Ultrasound is a research method in which pathological changes in tissues and organs of the human body are recognized using ultrasound. This method is based on the principle of echolocation, that is, the reception of signals sent and then reflected from the interfaces of tissue media that have different acoustic properties.
An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed in order to visually determine, based on certain echographic signs, the presence of any pathology in a woman (or the fetus during an obstetric ultrasound).
Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs can be carried out with an abdominal probe (through the abdomen), as well as a vaginal probe. During an ultrasound in a woman’s pelvis, I examine the following: vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, bladder, ovaries.
In the case of examination of the uterus, its shape, position, its main dimensions, as well as the structure of the walls of the uterus are determined.
In addition, the middle uterine structures can be examined separately: the uterine cavity, the endometrium (M-echo). In non-pregnant women, the uterine cavity is slit-like. The endometrium (the functional inner layer) begins to change during the menstrual cycle.
An ultrasound scan of the ovaries evaluates their size, position relative to the uterus, as well as the size of the follicles and corpus luteum (formations that remain in place of the follicles after the egg leaves the ovary). A comparison is made with the phase of the menstrual cycle.
If formations are detected in the ovaries, they are also described: structure, shape and size.
Specialist doctors also determine the presence of free fluid (normally there is little of it after the egg is released from the ovary) and the presence of tumor formations in the pelvic cavity.
In addition to the structure of the uterus and ovaries, ultrasound also evaluates the condition of the bladder (and if it is sufficiently filled).
Indications
The ultrasound method is widely used for suspected gynecological diseases, pregnancy, as well as for monitoring the treatment and cure of patients.
Using an ultrasound examination of the uterus, pregnancy can be diagnosed at the earliest stages.
Pelvic ultrasound in women should be performed in such cases as: menstrual irregularities (early onset of menstruation, delayed menstruation, bleeding in the middle of the cycle), heavy or scanty menstruation, absence of menstruation, various vaginal discharge, pain in the lower abdomen, the appearance of discharge during menopause.
Gynecological ultrasound can identify various diseases: gynecological inflammatory diseases, benign and malignant formations of the ovaries, uterus (including endometriosis, salpingoophoritis, endometritis, ovarian cysts, etc.).
Ultrasound examination of the uterus makes it possible to early diagnose uterine fibroids.
Ultrasound is also used to monitor the follicular apparatus of the ovaries during infertility treatment and pregnancy planning.
Doctors prescribe pelvic ultrasound when taking hormonal, contraceptive medications and in the presence of an intrauterine contraceptive device (“IUD”) in order to monitor and prevent any complications.
Obstetric ultrasound (ultrasound during pregnancy) allows you to monitor the normal development of the fetus and detect pathology in a timely manner.
In urology, pelvic ultrasound is used to determine the causes of urinary incontinence, urination disorders and pathology of the urethra (urethra).
Causes of vesiculitis
The causes of vesiculitis in men are infectious and stagnant.
Vesiculitis in men may appear due to the following factors:
- interruption of sexual intercourse;
- masturbation;
- no regularity of sexual activity;
- abstinence;
- defective ejaculations;
- alcohol and nicotine;
- hypothermia often occurs;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- expansion of hemorrhoidal veins and other pelvic inflammations.
Preparation
When visiting an ultrasound diagnostic room, the patient must have a towel or napkin with him in order to remove the remaining gel from the skin after the examination, as well as a diaper on which he will lie during the examination.
In non-pregnant women, an ordinary gynecological ultrasound is performed on a full bladder, unless, of course, the doctor specifies otherwise.
For greater accuracy and reliability of the results obtained, it is necessary to adhere to all established rules for preparing for a pelvic ultrasound:
- for transabdominal gynecological ultrasound (through the abdomen), preparation of the bladder is necessary: the patient should drink 1 - 1.5 liters of non-carbonated liquid an hour before the procedure and not urinate until the examination;
- transvaginal gynecological ultrasound (through the vagina) does not require special preparation, the study is carried out with an empty bladder;
- obstetric ultrasound (during pregnancy) is performed when the bladder is moderately full (you need to drink 2 glasses of liquid one hour before the procedure).
During an examination of the organs of the genitourinary system (bladder, uterus, prostate, ovaries), you need to drink 0.5 liters of liquid 1-1.5 hours before the examination or not urinate for 2 hours. All this is necessary to ensure that the bladder is full , which pushes aside the examined organs.
A mandatory and important condition for a successful ultrasound is an empty intestine, as well as the absence of gases in it. That is why you need to prepare in advance for an ultrasound examination: another 2-3 days before the upcoming examination, you must follow a diet that includes limiting foods that cause gas formation or constipation. Doctors recommend excluding foods that cause increased gas formation (fruits, brown bread, raw vegetables, milk, confectionery). The use of enzyme preparations is recommended: panzinorm, festal, creon, enzistal, etc.
Cleansing enemas are not recommended, as they often increase gas formation. In addition to everything, you can take activated carbon, dill water, and espumisan. If the patient is constipated, doctors recommend a laxative, especially if it is necessary to conduct an examination using a rectal probe.
Ultrasound is performed on an empty stomach (the last meal should be 8-12 hours before the examination) and immediately after bowel movement.
Examination of the mammary glands, appendages and uterus is recommended to be carried out in the first half or middle of the menstrual cycle.
A study on folliculogenesis is carried out at 5; 9; 11-14 and 15 days of the menstrual cycle.
Note that the accuracy and reliability of the ultrasound results will largely depend on how the patient himself prepares for it.
And only in emergency cases, ultrasound examination is performed without any preparation, but its effectiveness is lower.
Vesiculitis: treatment
Treatment methods for vesiculitis in men are selected depending on the factors that caused the disease. Infectious vesiculitis requires the prescription of antibacterial drugs. Treatment of congestive vesiculitis should eliminate congestion. If both factors are included, then the treatment of vesiculitis is combined, aimed at eliminating both manifestations.
To reduce discomfort, symptomatic therapy is used when treating vesiculitis in men. In the acute and chronic course of the disease, the temperature rises; after it decreases, physiotherapeutic procedures, compresses, and massage of the prostate and seminal vesicles are used in the treatment of vesiculitis.
Treatment of vesiculitis must be comprehensive; it is necessary to strengthen the body’s immunity (vitamins, microelements, immunomodulators are taken).
Surgical treatment of vesiculitis is allowed only when severe complications occur (for example, suppuration of the seminal vesicles). The bubbles are punctured and drained. In severe cases, to avoid sepsis, the seminal vesicles are removed.
Additional treatments are used to strengthen the immune system, stimulate tissue repair, eliminate inflammation and improve metabolism. These include:
- physiotherapy (UHF, etc.);
- reflexology (acupuncture);
- sanitary resort treatment (mud and mineral baths);
- electrotherapy;
- physical therapy.
Among other things, there are traditional methods of treatment that can also be prescribed by the attending physician - infusions, decoctions, juices, taking warm baths. Traditional methods must be used in combination with modern antibacterial drugs.
How is a pelvic ultrasound performed?
The patient lies down on the couch, having laid out a diaper in advance, with his head towards the doctor (ultrasound machine), exposing his stomach, as well as his lower abdomen. The doctor lubricates the ultrasound sensor with gel (during transvaginal ultrasound, he puts a condom on the sensor and lubricates it with gel), and then begins to move the sensor over the patient, occasionally pressing in order to view certain pelvic organs from a different angle.
The procedure itself is painless, with the exception of diagnostics in cases of acute inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs. An ultrasound lasts about 10-20 minutes, depending on the purpose of the study.
Traditional methods
Today, therapy based on alternative medicine recipes offers a wide variety of medicinal plants and agents that have a high level of antibacterial action and anti-inflammatory properties:
- These can be herbs such as elecampane, sage and St. John's wort.
- Field chamomile flowers are in every medicine cabinet, and they promote a speedy recovery by eliminating pain and inflammation.
- The herb hogweed or red brush helps restore the menstrual cycle after a course of treatment or surgery.
Additional traditional medicine allows the use of infusions, decoctions for douching and herbal tampons.
But it is worth understanding that the use of herbal remedies cannot be the main treatment; they are used only as additional therapy. Each recipe, despite its simplicity, has some contraindications, so even herbal medicine should be discussed with a doctor.
Alternative treatment methods help prevent an increase in fluid in the free space of the pelvic organs.
Interpretation of ultrasound results
Only an experienced doctor can correctly decipher the results of an ultrasound examination.
Pelvic ultrasound makes it possible to detect:
- Congenital developmental anomalies: Ultrasound, especially 3-dimensional, allows you to diagnose developmental anomalies of the uterus (bicornuate, unicornuate, saddle-shaped, duplex uterus).
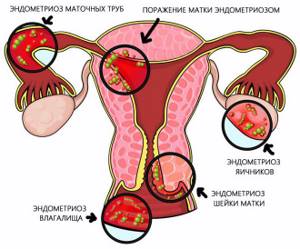
- Endometriosis is a pathological process characterized by the spread of the endometrium beyond the uterine cavity (ovaries, uterine walls, peritoneum, etc.). Ultrasound can reveal internal endometriosis or adenomyosis (growth of the endometrium into the wall of the uterus), as well as endometriotic ovarian cysts. Diagnosis of endometriosis is of greater importance for predicting the possibility of pregnancy and its bearing, since endometriosis can cause infertility.
- Congenital developmental anomalies. The presence of such anomalies can cause infertility, increase the risk of premature birth, intrauterine fetal death, and disruption of labor.
- Diagnosis of pregnancy: Ultrasound allows you to diagnose pregnancy starting from 3 to 4 weeks. Note that short periods of pregnancy are determined only with the help of a transvaginal sensor, a device with good resolution. Different types of ectopic pregnancy are diagnosed (tubal - when the fertilized egg is attached to the fallopian tube; ovarian - when it is attached to the ovary; cervical - when it is attached to the cervix). This allows the woman to remain healthy.
- Uterine fibroids are a benign tumor of the female reproductive system. During an ultrasound, the presence, location, number and size of myomatous nodes are determined. In addition, this method allows you to monitor their growth rate over time, so the examination is done several times a year. Diagnosis of fibroids is important when preparing for conception, since its presence can affect the course of pregnancy.
You can also detect hyperplastic processes of the endometrium (hyperplasia, malignant endometrial tumors, polyps) and ovarian mass formations.
Ascites in oncology
In oncology, fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity can develop with cancer of the ovaries, breast, intestines, stomach, pancreas, lungs, liver, uterus, and peritoneal mesothelioma.
The formation of ascites in cancer patients is a complex process in which many factors take part:
- Peritoneal carcinomatosis is a condition in which cancer cells spread along its surface. They irritate the peritoneum, causing it to produce more fluid. In this case, fluid absorption is impaired. In 52–54% of patients with malignant neoplasms of the abdominal cavity and peritoneal carcinomatosis, it is the manifestations of ascites that become the first symptoms of the disease.
- Increased vascular permeability. Due to this, proteins penetrate into the abdominal cavity, and fluid rushes after them.
- Damage to the lymph nodes, due to which the outflow of lymph is disrupted.
- Damage to the liver by a primary malignant tumor or, more often, metastases. This increases blood pressure in the portal vein. If the liver tissue is very damaged, it stops producing the required amount of protein, the oncotic pressure of the blood decreases, and fluid rushes into the body cavities.
Ascites in cancer patients is a dangerous complication that greatly worsens the prognosis. Treatment of this condition should be carried out by doctors with relevant experience in a clinic that specializes in working with cancer patients. The International Clinic Medica24 uses all available effective methods for treating malignant ascites.
What diseases may indicate fluid behind the uterus?
If a woman does not promptly contact a hospital for help, she will develop serious illnesses:
- Endometriosis is the excessive growth of tissue outside the uterus, undergoing cyclical changes. In parallel, an inflammatory process develops, against the background of which exudative fluid is generated, accumulating in the retrouterine space.
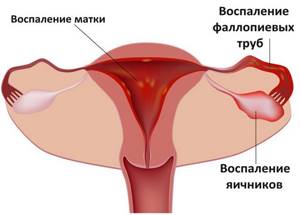
- Endometritis occurring in acute form.
- Purulent form of salpingitis.
- Ovarian cysts (endometrioid).
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Diffuse form of peritonitis (serous);
- Gastrointestinal diseases, in particular, pathologies occurring in the liver.
Diagnostics
Water accumulated in the retrouterine space is detected during an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs. Current equipment allows us to determine its volume with maximum accuracy.
After the ultrasound, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations to the patient:
- puncture;
- blood tests, urine tests;
- microscopic examination of a smear;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
Bloody fluid
Most of the pathological changes occurring in the genitourinary system are detected during ultrasound examination.
Sometimes water containing blood impurities is found in the retrouterine space. This condition is considered dangerous, as the patient may develop apoplexy. The following pathologies can provoke the appearance of bloody fluid:
- ovarian cyst;
- hyperemia;
- vessel rupture;
- inflammatory process;
- stroma;
- hard sex;
- follicle cyst.
Presence of liquid under normal conditions
A healthy woman should not have water accumulate in the area of the fallopian tubes, ovaries, or uterus. If an ultrasound reveals its small volume, up to 10 ml, then doctors consider this a natural phenomenon. Exceeding the permissible norm may indicate the presence of pathology or internal bleeding.
Fluid in the retrouterine space during ovulation
During ovulation, a woman's body becomes ready to conceive. If at this time the patient undergoes an ultrasound examination, then a slight accumulation of water may be detected in her retrouterine space, which is not considered by specialists as a pathology.
Other natural causes
The following factors can trigger the formation of fluid:
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- great physical activity;
- lifting heavy objects;
- engaging in traumatic, hard sex;
- excessive passion for extreme diets;
- abortions/miscarriages, etc.