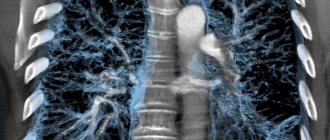
During a CT scan of the lungs, the tomograph takes many scans of the chest within a few seconds, the thickness of one step does not exceed 1 mm. Then the images (snapshots) are processed on a computer and combined into a three-dimensional model-reconstruction of the area under study. Computed tomography is a modern, improved version of radiography.
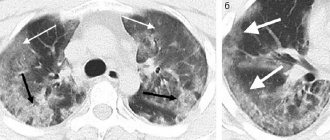
CT scan of the lungs and chest shows pneumonia, tuberculosis, mediastinal tumors, soft tissue and vascular injuries, injuries to the ribs and thoracic spine.
Due to the fact that a high-resolution volumetric image can be studied in three projections, and the thickness of one section is only a millimeter, based on the scanning results, differential diagnosis of tumors from 5 mm is possible, which other types of diagnostics will not show.
How is a CT scan of the lungs performed, and what should the patient pay attention to? Let's find out in this article.
What is multislice computed tomography (MSCT)?
Today in medical institutions you will find three types of tomographs: conventional, spiral and multispiral. What is the difference between a conventional and helical CT scanner? The key difference is in the mechanics of table movement, scanning speed and quality of tomograms.
During a scan on a traditional CT scanner, the scanner ring rotates one full rotation, then the table moves one step to take the next “slice” x-ray. Scanning one zone takes about 30 minutes.
SCT devices are more modern. The frame of the spiral tomograph rotates continuously, and the table moves gradually, due to this the sensor moves along the spiral path. Thus, the examination time is reduced to 1-5 minutes, CT scans are clearer and of higher quality. An improved SCT method is MSCT. What is “multispiral computed tomography”?
Diagnostics are carried out using high-speed spiral tomographs of a new generation, equipped with two X-ray tubes. Compared to traditional scanners, the number of sensitive sensors has been increased, and the examination time is reduced to several seconds - the time of one breath (with CT of the lungs without contrast). Scans from multislice tomographs have the highest resolution.
Minimal tumors, metastases, and lung lesions can be detected using multislice computed tomography (MSCT). Multispiral scanning is allowed for patients in serious health conditions. MSCT can be performed simultaneously with artificial ventilation in the intensive care unit.
In a specialized department, computed tomography is performed on a new generation multispiral device Siemens Somatom go.now with reduced radiation exposure.
Indications for computed tomography of the lungs
Computed tomography (CT) is prescribed for the following symptoms:
- persistent cough;
- the appearance of severe shortness of breath (including at rest);
- prolonged coughing attacks with the appearance of pus and blood in the sputum;
- the occurrence of whistling and wheezing when breathing;
- feeling of heaviness in the chest area.
You should also undergo a computed tomography scan of the lungs if you have an elevated temperature, which does not go down for a long time or decreases only temporarily, with a general deterioration in health (without signs of other diseases), decreased appetite, or weight loss. The doctor will issue a referral for the test after a preliminary examination and interview.
Some categories of patients should be diagnosed once a year.
It is recommended to be examined:
- Patients with chronic bronchitis and tuberculosis.
- Smokers (with smoking experience of more than 5-7 years).
- Persons who are constantly in contact with dangerous carcinogenic substances (asbestos, etc.).
Computed tomography is also performed if lung cancer is suspected. CT scan is prescribed not only when making a diagnosis, but also when adjusting therapy in order to increase its effectiveness, before some surgical interventions.
Important! It should be understood that timely research can save not only the health, but often the life of the patient.
CT lungs with contrast
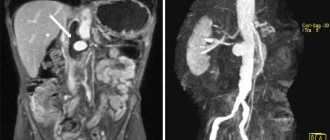
In some cases, the patient is advised to undergo a CT scan of the lungs with contrast. Contrast is a special iodine-containing drug that is administered intravenously to the patient before diagnosis. CT scan of the lungs with contrast allows you to visualize blood vessels and differentiate neoplasms.
The contrast agent passes through the circulatory system, “staining” the vessels and organs from the inside. The iodine molecules included in the contrast allow the drug to absorb x-rays more actively and make soft tissues brighter on tomograms. A chest CT scan with contrast is done to assess the condition of the pulmonary vessels, blood circulation, and also to increase the information content of the examination when necessary, for example, when diagnosing a neoplasm.
Typically, a contrast study is prescribed by a doctor. Sometimes such a need arises after the first scan without contrast, if the patient has detected signs of suspicious pathological processes that need to be excluded or examined in more detail. A single repeat scan is absolutely safe for the patient. It is also possible to initially distinguish a benign neoplasm from an oncogenic process using a CT scan of the lungs with contrast.
For fast, precise and painless administration of the drug, we use an injector device. The examination with contrast takes about 15-20 minutes.
The drug for contrast enhancement of CT scans does not harm the body and is eliminated from the body within 24 hours after a CT scan of the lungs. To assess the condition of the chest and lung organs, for example, to clarify the degree of their damage during pneumonia, detect tuberculosis, bronchitis, etc., native computed tomography without contrast is sufficient.
Transcript and research results
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
After the images are obtained, a radiologist examines them. He primarily turns his attention to: the presence or absence of tumors and granulomas; the presence of pathologies and, if any, their sizes; the nature of blood circulation; density of the respiratory system organs.
An accurate diagnosis is made by the attending physician who referred the patient for a CT scan. This could be a phthisiatrician, pulmonologist or therapist.
The advantages of this method of studying the lungs and bronchi are: a full scan does not take more than 30 minutes, CT is a non-invasive and painless procedure, the image is high-quality and informative, you can simultaneously analyze the condition of blood vessels, bone and soft tissues.
Computed tomography also successfully replaces other examination methods that require surgical intervention. CT is an indispensable procedure that allows for a comprehensive examination of any form of tuberculosis.
How is a CT scan of the lungs performed?
Before the examination, the patient should remove metal objects and jewelry located at chest level, as they may impair the quality of the scans. It is better for the patient to wear comfortable clothing that does not restrict movement.
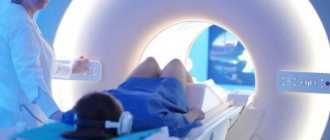
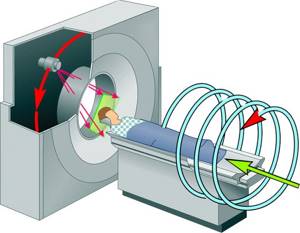
Next, the patient lies with his back on the tomograph table, which gradually moves inside the dynamically rotating ring (gantry). The beam tube delivers a stream of ionizing particles, and sensitive sensors record the response of tissues and internal organs. Only the chest area is scanned, so the x-ray dose is low and safe. The gantry - the frame of the tomograph - is wide and open enough so that the patient does not have the feeling of a closed space. Therefore, during a CT scan, patients with claustrophobia do not experience panic attacks (an MRI of the lungs may be difficult for this reason). A CT scan of the lungs is performed without pain or discomfort.
During a CT scan of the lungs, the patient should lie still and hold their breath for 5-10 seconds. If this is not done, artifacts may appear on the scans, reducing the quality of the scans. Throughout the examination, feedback is maintained with the radiologist.
Contraindications and side effects
Computed tomography is not performed if:
- acute mental disorders;
- pregnancy and during breastfeeding;
- heart failure;
- severe forms of stroke;
- diabetes mellitus;
- renal failure.
We can perform CT scans even on patients with significant body weight (up to 220 kg). Children are prescribed a test only if absolutely necessary.
If a CT scan with contrast is planned, a possible allergic reaction to the substance used during the examination should be ruled out in advance.
Important! Claustrophobia is not an absolute contraindication to CT scanning. Experienced specialists can set the patient up for a comfortable examination. Moreover, it does not take much time. You only have to spend a couple of minutes in the device. Even patients with claustrophobia can withstand the procedure.
After CT scan of the lungs
Immediately after the examination in our center, the patient receives a recording of the study (lung scans) on a high-resolution DVD and a commentary from a radiologist. No rehabilitation is required—immediately after a CT scan of the lungs, you can return to your usual activities. If a CT scan of the lungs with contrast (angiography) was performed, then after diagnosis you should drink more clean water than usual so that the iodine-containing drug is eliminated from the body faster.
The doctor will carefully examine scans of the lungs in three projections. A CT scan will show focal changes in the lungs with pneumonia, tuberculosis, as well as neoplasms, damaged vessels and other abnormalities, if any. Then the doctor will write a conclusion and send it to the patient by email.

Preparing for a CT scan of the lungs
A study without contrast does not require special preparation - a CT scan of the lungs can be done immediately by making an appointment for the study.
When preparing for a chest CT scan with contrast, adhere to the following algorithm:
- No more than 10 days before the tomography, do a blood test for creatinine. Since the iodine-containing drug will be excreted by the kidneys, it is necessary to check whether their function is impaired.
- You should take your last meal 3 hours before the examination.
- If you are taking glucose-lowering medications, you should stop taking them for 1-2 days before CT. However, this should be done only with prior agreement with an endocrinologist.
What is MRI of the lungs
Magnetic resonance imaging is a type of research in which the condition of internal organs is studied by exposure to a constant magnetic field and radio frequency radiation. This type of diagnostics allows you to study in detail the structure of tissues, including at the chemical level. In most cases, there is no need to administer a radiocontrast agent, which is important for patients who have an allergic reaction to it.
What does an MRI of the lungs show? Diagnostics makes it possible to distinguish soft tissues, blood vessels and nerves, but bone tissue is only indirectly visible in the images.
In this regard, MRI is prescribed in the following cases:
| Disease | The need to use contrast |
| Pneumonia | No |
| Cystic fibrosis | No |
| Tuberculosis | No |
| Pulmonary embolism | Yes |
| Focal formations larger than 3 mm | No |
| Pathologies of venous outflow | Yes |
| Pulmonary artery aneurysm | Yes |
| Vasculitis | Yes |
| Pleurisy with unspecified effusion | Yes |
For diseases of the bronchopulmonary system, CT and MRI of the lungs and bronchi are prescribed to confirm the diagnosis, which shows the result in this case:
- Thickening of the walls of the bronchi.
- Accumulation of fluid and mucus.
- The presence of tumors and metastases in the lungs.
- The presence of inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, empyema).
MRI may also be performed in pediatric patients, especially in those with equivocal CT findings, tumors, and cystic fibrosis.
Evgeniy Vasiliev, a radiologist of the highest category, chief expert at Dr. MC, tells the story. Spin :
What to pay attention to when making an appointment for an MRI
- Manufacturer of the MRI device: it is important that the device is not “made in China”, but of a well-known brand, for example Philips
- The power of the device must be at least 1 Tesla. Ideally – 1.5 Tesla
- Choose closed MRIs rather than open ones. Even though closed MRIs look scarier, make more noise and have a closed tube, still do MRIs for yourself and your loved ones only on closed machines! According to their principles of structure and operation, open MRI devices cannot be more powerful than 0.5 Tesla, and this is very important for effective research.
Magnetic resonance imaging is highly informative for cardiac pathologies. The heart is not a stone: 4 ways to examine it
- Electrocardiogram. Prescribed for arrhythmia, tachycardia, as well as for active sports.
- Holter monitoring. Threat of heart attack, heart rhythm disturbance.
- Echo KG. Congenital heart pathologies, murmurs, microinfarction. Diagnosis is necessary after heart surgery, in the presence of defects and tumors.
- MRI. Monitoring the condition during and after treatment, myocardial pathology. Problems with blood vessels (plaques, stenosis).
All of these types of studies are painless and safe, but they require prior consultation with a doctor.
Screening low-dose CT of the lungs
This study is specifically aimed at annual preventive health monitoring—diagnosis of lung cancer. According to WHO, about 10 million people die from lung cancer every year in the world, and this figure is growing rapidly. CT significantly reduces mortality from lung cancer, so annual screening is recommended for patients over 40 years of age. Patients who have a family history of cancer are at risk. In addition, smoking, working in hazardous industries and chronic lung diseases can also be a trigger for the development of malignant processes. In 20% of cases, lung cancer is caused by HBV, HCV and HPV infections. Screening low-dose CT scan of the lungs will show destructive malignant changes in the lungs in the early stages, when cancer is still amenable to successful and relatively easy treatment.
Carrying out the procedure
Based on the obtained images, it is possible to determine: a benign or malignant tumor, foci of tuberculosis, fistulas and abscesses. Using tomography, you can reflect the size, stage, see metastases and extent of cancer. Patients with enlarged lymph nodes and chest pain are referred for a computed tomography scan. Over the past few years, CT scans have helped detect lung carcinoma in the early stages of the disease and treat patients.
Research using a tomograph:
- painless;
- does not cause discomfort;
- relatively safe for human health;
- effective.
The examination takes a minimum amount of time - from 1 to 30 minutes, depending on the type of CT scan. If the patient cannot move or stay in the same place for a long time, it is recommended to perform multislice tomography. Its duration varies from 5 to 10 minutes.
The examination does not require special preparation. It is advisable to come for the study on a completely empty stomach, with a break from eating for at least 4-5 hours. It is necessary to wear loose clothing so that you can quickly remove it later. If the patient has claustrophobia or nervous system disorders, a CT scan can be done under general anesthesia.
Stages of undergoing computed tomography: first - the patient must remove all metal jewelry, a belt and undress to the waist; second – the patient lies down on a special couch; third - a contrast agent is injected (if necessary); fourth - the couch moves and stops under the arch of the apparatus; fifth - the specialist checks the equipment and leaves the room, he watches the person from another room; sixth – you cannot move so that the data is as reliable as possible; seventh - when the procedure has come to an end, the patient can get up and get dressed, then he waits for the transcript, which is done by the doctor.
If a person is very afraid of the procedure, he may be given a “pear”, which the patient will hold in his hand, and at the first discomfort or pain he presses on it, thereby informing the specialist that something went wrong during the diagnosis.
Benefits of Lung CT
- Diagnosis is quick and without discomfort. In certain cases, CT acts as an alternative to instrumental-invasive methods of examining the respiratory tract - bronchoscopy or pulmonary endoscopy.
- CT scans are highly informative compared to X-rays or fluorography. CT scan of the lungs is better than MRI in showing pneumonia, tuberculosis, and mediastinal tumors. With the help of computed tomography, respiratory tract organs, bones and blood vessels can be examined in different planes, and even initially determine the type of neoplasm detected (from 5 mm).
- Diagnostics is not contraindicated in patients with implants in the mediastinum and does not cause panic in claustrophobia.
- A CT scan of the lungs without contrast does not require special preparation - the examination can be completed immediately on the day of your visit.
- CT is suitable for annual preventive screening of lung cancer, as well as for monitoring the recovery of the airways after pneumonia, tuberculosis and other diseases.
- You don’t have to do X-rays and fluorography - a CT scan of the lungs will show everything that is necessary. The study is recorded in high definition on DVD, which meets the requirements of attending physicians and preparation for precision surgical operations.
MSCT of the lungs with high spatial resolution
This study is the most informative in diagnosing pulmonary pathology. It is a detailed study of the lungs in a layer-by-layer thin-section mode with subsequent processing of the obtained data and reformatting of the image in different planes with the possibility of 3D reconstruction, the creation of which allows you to study this anatomical area in as much detail as possible. It can be performed either without contrast or with a bolus injection of contrast agent.
Such a study may be prescribed if:
- infectious diseases (such as pneumonia, lung abscess, mediastinitis, pleurisy, tuberculosis);
- the presence of effusion in the pleural cavities or pneumothorax;
- cancer of the lungs, mediastinum and chest wall, in the presence of metastases and cysts in this area;
- bronchiectasis and emphysema;
- interstitial lung diseases and disseminated processes in them;
- enlarged lymph nodes of the roots of the lungs and mediastinum;
- in all cases of discrepancy between the clinical picture and X-ray data.
MSCT of the lungs with high spatial resolution reveals:
- infectious lung diseases (pneumonia, infectious destruction, respiratory tuberculosis, pneumoconiosis, parasitic infections);
- lung tumors (including central, peripheral, bronchioloalveolar cancers);
- metastatic lesions of the lungs and mediastinal lymph nodes;
- bronchial diseases (bronchiectasis, cysts, cicatricial bronchial stenosis, bronchial foreign bodies, bronchiolitis);
- pulmonary circulatory disorders (such as pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, septic pulmonary embolism, pulmonary vascular abnormalities);
- interstitial lung diseases (alveolitis, lymphogenous carcinomatosis, histiocytosis, sarcoidosis, silicosis and anthracosis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, emphysema);
- diseases and damage to the thoracic aorta and its branches;
- extrapulmonary pathological processes (mediastinal neoplasms, mediastinitis), pleural pathology (pleural effusion, pneumothorax, pleural tumors), chest wall, lymphadenopathy.
Study time: without contrast – up to 15 minutes, with contrast – 20-30 minutes.