Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography) is recommended for all children under one year of age, without exception. An informative, safe ultrasound examination makes it possible to detect pathologies and malformations at a very early age, and begin their correction in a timely manner.
Ultrasound of the child’s brain (USB) is a universal, highly informative and at the same time simple method of examination. This procedure is often prescribed to young children to diagnose congenital and acquired pathologies of the nervous system. Ultrasound examination in newborns is facilitated due to the presence in their skull of natural bone openings, closed only by connective tissue - fontanelles. Using ultrasound, a specialist examines the structures of the brain, determining their size, correct structure and symmetry. Ultrasound also allows you to detect various neoplasms, signs of inflammation and other pathologies.
Indications for the study
Starting from the 1st month after birth, neurosonography is performed on all children several times up to a year, even if there are no complaints. At an older age, the child’s fontanel becomes overgrown with bone tissue, and ultrasound becomes uninformative. Most often, an ultrasound examination of the brain is required in the following cases:
- premature birth, i.e. before the 37th week;
- low birth weight;
- presence of signs of intrauterine hypoxia during the mother’s pregnancy;
- clinical symptoms of pathologies of the nervous system;
- the presence of a genetic predisposition to brain diseases;
- suspicion of inflammation of brain structures and membranes;
- intrauterine infections;
- mental retardation.
NSG of the brain of newborns can be prescribed in case of complicated births and if birth trauma is suspected.
Ultrasound of the brain
Home » Diagnostics » Ultrasound of the brain
Neurosonography is an ultrasound examination of the brain, which can be used to identify any abnormalities in the structure of the nervous system.
An ultrasound of the brain is performed in children before they reach one year of age, since it is by the age of one that the large fontanel becomes overgrown—through which ultrasonic waves can pass.
Neurosonography of the brain is a completely safe study; it does not threaten tissue destruction, heating or harmful radiation. The study also does not require special preparation - it can be carried out at any time.
Mandatory examination (NSG) and observation by a pediatric neurologist is recommended in the following cases:
- the child was born premature
- the child was born with low birth weight
- if there is a suspicion of intrauterine or intrapartum (during childbirth) fetal hypoxia
- in the presence of birth trauma
- if an intrauterine infection is suspected
- if the child has an irregularly shaped head or face
- upon detection of anomalies in the development of internal organs, the musculoskeletal system and other systems
- in the presence of neurological symptoms
Thanks to timely research, it is possible to identify:
- congenital disorders of brain structures (developmental anomalies)
- cysts of the brain and its membranes
- ventricular dilation
- expansion of the subarachnoid space
- circulatory disorders
- neoplasms
The following types of ultrasound examinations are also available:
- Ultrasound of the hip joints
- Transcranial duplex scanning of blood vessels
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (liver and gall bladder, pancreas, spleen)
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands
- Ultrasound of the bladder
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes
- Ultrasound of the thymus
Preparation
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs - exclude gas-forming products the day before. Light dinner + activated carbon.
The study is carried out after a night's sleep on an empty stomach - do not feed or drink the child in the morning! DO NOT brush your teeth.
Children under 1 year - the interval between feeding and examination is at least 4 hours.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and pelvic organs - if possible, a full bladder. (Give the child any non-carbonated liquid, preferably water, 1-1.5 hours before the test)
Ultrasound of joints and glands does not require special preparation.
Prices
| Service code | Name of service | Cost, rub. |
| A04.12.005.003 | Duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries with color Doppler mapping of blood flow | 2500 |
| A04.14.002.001 | Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder to determine its function | 1 800 |
| A04.23.001 | Neurosonography | 1 500 |
| В03.052.001 | Comprehensive ultrasound examination of internal organs (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, ) | 1 700 |
| А04.06.002 | Ultrasound examination of lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 850 |
| A04.06.003 | Ultrasound examination of the thymus gland | 1 100 |
| A04.28.003 | Ultrasound examination of the scrotal organs with assessment of vascularization | 1 500 |
| A04.03.002 | Ultrasound examination of the spine (intervertebral discs) | 1 500 |
| A04.04.001 | Ultrasound examination of the hip joint | 1 100 |
| A04.09.001 | Ultrasound examination of the pleural cavity | 1 100 |
| A04.09.002 | Ultrasound examination of the lungs | 1 200 |
| А04.14.001 | Ultrasound examination of the liver | 1 000 |
| A04.14.002 | Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder | 1 000 |
| A04.28.001 | Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and adrenal glands | 1 000 |
| А04.06.001 | Ultrasound examination of the spleen | 1000 |
| A04.22.001 | Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland and parathyroid glands | 1000 |
| A04.28.002.003 | Ultrasound examination of the bladder | 900 |
| A04.01.001 | Ultrasound examination of soft tissues (one anatomical zone) | 1 000 |
| A04.28.002.001 | Kidney ultrasound | 800 |
What parameters are determined during ultrasound examination?
During an ultrasound examination, a specialist examines the child’s brain and compares the information received with normal indicators. All data about the study is entered into a special form, and based on the diagnostic results, a conclusion is given about the absence or presence of pathologies. As a rule, during the ultrasound procedure of the child’s brain, the following parameters are determined:
- symmetry of brain structure;
- homogeneity of structure;
- area and size of the ventricles;
- the condition of large blood vessels supplying the brain;
- area of the subarachnoid space;
- clarity of the contours of convolutions and grooves;
- the presence of fluid in the ventricles of the brain and its quantity.
With the conclusion of an ultrasound specialist, the child is usually sent for a consultation with a neurologist, who, if necessary, prescribes treatment or additional examination.
Features of the procedure
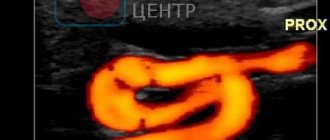
Doppler ultrasound is a painless and safe procedure, like any ultrasound examination. When performing diagnostics, a sensor moistened with a special gel is placed over the blood vessel. A picture of blood flow appears on the screen in real time. The method has no contraindications. No special preparation is required for the procedure, but the day before the test you should avoid tonic drinks: tea, coffee, energy drinks. You should also avoid tonic foods and medications that can distort diagnostic results.
Ultrasound scanning has several significant advantages:
- no contraindications, complete safety;
- high information content;
- painlessness;
- simplicity of the procedure;
- availability.
The patient is not exposed to radiation. Diseases can be diagnosed even in children. If the child is active, this will not distort the results of the study. The procedure usually does not make children nervous.
What can be diagnosed during an ultrasound?
Using an ultrasound of a child’s brain, the presence of the following pathologies can be determined:
- disturbance of the contours of the ventricles (observed with hemorrhages, various tumors, cysts and other brain tumors);
- increased volume of the ventricles (with hydrocephalus, rickets);
- intracranial hemorrhages (often found in premature infants in the first weeks of life);
- ischemia of brain structures (develops as a result of fetal hypoxia, occurs in premature infants and can lead to the death of nerve cells);
- meningitis (inflammation of the pia mater of the brain as a result of intrauterine or acquired infection after birth, with ultrasound signs of thickening or deformation of the choroid);
- encephalitis (inflammation of the brain substance, which can lead to the death of large areas of nerve cells and the formation of cysts);
- aneurysm of vessels supplying blood to the brain (a very dangerous pathology, since when a blood vessel suddenly ruptures, hemorrhage occurs in the medulla, intracranial hematomas are formed with compression of the brain);
- cysts (cavity formations that have a capsule and are filled with liquid contents).
Cysts can be of several types:
Choroid plexus cyst is a relatively common anomaly that develops even before the baby is born. In most cases, the formation resolves on its own and does not require any treatment.
Subependymal cysts are usually a consequence of previous oxygen deprivation of the brain. Such cystic cavities can negatively affect the development of the child, often provoke seizures and can be the cause of epileptic seizures. To monitor the dynamics of the process of NSG of the brain, newborns with this pathology are prescribed several times during the first year.
A cerebrospinal fluid or arachnoid cyst is usually the result of an inflammatory process or traumatic brain injury. It can increase in size and compress neighboring brain structures, which leads to serious neurological disorders. If an arachnoid (cerebrospinal fluid) cyst is present, surgical treatment may be required.
Another serious pathology that can be detected using neurosonography is a tumor. The malignancy and benignity of an intracranial tumor are of relative importance, because in any case the tumor leads to compression (mechanical compression) of the brain and disruption of its functions.
How does ultrasound ultrasound work?
Doppler ultrasound gives an accurate idea of the location of the problem. Sensors respond to blood movement. This establishes the intensity of blood flow in the vessels, the size of the lumen of the vessels and other necessary parameters. Any increase or decrease in blood flow indicates a problem area.
The ultrasound examination procedure is performed at any age. The technique does not require the patient to remain motionless for a long time. Ultrasound diagnostic technology, in addition, is absolutely safe and is allowed from birth. Therefore, such procedures are performed on children at any age.
The specialist must be professionally trained to carry out the diagnostic procedure, because the anatomy of a child differs from the anatomy of an adult, and the specialist must understand this.
Benefits of brain examination using NSG
NSG has many advantages:
- high information content;
- relative cheapness;
- accessibility, painlessness and safety of the procedure (ultrasound of the child’s brain can be performed several times in a row without fear of undesirable consequences);
- quick results;
- the ability to control the dynamics of the disease (if present).
Probably the only disadvantage of neurosonography is the impossibility of performing it in children after one year.
Causes of vascular problems
Problems with blood vessels in children arise for various reasons:
- birth injuries;
- fast growth;
- shocks, injuries, falls;
- diseases that affect the vascular system.
In babies, the problem arises as a complication after birth trauma, which is associated with the physiology of childbirth. Excessive hyperextension of the head occurs during the provision of obstetric care, which is associated with the peculiarities of the anatomy of the woman in labor. Also, excessive hyperextension occurs during Caesarean section. These processes affect the tortuosity of blood vessels and their tone.
Where to do NSG?
To conduct an ultrasound of the child’s brain, you just need to call our clinic’s one-stop help line. Preambula's highly qualified specialists have many years of practical experience and use the most modern equipment for their work. All this guarantees high accuracy of the information obtained during the study, which is then carefully deciphered by our doctors. Registration is made at a time convenient for you. The clinics are located close to your home, so you don’t have to travel long by public transport.
Neurosonography with Doppler - 2400 rubles.
How to reduce the cost? MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
multidisciplinary medical center
Ultrasound of the brachiocephalic arteries (USDG BCA) is a method of Doppler ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck , which provide blood supply and nutrition to brain cells, head tissues, and the upper limb girdle.
The undeniable advantage of this diagnostic method is its non-invasiveness and, therefore, painlessness, as well as the absence of contraindications for its implementation. In this connection, for the correct diagnosis of diseases, this type of ultrasound is often prescribed or recommended to patients by doctors in Voronezh.
In addition, ultrasound is a fairly informative method for diagnosing the pathology of blood vessels in the head and neck (for both children and adults), which makes it possible to determine in the early stages the presence of a pathological process in them, the condition of their walls, the nature of blood flow in the vessels, the nature of atherosclerotic manifestations if present, it also allows us to identify congenital vascular anomalies, such as tortuosity, uneven course of blood vessels and some others.
Planned BCA ultrasound (once a year or once every 2 years) is indicated for people with the following diseases: arterial hypertension and other vascular and heart diseases, diabetes mellitus, excess body weight, as well as degenerative changes in the cervical spine.
In addition, this ultrasound examination is indicated for everyone who has complaints of frequent dizziness, headaches, fainting, tinnitus, ringing in the head, people suffering from sleep disorders, impaired coordination, impaired concentration, impaired tactile sensations, and visual impairments.
Also, this ultrasound should be performed regularly for all persons with a long history of smoking.
To conduct an ultrasound of the neck vessels at the Center for Modern Pediatrics, you must :
1) 24 hours before the test - remove foods such as tea, coffee, energy drinks, alcohol and salty foods from the diet, as they can change vascular tone;
2) 2 hours before the start of the study, refrain from smoking and try not to be in smoky rooms.
Ultrasound diagnostic doctors at the multidisciplinary medical center in Voronezh - the Center for Modern Pediatrics inform: failure to comply with these recommendations may lead to unreliable results of the study.
In addition, the results of the study are influenced by medications that can change vascular tone and the nature of blood flow in them. Therefore, before an ultrasound, it is better to talk to your doctor about the need to stop certain medications.
Before starting the BCA ultrasound , you need to free the neck and upper torso area from clothing and jewelry. During an ultrasound, the patient lies down on the couch and periodically changes the position of the head and body (turning the head to the right, left; changing body position - on the back, on the side, on the stomach) for a more accurate examination of all vessels.
During an ultrasound, additional tests are sometimes performed to clarify the presence or absence of pathological changes in the vessels being examined.
After completing the diagnosis of ultrasound examination of the BCA, the doctor of the Center for Modern Pediatrics in Voronezh issues a conclusion indicating the condition of the vessels, blood flow characteristics and a description of the pathology.
In the future, this conclusion must be shown to the doctor who referred the patient for the study in order to compare the study results with the clinical picture and decide on further treatment and observation tactics.
Ultrasound diagnostics doctor Galina Viktorovna Vostrikova Ultrasound diagnostics doctor Tatyana Alekseenko Alekseenko