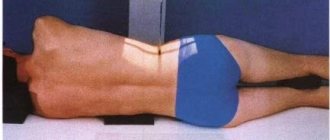
If possible, the doctor prescribes a safe examination for children - for example, an ultrasound. But for some diseases and pathologies, X-ray examination is the only option to obtain diagnostic information for prescribing the correct therapy.
X-rays can be performed on a child at any age. But only if there are fears for the life and health of the baby. And provided that alternative diagnostic methods are impossible or ineffective.
The need for X-ray examination
X-rays of the lungs of a child are prescribed very rarely, since radiation has a negative effect on the body, especially children. X-ray radiation can lead to mutations and damage to the DNA chain, which can subsequently cause the development of various diseases. However, such consequences can only occur with a high dose of radiation; with a simple x-ray, the dosage is not exceeded.
Refusal to perform chest x-rays in children is extremely undesirable if there is a need for such a study. The reason is the different functioning of the immune system of babies. For them, a common cold often develops into pneumonia, which progresses very quickly. Therefore, you should not take a long time to decide whether a chest x-ray for a child is harmful, because the lack of diagnostic results can even lead to death.
Security measures
X-ray machines used today cause virtually no harm to the body. Parents should inquire in advance whether the medical institution is using a modern device. It is important to ensure that the protective apron covers the abdominal cavity and pelvic area.
To conduct pediatric radiography, it is better to contact a modern, proven clinic, experienced professionals.
If all rules and precautions are followed, the diagnosis will be as effective as possible and will take place without negative consequences for the child’s health.
Indications for chest X-ray in children
A child's lung x-ray is prescribed solely to identify the causes and complexity of the pathology, but not for preventive purposes. This is based on the possibility of negative consequences from exposure to rays. It is worth familiarizing yourself with the situations when a chest x-ray of a child
extremely necessary.
Confirmation or exclusion of pneumonia (pneumonia)
A chest x-ray can often save a child's health and life. Pneumonia in children can progress very quickly and requires immediate diagnosis. After receiving the results, the doctor can choose an effective treatment strategy.
Severe cough accompanied by a high temperature (above 38ºC) for more than three days
May indicate a cold, which should be treated with medication. Using an image, doctors determine why such symptoms arose and persist.
Leukocytosis and shift of the leukocyte formula to the left in a blood test
A shift of the formula to the left indicates an increase in the number of “new” neutrophils in the blood. This may indicate an inflammatory or necrotic process, various intoxications, infections, and may also appear when taking certain medications. In this case, the child is given a chest x-ray to determine the cause of this phenomenon. The shift is not necessarily a sign of illness; sometimes it occurs after significant physical exertion, and over time the situation improves.
Impossibility or lack of information content of other examination methods
You will have to think about how often you can do an X-ray of a small child’s lungs if other diagnostic methods do not provide the amount of information that is needed. In such a situation, you need to resort to x-ray examination.
Suspicion of pathology of the thymus gland
A chest X-ray, which shows a large number of pathological processes in children, is informative when examining the thymus gland. The main diseases are: aplasia, hypoplasia and dysplasia, accidental involution, thymomegaly, atrophy and hyperplasia. X-rays of the lungs in children can determine the cause of deterioration in health, based on the results of which the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Suspicion of pulmonary tuberculosis
In such a situation, you should not think about at what age a child can have an X-ray of the lungs - it is mandatory, since the disease is very serious. The doctor will examine all the shadows in the resulting image and draw up a conclusion that will allow you to understand whether the preliminary diagnosis has been confirmed.
Diagnosis of neoplasms
You also need to find out how often a child’s lungs can be x-rayed if there are suspicions of tumor processes of various types. Their manifestations can sometimes be subtle or completely unnoticeable, but a prompt reaction from parents will provide a more optimistic prognosis.
Indications
Qualified specialists at our center prescribe examinations if the following diseases are suspected:
- heart disease;
- diseases of joints and bones;
- pneumonia;
- nasal pathologies;
- fractures and bone diseases;
- abnormal kidney development;
- thymus pathology;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
In order to avoid standing in lines and save time, we offer a paid x-ray for your child in our clinic in Moscow. The little patient will undergo a safe and high-quality examination in a comfortable and cozy environment. Processing of the results does not take long; parents will be provided with a transcript on the day of application.
How is the examination done in children?
First of all, you should know at what age children are given lung x-rays
. Ages over 14 years are considered safe. However, exceptions are possible.
Before undergoing the procedure, you need to find out how children get x-rays of their lungs. The examination of the chest organs of babies is somewhat different from that of adults. The fact is that in order to obtain clear images, it is necessary for the patient to remain absolutely still.
If you don’t know how a child’s chest X-ray is done, it’s worth knowing that a special device that looks like a stand is used for this. The child is placed on it and the legs, arms, head and torso are secured with belts. Organs that will not be examined are covered with a lead apron. At the time of the study, parents are with the child and are provided with radiation protection equipment. For 12-year-old and older children, a chest x-ray is performed without the presence of parents.
The examination will last a couple of seconds, the patient will not experience discomfort, except for possible inconvenience from fixation.
X-ray of the hip joints: the essence of the method
Classic X-ray examination is based on the ability of specific R-rays to pass through solid objects of different densities with different intensities. Radiation of this type was discovered at the end of the 19th century, and after 15-20 years it began to be used in medical institutions for diagnostic purposes.
Content:
- X-ray of the hip joints: the essence of the method
- What is dysplasia and why diagnose its presence?
- Stages of joint dysplasia
- In what cases are children prescribed x-rays of joint joints?
- Risks and dangers of performing an X-ray of the hip joint in a child
- Preparing the child and technique of the procedure
- The process of deciphering survey results
- Additional and alternative methods for examining the condition of joints
The patient is examined using a special device. The patient is placed in the beam projection area, and the image is captured, as if photographing the patient. Instead of photographic film, X-ray film is used, treated with a chemical composition containing silver bromide; instead of a camera, a device with an X-ray tube producing R-rays is used.
The images obtained in this way are highly accurate and informative; bone formations and joints, in particular the hip, are especially well and clearly visible.
How often can children have a chest x-ray?
It is important to find out not only whether it is harmful for a child to have a chest x-ray, but also how often the procedure can be performed. The frequency will depend on what disease is suspected or what diagnosed disease is being treated. For example, if there is a suspicion of tuberculosis, you need to be examined every three months to assess the condition and effectiveness of treatment.
In the case of pneumonia, after it is diagnosed, it is necessary to undergo the procedure 3-5 days after finishing the course of antibiotics. There is no need to worry about the negative impact on the child’s body. If you need to find out what a chest x-ray shows in children, it is best to carry out the study and not refuse it, since the benefits are much higher than the likely risks.
Radiation exposure
Parents need answers not only to questions about how an X-ray of a child’s lungs is done, at what age it is prescribed and what are the features, but also what the radiation dose will be. An image in a frontal projection assumes a load of 0.18 mSv, and in an additional side projection - 0.42 mSv. The annual norm, which should not be exceeded, is 1 mSv. After the first procedure, a passport is created for the patient, in which data on all scans is entered. There are few analogues of X-ray, except for computed tomography, but it is prescribed very rarely, because the radiation dose with it is several times higher.
In what cases are children prescribed x-rays of joint joints?
Responsibility for the health of the child from the first days, in addition to the parents, lies with the neonatologist and pediatrician. These doctors conduct the very first examination in the baby’s life. As for the orthopedist, parents and the child should see him no later than a month after his birth.
However, even before visiting an orthopedist, the parents or pediatrician themselves may suspect dysplasia during the initial examination. This is possible in severe forms of the pathology, if the head of the femur completely protrudes from the acetabulum. If dysplasia does not affect the articular apparatus so severely, only a specialist with appropriate qualifications can determine it.
Signs that should alert parents and pediatricians:
- impaired joint mobility, difficulty spreading the hips, to the point that the child cries when trying to move the leg to the side;
- asymmetry of the inguinal and gluteal folds: on the side where the joint is affected by dysplasia, they are more pronounced;
- shortening of the leg, if the pathology is developed in only one joint;
- clicking symptom: the head of the femur pops out of the socket of the joint with a characteristic sound when the child bends the legs at the knee and hip joints.
Diagnosis of pathology can occur directly in the maternity hospital, while the child is there with the mother after childbirth. Dysplasia can be identified by an orthopedist during the first appointment. In any case, if any of the doctors detects signs of dysplasia in a child, it becomes necessary to visually assess the degree of damage to the joint, its structure, the shape of its components and how they come into contact. For these purposes, the doctor sends the baby for diagnostic examinations.
X-rays of the hip joints in children are not performed in every case. Due to the fact that the procedure involves x-ray exposure of the patient, children under the age of three to four months are not recommended to undergo x-rays at all. An orthopedic surgeon may prescribe preventive measures without x-rays, for example:
- use of soft tires with spreading mechanisms;
- massage of the gluteal muscles;
- course of special therapeutic gymnastics.
In each specific case, the doctor decides whether to send the child for an ultrasound of the joint or for an x-ray. Some doctors are guided by the principle “any diagnosis is better than no examination and treatment.” X-rays are advisable if the benefit from the information received outweighs the likely threat to the baby’s health from radiation exposure. Otherwise, the doctor gives the little patient a referral for an ultrasound of the joint.
Decoding the results
An X-ray of a child’s lungs is interpreted by a radiologist. Each pathology has its own characteristics and is displayed differently on images. For example, pneumonia looks like darkening of areas of the lungs. The type of inflammation is determined by the location of the darkening. It can be total, segmental, lobar or focal. The intensity of the darkening demonstrates the degree of inflammation.
It is not possible to decipher a child’s lung x-ray on your own; this must be done by a doctor. Detection of tuberculosis will also have features; it looks different in the picture. The disseminated type of the disease looks like small focal darkening with clearly defined edges. Focal looks like darkening in one or a couple of places, the size can be up to 2 cm.
Thinking about the age at which children get x-rays of their lungs
, it is worth understanding that even adults cannot resort to it without clear indications.