The functioning of the endocrine system greatly influences the overall health of a person; if problems begin with one of the glands, this leads to dysfunction of other organs and systems. In this regard, the endocrinologist in Yeisk, the leading receptionist at the Sensitive LCC, reminds you that you should always consult a doctor as soon as you discover any alarming symptoms.
The parathyroid glands are important for the body because they synthesize parathyroid hormone. This substance controls the homeostasis of calcium, which constantly passes through the body. Much depends on calcium-phosphorus metabolism: the formation of bone tissue, the condition of teeth, the condition and strength of bones. If there is any abnormality in the parathyroid gland, it will certainly affect the condition of the bone tissue, regardless of whether there is a deficiency or excess of parathyroid hormone.
How is an ultrasound examination of the parathyroid glands done?
To determine if there is an enlarged parathyroid gland on ultrasound, the patient will be asked to lie on a couch near the machine. The area to be examined should be completely free, and there should be no jewelry on the neck that would interfere with the doctor’s examination. A small pillow may be placed under the patient's head for comfort. Sometimes it happens that the doctor asks the patient to tilt his head back strongly in order to better examine the parathyroid glands
.
After the person is placed on the couch, a special gel is applied to the area being examined to improve the glide of the ultrasound probe. The doctor begins the examination and runs an ultrasound probe on the sides of the neck and observes the image that is displayed on the screen. As a rule, such a study lasts no longer than twenty minutes, and during its conduct the patient does not experience any unpleasant sensations. Following the procedure, the patient may be asked to wait outside the office while the doctor draws up a report.
Monitoring patients after surgery
Monitoring of patients after surgery consists of dynamic monitoring of calcium and PTH levels in the blood, as well as regular ultrasound examination of the soft tissues of the neck in order to timely detect relapse of the disease. Most tumor recurrences occur 2–3 years after initial surgery, although recurrences after 20 years have also been described. If a relapse of the disease is suspected, the diagnostic search undertaken when the disease was initially detected is repeated.
In case of disease relapse, repeated surgical treatment is performed in the form of resection of all functional tumor tissue, including wide local excision in the neck and mediastinum. This principle also applies to metastases, since the goal of surgery is to reduce the tumor burden and help alleviate the symptoms of hypercalcemia, which significantly impair the quality of life of patients. Palliative surgeries may be performed several times on a patient due to the indolent nature of the disease and the relatively high relapse rate. As mentioned above, other treatment methods are not applicable in this case.
Normal size of the gland
Sometimes an ultrasound shows that the parathyroid glands are normal. If there is an enlargement of the parathyroid gland, the reason may be the presence of hyperparathyroidism or various neoplasms. Using ultrasound diagnostics, the doctor will determine whether the gland is normal, record its parameters and draw a conclusion based on the data obtained. Sometimes, after ultrasound diagnostics, it is necessary to do additional tests to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment tactics.
In men
The ultrasound technique of the parathyroid glands is very informative and allows you to determine the exact size of the organ. The following parameters for the size of the parathyroid gland are considered normal in men:
- width – 0.3-0.4 cm;
- length – 0.2-0.8 cm;
- thickness – 0.15-0.3 cm.
At the same time, the doctor also evaluates the general condition of the glands, which will be recorded in the report and confirmed with an image.
Among women
In women, the parathyroid gland should normally be the same as in men - in the ranges indicated above. Enlargement of the organ may be a prerequisite for the doctor to refer the patient for additional tests to determine the cause of the symptom.
Symptomatic treatment and control of calcemia
The manifestations of the disease stem mainly from hypercalcemia, and it is this that causes the deterioration in the quality of life of such patients. In these conditions, symptomatic therapy is one of the most important measures (along with surgery), and in the case of an inoperable tumor, the only possible treatment option. As symptomatic therapy in such patients, osteomodifying agents are actively used - biphosphanates and monoclonal antibodies to RANKL (a molecule that triggers the development of osteoclasts that “destroy” bone tissue). Among the former, the most prominent is zoledronic acid (Zometa). Among the latter, the world can only offer denosumab so far. Their action is aimed at increasing the accumulation (“sedimentation”) of calcium in bone tissue, which has a hypocalcemic (lowering calcium in the blood) effect and allows to neutralize the patient’s symptoms, as well as increase bone density and reduce the risk of pathological fractures.
With a sharp increase in calcium levels, the severity of symptoms is extremely high and in some cases it is life-threatening due to the risk of kidney failure and cardiac arrhythmias (ventricular fibrillation). In such cases, it is necessary to manage the patient in intensive care and intensive care with the use of hydration therapy, glucocorticosteroids, calcitriol and loop diuretics (furosemide); if ineffective, hemodialysis is required. All these measures are aimed at correcting the sharply increased concentration of calcium in the blood and preventing the development of potentially fatal complications.
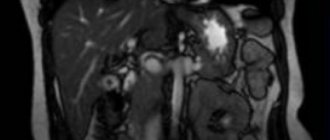
What does an ultrasound of the parathyroid glands show?
The doctor will be able to identify various formations on the parathyroid glands based on ultrasound results or the presence of any abnormalities during the course of the study. The condition of these glands is assessed according to the following parameters:
- structure;
- location;
- contours (clear, fuzzy);
- structure (homogeneous or heterogeneous);
- dimensions;
- echogenicity;
- condition of the lymph nodes;
- condition of the salivary glands and soft tissues.
Often during the examination, the doctor examines adjacent organs, for example the thyroid gland, and also evaluates the condition of the soft tissues.
The doctor records the results in the conclusion, and also attaches a photograph and a description of the progress of the study. Sometimes a patient receives a referral for an ultrasound scan of a parathyroid cyst, undergoes the procedure, and as a result it turns out that there are problems with visualizing the organ.
This may indicate either that the ultrasound machine has low resolution, or that there are no pronounced pathological processes in the parathyroid gland. In such a situation, the doctor will have to refer the patient for additional studies or select other diagnostic methods.
conclusions
Despite the lack of treatment options other than surgery, it can be said that parathyroid cancer is characterized by relatively high survival rates for this group of patients. Apparently, the way to increase this indicator lies in improving the surgical treatment used. At the same time, the potential possibilities of drug antitumor therapy are severely limited due to the rare occurrence of this disease and the impossibility of conducting adequate randomized clinical trials that could demonstrate the effectiveness of a particular drug. This means that in the coming decades, the only available treatment approaches for parathyroid cancer will remain surgical treatment and symptomatic therapy aimed at correcting hypercalcemia.
Bibliography:
- Endocrine pathology / M. Kettyle William, A. Arky Ronald, p.145 – 151, 2016
- Machado, Nikita N, and Scott M Wilhelm. “Parathyroid Cancer: A Review.” Cancers vol. 11.11 1676. 28 Oct. 2021, doi:10.3390/cancers11111676
- Primary Hyperparathyroidism and the Risk of Fracture: A Population-Based Study. Sundeep Khosla Joseph Melton III Robert A. Wermers Cynthia S. Crowson W. Michael O'Fallon B. Lawrence Riggs First published: December 02, 2009 https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.10.1700
- Tay, Yu-Kwang Donovan et al. “Occult urolithiasis in asymptomatic primary hyperparathyroidism.” Endocrine research vol. 43.2 (2018): 106-115. doi:10.1080/07435800.2018.1431275
- Parks J, Coe F, Favus M. Hyperparathyroidism in Nephrolithiasis. Arch Intern Med. 1980;140(11):1479–1481. doi:10.1001/archinte.1980.00330220049018
- Four Ultrasound and Clinical Pictures of Parathyroid Carcinoma Milan Halenka, David Karasek, and Zdenek Frysak.Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Endocrinology Volume 2012, Article ID 363690, 5 pages/ doi:10.1155/2012/363690
- Case Report Synchronous parathyroid carcinoma and papillary thyroid carcinoma: a case study and review of literature Chunyi Song, Jianbiao Wang, Xiujun Cai, Li Gao. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):302-309 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017732
- Ghada El-Hajj Fuleihan, MPHAndrew Arnold, Parathyroid carcinoma. UpToDate, 2021
- Randall P. et all, Parathyroid carcinoma: A review. J.of the sciences and specialties of the head and neck Volume33, Issue3, March 2011, Pages 429-436 https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.21376
- Current and future treatments for parathyroid carcinoma. Kristin L Long & Rebecca S SippelINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINE ONCOLOGYVOL. 5, NO. 1REVIEW. Published Online: 7 Feb 2018 https://doi.org/10.2217/ije-2017-0011
- Hsu, K. T., Sippel, R. S., Chen, H., & Schneider, D. F. (2014). Is central lymph node dissection necessary for parathyroid carcinoma?. Surgery, 156(6), 1336–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2014.08.005
- Asare, E. A., Sturgeon, C., Winchester, D. J. et al. Parathyroid Carcinoma: An Update on Treatment Outcomes and Prognostic Factors from the National Cancer Data Base (NCDB). Ann Surg Oncol 22, 3990–3995 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-015-4672-3
- Thomas E Green, Hypercalcemia in Emergency Medicine. MedScape, Updated: Apr 29, 2020
- Successful palliation of hypercalcemia secondary to metastatic parathyroid cancer: an unusual indication for hepatic resection. James J. Mezhir et all, Journal of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery. Volume14, Issue4, July 2007 Pages 410-413 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-006-1173-6
- Schulte, K.M., Talat, N., Miell, J. et al. Lymph Node Involvement and Surgical Approach in Parathyroid Cancer. World J Surg 34, 2611–2620 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-010-0722-y
Indications for thyroid ultrasound
The content of the article
Before scheduling a procedure, please read the important information regarding indications and contraindications. A classic ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is recommended to be done regularly as part of an annual medical examination, regardless of the patient’s age and the absence of characteristic symptoms. If the following symptoms appear, it is necessary to make an appointment with an endocrinologist as soon as possible and undergo an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland:
- visible increase in the volume of the neck, the appearance of a compacted formation;
- redness of the neck area near the location of the gland;
- hoarseness not associated with colds;
- difficulty breathing, discomfort during swallowing;
- increase in body temperature within 37-37.5 degrees;
- the appearance of swelling;
- weakness, apathy, drowsiness, severe irritability;
- sweating, feeling hot or, conversely, cold;
- trembling of limbs;
- sudden change in body weight;
- cardiopalmus;
- baldness.
These symptoms may be an indicator of a malfunction of the thyroid gland, and therefore require examination by ultrasound. An endocrinologist may refer you for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland if palpation reveals lumps or the patient complains of pain when palpating the gland. A direct indication for ultrasound diagnostics is unsatisfactory results of hormone tests.
In addition, the following groups of people should sign up for a thyroid ultrasound :
- Pregnant women or those who are planning to conceive a child in the near future.
- People living in iodine-deficient areas.
- Patients diagnosed with obesity.
- For those taking hormone-containing medications.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland is also prescribed to patients to monitor the treatment. In some cases, the frequency of such a procedure reaches several times a week, which is necessary for dynamic monitoring of the gland’s reaction to drug correction.
Ultrasound examination is completely safe for humans, has no contraindications, and if a pregnant woman undergoes it, it does not have any effect on the fetus. Therefore, ultrasound can be done as many times as needed.