, as well as men and women after 40 years.
Endocrinologists and gynecologists recommend that women undergo an ultrasound scan during pregnancy and when planning it. Sometimes hormonal disorders and pathology of the thyroid gland are one of the reasons for the inability to get pregnant.
The study is indicated for children who have experienced stress, as it can become a trigger in the development of thyroid disease.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland
For this test - ultrasound of the thyroid gland - no special preparation is required. There are no restrictions on foods that can be eaten on the eve of the study.
But there are a number of recommendations:
- Elderly people should not eat before the procedure, as they may feel nauseous. This is due to age-related changes in the body
- Preparation for ultrasound of the thyroid gland in women is due to the fact that they are recommended to undergo this examination on days 7-9 of the menstrual cycle in order to avoid possible distortion of the result
- Before the procedure, it is necessary to free the neck from various interfering elements: collars, jewelry, etc.
- Preparation for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland for children does not differ from that for adults. But so that the child does not get scared, parents need to tell him about exactly how the procedure will take place, what the doctor will do and why
Why is emotional state important?
The thyroid gland is directly related to the hormonal balance of the human body. Therefore, the release of excess adrenaline and other stress-related substances before diagnosis is definitely not necessary. Remember that ultrasound is an absolutely painless procedure, so you should not be afraid of it. Don't think too much about the test results or how bad they might be. Get in a positive mood and forget about negative emotions. If the examination is scheduled for a child, talk to your child in advance and explain to him what exactly will happen in the sonography room.
Can ultrasound be performed on pregnant women and children?
Since the procedure is safe and painless, it is also suitable for children and pregnant women.
Small child
can be examined while sitting on the parents' lap. If your baby has been exposed to any stress, it is recommended to consult a doctor, as this condition can affect the functioning of the glands.
Women
It is recommended to do an ultrasound of the endocrine gland both at the planning stage of pregnancy and when it has already occurred. Since the developing fetus takes resources from the mother’s body, it is necessary that all her organs work correctly. Disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland can lead to hypothyroidism and negatively affect the health of the developing child.
For those who are trying to get pregnant but cannot
, you also need to contact an endocrinologist for diagnosis, since the problem may be in this gland of the body.
What diseases and disorders can ultrasound detect?
Thyroid cysts
A thyroid cyst is a hollow formation containing fluid inside. In most cases, cysts do not pose any danger to humans. Thus, the inactive form of thyroid hormones is stored in reserve. If the formations are small, there are no signs of their malignancy, or an increase in the volume of the organ, then the cysts do not require treatment. They are simply monitored with regular ultrasound examinations.
However, large formations can cause pathological symptoms and lead to compression of neighboring internal organs. With large cysts, a person experiences difficulty breathing, hoarseness, neck deformation, bursting pain in the cervical spine, difficulty swallowing, and an unreasonable cough. In such situations, conservative and surgical treatment methods are used.
Ultrasound signs of thyroid cysts include:
- correct form;
- smooth, thin walls;
- anechoic contents;
- the presence of an acoustic shadow - an anechoic strip.
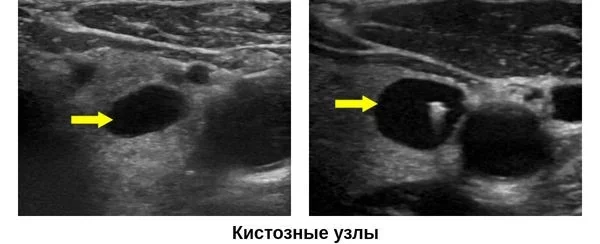
During an ultrasound examination, the risk of malignancy of cysts is assessed in points according to the ACR TI-RADS classification:
- 0-3 points - the risk of malignancy is low, additional diagnostic methods are not required;
- more than 3 points - the risk of malignancy is high, a fine-needle biopsy of the node is required.
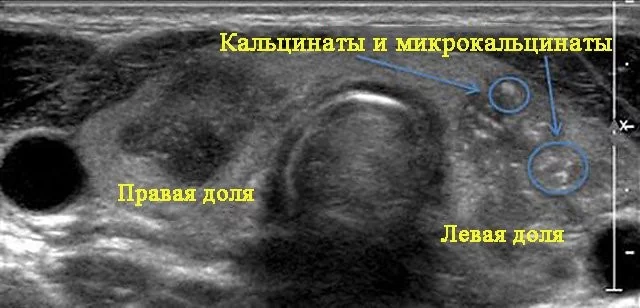
Diffuse toxic goiter
A disease of an autoimmune nature, which is based on hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. Clinically manifested by an increase in neck circumference, bulging eyes, rapid heartbeat, and difficulty swallowing.
Ultrasound signs of pathology:
- uniform increase in the volume of both lobes of the thyroid gland;
- smoothed and rounded edges of the organ;
- hypoechogenicity. The decrease in organ density is due to the high water content in the tissues;
- homogeneous structure;
- dilated vessels;
- in Doppler mode, increased blood circulation is visible;
- Cysts and calcifications may be observed.
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid tissue of an acute, chronic or autoimmune nature. The inflammatory process can affect a specific area or the entire organ. Depending on the type of thyroiditis, the pathology can lead to increased or decreased production of iodine-containing hormones, occur with clear signs or be asymptomatic.
Ultrasound signs of the most common types of pathology are presented in the table.
| Type of thyroiditis | Ultrasound signs |
| Acute thyroiditis is an inflammation of the thyroid tissue, which occurs with high fever, chills, and severe pain in the throat. In some cases, inflammation is accompanied by the formation of purulent exudate. | ● normal or enlarged size of the thyroid gland; ● heterogeneous echogenicity of the organ; ● abscesses (cavities with purulent contents) may be observed - hypoechoic areas; ● increased blood supply; |
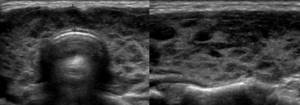
| Autoimmune thyroiditis (AIT) is a chronic inflammatory process of autoimmune origin. | ● the size of the thyroid gland can be normal, reduced in atrophic AIT, increased in hypertrophic AIT; ● heterogeneous structure; ● reduced echogenicity of organ tissues; ● abnormal shape of blood vessels; ● increased blood supply. |
AIT on an ultrasound image looks like this ⇓⇓⇓
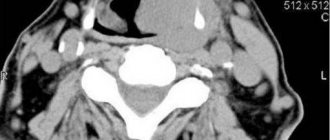
Thyroid oncology
Thyroid cancer is rarely diagnosed: it accounts for about 1% of all diagnosed cancer cases. The risk group includes people over 50 years of age, residents of regions with high radiation, and people with iodine deficiency.
The outcome of the disease depends on the timeliness of diagnosis. If the disease is detected at an early stage, the prognosis is favorable. The last stage of oncology reduces the patient’s chance of survival to zero.
Ultrasound signs of malignant thyroid formations include:
- uneven and unclear contour;
- hypoechogenicity;
- increased blood flow if the tumor is actively growing;
- in some cases, microcalcifications may be observed - white dots on a dark background of the node.
The photo below shows what papillary thyroid cancer looks like compared to a benign formation.
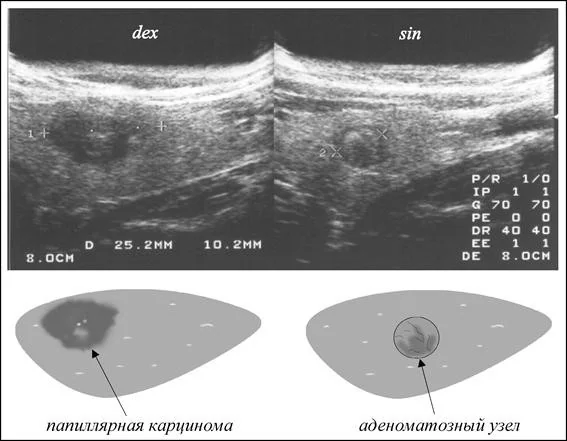
If an ultrasound reveals nodes with signs of malignancy, the patient is referred for a fine-needle biopsy.
Contraindications
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is suitable for all people, regardless of gender and age.
The only limitation
there is the presence on the patient’s neck, in the place where the gel should be applied and through which the study is carried out, of any skin disorders. It could be:
- Extensive painful rash
- Eczema
- Streptoderma is an inflammation caused by streptococcus
- Burn
Only in these cases, ultrasound of this endocrine gland is contraindicated.
Interpretation of ultrasound results: normal options
The doctor interprets the ultrasound results according to the following parameters:
- Structure. According to the standards, the structure of the thyroid gland should be clearly visible, the contours should be clear.
- Options. The length should be in the range from 2.5 to 4 cm, width - 1.5-2 cm, thickness - 1-1.5 cm. Standards may vary depending on the patient’s weight.
- Echogenicity. The density of the echo structure depends on the age and gender of the patient, but the image should be in light gray tones.
- Focal changes. Within the normal range - small cysts up to 4 mm. Benign tumors are viewed as isolated objects. Cysts are like areas filled with bubbles.
- Regional lymph nodes. According to the standards, the nodes should be smooth, with clear contours, without cysts and neoplasms.
Take care of your health - contact MEDSI
MEDSI specialists
– candidates and doctors of medical sciences, endocrinologists of the highest qualification categories – use the latest equipment for performing ultrasound of the thyroid gland:
Pro Focus 2202 Philips iU22.
Here each patient receives:
- Comfort and respectful treatment
- Diagnostics and support of qualified personnel
- Urgent consultations and ultrasound – appointments can be made by calling 8
- Modern examination equipment from Philips
How is the research going?
During the examination, the patient is placed on a couch. A special gel is applied to the skin of the neck in the area of the thyroid gland. The organ is scanned using an ultrasound probe, and the image is displayed on the monitor screen.
During the examination, the ultrasound doctor sees black and white images on the monitor screen. All tissues of internal organs reflect ultrasound in their own way: the higher the density of the tissue, the brighter the image. This property of tissues is called “echogenicity”.
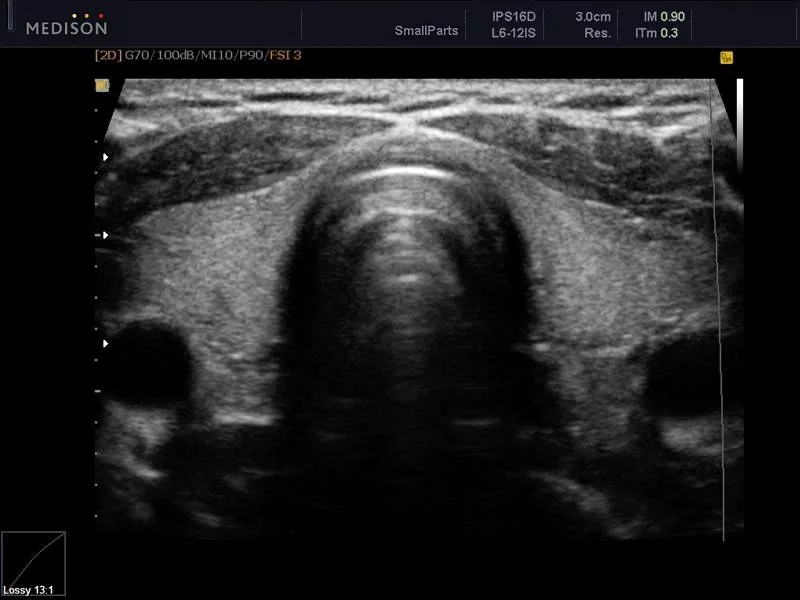
The condition of the thyroid tissue can be assessed by echogenicity:
- tissues without pathologies (isoechoic) are displayed on the monitor in gray;
- structures with reduced density (hypoechoic) look like dark spots;
- tissues with high density (hyperechoic) are displayed in light shades.
There are also anechoic structures that absorb ultrasound completely. On the monitor they appear as black spots.
Relationship
Does the day of your cycle really matter? In most cases, it is not particularly important, just a lot depends on the physical condition of the patient herself. The thyroid gland is involved in the production of hormones. The state of the reproductive system affects hormonal levels. To feel as comfortable as possible, it is best to wait until the end of menstruation and go for diagnostics after it.
However, if you need an ultrasound examination urgently, there is no need to wait. Go any day, regardless of the state of the reproductive system, this moment will not affect the diagnostic result in any way. You can do an ultrasound at the time of ovulation or immediately after it - the result will be exactly the same.
What additional thyroid tests can a doctor prescribe?
If a doctor issues a referral for an organ examination, then tests are usually taken at the same time for the main hormones secreted by the thyroid gland. Even if an ultrasound reveals nodes or other pathologies, if the hormones TSH, T3 and T4 are normal, as well as with normal tumor markers, there is no need to talk about the development of the disease. This will mean that the pathology will need to be monitored, but for now it is not dangerous
If, on the contrary, the indicators do not correspond to the norm, and ultrasound reveals minor pathological changes in the thyroid gland, then the patient is prescribed a comprehensive and more in-depth examination.
The examination will include the following additional methods for diagnosing the condition of the organ:
- Manual palpation of the thyroid gland -
this technique is considered quite subjective, but when carried out by a highly qualified specialist it provides additional information regarding the size and location of the organ. The doctor also studies the mobility of the gland, examines nearby lymph nodes and other structures. Sometimes even the patient’s voice or external signs give a clue to the presence of the disease - bulging eyes, the growth of unwanted facial hair, indicating an imbalance of sex hormones - the work of the ovaries is closely related to the work of other hormone-synthesizing organs, incl. and thyroid glands. and etc. - Doppler methods -
these methods are aimed at an objective assessment of the nature of blood flow and are considered especially informative from the point of view of diagnosing neoplasms of various natures. A Doppler ultrasound is a mid-range or high-end ultrasound that is equipped with a special Doppler probe. - Scintigraphy is
a diagnostic technique based on the use of radioactive isotopes. This method is highly informative for diagnosing patients with congenital anomalies of the anatomical structure of the organ, thyrotoxicosis and previously identified neoplasms of the thyroid gland. Essentially, this is an ordinary x-ray using a special contrast liquid, including a minimal dose of isotopes that penetrate the thyroid gland. Settled in the organ, they help visualize the entire gland. - Tissue biopsy is
the examination of tissue samples using high-power microscopes, which makes it possible to clearly determine the composition of the tissue and the condition of the cells. Biopsy remains the main method of differentiating benign and malignant neoplasms. This is a traumatic technique, so it is resorted to last. - Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the thyroid gland
are very informative methods of visualizing the gland, but use different types of radiation - X-ray and magnetic. These are the most expensive methods, so they are prescribed only when necessary. - Hormone tests
- namely, laboratory indicators of the hormones TSH, T3 and T4, corresponding to age and gender, are the main criteria for assessing the condition of the patient’s thyroid gland.