The paranasal sinuses (sinuses) are depressions in the bones of the skull. The mucous membranes of cavities are sensitive to the effects of bacteria and viruses and often become inflamed due to colds, flu, chronic diseases, and infections in the mouth. CT scan of the nose is one of the most accurate methods for diagnosing pathologies at any stage of development.
Sinuses are relatively small structures, and to study them requires a diagnostic device with high resolution. This condition is met by MSCT - modern multislice tomographs. The devices are equipped with a large number of X-ray wave emitters and detectors. During one rotation of the scanning system, several sections are recorded at once, which ensures maximum accuracy of information and reduces procedure time.
Total filling of the left maxillary sinus with fluid (blood?), damage to the nasal septum on a computed tomogram
What does a CT scan of the sinuses show?
The CT scan of the nose and paranasal sinuses makes it possible to study the structure of anatomical structures and identify the features of the pathological process. Examination of the area in question on a computed tomograph shows:
- congenital anomalies;
- destructive changes and traumatic injuries of facial bones;
- thickening of the mucous membrane of the nose and sinuses;
- deviated nasal septum;
- inflammation inside the sinuses (CT will show sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis, sphenoiditis);
- abscesses of the nasal septum;
- polyps, granulomas, cysts of the mucous membrane of the air cavities of the facial skull;
- tumors in the paranasal sinuses;
- accumulation of blood, exudate, pus in the sinuses;
- additional voids (ostia);
- foreign bodies in the nasal passages and bone cavities;
- hemorrhages in the sinuses and soft tissues;
- dental pathologies (root ingrowth or tooth displacement into the maxillary sinus);
- inflammation in the throat and nasopharynx;
- osteomyelitis of the facial bones;
- pathological communication of the sinus with the oral cavity in the form of an oroantral fistula.
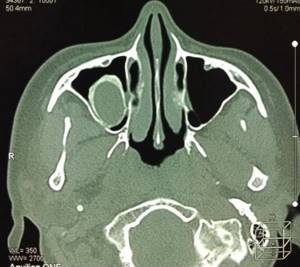
Cyst in the sinus
Sinuses and their diseases
The paranasal sinuses are cavities in the skull filled with air. The walls of the sinuses are covered with mucous membrane. The sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity by special canals - anastomoses. Sinuses play an important role in the human body. Thanks to these cavities, the weight of the skull is reduced. With their help, the inhaled air is moistened and heated to the desired temperature before entering the lungs. On the mucous membrane of the cavities there are tiny cilia that trap harmful particles and prevent them from penetrating further into the body. The sinuses are involved in speech production and smell recognition. Therefore, any inflammation or swelling can lead to a malfunction of several important systems and functions of the body.
There are four types of paranasal sinuses:
- maxillary (maxillary), the lesion of which is called sinusitis;
- frontal - when they become inflamed they speak of frontal sinusitis;
- wedge-shaped - when it is inflamed, a diagnosis of “sphenoiditis” is made;
- cells of the ethmoid labyrinth - its inflammation is called ethmoiditis.
How to do a CT scan of the sinuses
Not all patients know what a CT scan of the sinuses is, how the procedure is done, and how harmless it is. Like any x-ray examination, computed tomography gives a person a certain dose of radiation. But if you take precautions, there is no need to fear deterioration in your health.
The examination will not cause harm if the patient follows the following principles:
- undergo a CT scan as directed by a doctor if other diagnostic methods are insufficiently informative;
- take into account existing contraindications;
- take into account the total radiation dose during various studies throughout the year;
- if it is necessary to do a repeat analysis, consider not computer diagnostics, but MRI (it is considered safe even for small children).
The tomograph, which performs CT scans of the nose and paranasal sinuses, includes a mobile couch and an X-ray unit. The device scans the nasal sinuses, the images are sent to a computer monitor, a specialist analyzes them and prepares a description.
Before the procedure, the patient is asked to remove anything that contains metal: glasses, dentures, hairpins, earrings, hearing aids, etc., to avoid distortion of the images. The doctor briefly talks about CT scanning of the sinuses - what it is, how long the session lasts, how to behave and what to do if discomfort occurs. The patient is positioned on a couch, which is placed in the tomograph ring. The scan takes about 10 minutes: you must lie still the entire time.
If contrast is required, the procedure consists of two parts. First, regular photographs are taken, then the examination is stopped, the necessary drug is administered and the diagnosis continues.
A CT scan of the sinuses is absolutely painless. The only irritating factor is the characteristic clicks of the device, but this problem is easily solved with the help of anti-noise earbuds or headphones.
Photo: Computed tomography procedure of the paranasal sinuses
Rhinoscopy of the nose in children
Carrying out research in pediatric patients is generally no different from performing it in adults.
To ease the discomfort, the child’s mucous membrane is irrigated with a local anesthetic. Rhinoscopy of the nose in young children is carried out using ear specula, in older children - with small nasal speculum. The survey results can be provided on paper and electronic media.
If the procedure was prescribed by the attending physician, we advise you to listen to the opinion of a specialist. Take care of yourself and your health.
Preparation for examination of the paranasal sinuses
If you do not plan to use contrast, a CT scan of the nose does not require any preparation. You will not need to follow a diet or change your usual lifestyle.
Diagnosis with contrast is preceded by determining the level of creatinine in the blood. An increase in indicators indicates problems with the kidneys, for which the procedure is contraindicated.
CT scan with contrast: the process of intravenous injection of an amplifier - photo
Additional preparation is recommended for women during lactation. After the examination with contrast, you will have to give up two feedings in a row (the milk is expressed and poured out). It is better to take care of food supplies for the baby in advance.
Is it possible to perform echosinusoscopy on pregnant women and children?
It is possible, and the safety of this method allows this study to be carried out repeatedly, unlike radiography, which has absolute contraindications. Safety in the study of children, pregnant women, as well as in other cases when radiography is undesirable and risky, has ensured that ultrasound has its niche among instrumental diagnostic methods as an important, informative and sometimes irreplaceable diagnostic method.
It is important that ultrasound can be performed repeatedly, including for repeated studies, without additional risk to the patient’s health. X-rays are no more reliable than a properly performed ultrasound.
Which is better - MRI or CT scan of the sinuses?
Many patients are interested in the question of which is better – CT or MRI of the paranasal sinuses. These diagnostic methods solve different problems, so the choice of examination method depends on the specific case.
MRI is based on the effect of radiofrequency pulses on an object placed in a high-intensity magnetic field. This technology is best used to study solid soft tissues. CT uses X-rays that most clearly visualize bones and hollow organs. The latter include the nasal sinuses.
Magnetic tomography is done:
- to confirm/exclude perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus as a result of trauma or dental diseases;
- if you suspect a tumor, polyps, cysts;
- to assess the condition of the mucous membranes of the sinuses;
- for headaches of unknown origin.
MRI also shows inflammation and hemorrhages in the paranasal cavities.
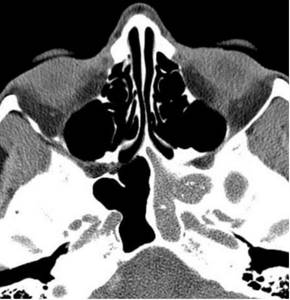
Magnetic tomography of the paranasal sinuses: left-sided sphenoiditis
CT diagnostics of the paranasal sinuses is done for acute inflammation and recurrent sinusitis. A computed tomography scan will show cracks and fractures of the facial bones, osteomyelitis complicating an injury or dental disease, metastases that have spread from neighboring anatomical areas.
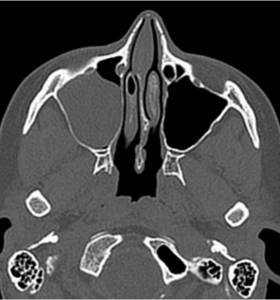
Computed tomography scan of the nasal sinuses: right-sided sinusitis
When giving preference to a magnetic resonance examination or CT scan of the nose, the doctor takes into account the limitations. MRI is not performed if there are metal elements on (in) the body. The processes occurring in the tomograph can cause damage to these structures and the device itself. A CT scan of the sinuses is not a magnet, but an x-ray. Metal objects do not interfere with the operation of the device, but may appear in the photo and cause errors in the description.
Due to radiation, pregnant women are not allowed to undergo CT examinations of the maxillary sinuses (any dose of radiation is harmful to the fetus). In such a situation, the best option is MRI; diagnostics are carried out strictly according to indications.
Methods for diagnosing sinusitis in adults
Only an otolaryngologist can accurately determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the maxillary sinuses during a face-to-face appointment. To do this, an ENT doctor can use the following methods for diagnosing sinusitis:
- Questioning the patient about complaints and collecting anamnesis of his life.
- General examination and palpation of inflamed areas.
- Rhinoscopy.
- Endoscopy, or video endoscopy of the nasal cavity.
- Sinus scanning.
- X-ray examination of the sinuses.
- CT scan.
- Puncture of the maxillary sinus.
- Lab tests.
An ENT doctor does not always use all of the above methods for diagnosing sinusitis. Sometimes it is enough to conduct an examination of the nasal cavity and a sinus scan to make a correct diagnosis. In some cases, a more thorough approach is required, which involves additional research methods.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
Analysis of patient complaints and medical history collection
When visiting a patient for the first time, any doctor does not immediately begin the examination. The first thing the doctor does is question the patient about complaints. When diagnosing sinusitis, the ENT doctor specifies what symptoms bother the patient, how long ago they appeared, whether any treatment was carried out previously; determines the presence, location and nature of pain; Is there any discharge from the nose, what does it look like, etc.
The patient's life history is a series of information obtained by the doctor in a conversation with the patient about his lifestyle. From the information received, the doctor finds out:
- does the patient have chronic diseases;
- does he suffer from allergies?
- whether his visit to the doctor was preceded by infectious diseases (for example, ARVI);
- whether he suffered any injuries to his nose;
- what infections did he have previously;
- whether the patient works in hazardous industries;
- has bad habits;
- what is the environmental situation in his place of residence?

All this information helps the otorhinolaryngologist identify factors that could influence the occurrence of sinusitis. A correctly collected anamnesis and its analysis significantly facilitates the ENT doctor’s process of recognizing the disease.
General examination and palpation
A visual examination helps the ENT doctor assess the presence of such signs of sinusitis as swelling and redness of the cheek in the area of the inflamed sinus; swelling of the eyelids; lacrimation; photophobia; protrusion of the eyeball forward.
Palpation is carried out by probing the locations of the maxillary sinuses. And if the sinuses are inflamed, when pressing with your fingers on these areas of the face, the patient experiences pain. The doctor also palpates the maxillary and cervical lymph nodes: with inflammation they can be enlarged.
Rhinoscopy
Rhinoscopy is a method of examining the nasal cavity using nasal mirrors and a nasal dilator. The patient sits comfortably opposite the ENT doctor. The doctor inserts a dilator into one nostril of the patient and carefully opens it.
What does the otolaryngologist observe during this procedure? He can evaluate:
- color and condition of the nasal mucosa (with sinusitis it is thickened and reddened);
- the condition of the anastomosis - the outlet openings through which secretions from the sinuses enter the nasal cavity (they can be swollen or completely blocked);
- size of turbinates;
- the degree of curvature of the nasal septum and its other defects;
- the presence, quantity and nature of nasal discharge (the presence of purulent discharge in the nose is an important sign of inflammation of the maxillary sinuses; but their absence does not mean that there is no inflammation. Perhaps the anastomosis is blocked, and pus cannot escape into the nasal cavity, accumulating inside the sinuses).
Before rhinoscopy, an ENT doctor can perform anemization of the mucosa - treating the mucosa with a vasoconstrictor drug. This measure helps to quickly relieve tissue swelling, providing the doctor with a better view.
It often happens that diagnostic measures for sinusitis end precisely at the stage of rhinoscopy, when the otolaryngologist has no doubt that we are dealing with inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. If the information obtained is not enough, the patient is prescribed and carried out other diagnostic methods.
Endoscopic examination
Endoscopic examination is an accurate and informative examination method that allows you to examine hard-to-reach areas of the nasal cavity that are not visible to the human eye during rhinoscopy and visual examination.
The examination is carried out using a thin tube with an eyepiece and a light source at its end (endoscope), which is carefully inserted into the nasal cavity. A more modern type of endoscopy is video endoscopy, which allows you to display an image of the patient’s nasal cavity on the screen in real time and, if necessary, record the progress of the study on an electronic medium. This may be necessary to assess the dynamics of the disease or when the patient is hospitalized for surgery.
The procedure is absolutely safe and painless, and can be performed even on children. There are not many contraindications to the study: allergies to the anesthetic used, problems with the blood coagulation system, neurotic disorders; Use with caution if you are prone to nosebleeds.
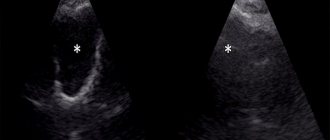
Sinus scanning
Sinus scanning is an ultrasound examination of the paranasal sinuses. It is used as an alternative to x-ray examination. But unlike X-rays, the patient is not exposed to radiation, so sinus scanning is often prescribed to pregnant women and children.
The study is carried out using a sinusscan device. The ENT doctor brings the sinus scan to the patient’s face in the sinus area, having previously lubricated it with a special gel. The sinus scan sends an ultrasound signal that is reflected from the walls of the sinus. The device analyzes how the signal is reflected and displays the result in the form of a graph. During inflammation, the signal is reflected from the fluid accumulated in the sinuses, and not from its walls. This can be seen in the final graph. Based on the image obtained, the ENT doctor makes a conclusion about the ongoing inflammatory process. Just a few minutes, and the study is completed, the result is ready!
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
What are the advantages of this method?
- The examination is safe and painless.
- It does not require special training.
- Done quickly.
- Can be performed multiple times, unlike x-rays.
- There is no need to wait long for the result to be interpreted.
X-ray examination of the sinuses
This is a classic method for diagnosing sinusitis. The first x-ray of the sinuses was performed at the beginning of the 20th century. The result of an X-ray examination is photographs of the sinuses in various projections. If the sinus is completely filled with purulent contents or exudate, it will be completely darkened in the image. Darkening in the lower part of the sinus indicates the level of pathogenic contents accumulated in the sinus. Depending on the intensity of the darkening, the ENT doctor draws conclusions about the nature of the secretions accumulated in the sinuses.
The procedure does not require special preparation. But it has a number of contraindications - pregnancy, mental disorders and children under one year of age. An alternative in this case would be a sinus scan procedure.
CT scan
Computed tomography (CT) is one of the most advanced diagnostic methods in many areas of medicine. It can also be used in the diagnosis of sinusitis, especially in difficult to diagnose cases. The study is also based on X-ray radiation, but the rays pass at different angles. The result is a whole series of photographs taken from different angles. The images are processed on a computer, and the patient is given a three-dimensional image, whereas with an x-ray only a two-dimensional image is provided. Another advantage of computed tomography is the fact that the radiation exposure to a person is lower than with a classic x-ray examination.
Some patients, if they suspect sinusitis, go on their own to do not a CT scan, but an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), considering this research method to be the most modern and reliable. But this is an erroneous judgment. MRI is suitable for examining soft tissue structures, such as the brain or mucous membranes. And bone structures, including the walls of the sinuses, are better visible on a computed tomogram.
Puncture of the maxillary sinus
Many patients have heard about puncture of the maxillary sinus as a medical procedure. Another name for this procedure is “puncture”. Surgical intervention is resorted to when the sinus is filled with purulent contents, which cannot come out with the help of drug therapy and rinsing. But few people know that the puncture is also performed for diagnostic purposes.
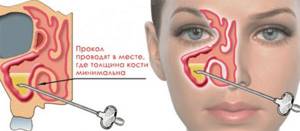
During puncture, the pathogenic contents of the sinuses are sent for laboratory analysis, which helps determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. Having identified the causative agent, it is easier for the otorhinolaryngologist to select an effective antibiotic that will be detrimental to the pathogenic microflora. Based on the nature, thickness, and smell of the contents of the sinuses, the doctor also preliminarily determines the type of sinusitis.
Puncture requires a lot of experience and skill of an ENT doctor. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia using a Kulikovsky needle, which is carefully inserted into the lower nasal passage. The patient does not feel pain at this moment. The only unpleasant moment during the procedure is the crunch that the patient hears at the moment the sinus wall is pierced. But the unpleasant sensations are limited to this. Using a syringe, the ENT doctor pumps out the contents of the sinus, which is sent for analysis, and rinses it with an antiseptic or other medicine.
There are not many contraindications to the procedure. These are children under five years of age, hypertension, problems with the blood coagulation system, and mental disorders.
Lab tests
One of the diagnostic methods is to prescribe a series of laboratory tests. They cannot accurately diagnose sinusitis, but they help determine the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. For this purpose, the patient is sent for general and biochemical blood tests. Test results show the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), the number of leukocytes, and the level of C-reactive protein.
A general urine test helps determine abnormalities in the functioning of organs.
Cytological examination of nasal discharge helps the ENT doctor determine the etiology of the disease, that is, its form - infectious, allergic sinusitis, etc.
An important study is taking a smear from the nasal cavity for microflora. It helps determine the type of bacteria that caused the inflammation and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
If the patient is often sick, has a weakened immune system, and frequent relapses of sinusitis occur, an HIV test is performed.
CT scan of the nose with contrast
Multispiral devices are able to provide enough information about bone structures and the presence of fluid in the sinuses, so CT analysis of the nose and paranasal sinuses is often done without contrast. If a tumor is suspected, more detailed images are needed. To improve the quality of the image, a contrast agent is used.
A special preparation containing iodine is injected into a vein. The substance quickly spreads throughout the tissues of the body and stains the smallest vessels, including those that feed the tumor. After a new series of CT images of the nasal cavity, the doctor receives reliable information about the location and size of the tumor, which has its own vascular network. By identifying areas of additional blood supply, spiral tomography (MSCT) helps detect tumors in the initial stages.
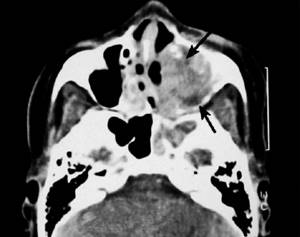
Squamous cell carcinoma on CT scan of the nasal sinuses with contrast. The tumor tissue is marked with a long arrow, destructive changes in the bone of the left maxillary sinus are marked with a short arrow.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy (instead of tomography it is recommended to do a sinus scan);
- body weight more than 200 kg;
- thyroid diseases;
- kidney diseases;
- severe diabetes mellitus;
- multiple myeloma;
- allergy to the contrast agent administered during CT scanning.
A tomogram of the paranasal sinuses is not recommended for children, since the procedure requires perseverance and the need to lie still for several minutes. It is extremely difficult to force a child to do this.
Indications and contraindications for tomography
First of all, computed tomography of the sinuses is done to diagnose inflammation of the mucous membranes, especially with the formation of pus or recurrent sinusitis.
Other indications for the procedure:
- craniofacial injuries;
- frequent headaches, facial pain, toothaches due to nasal congestion and heavy discharge;
- chronic colds with regular exacerbations;
- repeated nosebleeds not associated with increased blood pressure;
- pain, feeling of fullness in the sinuses;
- chronic rhinitis;
- difficulty in nasal breathing;
- inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct;
- suspicion of a cyst, polyp, abscess, tumor;
- orbital and intracranial complications of infectious diseases of the ENT organs;
- entry of a foreign object into the air cavity;
- suspicion of hemorrhage in the sinuses;
- swelling, pain in the nasal area;
- granulomas, cysts near the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw.
CT scanning of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses is an important measure in planning operations and monitoring dynamics after surgery. Examinations are carried out when treatment for sinusitis is ineffective in order to correct treatment tactics.
Contraindications to computed tomography:
- pregnancy;
- early age (due to the harm of radiation, CT scans are not recommended for children under 5 years of age);
- The patient's weight is more than 150 kg and chest (abdomen) girth is more than 150 cm.
Examination with contrast is not performed if:
- allergies, iodine intolerance;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- severe liver or kidney failure;
- taking metformin in patients with diabetes.
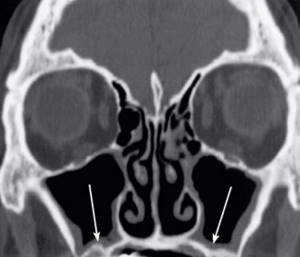
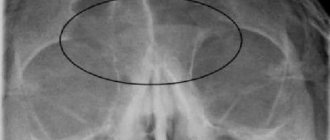
CT scan of the nasal sinuses (frontal section). Arrows indicate thickening of the mucous membranes
Is it possible to diagnose sinusitis yourself?
Some patients are not too fond of going to the doctor and try to recover at home. But sinusitis is not a common runny nose or cold. This is a serious disease that, if not treated correctly, can cause dangerous complications, including death. Therefore, the treatment regimen should be selected exclusively by an otolaryngologist, and he should also make a diagnosis.

The patient can only recognize the first signs of sinusitis in order to consult an ENT doctor in time. What symptoms indicate an inflammatory process in the sinuses?
- Pain in the bridge of the nose and the area of the maxillary sinuses, which becomes stronger when tilting the head or in the late afternoon.
- Thick nasal discharge of yellow-green color.
- Nasal congestion.
- Purulent discharge from the nose.
- Deterioration of sense of smell.
- Swelling of the eyelids, swelling of the face.
- Increased body temperature.
- Poor health, constant weakness.
Photo tomography of the sinuses
MSCT images show the contours, structure, and density of all parts of the sinuses. Based on the photo, the doctor can assess:
- sinus conditions;
- location of the nasal septum;
- sinus drainage pathways;
- symmetry of the sides of the nose and sinuses;
- degree of pneumatization of the accessory cavities;
- condition of the tear ducts.
CT provides images in a transverse (axial) projection. In a special program, you can enlarge the photo and see the smallest details. Using reformatting, the radiologist reconstructs the image in the desired anatomical plane. Most often, these are two additional projections - coronal (frontal) and sagittal (divides the object into left and right parts). It is also possible to create a three-dimensional model and cut off “extra” fragments, which simplifies the study of the area of interest and facilitates the interpretation of data.
Physician evaluation process of CT scan
How the research is carried out
No special preparation is required for the procedure. You must remove all metal objects or clothing with metal elements. The patient is placed on the couch and his body is secured with belts, and his head is placed on a special headrest. You should not move during the entire procedure, as movement may affect the accuracy of the result. If the patient cannot lie still (for example, children or people with mental disabilities), the doctor may use anesthesia.
If the CT procedure requires the injection of a contrast agent, such as iodine, into the patient’s blood, you should refrain from eating for several hours before the procedure.
Then the couch on which the patient lies is pushed into the tomograph. After this, the doctor retires to another room where a computer is installed that records the tomograph signals. All this time, with the help of sound equipment, the doctor and the patient are in touch. If the patient feels any discomfort, he reports it, and the doctor hears it. The study itself lasts no more than ten minutes.
Then the specialist deciphers the tomogram and gives the patient an x-ray and a disk recording the results of the study, as well as a medical report.
CT, as a method of radiation diagnostics, involves radiation exposure to the body. Therefore, it is recommended to do CT scans no more than three times a year. The cost of this study varies from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles.
Preparation process and technique for echosinusoscopy
A diagnostic session using the properties of ultrasonic waves does not require special preparation from the patient. You may eat and drink food and fluids before the test. If an ultrasound is being performed on a small child, parents tell him about the procedure in advance and convince him that the diagnosis is painless and there is no need to be afraid of it.
During the procedure, the patient sits motionless on the couch. In some cases, the diagnostician asks him to lie on his back or stomach. The doctor applies a special gel to the area being examined.

The doctor determines the location of the cavity he is interested in and installs the sensor according to anatomical landmarks in the area of its projection. In this case, the position of the sensor must be strictly perpendicular to the bone in order to minimize the interference created by the bone tissue.
The peculiarity of the method is that cavities are visualized on the monitor only if they contain contents, otherwise the echogenic signal is reflected from the air-bone border.
For this reason, during the ultrasound, the doctor asks the subject to change the position of the head, for example, bend it forward or tilt it back, in order to change the boundary of the location of the fluid, if any.
Ultrasound examination of the paranasal sinuses takes no more than 10-15 minutes and is absolutely painless.